自体肌腱与同种异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带早期对比研究
关和宇
自体肌腱与同种异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带早期对比研究
关和宇
目的比较自体肌腱与同种异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带术后早期疗效差异。方法自2011年10月~2012年10月行前交叉韧带重建患者163例。根据采用移植物的不同将患者分为自体组85例,异体组78例。术后随访1个月, 比较两组患者的手术时间、引流量、发热天数、术后第7天患肢肿胀程度、患肢肌力恢复程度、术后第3天及第7天CRP值。结果异体组的手术时间(39.2±1.3)min显著低于自体组(52.6±1.7 )min, 术后异体组引流量(106.7±2.6)ml与自体组(102.6±4.3)ml无明显差异, 异体组发热天数(4.6±0.5)d显著长于自体组(1.3±0.2)d, 异体组术后患肢早期肌力恢复程度显著高于自体组, 异体组的患肢肿胀程度显著低于异体组, 异体组术后第3天CRP值(32.9±1.2)mg/L与自体组(31.5±0.8 ) mg/L无显著差异, 异体组术后第7天CRP值(91.7±9.6)mg/L显著高于自体组(12.8±6.1)mg/L。结论异体组术后早期临床疗效优于自体组。
前交叉韧带;重建;关节镜;自体肌腱;异体肌腱
前交叉韧带是维持膝关节稳定的重要结构, 防止胫骨过度前移及旋转不稳[1,2]。前交叉韧带严重损伤或断裂可导致膝关节不稳, 引起膝关节功能障碍和膝关节软骨面的损伤。关节镜下前交叉韧带重建是目前治疗前交叉韧带断裂的主要方法。广泛认为应用自体髌韧带重建前交叉韧带是该手术的金标准[3]。在过去的10年里, 自体半腱肌和股薄肌的应用急剧增加[4]。目前随着材料的发展前交叉韧带重建可选用自体肌腱, 同种异体肌腱及Leeds-Keio人工韧带等[5]。沈阳市骨科医院自2011年10月~2012年10月共收治前交叉韧带患者163例, 分别应用自体肌腱及同种异体肌腱重建损伤前交叉韧带。现报告如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料 自2011年10月~2012年10月本院行膝关节镜下前交叉韧带重建患者163例。其中, 自体组85例, 男性48例, 女性37例, 平均年龄36.7岁。单纯前交叉韧带断裂40例, 合并内侧副韧带损伤的18例, 合并半月板损伤的27例。异体组78例, 男性42例, 女性36例, 平均年龄35.3岁。单纯韧带断裂34例, 合并半月板损伤的32例, 合并内侧副韧带损伤的12例。术前两组患者均行膝关节磁共振检查明确诊断。两组手术均由同一医师在同一套关节镜设备下完成。
1.2植入物准备 自体组:膝关节屈曲90°, 在胫骨结节内侧做一长约3 cm的斜行切口。逐层分离至半腱肌及股薄肌的止点。用取腱器取下半腱肌及股薄肌。清理肌腱表面的软组织后, 游离端应用可吸收线编织缝合3 cm。用10 kg力量持续牵拉10 min, 含8万单位庆大的生理盐水浸泡20 min。异体组:选择合适的由山西骨组织库提供的异体肌腱,游离端用可吸收线编织缝合3 cm, 用10 kg力量持续牵拉10 min, 含8万单位庆大的生理盐水浸泡20 min。
1.3手术方法 患者取仰卧位, 膝关节屈曲90°。取膝关节的前内、前外侧入路, 置入关节镜检查膝关节内损伤情况,清理病变滑膜并修复半月板。安装定位器, 将定位器的尖端固定在外侧半月板前脚后缘与胫骨髁间嵴连线中点处。沿定位器的胫骨尖端向胫骨平台尖端钻入一枚定位针, 取下定位器应用与植入肌腱直径相等的空心钻沿定位针钻胫骨隧道。经胫骨隧道安装股骨隧道定位器, 应用定位针定位, 用与植入肌腱直径相等的空心钻钻入30 mm后改用Endobutton专用空心钻钻透股骨对侧皮质。应用合适长度的Endobutton带绊钢板固定股骨端, 确保钢板紧贴骨皮质, 将膝关节屈曲30°~40°后拉紧韧带应用可吸收挤压螺钉沿胫骨隧道方向拧入至螺帽与胫骨皮质相平。测试膝关节的稳定性证实韧带无撞击后冲洗膝关节, 放置引流, 缝合手术切口。
1.4术后处理 手术完毕后膝关节均留置引流管, 冰敷24 h,患肢均用弹力绷带加压包扎, 24 h候拆除弹力绷带, 拔除引流管。术后第1天嘱患者型行股四头肌等长收缩及踝泵练习。术后第1周患肢在0°~30°之间主动屈伸锻炼。术后第4周主动屈伸膝关节膝关节至90°。
1.5早期观察项目 手术时间、术后24 h术区引流量, 发热天数, 术后患肢直腿抬离床面的时间, 术后第7天患侧与健侧大腿周径比值, 术后第3天及第7天C反应蛋白值。
1.6统计学方法 采用SPSS17.0软件进行统计。两组数据均以表示, 计量资料采用t检验, 计数资料采用χ2检验。
2 结果
两组患者均获得随访, 随访时间为1个月。自体组患者均未出现手术切口愈合问题。异体组出现两例术区排异反应,给予换药处理后手术切口愈合, 其余患者均正常。异体组的手术时间显著低于自体组, 术后两组的引流量无明显差异,异体组发热天数显著长于自体组, 异体组术后患肢早期肌力恢复程度显著高于自体组, 异体组的患肢肿胀程度显著低于异体组, 两组患者术后第3天CRP值无显著差异, 异体组术后第7天CRP值显著高于自体组, 见表1。
表1自体组与异体组术后早期比较
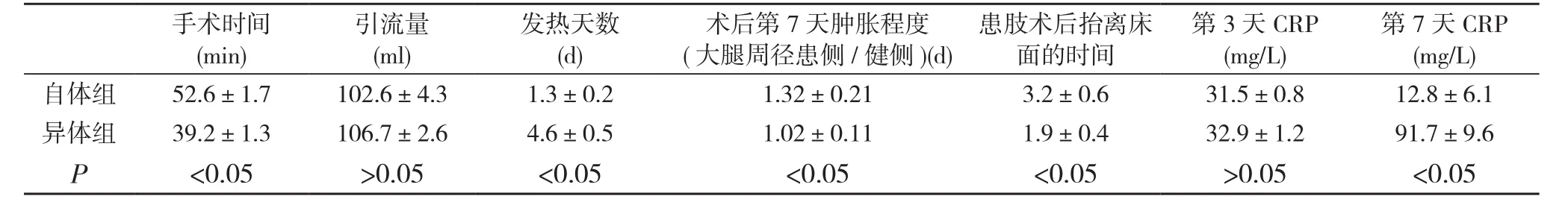
表1自体组与异体组术后早期比较
第7天CRP (mg/L)自体组52.6±1.7102.6±4.31.3±0.21.32±0.213.2±0.631.5±0.812.8±6.1异体组39.2±1.3106.7±2.64.6±0.51.02±0.111.9±0.432.9±1.291.7±9.6 P<0.05>0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05>0.05<0.05手术时间(min)引流量(ml)发热天数(d)术后第7天肿胀程度(大腿周径患侧/健侧)(d)患肢术后抬离床面的时间第3天CRP (mg/L)
3 讨论
前交叉韧带是保持膝关节稳定的重要结构之一, 它可以限制胫骨过度前移。前交叉韧带损伤是在年轻人当中最常见的一种运动损伤[6]。前交叉韧带损伤后引起不同程度的膝关节不稳可导致关节内其他结构的损伤如半月板损伤、关节软骨损伤等。由于前交叉韧带长期承受拉力导致其损伤后自行修复能力极差[7]。目前认为应用自体骨-髌韧带-骨重建前交叉韧带是治疗前交叉韧带损伤的“金标准”[3]。随着前交叉韧带重建手术的增多, 可供医生选择的材料也随之增多。目前应用于前交叉韧带重建的移植物主要包括自体肌腱,同种异体肌腱, 人工韧带。由于人工韧带的长期疗效不确切,同种异体肌腱已成为替代自体肌腱的主要移植物。
应用自体肌腱的优点是韧带与骨组织较早的愈合[8], 避免发生排异反应及血液传播疾病, 术后膝关节的本体感觉恢复早于同种异体肌腱[9]。但自体肌腱的来源受到限制, 不可反复取材。应用异体肌腱的优点是创伤小, 不破坏肌腱原有的功能, 术后患肢肌力恢复较快。可根据手术的需要进行取材。手术时间短, 缩短了止血带的应用时间从而降低了下肢深静脉血栓形成的风险。与自体肌腱相比术后发生膝关节僵硬的概率降低[10]。但应用异体肌腱可增加血液传播疾病、细菌感染性疾病及免疫排异反应发生的风险[11,12], 可引起手术切口延迟愈合。目前采用深低温(-70~-80℃)保存异体肌腱可以使其抗原性大大降低, 减少免疫排斥反应, 而基本不破坏韧带本身的生物力学性能。
一些文献报道同种异体和自体移植物重建ACL的疗效相近[13-15]。本次研究只是对比观察两组患者术后早期的一些指标。异体组患者术后发热天数及第7天CRP明显高于自体组。提示异体早期存在显著地免疫反应。免疫反应引起的炎性渗出增多, 本研究中异体组2例患者切口愈合欠佳可能与此有关。自体组由于自体腘绳肌腱的缺失, 术后早期患者疼痛程度高于异体组[16], 患肢肌力低于异体组。Isokinetic测试[17,18]表明, 自体腘绳肌腱移植前交叉韧带重建术后, 经系统腘绳肌肌力练习, 内旋肌力可恢复至健侧的80%和85%左右, 与健侧相比任由差距。
总之, 应用异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带手术时间短、创伤小, 肌力恢复快、可根据手术需要随意取材, 其早期临床疗效优于自体组。由于本次研究随访时间较短, 两组患者的长期临床疗效有待于进一步随访验证。
[1] Katz JW, Fingeroth RJ.The diagnostic accuracy of rupturesof the anterior cruciate ligament comparing the Lachman test, the anterior drawer sign, and the pivot shift test in acute and chronic knee injuries.Am J Sports Med, 1986(14): 88-91.
[2] Marrale J, Morrissey MC, Haddad FS.A literature review of autograft and allograft: Anterior ligament reconstruction.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol.Arthroscopy, 2007(15):690-704.
[3] Hospodar SJ, Miller MD.Controversies in ACL reconstruction:Bonepatellar tendon-bone anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction remains the gold standard.Sports Med Arthrosc, 2009(17):242-246.
[4] Kang Sun, Jihua Zhang, Yan Wang, et al.Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With at Least 2.5 Years’ Followup Comparing Hamstring Tendon Autograft and Irradiated Allograft.Arthroscopy, 2011, 27(9):1195-1202.
[5] FujikawaK, KobayashiT, SasazakiY, et al.Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with the Leeds-Keio artificial ligament.J Long Term Med Implants, 2000(10): 225-238.
[6] Boni DM, Herriott GE.Hamstring tendon graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.AORN J , 2002(76):610-627.
[7] Nau T, Lavoie P, Duval N.A new generation of artificial ligaments in reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament:two year follow-up of a randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2002, 84(3):347-354.
[8] Jackson DW, Grood ES, Goldstein JD, et al.A comparison of patellar tendon autograft and allograft used for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in the goat model.Am J Sports Med, 1993(21):176-185
[9] 谢磊, 陈百成, 王晓峰, 等.自体及同种异体肌腱重建前交叉韧带术后本体感觉恢复的比较研究.中国修复重建外科杂志, 2011, 25(8):907-911.
[10] Goertzen MJ, Clahsen H, Biirrig KP.Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using cryopreserved irradiated bone-ACL-boneallograft transplants.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthroscopy , 1994(2): 150-157.
[11] Cohen SB, Sekiya JK.Allograft safety in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Clin Sports Med, 2007, 26(4):597-605.
[12] Strickland SM, MacGillivray JD, Warren RF.Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with allograft tendons.Orthop Clin North Am, 2003, 34(1):41-47.
[13] Nyland J, Caborn DN, Rothbauer J, et al.Two-year outcomes following ACL reconstruction with allograft tibialis anterior tendons: a retrospective study Knee Surg Sports Traumatol.Arthroscy, 2003(11): 212-218.
[14] Chang SK, Egami DK, Shaieb MD, et al Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: allograft versus autograft.Arthroscopy, 2003(19): 453-462.
[15] Lawhorn KW, Howell SM Scientificjustificationandtechniquefo r anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using autogenous and allogeneicsoft-tissuegrafts.OrthopClin North Am, 2003(34): 19-30
[16] 王佳时, 白伦浩, 王勇, 等.自体与异体腘绳肌腱移植重建前交叉韧带对比研究.大连医科大学学报, 2010, 32(4):422-425.
[17] Andrea Ferrett, i Antonio Vada, l et al .Minimizing InternalRotation Strength Deficit After Use of Semitendinosus for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Modified HarvestingTechnique.Arthroscopy: JArthroscopic Related Surg, 2008, 24(7): 786-795.
[18] 刘晓鹏, 安华, 于长隆.应用等速肌力测试评价膝前交叉韧带断裂重建术后康复的效果.中国运动医学杂志, 2008, 27(3): 286-289.
Early postoperation research of autograft tendon versus allograft tendon in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
GUAN He-yu.
Shenyang Orthopaedic Hospital, Shenyang 110044, China
ObjectiveTo campare the early clinical efficacy of autograft and allograft tendon in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.MethodsFrom October 2011 to October 2012, 163 patients of injured Anterior Cruciate Ligament were reconstructed.According to different graft was used in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, they were divided into two groups.85 cases of patients were reconstructed by autograft is Group A, 78 cases of patients were reconstructed by allograft is Group B.After 1 month follow up, to compare the operation time, the drainage amount, postoperative fever days, the degree of limb myodynamia recovery, the seventh day of postoperative limb swelling degree, the CRP value about the third and seventh day of postoperative.ResultsThe time of operation in Group B(39.2±1.3)min was significant shorter than that in Group A(52.6±1.7 )min, the drainage amount was no significant difference between Group B(106.7±2.6)mland Group A(102.6±4.3)ml, the postoperative fever days in Group B (4.6±0.5)d was significant longer than that in Group A(1.3±0.2)d, the degree of limb myodynamia recovery in Group B was significant higher than that in Group A , the seventh day of postoperative limb swelling degree in Group B was significant lower than that in Group A, the CRP value about the third day of postoperative was no significant difference between Group B (32.9±1.2)mg/L and Group A (31.5±0.8 )mg/L, the CRP value about the seventh day of postoperative in Group B (91.7±9.6)mg/L was significant higher than that in Group A (12.8±6.1)mg/L.ConclusionThe early postoperative clinical effects of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with allograft was better than that with autograft.
Anterior cruciate ligament;Reconstruction;Arthroscopy;Autograft tendon;Allograft tendon
110044 沈阳市骨科医院

