改进的乘积型核函数二次调频信号的参数估计
李亚超 于胜韬 全英汇 邢孟道
改进的乘积型核函数二次调频信号的参数估计
李亚超*于胜韬 全英汇 邢孟道
(西安电子科技大学雷达信号处理国防科技重点实验室 西安 710071)
该文提出一种基于改进乘积型核函数的二次调频信号的参数估计方法。首先,对信号乘以自身的共轭反转并做相位匹配变换,通过积累后信号最大值位置得到信号的调频率估计值;然后,再补偿掉原信号的调频率,对解调频(dechirp)后的信号构造新的乘积型核函数,并变换到2维时间-时延域,沿时间和时延轴分别做相位匹配变换和傅里叶变换,在变换后的调频率变化率-频率平面通过最大值的位置即可同时得到调频率变化率和中心频率的估计值,对补偿掉相位的信号取均值并求模得到幅度值,从而实现二次调频信号的参数估计和重构。可见,该方法避免了对所有相位参数的迭代搜索,提高了运算效率。最后,对单分量和多分量二次调频信号的仿真结果证明了该方法的有效性。
信号处理;乘积型核函数;二次调频信号;参数估计;相位匹配变换;FFT
1 引言

因此,针对以上问题,本文提出了一种基于改进乘积型核函数的多分量QFM信号的参数估计方法,先估计信号的调频率,再同时估计信号的调频率变化率和中心频率,最后估计信号的幅度,从而重构原信号。仿真结果证明了该方法的有效性。
2 QFM信号的时频分布
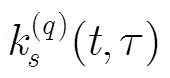
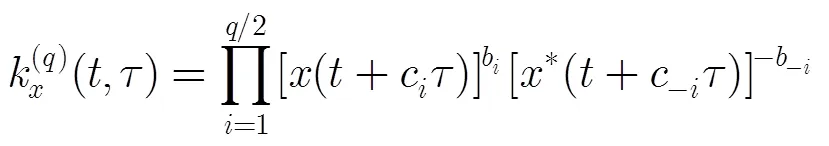
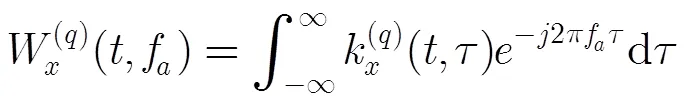
考虑单分量的QFM信号,表示为


或[15]

经过变换后所得到的信号相位为
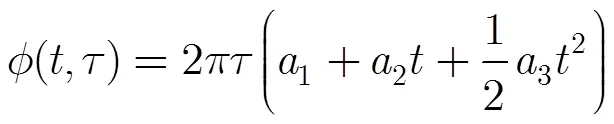
则信号对应的PWVD为

3 基于乘积型核函数的QFM信号的参数估计
针对QFM信号,构造一种新的乘积型的变换核函数:
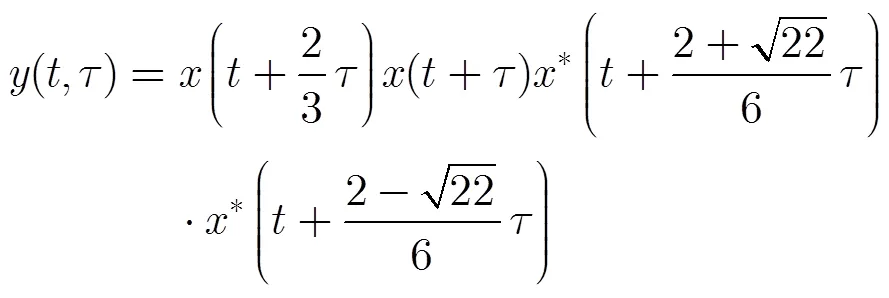
将式(3)代入式(8)得
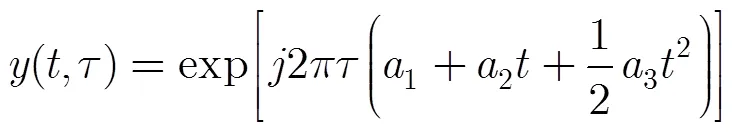
可以看出单分量QFM信号经过该变换后仍具有最佳的时频聚集性。
将式(7)得到的瞬时频率曲线改写为




3.1 单分量QFM信号的参数估计
信号形式如式(3)所示,首先构造函数:

将式(3)代入,得
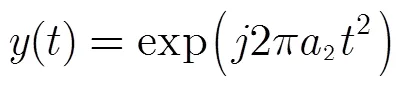
对式(13)做相位匹配变换
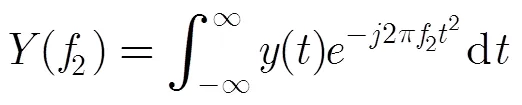
然后,将式(13)代入,得


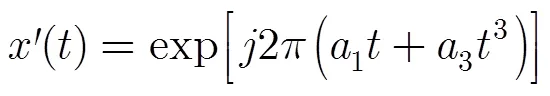
对新的信号式(17)作式(8)所示的变换,得到
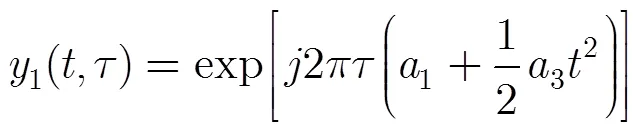
对式(18)做相位匹配变换得






3.2 多分量QFM信号的参数估计

再做相位匹配变换为
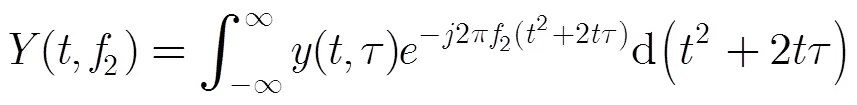

现有的如PHMT和PGCPF方法都是顺序估计信号的三次项,二次项和一次项系数。由于低次项系数的估计是在高次项估计并补偿之后进行的,因次高次项系数的估计精度会影响低次项的估计精度,并且三次项系数的估计值是在构造高阶核函数(PHMT构造6阶核函数,PGCPF构造4阶核函数)得到的,信噪比门限会比较高。与PHMT和PGCPF方法不同,本文的方法先通过构造2阶核函数(式(12)和式(25))估计二次项的系数,信噪比门限更低,在多分量信号情况下可以更好地检测并估计信号的参数,新的乘积型的变换核函数(式(8)和式(34))保证了三次项的系数和一次项的系数分别沿时间轴和时延轴彼此独立,因此可以同时估计三次项和一次项的系数,这样可以避免高次项的估计精度对低次项的估计精度的影响,可见,本文的方法具有一定的优势。
3.3 QFM信号参数估计的实现
多分量QFM信号的离散化表达形式为


多分量QFM信号的参数估计步骤为:
步骤2 构造式(25)的离散函数
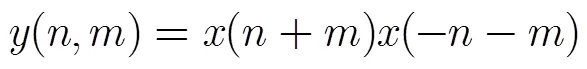



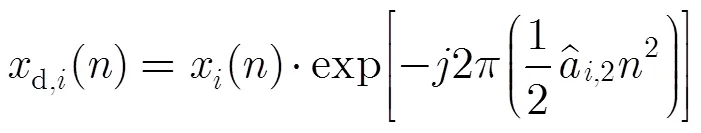





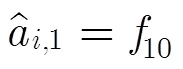

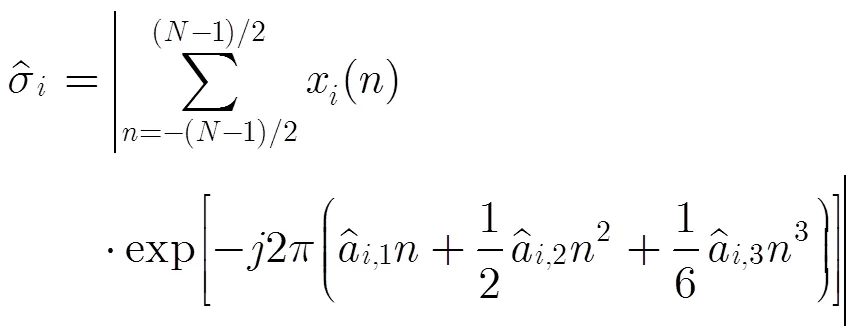

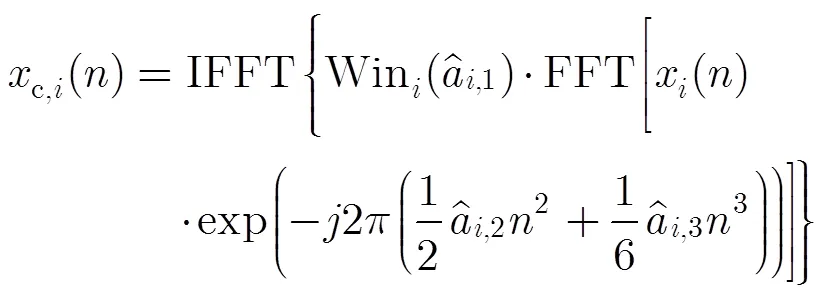
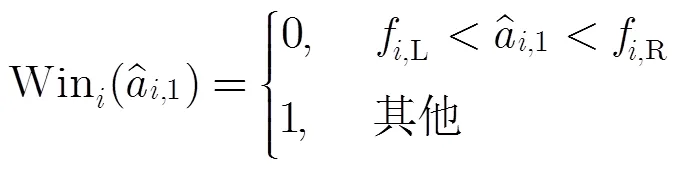

为了更好地抑制旁瓣,可以选用其他的窗函数[22]来替代式(43)中的矩形窗。
步骤8 计算剩余信号能量
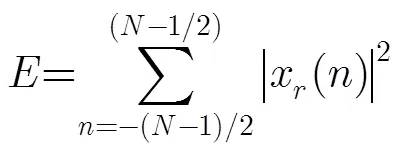
剩余能量与原信号能量的比值为
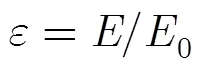
4 仿真分析
仿真1 为了验证乘积型核函数自身对外部交叉项的抑制能力,现取信号为
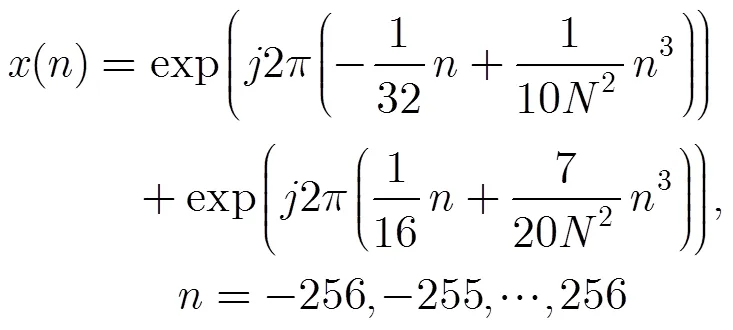
直接对信号进行步骤4的操作,结果如图1所示,通过峰值点的位置即可估计原信号的调频率变化率和中心频率,可以看出,两分量能够很好地分离,很好地抑制了外部交叉项的干扰,能实现信号各分量的参数估计。

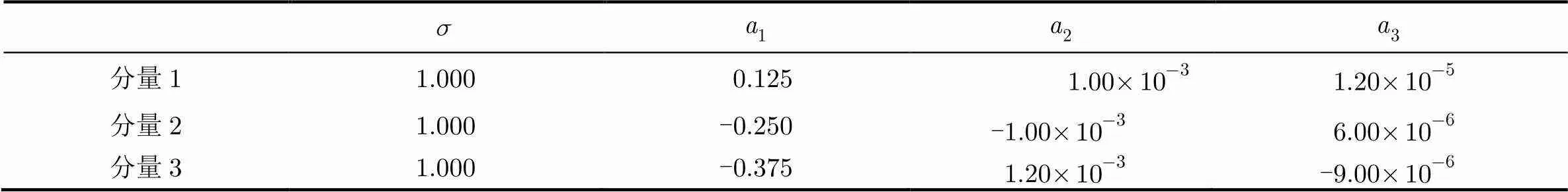
表1 QFM信号真实值
表2 信噪比条件下QFM信号估计值
表3 信噪比条件下QFM信号估计值
表4 信噪比条件下QFM信号估计值
当信号分量个数较少且信噪比较高时,本文提出的方法与PHMT和PGCPF方法的估计精度相差不大,但是当分量个数较多或者多分量信号的二次项系数差别较小时,本文提出的方法具有更为准确的估计结果,为此对两种情况下参数估计性能分别进行验证。
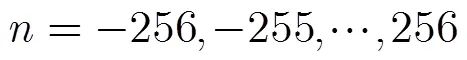
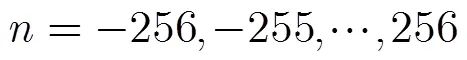

图2 信噪比下多分量QFM信号在调频率变化率-频率平面的3维分布图

表5 QFM信号真实值

5 结束语
本文针对多分量QFM信号提出了一种基于乘积型核函数的参数估计方法。该方法首先构造核函数估计QFM信号的调频率参数,接着补偿掉原信号的调频率,接下来通过构造新的乘积型的核函数将信号变换到2维时间-时延平面,在时间-时延平面分别沿时间和时延方向做相位匹配变换和FFT,将信号变换到新的2维调频率变化率-频率平面。在新的平面通过信号最大值的位置即可同时得到原信号的调频率变化率和中心频率的估计值。当原信号由多分量构成时,结合CLEAN技术逐渐分离并最终重构所有的二次调频信号。最后,仿真结果验证了本文提出的方法在估计多分量QFM信号参数方面的有效性。
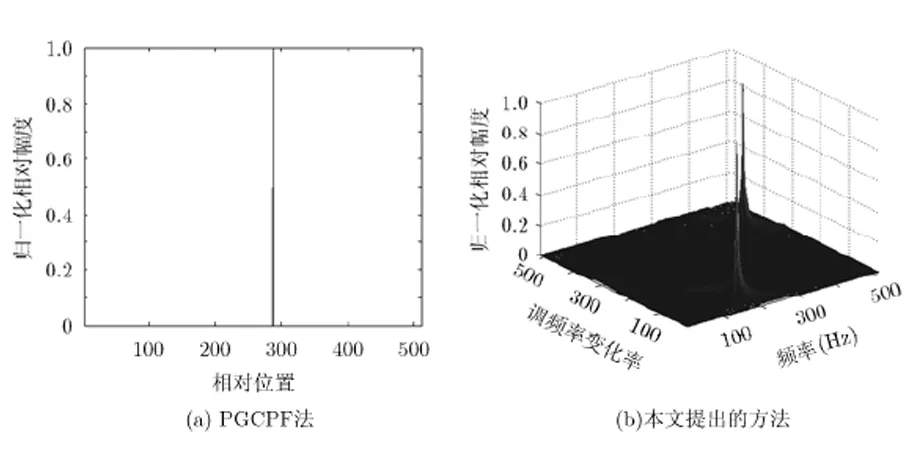
图4 多分量QFM信号的估计结果
[1] Zhang Lei, Qiao Zhi-jun, Xing Meng-dao,.. High- resolution ISAR imaging with sparse stepped-frequency waveforms[J]., 2011, 49(11): 4630-4651.
[2] Blomberg A E A, Nilsen C C, Austeng A,.. Adaptive sonar imaging using aperture coherence[J]., 2013, 38(1): 98-108.
[3] 陈倩倩, 徐刚, 李亚超, 等. 短孔径ISAR方位定标[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2013, 35(8): 1854-1861.
Chen Qian-qian, Xu Gang,Li Ya-chao,.. Cross-range scaling for ISAR with short aperture data[J].&, 2013, 35(8): 1854-1861.
[4] Hlawatsch F and Boudreaux-Bartels G F. Linear and quadratic time-frequency signal representations[J]., 1992, 9(2): 21-67.
[5] Spigai M, Tison C, and Souyris J. Time-frequency analysis in high-resolution SAR imagery[J]., 2011, 49(7): 2699-2711.
[6] Oswald N, Stark B, Holliday D,.. Analysis of shaped pulse transitions in power electronic switching waveforms for reduced EMI generation[J]., 2011, 47(5): 2154-2165.
[7] Lowry K, Roche J, Redfern M,.. A comprehensive assessment of gait accelerometry signals in time, frequency and time-frequency domains[J]., 2014, 22(3): 603-612.
[8] Galleani L. Time-frequency representation of MIMO dynamical systems[J]., 2013, 61(17): 4309-4317.
[10] Boashash B and O’Shea P. Polynomial Wigner-Ville distributions and their relationship to time-varying higher-order spectra[J]., 1994, 42(1): 216-220.
[11] Abotzoglou T. Fast maximum likelihood joint estimation of frequency and frequency rate[J]., 1986, 22(6): 708-715.
[12] O’Shea P. A fast algorithm for estimating the parameters of a quadratic FM signal[J]., 2004, 52(2): 385-393.
[13] Wang Yong and Jiang Yi-cheng. ISAR imaging of a ship target using product high order matched-phase transform[J]., 2009, 6(4): 658-661.
[14] Wang Yong and Jiang Yi-cheng. Inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of maneuvering target based on the product generalized cubic phase function[J]., 2011, 8(5): 958-962.
[15] Morelande M, Senadji B, and Boashash B. Complex-lag polynomial Wigner–Ville distribution[C]. IEEE Regio 10 Annual Conference, Speech and Image Technologies for Computing and Telecommunications,TENCON’97, 1997, 1: 43-46.
[16] Lu Hao, Zhang Shun-sheng, and Kong Ling-kun. A new WVD algorithm jointed CLEAN technique in ISAR imaging[C]. 2012 Second International Conference on Intelligent System Design and Engineering Application, Sanya, 2012: 69-72.
[17] 邢孟道, 保铮. 外场实测数据的舰船目标ISAR成像[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(12): 1271-1277.
Xing Meng-dao and Bao Zheng. ISAR ship imaging of real data[J].&,
2001, 23(12): 1271-1277.
[18] Stankovic L. Time-frequency distributions with complex argument[J]., 2002, 50(3): 475-486.
[19] Peleg S and Friedlander B. The discrete polynomial-phase transform[J]., 1995, 43(8): 1901-1914.
[20] O’Shea P and Wiltshire R A. A new class of multilinear functions for polynomial phase signal analysis[J]., 2009, 57(6): 2096-2109.
[21] 李亚超. ISAR目标运动参数估计及成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2008.
[22] 黄翀鹏, 王剑, 徐保国. 旁瓣抑制对线性调频脉冲移频干扰的影响[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(3): 270-276.
Huang Chong-peng,Wang Jian, and Xu Bao-guo. The impact of sidelobe suppression in shift-frequency jamming against LFM[J]., 2012, 1(3): 270-276.
李亚超: 男,1981年出生,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为雷达信号处理﹑SAR成像及信号检测.
于胜韬: 男,1989年出生,硕博连读生,研究方向为信号检测、参数估计和雷达成像.
全英汇: 男,1981年出生,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为雷达信号处理﹑SAR成像及实时信号处理.
邢孟道: 男,1975 年出生,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为雷达成像和目标识别等.
Parameter Estimation of Quadratic Frequency Modulated Signal Based on Improved Product Kernel Function
Li Ya-chao Yu Sheng-tao Quan Ying-hui Xing Meng-dao
(,,710071,)
A new method for estimating parameters of quadratic frequency modulated signals is proposed basing on a product kernel function. Firstly, the signal is multiplied by its conjugate reverse signal with the phase-matching transformation being performed, and then the estimated value of the chirp rate can be obtained by searching one-dimension maximum position of accumulated signals. Secondly, the chirp rate of the signal is compensated and a new product kernel function for the dechirped signal is structured to transform it into the two-dimensional time-lag domain, and the phase-matching transformation and FFT respectively are performed along time and lag axis. As a result, by the maximum searching in the new change rate of the chirp rate-frequency domain after transformation, the estimated values of both the change rate of the chirp rate and the center frequency can be obtained, with the phase of the signal being able to compensated and the amplitude estimated by calculating the magnitude of its average, thereby leading to the reconstruction of the signal. It is shown that the proposed method precludes the iterative search of all phase parameters and improves the operational efficiency.Finally, the paper presents the simulated results that confirm the effectiveness of this method.
Signal processing; Product kernel function; Quadratic frequency modulated signals; Parameter estimation; Phase-matching transformation; FFT
TN911.7
A
1009-5896(2014)11-2621-07
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01578
李亚超 ycli@mail.xidian.edu.cn
2013-10-14收到,2014-07-03改回
国家自然科学基金(61001211, 61303035),航空基金(20110181004)和中央高校基本科研业务费(K5051202016)资助课题

