以蛋白质组学技术筛选人肝细胞癌组织中失调蛋白相互作用的网络分析
肖忠华 苗加伟 黄海兵
作者单位:404120 重庆万州 重庆三峡医药高等专科学校
基础研究
以蛋白质组学技术筛选人肝细胞癌组织中失调蛋白相互作用的网络分析
肖忠华 苗加伟 黄海兵
作者单位:404120 重庆万州 重庆三峡医药高等专科学校
目的 分析从人肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)组织中发现并经验证的失调蛋白相互作用,探讨失调蛋白可能共同参与的生物学途径。方法以蛋白质组学和肝细胞癌为关键词搜索Pubmed数据库,人工筛选出从人HCC组织中发现并经验证的失调蛋白;以蛋白质相互作用数据分析软件PRINCESS分析失调蛋白的相互作用。结果 发现8个蛋白间存在9对置信度评分大于2.0的失调蛋白相互作用,APEX1分别与ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、MATR3两两相互作用,SULT1A1与PDIA6两两相互作用。结论 APEX1、ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、MATR3、IQGAP2可能在HCC发生、发展中经历同一生物学通路。
肝细胞癌;失调蛋白;蛋白质相互作用;生物学通路
肝细胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)是全球病死率较高的常见恶性肿瘤之一[1]。近十年来,高通量蛋白质组学技术从人HCC组织中寻找潜在的HCC早期诊断、预后监测生物标志物和治疗的药物靶标成为最有效的研究方法之一[2],而蛋白质相互作用网络构建和分析方法的发展则为进一步揭示HCC发生、发展及预后机制提供了新的有力工具。PRINCESS(protein interaction confidence evaluation system with multiple source)为北京蛋白质组学中心开发的在线免费蛋白质相互作用数据分析软件,采用贝叶斯网络算法,利用多种高通量蛋白质相互作用生物学证据,包括model organism protein-protein interaction(模式生物蛋白相互作用)、interaction domain(蛋白相互作用结构域)、GO coannotation(GO数据库共注释)、gene coexpression(基因共表达)、genome context(基因组上下文)、network topology(网络拓扑结构)等评估蛋白质相互作用置信度,蛋白质相互作用置信度评分大于2.0,表明该相互作用可信度高并为已有研究所证实,因而是一种灵敏性和特异性均较高的预测蛋白质相互作用的工具[3]。本实验利用Pubmed数据库筛选近年以蛋白质组学技术从人HCC组织发现并验证失调蛋白研究的文献,采用PRINCESS分析筛选文献中人HCC组织失调蛋白的相互作用,以期为从人HCC组织失调蛋白的相互作用揭示HCC发生、发展及预后的可能机制提供依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 人HCC组织失调蛋白的获得
以“HCC and proteomics”为关键词,限制条件为近5年和人类,搜索Pubmed数据库。按照以下条件人工筛选文献:⑴以人HCC组织为研究对象;⑵失调蛋白经Western Blot或免疫组化等方法验证,逐一阅读文献摘要或全文,获得以蛋白质组学方法从人HCC组织中发现并经验证的失调蛋白。
1.2 人HCC组织失调蛋白相互作用的网络分析
将以上1.1获得的失调蛋白在线提交PRINCESS(http://61.50.138.118/picasso/),在提交可能相互作用蛋白对列表下选项select organism(选择物种)项下选择homo sapiens(人类);在输入蛋白质或基因名类型项下选择entrez Gene symbol(entrez基因符号);在置信度评估选择相互作用生物学证据源项下勾选Model organism protein-protein interaction、interaction domain、GO coannotation、gene coexpression、genome context、network topology等全部选项,以上6项选项均设置为默认设置;输入相互作用置信度评分截断值2.0;点击”start”(开始),PRINCESS自动进行蛋白相互作用分析并构建网络;将置信度评分大于2.0的相互作用失调蛋白再次在线提交PRINCESS,构建置信度评分大于2.0失调蛋白相互作用的网络。
2 结果
2.1 获得的人HCC组织失调蛋白
按照1.1筛选的文献18篇,共获得22个失调蛋白,其中,在人HCC组织中上调蛋白分别为:CapG(macrophage-capping protein,巨噬细胞加帽蛋白)[4]、hnRNP K(heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K,核内不均一核糖核蛋白K)[5]、hnRNP A2/B1(heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1,核内不均一核糖核蛋白A2/B1)[6]、PRDX3(peroxiredoxin 3,硫氧还原蛋白过氧化物酶3)[7]、ANP32A(acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A,酸性富亮氨酸核磷蛋白32家族成员A)[8]、APEX1(apurinic/ apyrimidinic exonuclease 1,脱嘌呤/脱嘧啶外切核酸酶1)[8]、TUBA1C(tubulin alpha-6 chain,微管相关蛋白α6)[9]、MATR3(matrin 3,核基质蛋白3)[10]、LETM1(Leucine zipper/EF-hand-containing Transmembrane protein 1,亮氨酸拉链EF-hand结构域跨膜蛋白1)[10]、ILF2(interleukin enhancer binding factor 2,白介素增强子结合因子2)[10]、CIB1(calcium and integrin-binding protein 1,钙整合素结合蛋白1)[11]、TLN1(talin-1,踝蛋白 1)[12]、NDRG1(N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1,N-myc下游调控蛋白1)[13]、PDI A6(protein disulfide-isomerase A6,蛋白质二硫键异构酶A6)[14]、RhoA(Ras homolog gene family member A,Ras同源基因家族成员A)[15]、c-kit(原癌基因C-KIT编码的Ⅲ型受体酪氨酸蛋白激酶家族成员)[16]、GS(glutamine synthetase,谷氨酰胺合成酶)[17]、vimentin(波形蛋白)[18]、FUBPs(far upstream element binding proteins,远距上游结合蛋白)[19]、EB1(endbinding protein EB1,微管相关末端结合蛋白1)[20];人HCC组织中下调蛋白分别为IQGAP2(IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 2,含IQ基元GTP酶激活蛋白2)[10]和SULT1A1(sulfotransferases 1A1,硫酸基转移酶)[21]。
2.2 人HCC组织失调蛋白相互作用的网络
按照2.1在线提交“PINCESS”22个失调蛋白之间231对可能失调蛋白相互作用组合,结果22个蛋白中10个蛋白之间有45对蛋白相互作用,这10个蛋白分别为APEX1、ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、IQGAP2、MATR3、SULT1A1、PDIA6、NDRG1、LETM1;其中APEX1、ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、IQGAP2、MATR3、SULT1A1、PDIA6等8个蛋白之间有9对蛋白相互作用置信度评分大于2.0,在interaction domain、GO coanotation、gene coexpression、network topology等方面有生物学证据;其余36对蛋白相互作用评分介于0~2.0之间。10个蛋白之间45对蛋白相互作用的网络如图1;8个蛋白之间9对置信度评分大于2.0蛋白相互作用的网络如图2;8个蛋白之间9对置信度评分大于2.0蛋白相互作用的生物学证据如表1。
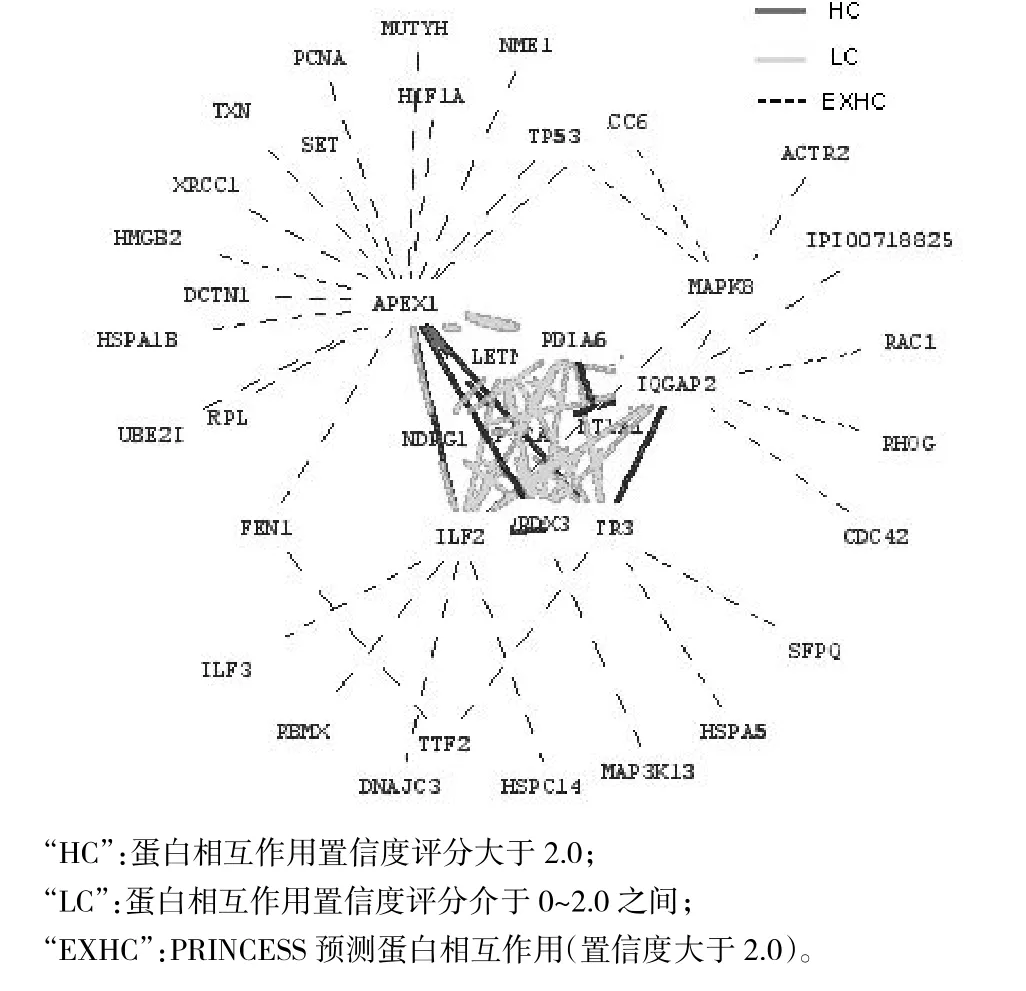
图1 10个蛋白之间45对蛋白相互作用的网络
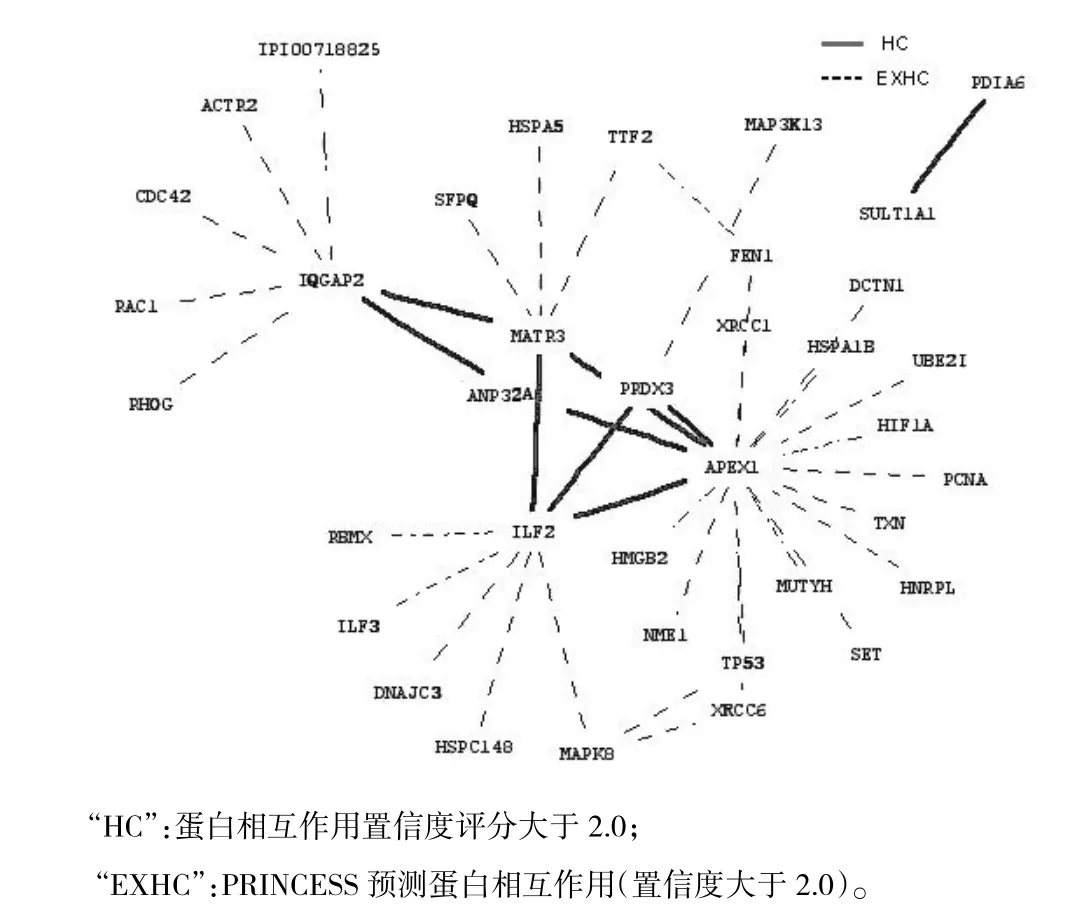
图2 8个蛋白之间9对蛋白质相互作用的网络
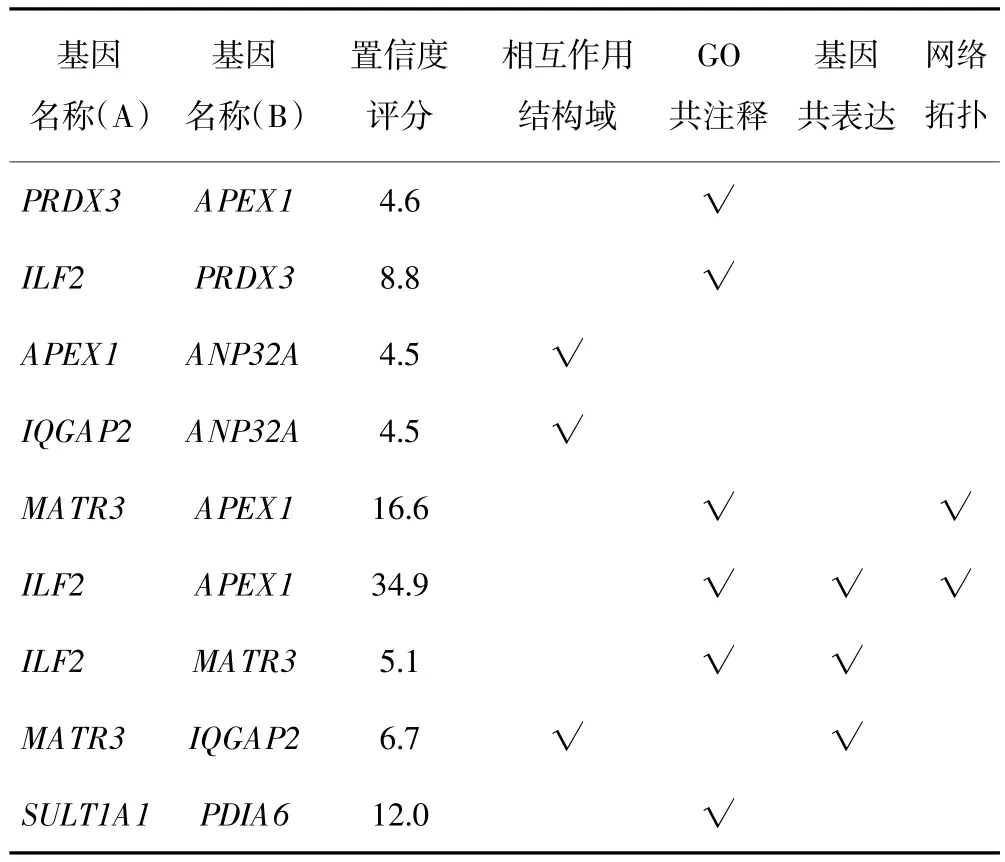
表1 PRINCESS分析失调蛋白相互作用的生物学证据
3 讨论
通过Pubmed数据库筛选期刊文献,获得近年以蛋白质组学技术从人HCC组织中发现并验证的失调蛋白22个,以蛋白质相互作用评估软件分析,置信度评分大于2.0的9对蛋白相互作用由8个蛋白产生。在这些蛋白中,PRDX3属于过氧化物酶基因蛋白家族,定位于线粒体。Qiao等[7]的研究表明,PRDX3不仅在HCC组织中高表达,而且其表达水平与HCC临床分期相关,尤其在转移HCC中的表达最多,HCC组织上调PRDX3,减少细胞氧化应激产生的过氧化氢诱导的细胞凋亡。MATR3、ILF2、IQGAP2为同一研究所发现[10],MRTR3和ILF2在细胞核中的表达上调,而IQGAP2在细胞骨架中的表达下调,MATR3、ILF2在调控细胞转录活性中起着重要作用,IQGAP2对维持细胞正常形态与功能具有重要的作用,可能是一种新的抑癌基因。APEX1具有氧化应激、转录共激活、DNA修复酶等多种生物学功能,ANP32A可参与细胞增殖、分化、caspase依赖或caspase不依赖凋亡、肿瘤抑制、mRNA运输调节等多种生物学过程。Li等[8]在蛋白质组学定量研究HCC组织中上调蛋白分子复合物研究中揭示:ANP32A、APEX1在HCC组织全细胞中高表达,细胞核中的高表达与临床分期密切相关;核内ANP32A、APEX1、SET(HLA-DR-associated proteinⅡ,HLA-DR相关蛋白2亚型1)、HMGB2(high mobilitygroup protein B2,高迁移家族蛋白B2)4个蛋白形成以SET为中心的分子复合物参与细胞氧化应激过程中GzmA(Granzyme A,颗粒蛋白酶A)介导的凋亡通路。而我们的研究中APEX1、ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、IQGAP2、MATR3 6个蛋白处于一个相互作用网络,除IQGAP2与APEX1间接相互作用外,其余4个蛋白均直接与APEX1有高置信度的直接相互作用,推测这6个蛋白可能在HCC发生、发展中经历同一生物学通路,或有可能也以SET蛋白为中心组成分子复合物参与HCC进程。硫酸基转移酶1A1是一种重要的解毒酶,在Yeo等[21]的研究中该蛋白的表达下调导致细胞解毒能力下降可能增加HCC发生的风险,而PDIA6属于蛋白质二硫化异构酶家族,可能激活组织因子的损伤响应信号从而促进癌栓形成[22]。在我们构建的置信度大于2.0的失调蛋白相互作用的网络中,SUL1A1和PDIA6直接相互作用,推测SUL1A1下调和PDIA6上调可能为同一生物学通路激活。
发现机体疾病生物学通路是研究机体疾病发生、发展机制的重要策略[23,24],其意义远高于疾病过程中单个蛋白质标志物的失调,从失调蛋白出发,发现不同研究所得失调蛋白之间的整体联系,能更客观反映疾病发生、发展的关键生物学通路。本文从Pubmed数据中以蛋白质组学技术筛选在人HCC组织中发现并经验证的失调蛋白,经蛋白质相互作用分析软件PRINCESS分析失调蛋白间的相互作用并构建相互作用网络,推测APEX1、ILF2、PRDX3、ANP32A、IQGAP2、MATR3可能组成以SET为中心的分子复合物参并与HCC进程,同时SUL1A1和PDIA6可能为同一生物学通路。下一步,我们将设计试验验证以上可能的生物学通路。
应该指出的是,没有参与构建相互作用网络的失调蛋白和所构建网络中没有显示为高置信度相互作用的失调蛋白,并不代表他们之间没有高置信度相互作用,而只是目前的研究中尚未涉及而已。蛋白质相互作用网络中还给出了PRINCESS预测的与当前研究中发现的失调蛋白高置信度相互作用的蛋白,同时研究网络中有兴趣的蛋白可能更全面地发现HCC发生、发展机制中的生物学通路,从而为探索HCC发生、发展的机制或寻找药物靶标提供进一步的依据。
(致谢:北京蛋白质组学中心)
[1] Ferenci P,Fried M,Labrecque D,et al.Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC):a global perspective[J].J Clin Gastroenterol,2010,44(4):239-245.
[2] Song HY,Liu YK,Feng JT,et al.Proteomic analysis on metastasis associated proteins of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues[J].J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2006,132(2):92-98.
[3] Li D,Liu W,Liu Z,et al.PRINCESS,a protein interaction confidence evaluation system with multiple data sources[J].Mol Cell Proteomics,2008,7(6):1043-1052.
[4] Kimura K,Ojima H,Kubota D,et al.Proteomic identification of the macrophage-capping protein as a protein contributing to the malignant features of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].J Proteomics,2013,78:362-373.
[5] Guo Y,Zhao J,Bi J,et al.Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K(hnRNP K)is a tissue biomarker for detection of early hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis[J].J Hematol Oncol,2012,5:37.
[6] Mizuno H,Honda M,Shirasaki T,et al.Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 in association with hTERT is a potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Liver Int,2012,32(7):1146-1155.
[7] Qiao B,Wang J,Xie J,et al.Detection and identification of peroxiredoxin 3 as a biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma by a proteomic approach[J].Int J Mol Med,2012,29(5):832-840.
[8] Li C,Ruan HQ,Liu YS,et al.Quantitative proteomics reveal up-regulated protein expression of the SET complex associated with hepatocellular carcinoma[J].J Proteome Res,2012,11(2):871-885.
[9] Kuramitsu Y,Takashima M,Yokoyama Y,et al.Up-regulation of 42 kDa tubulin alpha-6 chain fragment in well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma tissues from patients infected with hepatitis C virus[J]. Anticancer Res,2011,31(10):3331-3336.
[10]Lee YY,McKinney KQ,Ghosh S,et al.Subcellular tissue proteomics of hepatocellular carcinoma for molecular signature discovery[J].J Proteome Res,2011,10(11):5070-5083.
[11]Junrong T,Huancheng Z,Feng H,et al.Proteomic identification of CIB1 as a potential diagnostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Biosci,2011,36(4):659-668.
[12] Kanamori H,Kawakami T,Effendi K,et al.Identification by differential tissue proteome analysis of talin-1 as a novel molecular marker of progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Oncology,2011,80(5-6):406-415.
[13]Cheng J,Xie HY,Xu X,et al.NDRG1 as a biomarker for metastasis,recurrence and of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Lett,2011,310(1):35-45.
[14]Xu X,Wei X,Ling Q,et al.Identification of two portal vein tumor thrombosis associated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma:protein disulfide-isomerase A6 and apolipoprotein A-I[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2011,26(12):1787-1794.
[15]Gou L,Wang W,Tong A,et al.Proteomic identification of RhoA as a potential biomarker for proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].J Mol Med(Berl),2011,89(8):817-827.
[16]Guo W,Xue J,Shi J,et al.Proteomics analysis of distinct portal vein tumor thrombi in hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J].J Proteome Res,2010,9(8):4170-4175.
[17]Long J,Lang ZW,Wang HG,et al.Glutamine synthetase as an early marker for hepatocellular carcinoma based on proteomic analysis of resected small hepatocellular carcinomas[J].Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int,2010,9(3):296-305.
[18]Sun S,Poon RT,Lee NP,et al.Proteomics of hepatocellular carcinoma:serum vimentin as a surrogate marker for small tumors(<or=2 cm)[J].J Proteome Res,2010,9(4):1923-1930.
[19]Zubaidah RM,Tan GS,Tan SB,et al.2-D DIGE profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma tissues identified isoforms of far upstream binding protein(FUBP)as novel candidates in liver carcinogenesis[J].Proteomics,2008,8(23-24):5086-5096.
[20] Orimo T,Ojima H,Hiraoka N,et al.Proteomic profiling reveals the prognostic value of adenomatous polyposis coli-end-binding protein 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Hepatology,2008,48(6):1851-1863.
[21]Yeo M,Na YM,Kim DK,et al.The loss of phenol sulfotransferase 1 in hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J].Proteomics,2010,10(2):266-276.
[22]Manukyan D,von Bruehl ML,Massberg S,et al.Protein disulfide isomerase as a trigger for tissue factor-dependent fibrin generation[J]. Thromb Res,2008,122(Suppl.1):S19-22.
[23]Hartwell LH,Hopfield JJ,Leibler S,et al.From molecular to modular cell biology[J].Nature,1999,402:C47-C52.
[24] Bray D.Molecular networks:the top down view[J].Science,2003,301(5641):1864-1865.
[2014-07-23收稿][2014-08-25修回][编辑 阮萃才]
Identifying deregulated networks of protein-protein interactions through proteomics analysis of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue
XIAO Zhong-hua,MIAO Jia-wei,HUANG Hai-bing(Chongqing Three Gorges Medical School,Chongqing Wanzhou 404120,P.R.China)
XIAO Zhong-hua.E-mail:xiaozhonghua1010@126.com
Objective To analyze human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue using proteomics to identify possible deregulated networks of protein-protein interactions.Methods PubMed was searched using keywords“hepatocellular carcinoma”and“proteomics”to identify reports of proteins that are deregulated in the cancerous state.Then the proteins were analyzed for interactions using PRINCESS.Results Nine protein-protein interactions involving 8 proteins were assigned confidence scores>2.0:APEX1 interacts directly with ILF2,PRDX3,ANP32A,and MATR3 and indirectly with IQGAP2.SULT1A1 interacts directly with PDIA6.Conclusion APEX1,ILF2,PRDX3,ANP32A,MATR3,and IQGAP2 may participate in a single network associated with onset and/or progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatocellular carcinoma;Deregulated proteins;Protein-protein Interaction;Biological pathway
R735.7
A
1674-5671(2014)04-05
10.3969/j.issn.1674-5671.2014.04.08
重庆市教委科学技术研究基金资助项目(KJ131804)
肖忠华。E-mail:xiaozhonghua1010@126.com

