量化状态信息下多智能体Gossip算法及分布式优化
王长城 戚国庆 李银伢 盛安冬
量化状态信息下多智能体Gossip算法及分布式优化
王长城*戚国庆 李银伢 盛安冬
(南京理工大学自动化学院 南京 210094)
基于量化状态信息的异步随机Gossip算法大多以均匀选择概率的时间模型为基础,未充分考虑网络拓扑结构对局部信息传递的影响。为此,该文提出了一种以非均匀选择概率为时间模型的改进算法。首先给出了非均匀选择概率下的多智能体系统时间模型,在随机性量化策略下给出了一致性误差的收敛性质;并讨论了量化精度和概率化权重矩阵第2大特征值对一致性误差收敛速度的影响,进而利用投影次梯度给出了选择概率的分布式优化方法。仿真结果表明,该基于量化状态信息的算法可通过选择概率的分布式优化,提高一致性误差的收敛速度。
多智能体系统;量化;分布式一致;非均匀选择概率;优化
1 引言
随着多智能体系统在机器人编队控制[1]、无人机协调控制[2]、多传感器状态估计[3]等领域的广泛应用,分布式一致问题吸引了众多国内外学者,成为当前热点研究领域之一[4,5]。在多智能体系统中,分布式一致是指各个具有感知、通信和决策能力的智能体在没有协调中心的情况下,仅通过局部的信息交互最终使其状态达到全局一致。随机分布式一致是多智能体中一个重要的研究分支。在这类问题中,通信拓扑被建模成随机图,各智能体之间随机建立通信链路。这种随机拓扑结构可有效避免信道冲突,降低单个智能体的计算和通信负担。
在多智能体系统中,受网络信道通信容量和各智能体数据储存、计算能力的限制,各智能体之间只能处理、传递有限字节的信息量,因此,研究量化状态信息下随机分布式一致性具有更大的现实意义。2009年,Lavaei等人[13,14]利用凸优化方法研究了量化状态信息下ARG算法的平均收敛时间。随后,Carli等人[15]分别研究了确定性量化策略与随机性量化策略下的ARG算法,指出随机性量化优于确定性量化;并根据智能体是否能够获得其自身非量化信息,讨论了完全量化、部分量化、信息补偿3种状态更新方式下的收敛性。Yuan等人[16]研究了可变加权系数下的量化ARG算法,并讨论了算法渐近误差的上界与量化精度、加权系数的关系,并得出加权系数最优取值为1/2。2012年,Cai等人[17]研究了通信拓扑为完全有向图时的量化ARG算法,并给出了平均收敛时间。上述针对量化ARG算法的研究大多基于文献[6]中以均匀选择概率为基础的时间模型,该模型未充分考虑网络拓扑结构对局部信息传递的影响。鉴于此,本文基于非均匀选择概率的时间模型,给出了量化状态信息下异步随机Gossip算法;在概率意义下研究了多智能体系统一致性误差的收敛性质,分析了选择概率和量化精度对多智能体收敛速度的影响,并给出了选择概率的分布式优化方法。
2 问题描述
2.1 网络拓扑
2.2量化策略
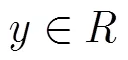
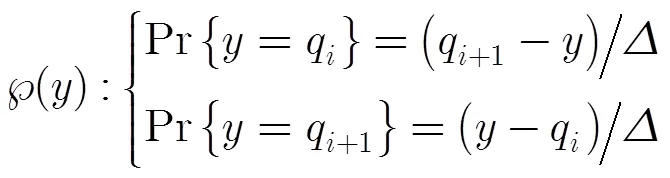
2.3 量化状态信息下异步随机Gossip算法

不难发现,不同于传统的Gossip算法中所采用的时钟模型,本文给出的模型将能以不同的概率选择各智能体发起信息交互。
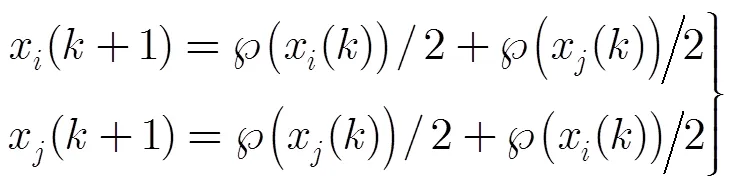
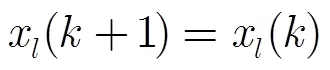
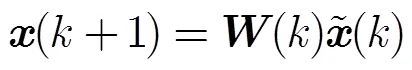

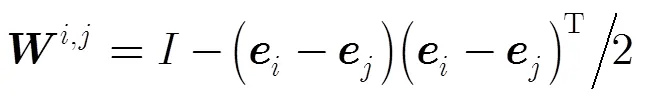
3 NQARG算法收敛性分析
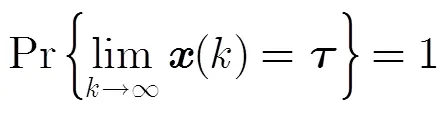
根据文献[16,18]的证明方法,易得上述结论。
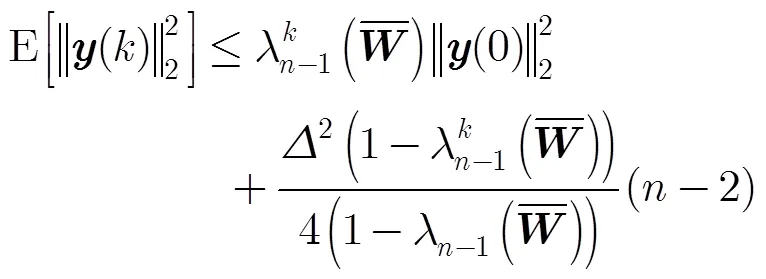
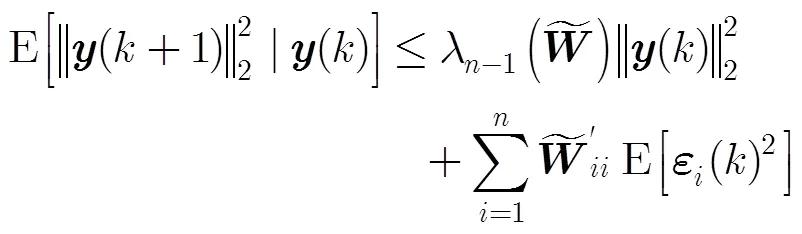
其中
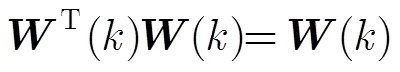
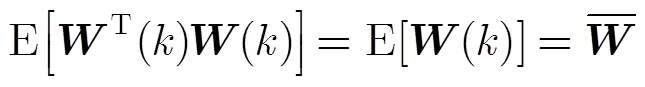
注意到


即
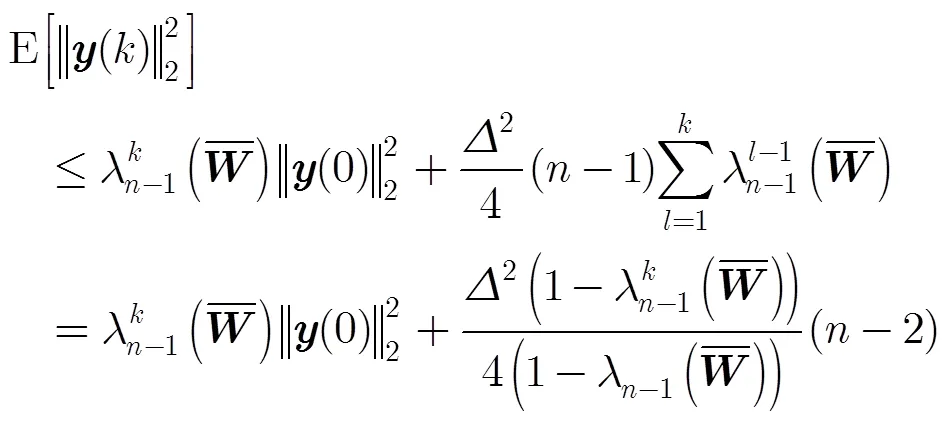
证毕
4 选择概率分布式优化
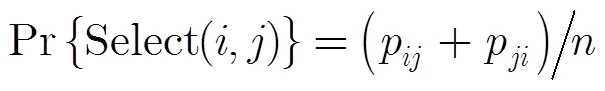
而在非均匀选择概率下:
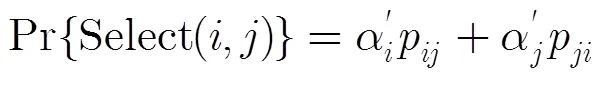
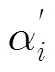

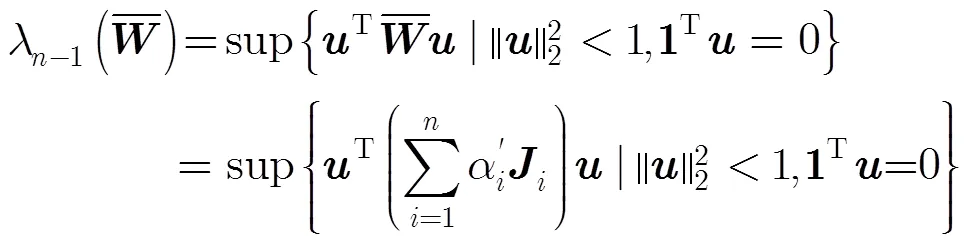
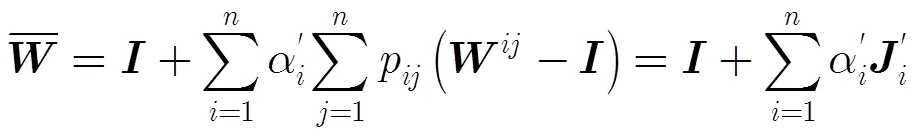
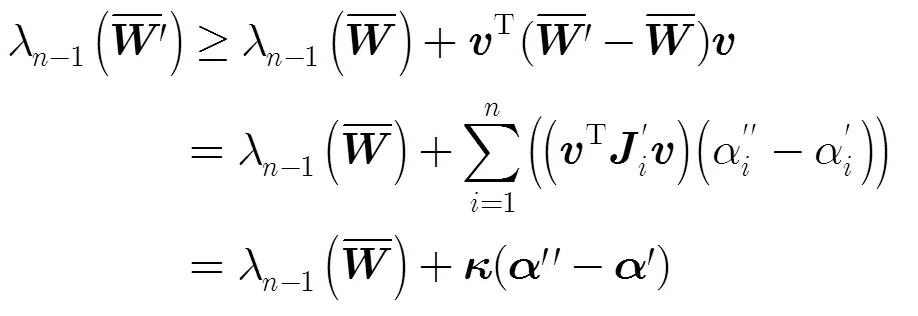
其中

不难发现,若智能体可获取特征向量中所对应的分量与其邻居节点所对应的分量,即可以分布式方式进行优化。根据文献[18]和文献[19]的研究结果,可利用图1所示流程计算。
表1选择概率分布式优化算法
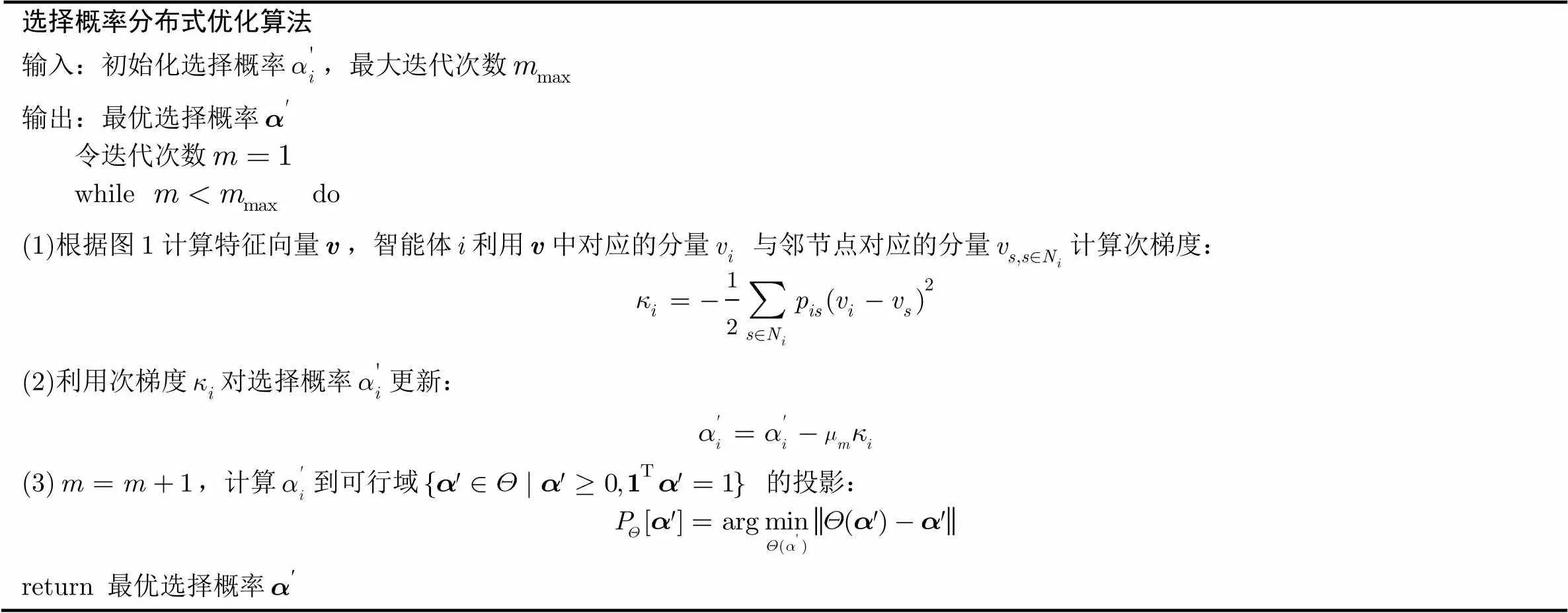
选择概率分布式优化算法输入:初始化选择概率,最大迭代次数 输出:最优选择概率令迭代次数while do(1)根据图1计算特征向量,智能体利用中对应的分量 与邻节点对应的分量计算次梯度:(2)利用次梯度对选择概率更新:(3),计算到可行域 的投影:return 最优选择概率
5 仿真分析
考虑在25×25的矩形区域内随机散布的10个智能体,并以10为各节点的最大通信半径构造无向连通网络,如图3所示。各智能体的初始状态在区间[-100,100]中随机取值。
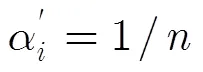
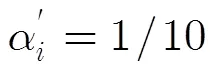
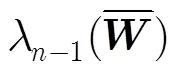

表2不同量化比特位数下的收敛速度

比特位数1012141618 迭代次数k782681643626622
表3各智能体最优选择概率

智能体12345678910 概率000.21210.012000.26150.214200.30020
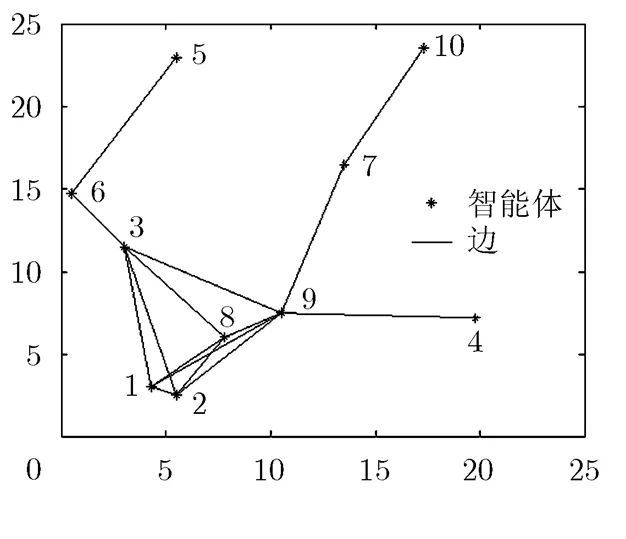
图3 随机生成的网络拓扑图
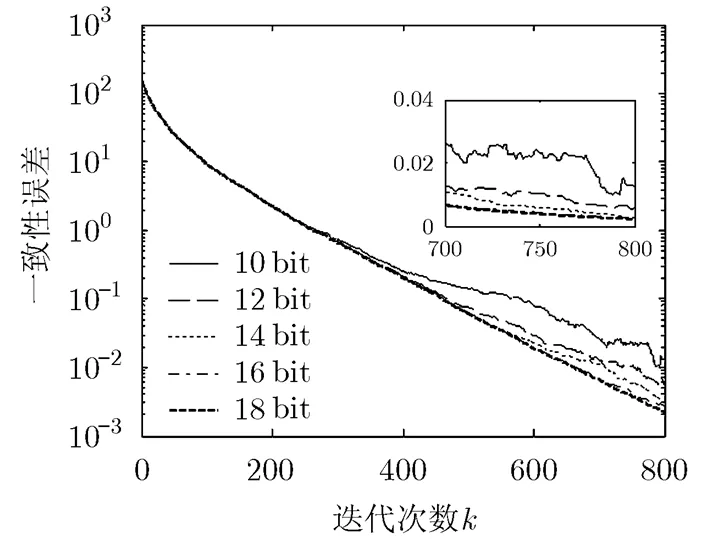
图4 不同量化比特位数下一致性误差比较
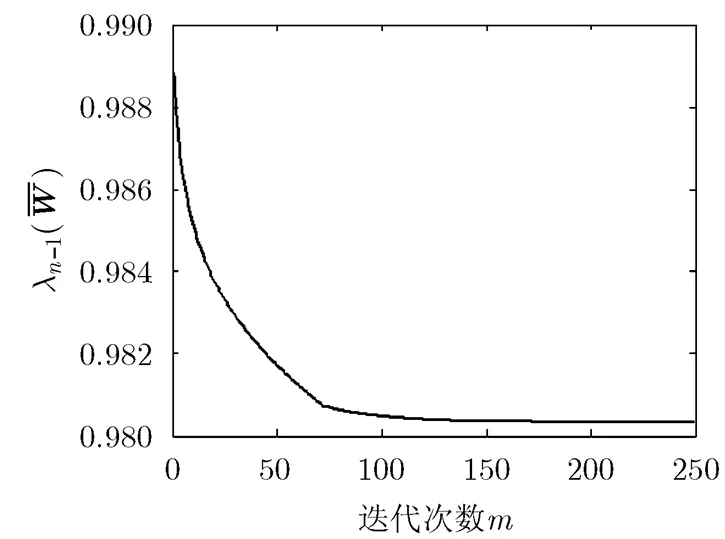
图5 特征值优化
表4各智能体最优选择概率

智能体12345678910 概率 0.0470 0.0460 0.1783 0.0670 0.1151 0.0894 0.0950 0.0462 0.2035 0.1125
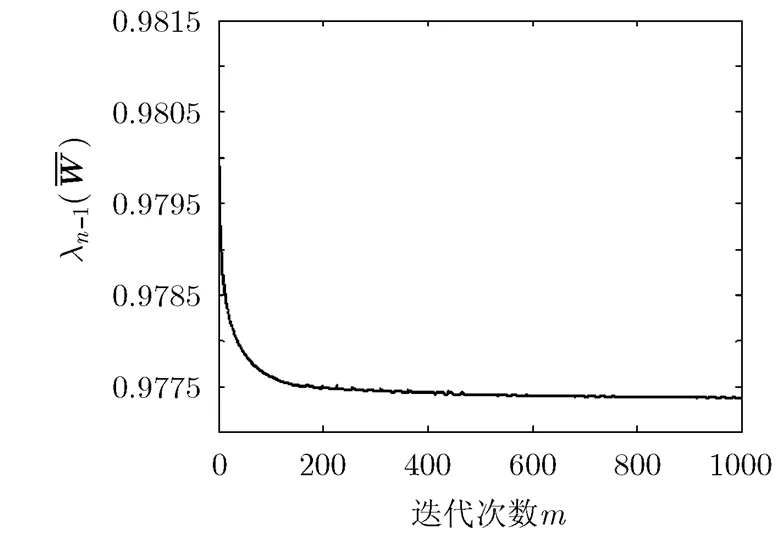
图7 特征值优化
表5给出了不同优化方法下的结果对比。不难发现,通信概率优化方法对算法收敛速度的改进有限,其原因在于没有充分考虑各智能体在网络中获取信息的差异。而本文方法基于非均匀选择概率时间模型,可进一步对选择概率进行优化,从而改善收敛速度。同时,单一的优化通信概率矩阵或优化选择概率对收敛速度的提高均存在局限性,将两者结合可获得更好的结果。
表5特征值优化结果对比

初值文献[6]方法本文方法文献[6]与本文方法联合 0.98880.98110.98030.9774
6 结束语
本文基于量化状态信息,提出了一种非均匀选择概率下的异步随机Gossip算法,分析了算法的收敛性质,在分布式环境下给出了选择概率的优化方法。结果表明,多智能体一致性收敛速度取决于概率化权重矩阵的第2大特征值和量化水平;在初始阶段,误差收敛速度主要依赖于权重矩阵的第2大特征值,随着误差的减小,量化水平对其影响占主导地位。其次,可通过对选择概率的分布式优化提高收敛速度,且优化结果优于传统的通信概率矩阵优化方法。同时,本文为突出重点假设所建立的通信链路是理想的,实际网络系统中存在的信道随机干扰、数据丢包等现象仍是值得进一步探讨的问题。
[1] Do K D. Formation control of multiple elliptical agents with limited sensing ranges[J]., 2012, 48(7): 1330-1338.
[2] Manathara J G and Ghose D. Rendezvous of multiple UAVs with collision avoidance using consensus[J]., 2012, 25(4): 480-489.
[3] 王长城, 戚国庆, 李银伢, 等. 传感器网络分布式一致性滤波算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(12): 1645-1650.
Wang Chang-cheng, Qi Guo-qing, Li Yin-ya,.. Consensus-based distributed filtering algorithm in sensor networks[J].&, 2012, 29(12): 1645-1650.
[4] Zhou Z, Fang H, and Hong Y. Distributed estimation for moving target based on state-consensus strategy[J]., 2013, 58(8): 2096-2101.
[5] 朱旭, 闫建国, 屈耀红. 不同延迟下离散多智能体系统的一致性[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(6): 1516-1520.
Zhu Xu, Yan Jian-guo, and Qu Yao-hong. Consensus for the discrete-time multi-agent system with diverse delays[J].&, 2012, 34(6): 1516-1520.
[6] Boyd S, Ghosh A, Prabhakar B,.. Randomized gossip algorithms[J]., 2006, 52(6): 2508-2530.
[7] Dimakis A G, Sarwate A D, and Wainwright M J. Geographic gossip: efficient averaging for sensor networks[J]., 2008, 56(3): 1205-1216.
[8] Tuncer C A, Mehmet E Y, Anand D S,.. Broadcast gossip algorithms for consensus[J]., 2009, 57(7): 2748-2761.
[9] Ustebay D, Oreshkin B N, Coates M J,.. Greedy gossip with eavesdropping[J]., 2010, 58(7): 3765-3776.
[10] Kar S and Moura J M F. Gossip and distributed Kalman filtering: weak consensus under weak delectability[J]., 2011, 59(4): 1766-1784.
[11] Cai K and Ishii H. Average consensus on general strongly connected digraphs[J]., 2012, 48(11): 2750-2761.
[12] Lavaei J and Murray R M. Quantized consensus by means of gossip algorithm[J]., 2012, 57(1): 19-32.
[13] Lavaei J and Murray R M. On quantized consensus by means of gossip algorithm part I: convergence proof[C]. Proceedings of the American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, 2009: 394-401.
[14] Lavaei J and Murray R M. On quantized consensus by means of gossip algorithm Part II: convergence time[C]. Proceedings of the American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, 2009: 2958-2965.
[15] Carli R, Fagnani F, Frasca P,.. Gossip consensus algorithms with quantized communication[J]., 2010, 46(1): 70-80.
[16] Yuan D M, Xu S Y, Zhao H Y,.. Distributed average consensus via gossip algorithm with real-valued and quantized data for 0 < q < 1[J].&, 2010, 59(9): 536-542.
[17] Cai K and Ishii H. Convergence time analysis of quantized gossip consensus on digraphs[J]., 2012, 48(9): 2344-2351.
[18] Xiao L and Boyd S. Fast linear iterations for distributed averaging[C]. Proceedings of 2003 Conference on Decision and Control, Hawaii, 2003: 4997-5002.
[19] Kempe D and McSherry F. A decentralized algorithm for spectral analysis[C]. Proceedings of the 36th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Chicago, 2003: 561-568.
王长城: 男,1985年生,博士生,研究方向为多源信息融合、分布式状态估计.
戚国庆: 男,1977年生,副研究员,研究领域为随机状态估计与信息融合.
李银伢: 男,1976年生,副教授,研究领域为目标跟踪、火力与指挥控制.
盛安冬: 男,1964年生,研究员,研究领域为多源信息融合理论及应用.
Multi-agent Gossip Consensus Algorithm with Quantized Data and Distributed Optimizing
Wang Chang-cheng Qi Guo-qing Li Yin-ya Sheng An-dong
(,210094,)
As the traditional quantized asynchronous randomized gossip consensus algorithm is based on uniform selection probability time mode, the impact of network topology on local information transfer is not been fully considered. Thus, an improved quantized asynchronous randomized gossip consensus algorithm with non-uniform selection probability is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the asynchronous time model with non-uniform selection probability is proposed. Then the convergence of the algorithm is analyzed with randomized quantized information. The impact of the quantization resolution and the second largest eigenvalue of the probabilistic weighted matrix on convergence rate is also discussed. Furthermore, this paper proposes an optimization algorithm for selection probabilities with projection subgradient method in a distributed manner. The numerical example indicates that, the proposed algorithm improves the convergence rate by optimizing selection probabilities of agents.
Multi-agent system; Quantization; Distributed consensus; Non-uniform selection probability; Optimizing
TP391
A
1009-5896(2014)01-0128-07
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00297
2013-03-12收到,2013-10-22改回
国家自然科学基金(61104186, 61273076)和江苏省自然科学基金(BK2012801)资助课题
王长城 w308101484@126.com

