ATF4基因在小鼠动情周期中子宫内膜的表达
凌 康,柴路维,何晓茜,姜 蓉*
(重庆医科大学 1.附属第一医院 普外科; 2.干细胞与组织工程研究室, 重庆 400016)
研究论文
ATF4基因在小鼠动情周期中子宫内膜的表达
凌 康1,柴路维2,何晓茜2,姜 蓉2*
(重庆医科大学 1.附属第一医院 普外科; 2.干细胞与组织工程研究室, 重庆 400016)
目的探讨转录激活因子4(ATF4)在小鼠动情周期中子宫内膜的表达规律。方法采用RT-PCR、免疫组织化学和Western blot法分别检测小鼠子宫内膜中ATF4 mRNA和蛋白在动情前期、动情期、动情间期和动情后期的表达规律。结果ATF4 mRNA在动情期表达显著高于其他3期(Plt;0.05);ATF4蛋白主要在腺上皮细胞和腔上皮细胞胞质表达,其表达规律与RT-PCR的结果基本一致。结论ATF4在小鼠动情周期子宫内膜中呈动态表达,提示ATF4可能参与了动情周期子宫内膜变化的调控。
转录激活因子4;小鼠;动情周期;子宫内膜
转录激活因子4(activating transcription factor4,ATF4)是ATF家族的一员,该家族识别顺式作用转录增强子cAMP效应元件,是一种包含Jun和Fos结合位点的DNA结合蛋白,属于较大的碱性白氨酸链超家族[1]。近年来研究表明它能使肿瘤细胞在乏氧或其他应激的肿瘤微环境中促进细胞存活,在多种恶性肿瘤的发生、发展中起着重要的作用。ATF4基因在肿瘤中的机制主要有抑制细胞的凋亡、促进细胞的增殖和分化、诱导血管的生成[2-5,9]。然而目前国内外对于ATF4在妊娠过程中的表达情况仍鲜有报道。本研究采用RT-PCR、免疫组织化学法和Western blot法分析了ATF4 mRNA和蛋白在小鼠动情周期子宫内膜中的表达情况,探讨它在生殖过程中可能的作用。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验动物:清洁级KM雌性小鼠,6~8周龄,体质量25~30 g[重庆医科大学实验动物中心提供,合格证号:SCXK(渝) 20050002 ]。室温22 ℃,光照14 h,10 h黑暗,自由取食、饮水。根据动情周期分期标准,阴道脱落细胞涂片将未孕小鼠分为动情前期、动情期、动情后期、动情间期4组,每组30只。其中每组随机选10只分别用于RT-PCR和Western blot实验,另10只取子宫石蜡包埋,用于免疫组化。
1.1.2 主要试剂:RT-PCR引物由上海生工设计和合成, RT-PCR试剂(TaKaRa公司);一抗(兔抗小鼠ATF4抗体)(Proteintech Group公司);二抗(辣根酶标记山羊抗兔IgG)(Santa cruz公司);免疫组化试剂盒(北京中山生物公司);蛋白提取试剂盒(凯基公司)、化学发光检验试剂盒ECL(上海碧云天公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 RT-PCR:按试剂盒说明提取总RNA,判定 RNA纯度及浓度;取部分RNA凝胶电泳,确定其完整性。ATF4基因(NM009716)上游引物:5′-CAA AACAAGACAGCAGCCACTA-3′,下游引物:5′-CTT CTTCCCCCTTGCCTTAC-3′,扩增片段长度为186 bp;内对照引物β-actin基因上下游引物分别为:5′-C CTGAGGCTCTTTTCCAGCC-3′,5′-TAGAGGTCTTTA CGGATGTCAACGT-3′,扩增片段长度为110 bp。严格按照产品说明操作:将总RNA先反转录为cDNA。20 μL PCR反应体系,先94 ℃变性4 min,然后进入循环:94 ℃变性30 s, 57 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,循环35次,最后再延伸5 min。PCR产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳,图像分析仪扫描分析并摄像。用Quantity one 4.0软件分析各条带吸光度值/mm2,计算各组吸光度比值。
1.2.2 免疫组织化学:常规石蜡包埋子宫组织,制备切片,二甲苯脱蜡、梯度乙醇水化,一抗ATF4工作浓度1∶200,操作过程均按组织化学染色试剂盒说明进行。棕黄色为阳性结果。对每张切片取10个视野,每份标本取5张切片观察,通过Image-Pro Plus 6.0图像分析软件进行图片的平均吸光度分析,测定ATF4蛋白的相对表达量。
1.2.3 Western blot:按照试剂盒说明操作,常规裂解组织获取总蛋白、测定蛋白浓度。等量上样PAGE分离,PAGE分离蛋白用10%的分离胶,5%积层胶;将 PAGE分离的蛋白转到PVDF膜上;加入一抗、二抗。以ECL化学发光试剂在X线片上曝光、显影、定影。以GAPDH为内参。用Quantity One 4.0软件分析成像图谱,计算各组小鼠子宫内膜ATF4蛋白的比值。
1.3 统计学分析
2 结果
2.1 RT-PCR产物定性与半定量分析
ATF4基因在小鼠动情周期各期子宫内膜均有表达,在动情期其表达明显高于其他3期(Plt;0.01),其他3组间无显著差异(图1)。
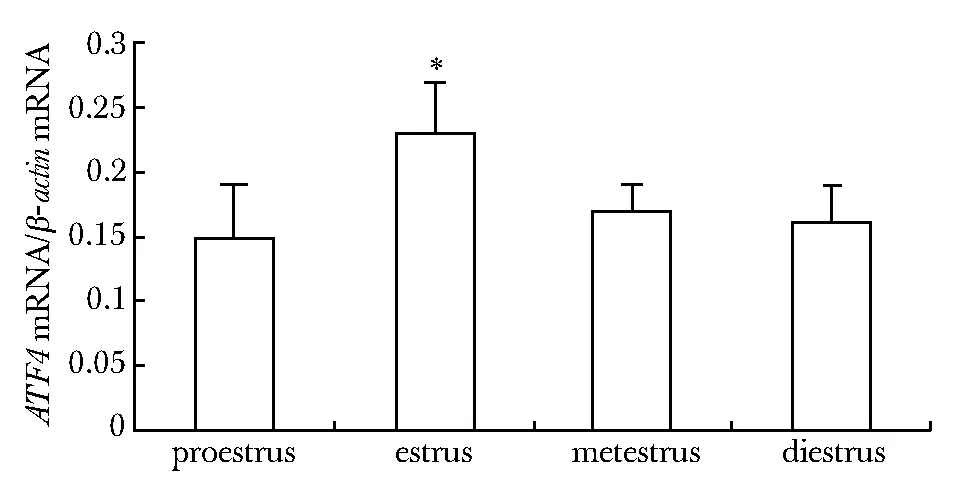
*Plt;0.01 compared with estrus group图1 动情周期各期 ATF4 mRNA的相对表达Fig 1 Expression of ATF4 mRNA during the estrus cycle
2.2 免疫组织化学结果
ATF4在动情周期各期小鼠子宫内膜组织中均有表达。可见棕黄色阳性物质主要分布于内膜腔上皮和腺上皮胞质。动情期与其他3期相比表达明显增强(Plt;0.05), 其他3组之间无明显差异(图2)。

A.proestrus; B.estrus; C.metestrus; D.diestrus; E.control图2 ATF4 在动情周期小鼠子宫内膜的表达Fig 2 Expression of ATF4 in mouse endometrium during the estrus cycle(×200)
2.3 Western blot结果
ATF4在动情周期各期小鼠子宫内膜组织中均有表达,动情期与其他3期相比表达明显增强(Plt;0.05), 其他3组之间无明显差异(图3)。
3 讨论
ATF4最早在低氧组织被发现,是一种应激诱导转录因子。当发生缺氧时,蛋白激酶R样内质网激酶(protein kinase R-like ER kinase,PERK)被激活,通过磷酸化真核细胞起始因子2α(eukaryotic initiation factor 2α, eIF2α)抑制蛋白质合成并活化ATF4, 继而上调C-EBP同源蛋白(C-EBP homologous protein,CHOP)基因表达,启动细胞增殖,使细胞适应缺氧环境[6-7]。

图3 ATF4在动情周期小鼠子宫内膜的Westernblot成像图 Fig 3 Imaging of ATF4 protein in mouse endometrium during the estrus cycle by Western blot
雌性成年小鼠的动情周期一般为 4~5 d, 可分为动情前期、动情期、动情后期、动情间期 4 个不同的时期, 子宫内膜的结构及功能在这4 个阶段都将发生一系列的改变。本实验结果显示:ATF4 mRNA和蛋白在小鼠动情周期子宫内膜中的表达呈规律性变化,在动情期表达明显增强,其他3期间无显著性差异。ATF4蛋白主要表达在子宫内膜腔上皮细胞和腺上皮细胞胞质。
正常小鼠血浆雌激素水平在动情前期开始上升, 至动情期达到高峰, 此期细胞不断分裂增殖、发生排卵并接受交配, 随后子宫内膜的环境变得有利于胚胎的植入[8]。近年来研究表明,在多种恶性肿瘤中ATF4基因能使肿瘤细胞在应激的肿瘤微环境中启动细胞增殖,促进细胞存活[2-5]。本研究中ATF4在动情期高表达,与这一时期雌激素变化一致,因此推测ATF4可能是受到雌激素、孕激素等卵巢激素的调控而高表达,从而有利于细胞大量增殖分化。此期若未受精依次进入动情后期、间期,子宫随即开始缩小、内膜萎缩,ATF4的表达亦迅速降低。
此外,据相关文献报道,ATF4通过调控其下游基因血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)的表达而在血管生成和生长中发挥作用。如在乳腺癌细胞中,ATF4被激活后诱导VEGF促进肿瘤新生血管的形成[9]。在修复血管损伤实验中[10-12],ATF4通过诱导VEGF的表达可使损伤的血管内膜增厚,且过表达的ATF4在血管损伤后能刺激平滑肌细胞增殖。结合我们的实验结果,动情期雌激素水平迅速达到峰值,在雌激素水平的作用下,细胞增殖分裂活跃,间质出现水肿,压迫上皮组织,使子宫内膜处于相对缺氧状态,此时ATF4表达比其他组显著增加,可能是由于应激作用导致PERK磷酸化从而激活elF2α-ATF4途径,导致ATF4蛋白活化表达上调,从而诱导VEGF促进子宫内膜血管形成和血管平滑肌细胞的增殖分化,最终形成有利于着床的子宫内环境,为胚胎植入做好准备。
总之,本研究初步探讨了ATF4基因在小鼠动情周期子宫内膜的表达模式,为进一步探讨此分子在雌性生殖中的作用提供了依据。
[1] Ameri K, Harris A L.Activating transcription factor 4[J]. J Biochem Cell Biol,2008,40:14-21.
[2] Ye JB, Koumenis C.ATF4,an ER stress and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor and its potential role in hypoxia tolerance and tumorigenesis [J]. Curr Mol Med,2009,9:411-416.
[3] Busk M, Toustrup K, Sørensen BS,etal.Invivoidentification and specificity assessment of mRNA markers of hypoxia in human and mouse tumors[J]. BMC Cancer,2011,11:63.
[4] Namba T,Hoshino T,Tanaka K,etal.Up-regulation of 150-kDa oxygen-regulated protein by celecoxib in human gastric carcinoma cells[J]. Mol Pharmacol,2007,71:860-870.
[5] Zhang Z, Yin J, Zhang C,etal.Activating transcription factor 4 increases chemotherapeutics resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2012,13:435-442.
[6] Gomez E,Powell ML,Bevington A,etal.A decrease in cellular energy status stimulates PERK-dependent eIF2alpha phosphorylation and regulates protein synthesis in pancreatic beta-cells[J]. Biochem J,2008,410:485-493.
[7] Cao J, Dai DL, Yao L,etal.Saturated fatty acid induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in human liver cells via the PERK/ATF4/CHOP signaling pathway[J]. Mol Cell Biochem,2012,364:115-129.
[8] Fata JE, Chaudhary V, Khokha R.Cellular turnover in the mammary gland is correlated with systemic levels of progesterone and not 17beta- estradiol during the estrous cycle[J]. Biol Reprod,2001,65:680-688.
[9] Chakraborty G, Jain S,Kundu GC.Osteopontin promotes vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent breast tumor growth and angiogenesis via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms[J]. Cancer Res, 2008,68:152-161.
[10] Malabanan KP, Kanellakis P, Bobik A,etal.Activation transcription factor-4 inducedby fibroblast growth factor-2 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-A transcription invascular smooth musclecells and mediates intimal thickening in rat arteries following balloon injury[J].Circ Res, 2008,103:378-387.
[11] Oskolkova OV, Afonyushkin T, Leitner A,etal.ATF4-dependent transcription is a key mechanism in VEGF up-regulation by oxidized phospholipids: critical role of oxidized sn-2 residues in activation of unfolded protein response[J].Blood, 2008,112:330-339.
[12] Roybal CN, Hunsaker LA, Barbash O,etal. The oxidative stressor arsenite activates vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA transcription by an ATF4-dependent mechanism[J].J Biol Chem, 2005,280:20331-20339.
Expression of ATF4 in mouse endometrium during the estrus cycle
LING Kang1, CHAI Lu-wei2, HE Xiao-xi2, JIANG Rong2*
(1.Dept. of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University;2.Laboratory of Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400016,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression pattern of ATF4 in mouse endometrium during the estrus cycle.MethodsReverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT- PCR), immunohistochemistry and Western blotting were used to detect the expression of ATF4 mRNA and protein in mouse endometrium during at each stage of the estrus cycle.ResultsATF4 mRNA expression in estrus stage was higher than those of the other 3 stages, and there was significant difference between estrus stage and the other 3 groups (Plt;0.05). The prominent expression of ATF4 protein was primarily limited to the glandular epithelium cell and luminal epithelium cell cytoplasm in the endometrium. Expression of ATF4 protein was similar with that of the mRNA.ConclusionsATF4, expressed in endometrium periodically in the estrus cycle, might play an important role in endometrial cyclical variation during the estrus cycle.
ATF4;mice;estrus cycle;endometrium
2013-02-18
2013-06-03
重庆市教委课题(KJ110307)
*通信作者(correspondingauthor): ganxibaoyanjiushi@126.com
1001-6325(2014)01-0078-04
R 394
A

