In vitro modulation of TH1 and TH2 cytokine expression by edible tuber of Dioscorea alata and study of correlation patterns of the cytokine expression
Priyankar Dey,Tapas Kumar Chaudhuri
Cellular Immunology Laboratory,Department of Zoology,University of North Bengal,Siliguri 734013,West Bengal,India
Abstract The underground tuber of Dioscorea alata is a palatable food and is also claimed to have therapeutic effects.Various groups of researchers demonstrated different activities of this tuber such as antioxidant,hepatoprotective,anti-ulcer and anti-diabetic activities.Therefore,the aim of the present study was to evaluate the immunomodulatory potentialities of 70%hydro-methanolic extract of D.alata underground tubers by investigating different parameters like the expression of interferon gamma(IFN-γ),interleukin(IL)-2,IL-4 and IL-10,in addition to its effect on the proliferation of murine splenic T-lymphocytes in vitro.Results demonstrated that D.alata can actively polarize the TH0 lymphocyte population towards the expression of TH1 immune response by up-regulating the IFN-γ and IL-2 expression and down-regulating the IL-4 and IL-10 expression.The tuber extract also proved to possess mitogenic activity as evidenced by the proliferation of lymphocytes in vitro.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory;Cytokine;Dioscore a(yam);Immunomodulation;Lymphocyte;MTT;Proliferation
1.Introduction
CD4+T-helper cells differentiate from the precursor TH0 cells to either TH1 or TH2 cells.These cells differ in their cytokine expression patterns which primarily governs their functional nature.In general,TH1 cytokine response leads towards cell-mediated and inflammatory immune response whereas TH2 cytokine response mediates humoral immune response.Cytokines are the major immunoregulators of the body.Interferon gamma(IFN-γ)is a TH1 cytokine which primarily displays antiviral,anti-tumour and counter-autoimmune capacities [1].Activation and increase in antigen presentation by macrophages,augmentation in leukocyte migration,up-regulation of MHC expression and co-stimulatory signals are other salient features of IFN-γ.Patients under clinical studies with recombinant IFN-γ exhibit a vast spectrum of activities which include enhancement of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and increase in oxidative metabolism of macrophages [2].IFN-γ expression on tumour growth induces CD8+cytotoxic T-cells and thus results in potent tumour immunity against neuroblastoma,breast cancer and in methyl cholanthrene-mediated tumour models [3].Currently IFN-γ therapy is active in the treatment of chronic granulomatous disease,osteoporosis,idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and ovarian cancer[4].Another TH1 cytokine interleukin(IL-2)also displays a broad array of activities which include body’s innate response against microbial infections,‘self’ and ‘non-self’ recognition and proliferation of antigenspecific CD8+and CD4+T-cells.Impairment of IL-2 signalling due to the absence of IL-2 or IL-2 receptors results in generalized inflammatory syndrome and often cause fatal autoimmune colitis[5].At present,IL-2 immunotherapy has been approved for the treatment of asthma,renal transplantation,multiple sclerosis,psoriasis and ulcerative uveitis[4].Pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ and IL-2 are the principal cytokines to mediate natural killer(NK)cell activity and increases the number of CD4+cells in HIV-infected patients [6].The anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 belong to TH2 sub-set.IL-4 mediates allergic inflammation and may induce class switching to form ε isotype immunoglobulin(Ig)E secreted by B-lymphocytes and be responsible for allergic reactions[7].High concentration of IL-4 in the serum and bronchoalveolar lavage due to dust-mite allergens is the hallmark of atopic individuals [8].Increased IL-4 expression is seen in cases of asthma,various allergies,hepatitis C infection,cutaneous T cell lymphoma,malaria and leishmaniasis.On the other hand,the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10 down-regulates the cell-mediated immune response by inhibiting prostaglandin E production and suppression of various pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-2,TNF-α,IL-1,IL-6,and IL-8[9,10].In various B cell lymphoproliferative diseases,IL-10 may function as growth factor for malignant B cells[11]and elevated levels of IL-10 was found to be associated with the systemic infection,leprosy,HIV infection,rheumatoid arthritis,multiple sclerosis,lung cancers,melanomas,gliomas,leukaemia and lymphomas [5].Both IL-4 and IL-10 polarize the TH0 lymphocyte differentiation towards TH2 response and both are natural antagonist to the expression and functionality of IFN-γ.Immunomodulation of the T-cells by nutritive supplements and herbal medicines towards either TH1 or TH2 pathway chiefly determines the pattern of the immune response.
The underground tuber ofDioscorea alataL.is a dietary supplement in south-eastern Asia and Africa[12].It is also used as traditional medicine in China[13].Antioxidant[14],antidiabetic [15],antiosteoporotic [13],hepatoprotective [16]and anti-ulcer [17]activities ofD.alatawere reported previously.The effect ofD.alatatuber mucilage on splenocyte-mediated cytotoxicity,stimulation of antibody production and the phagocytic capacity of monocyte and granulocytes were studied by Shang et al.[18].Previous report suggests that 70% methanolic extract ofD.alataunderground tuber possesses stimulatory effect on various activities of murine macrophage,suppression of lipopolysaccharide stimulated nitric oxide level and stimulation of humoral immune response [19].Moreover,the same extract was also chemically characterized and found to contain high phenolic and flavonoid content which contributed to its antioxidant capacity[20].
Therefore,the objective of the present study was to further evaluate the effect of the 70% hydromethanolic extract ofD.alataunderground tuber for modulating TH1(IL-2 and IFN-γ)and TH2 (IL-4 and IL-10) cytokine expression and its effect on the proliferation pattern of murine splenic T-lymphocytes.In addition,the correlation patterns of the cytokine expressions and the cell proliferation were also studied.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Chemicals and reagents
All the cell culture reagents including RPMI-1640 (AL-162S),concanavalin A (con A),foetal bovine serum(FBS),EZcountTM3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide(MTT)Cell Assay Kitetc.were procured from HiMedia Laboratories Pvt.Ltd.(Mumbai,India),unless otherwise indicated.Nystatin was obtained from Sigma Aldrich(USA).Mouse IL-2,IFN-γ,IL-4 and IL-10 ELISA kits were procured from RayBio(Georgia,United States).
2.2.Preparation of plant extract
D.alatatubers were collected from Sonitpur district of Assam,India and authenticated by Botanical Survey of India,Shillong,Meghalaya,India(accession number 78051).Seventy percent hydro-methanolic extract of underground tubers ofD.alatawas prepared according to a previously described method[21].In brief,the tubers were washed properly with double distilled water and dried in the shade at room temperature for 2 weeks followed by grinding to powder.The powder (100 g)was mixed with 70% methanol (1000 mL) and kept overnight at 37°C in a shaking incubator (160 r/min).The mixture was centrifuged at 5000 r/min for 15 min and the supernatant (liquid phase)was collected.The remaining pellet was mixed with 70% methanol (1000 mL) and kept in a shaking incubator as previously described.The supernatant(liquid phase)was again collected after centrifugation and mixed with the supernatant of previous phase.The liquid was then filtered and the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure in a rotary evaporator.The resultant was lyophilized and stored at −20°C until further use.
2.3.Preparation of murine splenocytes
Swiss albino mice were sacrificed under proper anaesthesia and the spleen was removed aseptically.The cells of the spleen were passed through the mesh of a tissue grinder and the suspension was prepared in RPMI-1640.The cell suspension was washed thrice for 10 min using RPMI-1640 (2000 r/min)and then resuspended in 1 mol/L NH4Cl to eliminate red blood cells(RBC).After 10 min the cells were again centrifuged and resuspended in RPMI-1640.
All the experiments were approved by the ethical committee of the Department of Zoology,University of North Bengal(date: 15/09/10) and in accordance with the legislation for the protection of animals used for scientific purposes.
2.4.MTT cell proliferation assay
The cell proliferation assay was performed using EZcountTMMTT Cell Assay Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.Briefly,splenocyte suspension was made(2×106cells/mL)in RPMI-1640(supplemented with 50 U/mL penicillin,50 U/mL streptomycin,50 U/mL nystatin and 10%FBS)and the cells were seeded into different wells of 96 well culture plates in presence of 5 μg/mL con A.To this,50 μL of different concentrations (0–80 μg/mL in RPMI-1640) ofD.alataextract was added.The plate was incubated for 24 h under 5%CO2and humidified atmosphere of 90%air at 37°C temperature.After the incubation 10 μL MTT (5 mg/mL)solution was added to each well.The plate was wrapped with aluminium foil to avoid exposure to light and incubated for 4 h.Then 100 μL solubilizing reagent was added to each well and the absorbance was measured at 570 nm using Bio-Rad iMarkTMmicroplate absorbance reader.
2.5.Estimation of cytokines
Mouse splenocytes were cultured with varying concentrations (0–80 μg/mL) ofD.alatatuber extract as previously described(Section 2.4)for 48 h.After incubation,suspensions from each well were centrifuged (2850×g) for 5 min and the culture supernatants were collected to estimate the concentrations of IL-2,IFN-γ,IL-4 and IL-10 using RayBio ELISA kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions.Briefly,100 μL culture supernatant from different experimental groups were added to the anti-mouse cytokine (IL-2,IFN-γ,IL-4,IL-10)coated wells of the 96 well ELISA plate.The plate was covered and incubated at room temperature for 2.5 h.The solution were then discarded and the wells were washed 4 times with assay buffer (300 μL).Next,100 μL biotinylated anti-mouse cytokine(IL-2,IFN-γ,IL-4,IL-10)antibody was added to each well and the plate was incubated at room temperature with continuous but gentle shaking.After 1 h,the wells were washed with assay buffer as previous.Then 100 μL of horseradish peroxidase (HRP)–streptavidin conjugate solution was added and the plate was incubated for 45 min at room temperature with gentle shaking.Next,the wells were washed as previous and 100 μL 3,3,5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine(TMB)one-step substrate reagent was added followed by 30 min incubation at room temperature in dark.Then 50 μL of 0.2 mol/L sulphuric acid was added to each well to stop the reaction.Absorbance was immediately measured at 450 nm using a Bio-Rad iMarkTMmicroplate absorbance reader.Standards were run in parallel to the samples.
2.6.Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean±SD of six measurements.The comparisons between the control group and the test groups were performed by one-way analysis of variance(ANOVA)with Dunnett’s test using KyPlot version 2.0 beta 15(32 bit).P<0.05 was considered significant.The linear correlation analysis was performed by Microsoft Excel 2010.Principal component analysis (PCA) based on the correlation matrix was performed in order to analyse the pattern and inter-relations of up-and downregulation of the cytokines using IBM SPSS statistics version 20.0.
3.Results
3.1.Cell proliferation assay
Fig.1 displays the results of the splenic lymphocyte proliferation using plant extract.Increased metabolic activity of the cells in a dose-dependent manner were found as evidenced from the cell proliferation.At 80 μg/mL dose,the percentage of cell viability was (178.46±6.08)%,much higher than that of the control.
3.2.Estimation of cytokines

Fig.1.Effect of D.alata on the proliferation of splenic lymphocytes.All data are presented as the mean±SD of six measurements.Murine splenic lymphocytes (2×106 cells/mL) were cultured in vitro with con A (5 μg/mL) along with different doses of D.alata(0–80 μg/mL)extract.After 24 h of incubation,the lymphocyte viability was measured by MTT method.**, P<0.01;***;P<0.0001 compared with 0 μg/mL.
The results after 48 h of incubation displayed significant(P<0.05) dose-dependent up-regulation of IL-2 and IFN-γ and down-regulation of IL-4 and IL-10 (Fig.2),compared to the control (0 μg/mL).At 80 μg/mL,the concentration of IL-2 ((28.7±2.24)pg/mL) was significantly (P<0.001)higher than that of the control((9.94±1.56)pg/mL),accounting for (195.06±65.75)% increase in the IL-2 secretion(Fig.2A).IFN-γ concentration increased (100.22±23.48)%compared to control group (Fig.2A).At 80 μg/mL dose,the IFN-γ concentration was (356.00±12.52)pg/mL,which was significantly higher (P<0.001) than the 0 μg/mL group((179.04±16.09)pg/mL).
D.alatatuber extract considerably down-regulated IL-4 secretion to 50.06±10.76%.At the dose of 80 μg/mL(Fig.2C),the concentration of IL-4 in the culture supernatant was(1.35±0.20)pg/mL and this was significantly(P<0.001)lower than that of the control group ((3.22±0.20)pg/mL).The secretion of IL-10 was down-regulated by the plant extract from 2206.33±184.69 pg/mL in the control group to(1101±132.71)pg/mL at the highest dose (Fig.2D).Compared to the control,the IL-10 concentration has significantly(P<0.01) decreased at 80 μg/mL dose,which accounted for a total of(49.71±8.79)%decrease in IL-10 secretion.
The IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio,a major determinant of immunomodulatory activity,was also found to be elevated from 0 μg/mL to 80 μg/mL.At 0 μg/mL the ratio was 56.02±4.91 whereas at 80 μg/mL the ratio was increased up to 268.86±51.05.

Fig.2.Effect of D.alata on the expression pattern of various cytokines.All data are presented as the mean±SD of six measurements.Murine splenic lymphocytes(2×106 cells/mL)were cultured in vitro with con A(5 μg/mL)along with different doses of D.alata(0–80 μg/mL)extract.After 48 h of incubation estimation of cytokines(pg/mL)were performed from the culture supernatants by ELISA method.(A)Increase in IFN-γ expression;(B)increase in IL-2 secretion;(C)decrease in IL-4 secretion;and(D)decrease in IL-10 secretion.N.S.:non-significant(P>0.05);*.P<0.05;**.P<0.01;***.P<0.001,compared with 0 μg/mL.
3.3.Correlation study
The correlation analysis of the results revealed that IFNγ was highly correlated with IL-2 (R2=0.9496) and IL-4(R2=0.9053).Similarly,IL-4 and IL-2 was also found to be highly correlated(R2=0.9122).
Linear negative correlation resided between IL-10 and IFNγ (R2=0.8073),IL-2 (R2=0.8456) and IL-4 (R2=0.6278) as displayed in Fig.3.The correlation between the cell viability and cytokine expression is demonstrated in Fig.4.
Under given parameters,the variables were subjected to PCA and the results of the loading plot(Fig.5)completely matched with the correlation matrix (Table 1).The loading of the first and second principal component(PC1 and PC2)accounted for 94.19% and 4.29% of the variance,respectively.The loading plot demonstrated that cell viability,IL-2 and IFN-γ are heavily loaded on PC1 with component score of 0.691,0.767 and 0.748,respectively.

Fig.3.Correlation between the expression patterns of various cytokines form splenic lymphocytes.Linear correlation analysis was performed by Microsoft Excel 2010.(A)Positive correlation between IL-2 and IFN-γ;(B)negative correlation between IL-10 and IFN-γ;(C)negative correlation between IL-4 and IFN-γ;(D)negative correlation between IL-4 and IL-2;(E)negative correlation between IL-10 and IL-2;and(F)positive correlation between IL-10 and IL-4.R2:coefficient of determination unless otherwise stated.
4.Discussion
The complex interactions between the lymphoid,inflammatory and hematopoietic cells are chiefly governed by the cytokines which are generally divided into TH1 and TH2 sub-sets.TH1 cells are the primary source of IL-2,IFN-γ,lymphotoxins and other factors which characterize the cellmediated immune responses [22].IL-4,IL-5,and IL-10 are produced by the TH2 cells which not only mediate the humoral immune responses,but also promote allergic reactions by inducing the function of IgE formation [7].In the present study,found to stimulate the splenic T-lymphocyte proliferation and modulate cytokine expressionsin vitro.

Fig.4.Correlation between splenic lymphocyte viability and cytokine expression.Linear correlation analysis was performed by Microsoft Excel 2010.(A)Positive correlation between IFN-γ and cell viability;(B)positive correlation between IL-2 and cell viability;(C)negative correlation between IL-4 and cell viability;(D)negative correlation between IL-10 and cell viability.

Fig.5.Loading plot of PCA for cell viability,IFN-γ,IL-2,IL-4 and IL-10.PC1 and PC2 accounted for 94.19%and 4.29%variance,respectively.The expression patterns of IFN-γ and IL-2 are highly similar.Thus,they overlap each other in the loading plot.PCA was performed using IBM SPSS statistics version 20.0.hydro-methanolic extract of D.alata underground tuber was
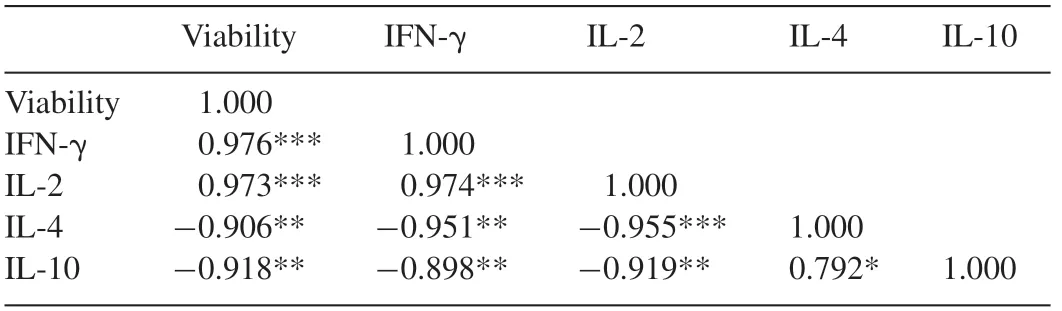
Table 1 Correlation matrix of cell viability,IFN-γ,IL-2,IL-14 and IL-10.
Spleen functions primarily against the antigens in the blood stream.The outer red pulp of spleen is abundant in lymphocytes.Con A,which is a typical T-lymphocyte mitogen,responsible for blastoid differentiation of the T-lymphocytes[23],must have stimulated T-lymphocyte population out of the whole splenocyte cells to secret the cytokines in our experiments as well.This is evidenced from the increase in the number of cells.Previously,Liu et al.[24]have also demonstrated the mitogenic effect of dioscorin,the storage protein ofD.alataon the phytohemagglutinin induced cell proliferation.Besides 70%methanolic extract ofD.alataformerly showed the capacity to increase the splenic cellularity in murine modelin vivo[19].Here,we have shown that the degree of stimulation of splenocytes byD.alataextract at 80 μg/mL concentration along with con A was 178.46±6.08%,much higher than that of the stimulation of con A alone in group I (0 μg/mL).It may be hypothesized thatD.alatahydro-methanolic extract acted synergistically with the external mitogenic stimulators to trigger mitosis of the splenic cells.Therefore,D.alatapossess potent immunogenicity towards the activation and proliferation of the splenic cells.
Profound increases in the TH1 cytokine(IL-2,IFN-γ)levels and decrease in TH2 cytokine(IL-4 and IL-10)levels were evident by the stimulation ofD.alata.Similar findings[25,26]also suggest the potentiality of various other plant materials to upregulate the TH1 response.In the present study,dose-dependent increase in the splenic T-lymphocyte was evident and the radius of proliferation was much higher in case of con A along with the plant extract than con A alone induced stimulation.This could possibly be due to the fact that theD.alatainduced increased expression of IL-2,which is a natural T-lymphocyte stimulating factor or the plant extract itself may posses mitogenic effect,perhaps,which have mimicked the function of IL-2 in the stimulation of splenic T-lymphocytes.
IL-4 and IL-10 are known to suppress the expansion of TH1 subsets.Thus in the present study (Fig.3),high negative correlation between IFN-γ and IL-4 (R2=0.9053) and IL-10(R2=0.8073)were evident and positive correlation between IL-2 and IFN-γ(R2=0.9496)were found,both of which are TH1 cytokines.Considering the dose-dependent expression patterns of the four cytokines,the correlation matrix(Table 1)also displayed very high positive correlation(0.974)between IL-2 and IFN-γ and very high negative correlation of IL-4 with IFN-γ(−0.951)and IL-2(−0.955).
Principal component analysis is a multivariate data reduction technique which statistically allows visualizing the pattern of inter-relations among the variables of the experiments [27].Groups of data with correlated immunological parameters can be visualized in a simplified manner using this data reduction technique[28].Under univariate correlation analysis,bias may emerge due to antagonist or stimulatory relations of different cytokines.This bias is eliminated and the overall inter-correlation patterns are visualized using this technique.Previously,PCA analysis have been extensively used to analyse the cytokine correlation patterns in different immunological studies[29,30].
It is interesting to note the correlation patterns of splenic T-lymphocyte proliferations with the levels of cytokine expressions.IFN-γ and IL-2 increased expression pattern were found to be similar to the PCA loading plot(Fig.5)and thus,remain overlapped.The increase in cell viability,which correlated with the TH1 cytokine release,was also placed in the same doublepositive quadrant in the loading plot.Consequently,under given condition theD.alata-mediated modulation pattern of IL-2 and IFN-γ are very much similar,followed by nearly similar patterns of increase in cell viability.On the other hand,due to the similar down-regulation in the expression of TH2 cytokines,IL-4 and IL-10 remained in the double-negative quadrant,but their apartness in the loading plot(Fig.5)was resulted due to the difference in expression patterns of both the cytokines.Under the presentin vitrocondition when linear correlation between any two cytokine expression were considered(Fig.3A),the highest correlation (R2=0.9496) was found between IFN-γ and IL-2.Therefore,with the help of PCA coupled with correlation matrix it is now feasible to analyse the regulation and correlation patterns considering multiple variables at a time in a single plot.The allocated quadrants of the four cytokines and viability in Fig.5 are fixed for immunomodulation byD.alataextract under exact given conditions.Increase or decrease in variables under altered conditions may change the correlation patterns in the PCA loading plot.
Recently,modulation of TH1 and TH2 balance has emerged as a major determinant for the therapeutic activity of plant extracts.Based on the regulatory patterns of TH1/TH2 cytokine expression,immunomodulators are classified into TH1,TH2 or mixed TH1/TH2 agents [31].Moreover,TH1/TH2 balance has also been implicated in anti-tumour immunity where IFN-γ and IL-2 producing TH1 cells-mediate cellular and tumour immunity,whereas IL-4 producing TH2 cells are responsible for suppression of cytolytic activity[32].In the present study polarization of the TH1 pathway was evident from the increase in the expression of IFN-γ and IL-2.Besides,the relative immunomodulatory effect [31]ofD.alatawas higher for TH1 subset as evident from the IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio,which is a commonly used index of TH1/TH2 immunity[33].
5.Conclusion
The results from our experiments revealed the potent immunomodulatory activity of the edible tubers ofD.alata,consumption of which may in turn stimulate the lymphocyte proliferation and navigate the immune response towards the TH1 phenotype.We also hypothesize that the extract may possess mitogenic activity and exert excellent pro-inflammatory response upon consumption.The TH1/TH2 fate regulatory role ofD.alatawas investigated through ELISA method by estimating the expressed proteins in the culture medium.It is difficult to conclude from the present study whetherD.alatapossess the potentiality to regulate the mRNA levels of the cytokines or it simply regulates the protein expression patterns.Therefore,RT-PCR and FACS analysis are further required in addition to modulation study of cyclooxygenase,prostaglandin E2 and nuclear factor-kappa β for in-depth analysis of the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory activities ofD.alata.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance was provided by Department of Biotechnology,Government of India (sanction order no.BT/09/NE/TBP/2010).The authors are thankful to Prof.Anupam Chatterjee of the Department of Biotechnology &Bioinformatics,North-Eastern Hill University for supplying the plant material and to Dr.Nripendranath Mandal,Division of Molecular Medicine,Bose Institute for his kind help in preparation of the plant extract.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- Effects of Co-60 gamma-irradiation and refrigerated storage on the quality of Shatang mandarin
- In vitro antioxidant,anti-diabetic,cholinesterase and tyrosinase inhibitory potential of fresh juice from Citrus hystrix and C.maxima fruits
- Anti-inflammatory effects of characterized orange peel extracts enriched with bioactive polymethoxyflavones
- A comparative study on antioxidant potentials,inhibitory activities against key enzymes related to metabolic syndrome,and anti-inflammatory activity of leaf extract from different Momordica species
- About the Beijing Academy of Food Sciences
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS

