ARRB1融合蛋白表达载体ARRB1-EGFP的构建及其在神经胶质瘤细胞中的表达
文普帅,高 静辽宁医学院病理生理学教研室,辽宁锦州 000;辽宁医学院附属第一医院 超声科,辽宁锦州000
ARRB1融合蛋白表达载体ARRB1-EGFP的构建及其在神经胶质瘤细胞中的表达
文普帅1,高 静21辽宁医学院病理生理学教研室,辽宁锦州 121000;2辽宁医学院附属第一医院 超声科,辽宁锦州121000
目的 构建重组表达载体ARRB1-EGFP,在细胞中表达与鉴定,为进一步研究其功能奠定基础。方法 RT-PCR获得编码人ARRB1的全基因序列,克隆到真核表达载体pEGFPN1,构建重组表达载体ARRB1-EGFP,并转化于E.coli DH5α中筛选阳性重组子,通过限制性内切酶酶切电泳鉴定和DNA序列测定正确后,转染入HEK293细胞中表达,表达产物经Western blot检测蛋白的特异性,应用免疫荧光方法比较融合蛋白与内源性ARRB1在SNB19细胞的定位。结果 成功构建了ARRB1融合蛋白的真核表达载体,并经Western blot鉴定正确。免疫荧光提示融合蛋白与内源性ARRB1定位相似。结论 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白可以安全、高效地转导入HEK293以及SNB19细胞中。
ARRB1蛋白;载体构建;表达;融合蛋白
ARRB1(β-arrestin1)是Arrestin家族成员之一,在全身各组织广泛表达,在脑和脾组织中表达最多,分布于细胞质和细胞核中[1-2]。最初发现,ARRB家族能够负向调节GPCR受体信号通路[3]。后续研究表明,该家族作为内吞适配器、信号转导子以及支架蛋白可以调控细胞多种生理功能,例如调节Wnt、TGFB、Notch与IGF-1受体等信号通路,调节细胞骨架,参与转录调控等[4-13]。也有报道发现ARRB1能够调节肿瘤的增殖、存活、迁移以及肿瘤血管发生等行为[14-22]。近年来的研究表明ARRB1在肿瘤组织中异常表达。Li等[23]发现,在乳腺癌和黑色素瘤细胞中ARRB1的mRNA水平明显增高;而Michal等[21]的结果恰恰相反,发现ARRB1水平降低,并与患者的不良预后呈正相关。本文构建了含有ARRB1和增强型绿色荧光蛋白融合蛋白的表达质粒,成功在细胞内表达,并观察到与内源性ARRB1相似的定位,为深入探讨ARRB1在神经胶质瘤细胞中的作用奠定基础。
材料和方法
1 材料和试剂 载体pEGFPN1购自Addgene公司;人胚肾细胞HEK293和神经胶质瘤SNB19细胞由中国科学院生物物理研究所提供;PCR回收试剂盒、质粒提取试剂盒、凝胶回收试剂盒购自康为世纪公司;XhoⅠ、HindⅢ、EcoRI、T4 DNA连接酶以及Phusion超保真DNA聚合酶购自NEB公司;核酸相对分子质量标准参照物(DM2000和1K) (康为世纪),蛋白预染标准参照物均为美国Fermentas公司产品;质粒转染试剂LipofectamineTM2000购自Invitrogen公司;感受态大肠埃希菌DH5α购自全式金公司;寡核苷酸引物合成及DNA序列测定由华大基因公司完成;ARRB1多克隆抗体购自武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司、辣根酶标记山羊抗兔IgG二抗、FITC标记山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)二抗购自Invitrogen公司。
2 ARRB1基因引物设计与扩增 用RT-PCR从人胚肾细胞的poly(A+)RNA中扩增ARRB1的cDNA,两端分别引入XhoⅠ和HindⅢ酶切位点。上游引物:5'-TATCTCGAGGCCACCATGGGCGACAAAGG GACC-3';下游引物:5'-TATAAGCTTTCTGTTGTT GAGCTGTGG。PCR扩增条件:95℃预变性5 min,然后95℃变性30 s、58℃退火30 s、72℃延伸2 min,循环35次后,72℃保温10 min。1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定扩增结果。
3 ARRB1-EGFP载体的构建 ARRB1基因PCR扩增产物及载体pEGFPN1经XhoⅠ和HindⅢ双酶切后应用琼脂糖凝胶DNA回试剂盒纯化回收,在T4连接酶的作用下16℃连接过夜后,转化DH5α感受态,在卡那霉素阳性细菌平板筛选出单个阳性克隆,提取细菌质粒行EcoRI单酶切鉴定,并送华大基因公司测序。待测序正确后,再大量提取该质粒,命名为ARRB1-EGFP。
4 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白的表达及Western blot检测 利用LipofectamineTM2000将ARRB1-EGFP及对照质粒pEGFPN1分别转染HEK293细胞,6 ~8 h后更换新鲜培养基,转染24 h后收集细胞,提取蛋白进行蛋白质印迹,以抗GFP多克隆抗体为一抗,以HRP标记的羊抗兔IgG为二抗检测融合蛋白的表达。
5 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白及内源ARRB1在细胞内定位的比较 将ARRB1-EGFP质粒转染至SNB19细胞中,36 h后弃培养基,PBS洗3次,4%多聚甲醛固定细胞30 min,PBS洗3次,DAPI室温5 min,PBS洗3次,封片,荧光显微镜观察。免疫荧光检测内源ARRB1时,常规固定、封闭后,加入抗ARRB1多克隆抗体(浓度为1∶500),4℃孵育过夜,PBS洗3次,加入山羊抗兔IgGFITC(浓度为1∶500),37℃孵育1 h,PBS洗3次,DAPI室温5 min,PBS洗3次,封片,荧光显微镜观察。
结 果
1 ARRB1基因的扩增 经RT-PCR反应后,1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳见约1.3 kb处有亮带,与预计ARRB1基因片段大小相符。见图1。
2 ARRB1-EGFP的酶切鉴定及测序报告 挑取单个白色菌斑,扩大培养后小量提取质粒,由于载体pEGFPN1和距ARRB1基因其实位点483 bp处存在EcoRI位点,所以,质粒经EcoRI酶切鉴定,酶切后产生5 126 bp和785 bp的两个条带,分别为载体和ARRB1基因片段(图2),说明酶切片段的大小和插入方向均与预计相同,将鉴定正确的菌液送华大基因公司进行测序,利用NCBI的BLAST服务器将测序结果与基因库中已登记的ARRB1序列进行比对分析,同源性达到100%,以上结果均表明表达载体ARRB1-EGFP构建成功。

图 1 ARRB1基因的PCR扩增M: DM2000标准参照物;1: ARRB1基因Fig. 1 Application of ARRB1gene by RT-PCRM: DM2000 DNA ladder; 1: ARRB1 Gene
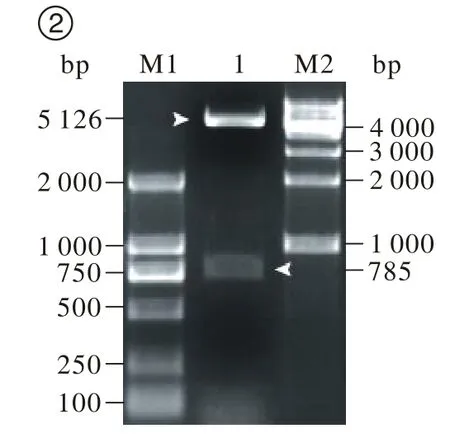
图 2 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白载体的酶切鉴定M1: DM2000标准参照物; 1: ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白载体; M2: 1K标准参照物Fig. 2 Restriction enzyme digestion of ARRB1-EGFP vector M2: DM2000 DNA ladder; 1: ARRB1-EGFP fusion protein vector;M2:1K DNA
3 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白在HEK293细胞中的表达 将ARRB1-EGFP质粒转染至HEK293细胞,24 h后提取蛋白,经蛋白免疫印迹检测在相对分子质量80 kU附近检测到一特异性条带,与预期的融合蛋白大小一致(图3)。上述结果显示成功在HEK293细胞中特异表达ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白。
4 ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白与内源性ARRB1细胞内定位比较 重组质粒转染24 h后,通过荧光显微镜观察,可检测到ARRB1胞质区域内有强烈的绿色荧光表达,同时细胞核内也有荧光表达,与内源性ARRB1的亚细胞定位相似,提示ARRB1-GFP能够在神经胶质瘤中表达良好。见图4。
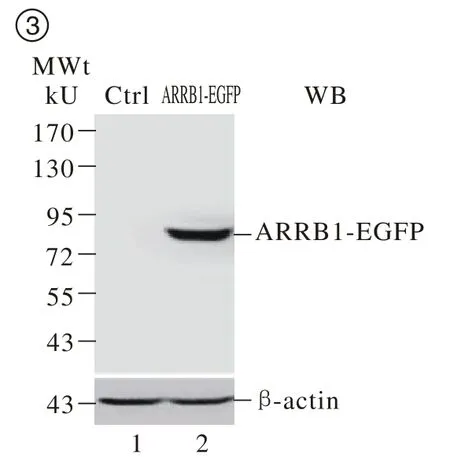
图 3 蛋白质印迹检测ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白的表达Fig. 3 Expression of ARRB1-EGFP d e t e c t e d b y Western blot
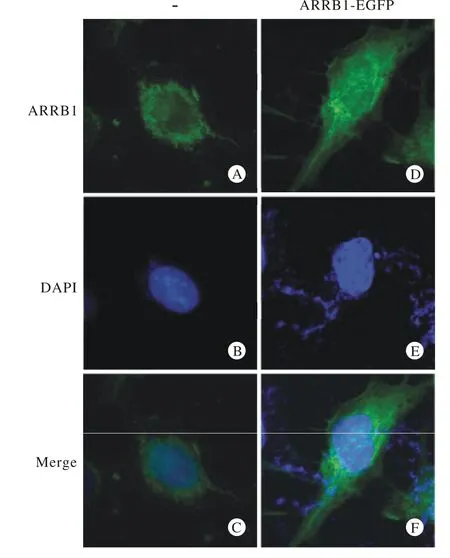
图 4 免疫荧光检测ARRB1-EGFP在神经胶质瘤SNB19细胞中的表达与定位A: FITC标记的内源性ARRB1; B: DAPI标记的细胞核; C:绿色与蓝色荧光重叠双染; D: 融合蛋白ARRB1-EGFP荧光; E: DAPI标记的细胞核; F: 绿色与蓝色荧光重叠双染;标尺: 25 μmFig. 4 Expression and localization of ARRB1-EGFP in SNB19 cells detected by immunofluorescenceA: FITC- labled endogenous ARRB1; B: DAPI- labled nucleus; C: merge of A and B; D: fluorescence of fusion protein ARRB1-EGFP; E: DAPI- labled nucleus; F: merge of D and E; scale bar: 25 μm
讨 论
Benovic等[24]从牛脑中纯化能够引起G蛋白偶联受体(G Protein-Coupled Receptors,GPCRs)脱敏的β-肾上腺素受体激酶(beta adrenergic receptor kinase,βARK)时发现,β-ARK的纯度越高引起β2-肾上腺素能受体脱敏的作用越弱,猜测存在一种对调节GPCRs脱敏起至关重要的蛋白质。随后即发现了ARRB1以及家族其他成员,从而开始了对ARRB家族的功能学研究。近几年研究发现ARRB1在多种肿瘤组织中存在异常表达,并与患者预后相关[21,23]。另外,有研究表明ARRB1参与调节肿瘤细胞的恶性生物学行为:Buchanan等[25]发现ARRB1能够与前列腺素E受体和c-Src形成信号转导复合物,进而转录激活表皮生长因子受体和下游分子Akt,从而调节结直肠癌细胞的迁移。Feigin等[20]发现表达ARRB1显性负性突变体能够降低PAR-2引起的细胞迁移,沉默ARRB1能够降低MDA MB-231细胞基础迁移能力。此外,ARRB1转基因小鼠血浆中VEGF浓度以及肿瘤组织中新生血管形成高于对照组[22]。这些研究结果提示ARRB1参与调节肿瘤迁移、血管形成等过程。然而,ARRB1在神经胶质瘤中的研究鲜有报道。
我们未发表的实验结果表明:ARRB1在神经胶质瘤中表达降低,并与患者生存时间存在相关性,为了研究ARRB1在神经胶质瘤中的生物学功能,根据ARRB1 cDNA序列,本研究设计正反向特异性引物,并在引物中加入XhoⅠ和HindⅢ酶切位点,以HEK293细胞的cDNA为模板,扩增出ARRB1 cDNA全长序列,成功克隆ARRB1-EGFP真核表达载体,经免疫印迹鉴定了ARRB1-EGFP融合蛋白的表达。并对比了ARRB1-EGFP与内源ARRB1在神经胶质瘤细胞中的定位,这些结果表明成功构建并表达了ARRB1-EGFP重组蛋白。本研究构建的ARRB1-EGFP重组质粒具有以下优点:1)选用带有报告基因的pEGFPN1质粒,可编码增强绿色荧光蛋白,具有荧光强、分子量较小、对宿主细胞无毒性、检测方便、不影响目的基因的表达及其后续的生物活性等优点;2)该质粒具有Neo基因,可以采用G418来筛选已成功转染了该质粒的靶细胞。
本研究构建的ARRB1-EGFP重组蛋白可用于体外或在体水平观察ARRB1对神经胶质瘤的影响,为探讨ARRB1在神经胶质瘤中的作用以及研究ARRB1新的相互作用蛋白及其信号转导通路奠定了基础。
1 Sterne-Marr R, Gurevich VV, Goldsmith P, et al. Polypeptide variants of beta-arrestin and arrestin3[J]. J Biol Chem, 1993, 268(21): 15640-15648.
2 Oakley RH, Laporte SA, Holt JA, et al. Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G proteincoupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(22): 17201-17210.
3 Ferguson SS, Downey WE, Colapietro AM, et al. Role of betaarrestin in mediating agonist-promoted G protein-coupled receptor internalization[J]. Science, 1996, 271(5247): 363-366.
4 Kríz V, Pospíchalová V, Masek J, et al. β-arrestin promotes wnt-induced low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (Lrp6)phosphorylation via increased membrane recruitment of Amer1 protein[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(2): 1128-1141.
5 Bonnans C, Flacelière M, Grillet F, et al. Essential requirement for β-arrestin2 in mouse intestinal tumors with elevated Wnt signaling[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012, 109(8): 3047-3052.
6 Mythreye K, Knelson EH, Gatza CE, et al. TβRIII/β-arrestin2 regulates integrin α5β1 trafficking, function, and localization in epithelial cells[J]. Oncogene, 2013, 32(11): 1416-1427.
7 Puca L, Chastagner P, Meas-Yedid V, et al. Α-arrestin 1(ARRDC1) and β-arrestins cooperate to mediate Notch degradation in mammals[J]. J Cell Sci, 2013, 126(Pt 19): 4457-4468.
8 Spartà A, Baiula M, Campbell G, et al. beta-Arrestin 2-mediated heterologous desensitization of IGF-IR by prolonged exposure of SHSY5Y neuroblastoma cells to a mu opioid agonist[J]. FEBS Lett,2010, 584(16): 3580-3586.
9 Zheng H, Shen H, Oprea I, et al. β-Arrestin-biased agonism as the central mechanism of action for insulin-like growth factor 1 receptortargeting antibodies in ewing’s sarcoma[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2012, 109(50): 20620-20625.
10 Barnes WG, Reiter E, Violin JD, et al. beta-Arrestin 1 and galphaq/11 coordinately activate RhoA and stress fiber formation following receptor stimulation[J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(9):8041-8050.
11 Zoudilova M, Kumar P, Ge L, et al. Beta-arrestin-dependent regulation of the cofilin pathway downstream of protease-activated receptor-2[J]. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282(28): 20634-20646.
12 Gao H, Sun Y, Wu Y, et al. Identification of beta-arrestin2 as a G protein-coupled receptor-stimulated regulator of NF-kappaB pathways[J]. Mol Cell, 2004, 14(3): 303-317.
13 Witherow DS, Garrison TR, Miller WE, et al. beta-Arrestin inhibits NF-kappaB activity by means of its interaction with the NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2004, 101(23): 8603-8607.
14 Jin G, Westphalen CB, Hayakawa Y, et al. Progastrin stimulates colonic cell proliferation via CCK2R- and β-arrestin-dependent suppression of BMP2[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145(4):820-30.e10.
15 Raghuwanshi SK, Nasser MW, Chen X, et al. Depletion of betaarrestin-2 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a murine model of lung cancer[J]. J Immunol, 2008, 180(8): 5699-5706.
16 Sun X, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. Beta-arrestin 2 modulates resveratrol-induced apoptosis and regulation of Akt/GSK3?pathways[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2010, 1800(9): 912-918.
17 Wu JX, Shan FX, Zheng JN, et al. β-arrestin promotes c-Jun n-terminal kinase mediated apoptosis via a GABA(B)R·βarrestin·JNK signaling module[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2014, 15(2): 1041-1046.
18 Rosanò L, Cianfrocca R, Masi S, et al. Beta-arrestin links endothelin A receptor to beta-catenin signaling to induce ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2009, 106(8): 2806-2811.
19 Kim JI, Lakshmikanthan V, Frilot N, et al. Prostaglandin E2 promotes lung cancer cell migration via EP4-betaArrestin1-c-Src signalsome[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2010, 8(4): 569-577.
20 Feigin ME, Xue B, Hammell MC, et al. G-protein-coupled receptor GPR161 is overexpressed in breast cancer and is a promoter of cell proliferation and invasion[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2014,111(11): 4191-4196.
21 Michal AM, Peck AR, Tran TH, et al. Differential expression of arrestins is a predictor of breast cancer progression and survival[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2011, 130(3): 791-807.
22 Zou L, Yang R, Chai J, et al. Rapid xenograft tumor progression in beta-arrestin1 transgenic mice due to enhanced tumor angiogenesis[J]. FASEB J, 2008, 22(2): 355-364.
23 Li TT, Alemayehu M, Aziziyeh AI, et al. Beta-arrestin/Ral signaling regulates lysophosphatidic acid-mediated migration and invasion of human breast tumor cells[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2009, 7(7):1064-1077.
24 Benovic JL, Kühn H, Weyand I, et al. Functional desensitization of the isolated beta-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: potential role of an analog of the retinal protein arrestin (48-kDa protein)[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1987, 84(24):8879-8882.
25 Buchanan FG, Gorden DL, Matta P, et al. Role of beta-arrestin 1 in the metastatic progression of colorectal cancer[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2006, 103(5): 1492-1497.
Construction of ARRB1-EGFP fusion protein and its expression in glioma cells
WEN Pu-shuai1, GAO Jing21Department of Pathophysiology, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China;2Department of Ultrasound, The First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
GAO Jing. Email: gaojinggg@163.com
Objective To construct the recombinant expression vector ARRB1-EGFP, identify its expression in cells, and lay foundations for further functional study. Methods The full gene sequence encoding human ARRB1 was obtained by RT-PCR and subcloned into the eukaryotic expression vector pEGFPN1. Recombinant expression vector, ARRB1-EGFP, was transformed into E.coli DH5α and screened by restriction enzyme digest, gel electrophoresis and DNA sequence. Then the expression vectors were transfected into HEK293 cells, and its expression products were detected by Western Blot. The subcellular localization between endogenous ARRB1 and ARRB1-GFP in the SNB19 cells was detected and compared by using immunofluorescence staining. Results ARRB1-EGFP fusion protein eukaryotic expression vector was successfully constructed, and identified by Western Blot. Localization of the fusion protein, ARRB1-GFP, was similar with that of the endogenous ARRB1. Conclusion ARRB1-EGFP fusion protein can be safely and efficiently transfected into HEK293 cells and SNB19.
ARRB1; vector construction; expression; fusion proteins
R 34
A
2095-5227(2014)10-1059-04
10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2014.10.023
时间:2014-06-06 11:07
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3275.R.20140606.1107.002.html
2014-04-02
文普帅,男,硕士,讲师。Email: wenpushuai@gmail.com
高静,女,硕士,主治医师。Email: gaojinggg@163.com

