肝血管瘤治疗中不同介入栓塞方法的比较
李 辉,段 敏,曹景勤
1济宁市第一人民医院 介入科,山东济宁 272000;2济宁市中区人民医院,山东济宁 272000
肝血管瘤治疗中不同介入栓塞方法的比较
李 辉1,段 敏2,曹景勤1
1济宁市第一人民医院 介入科,山东济宁 272000;2济宁市中区人民医院,山东济宁 272000
目的探讨不同介入栓塞方案治疗肝血管瘤的疗效及安全性。方法收集2010年8月- 2013年4月在济宁市第一人民医院介入放射科接受治疗的肝血管瘤患者的临床资料。入组患者根据栓塞方法不同分为明胶海绵微粒 + 平阳霉素碘化油乳剂组(观察组)和单纯的平阳霉素碘化油乳剂组(对照组),比较两组患者的治疗效果、术后并发症、下床时间、住院时间以及治疗前后总胆汁酸(total bile acid,TBA)的变化。结果本研究共纳入研究对象60例,其中观察组和对照组各30例。观察组患者治疗有效率和显效率均优于对照组(χ2=6.734,P=0.034);两组并发症发生率差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.098,P=0.75),观察组下床时间(t=19.39,P<0.01)、住院时间(t=7.257,P<0.01)均显著少于对照组;治疗前两组患者TBA水平差异无统计学意义(t=0.073,P=0.94),治疗后3 d观察组TBA水平低于对照组(t=3.195,P<0.01)。两组患者的谷丙、谷草转氨酶、白蛋白、总胆红素、凝血酶原时间等指标均无统计学差异(P均>0.05)。结论明胶海绵微粒加平阳霉素碘化油乳剂相对于单纯平阳霉素碘化油乳剂治疗肝血管瘤,不仅有效、安全,而且患者术后恢复速度更快。
肝血管瘤;介入栓塞;明胶海绵微粒;平阳霉素碘化油乳剂
2 研究方法 根据两种治疗方案从符合标准的治疗人群中随机抽取各30人入组,分为观察组和对照组。观察组患者给予明胶海绵微粒 + 平阳霉素碘化油乳剂,对照组患者予平阳霉素碘化油乳剂治疗。具体操作为:患者取仰卧位,选取最佳穿刺点,于股动脉插入5FRH导管,根据血管走向继续将导管置入肝动脉,行肝动脉造影以确认供应肝血管瘤的动脉,将插管送至目标血管部位,将碘化油与平阳霉素按1∶1.5比例配置的平阳霉素碘化油乳剂注入,根据瘤体状况行硬化栓塞治疗。而观察组操作过程类似,而将明胶海绵微粒 + 平阳霉素碘化油乳剂行硬化栓塞治疗。入组患者治疗成功后6个月再入院行影像学复查。治疗评价:各种症状及体征消失,且复查CT提示瘤体缩小>50%为显效;症状、体征消失,复查CT提示瘤体缩小体积≤50%为有效;症状、体征无明显改善,CT复查示瘤体无明显变化或有所增大为无效。比较两组患者的一般资料、治疗效果、术后并发症、下床时间、住院时间以及治疗前后总胆汁酸(total bile acid,TAB)、转氨酶、白蛋白、胆红素和凝血酶原时间等指标的变化。
3 统计学方法 数据采用SPSS19.0软件进行分析。计量资料以±s表示,比较采用t检验。率的比较使用χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结果
1 两组一般资料比较 本研究共纳入研究对象60例,其中观察组和对照组各30例。两组患者的性别、年龄、体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)、血管瘤单双侧病例数、肿瘤直径差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05)。见表1。
2 两组治疗效果比较 观察组疗效优于对照组(χ2=6.734,P=0.034)。见表1。
3 两组下床、住院时间及并发症比较 介入治疗后两组患者出现的主要并发症为疼痛、发热和恶心。两组并发症发生率差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.098,P=0.75),而观察组下床时间(t=19.39,P<0.01)、住院时间(t=7.257,P<0.01)均低于对照组。见表1。
4 两组治疗前后肝功能比较 治疗前两组TBA水平差异无统计学意义(t=0.073,P=0.94),治疗后3 d观察组的TBA水平显著低于对照组(t=3.195,P<0.01)。两组患者的谷丙、谷草转氨酶、白蛋白、总胆红素、凝血酶原时间等指标均无统计学差异(P均>0.05)。见表1。
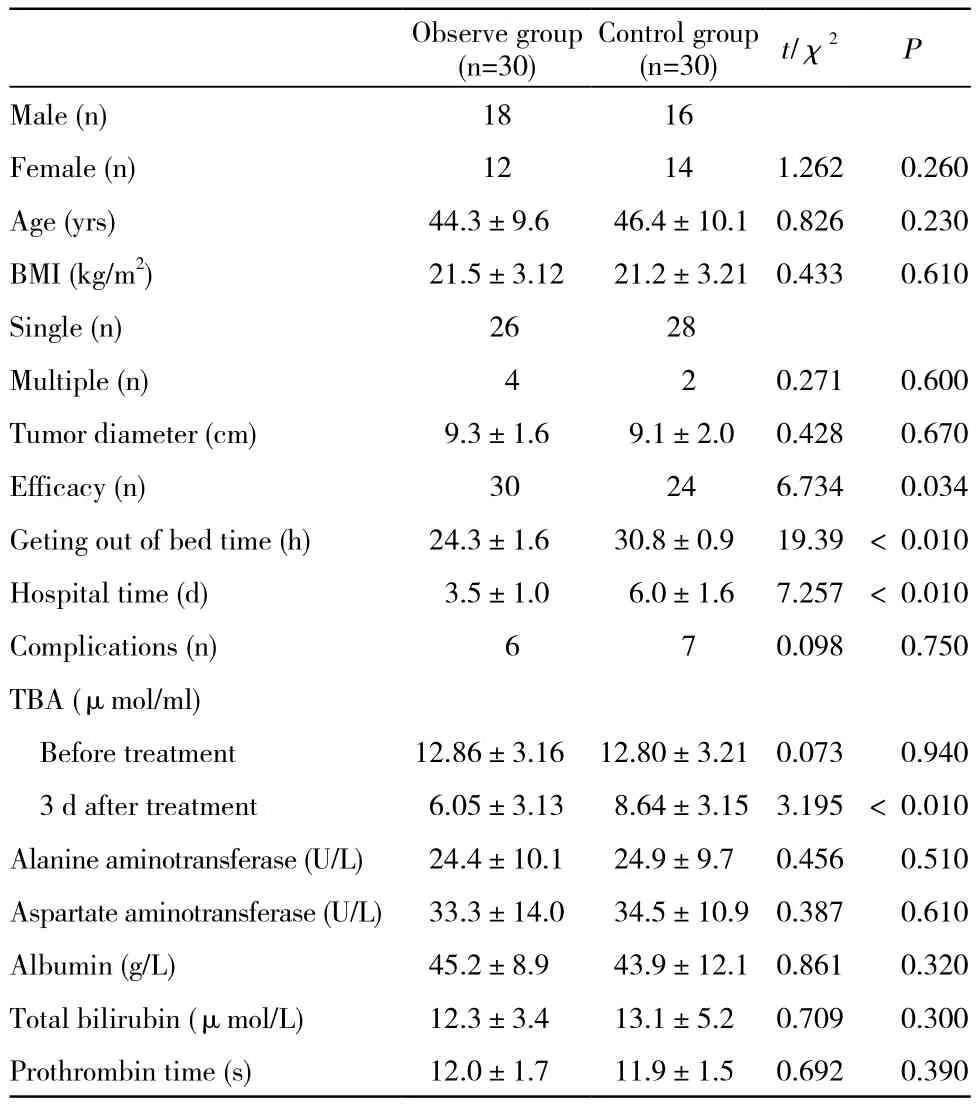
表1 观察组与对照组临床资料、治疗疗效及肝功能比较Tab. 1 Comparison of clinical data, therapeutic effect and liver function between observe group and control group
讨论
肝血管瘤是肝较为常见的一种良性肿瘤,好发于中年人,常单发,亦可多发,肝右叶多见,早期患者常无明显症状和体征,瘤体较小无需特殊治疗,瘤体增大后可引起相应的压迫症状,需进行治疗,治疗方案多样[5-6]。肝血管瘤的主要构成为扩大并且充满血液的肝血窦,在影像学辅助下通过动脉介入注入的栓塞剂能够留在这些靶血管窦中,破坏血管窦的内皮细胞,并形成血栓,从而闭塞血窦,达到将血管瘤缩小或消失的目的[7-8]。本研究结果发现,明胶海绵微粒 + 平阳霉素碘化油乳剂(观察组)相比于单纯的平阳霉素碘化油乳剂(对照组)对于肝血管瘤的治疗,并发症比例差异无统计学意义,但观察组有着更佳的治疗效果。研究结果还发现,观察组患者治疗前后的TBA水平下降程度超过对照组,提示术后恢复速度优于对照组;故而相应的下床时间和住院时间均低于对照组[9]。
明胶海绵是一种安全,无不良反应,且可吸收的栓塞剂[10-11]。作为碘化油化疗药物乳剂栓塞瘤体后的补充栓塞剂,目前已广泛应用于临床[12]。明胶海绵可以阻断瘤体滋养动脉,对于大多数直径的血管均可起到良好的栓塞作用[13]。碘油乳剂是首选的栓塞材料,临床疗效亦较为理想。但合并动静脉瘘的时候,其疗效则较差[14]。
综上,我们的研究结果表明,明胶海绵微粒 +平阳霉素碘化油乳剂治疗肝血管瘤,不仅有效、安全,而且患者术后恢复速度快,值得推广[15]。
1 Gupta S, Agarwal V, Acharya AN. Spontaneous rupture of a giant hepatic hemangioma-report of a case[J]. Indian J Surg, 2012, 74(5): 434-436.
2 Maruyama M, Isokawa O, Hoshiyama K, et al. Diagnosis and management of giant hepatic hemangioma: the usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography[J/OL]. http://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijh/2013/802180
3 Aydin C, Akbulut S, Kutluturk K, et al. Giant hepatic hemangioma presenting as gastric outlet obstruction[J]. Int Surg, 2013, 98(1):19-23.
4 Yamashita S, Okita K, Harada K, et al. Giant cavernous hepatic hemangioma shrunk by use of sorafenib[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol,2013, 6(1): 55-62.
5 Marković V, Eterović D, Punda A, et al. Unusual bone scan finding:gigantic hepatic hemangioma visualized on bone scintigraphy[J]. Hell J Nucl Med, 2013, 15(3): 260.
6 Tateyama A, Fukukura Y, Takumi K, et al. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging features of hepatic hemangioma compared with enhanced computed tomography[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2012, 18(43): 6269-6276.
7 Szavay P, Kurth R, Schaefer J, et al. A rare cause for extrahepatic biliary tract obstruction: juvenile hepatic hilar hemangioma[J]. Eur J Pediatr Surg, 2013, 23(5): 415-417.
8 Okano A, Sonoyama H, Masano Y, et al. The natural history of a hepatic angiosarcoma that was difficult to differentiate from cavernous hemangioma[J]. Intern Med, 2012, 51(20): 2899-2904.
9 Yamada S, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, et al. Hepatic screlosed hemangioma which was misdiagnosed as metastasis of gastric cancer:report of a case[J]. J Med Invest, 2012, 59(3/4): 270-274.
10 Vergine G, Marsciani A, Pedini A, et al. Efficacy of propranolol treatment in thyroid dysfunction associated with severe infantile hepatic hemangioma[J]. Horm Res Paediatr, 2012, 78(4):256-260.
11 孟冉冉,赵广生,张跃伟.明胶海绵微粒联合TACE治疗肝癌合并弥漫性动静脉瘘一例[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(11):896-897.
12 敖劲,张跃伟,徐克.明胶海绵微粒经动脉栓塞治疗原发性肝癌的研究现状[J].介入放射学杂志,2011,20(12):1010-1013.
13 Imteyaz H, Karnsakul W, Levine MA, et al. Unusual case of hypothyroidism in an infant with hepatic hemangioma[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2012, 54(5): 692-695.
14 Sciveres M, Marrone G, Pipitone S, et al. Successful first-line treatment with propranolol of multifocal infantile hepatic hemangioma with high-flow cardiac overload[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr,2011, 53(6): 693-695.
15 Tamada T, Ito K, Ueki A, et al. Peripheral low intensity sign in hepatic hemangioma: diagnostic pitfall in hepatobiliary phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI of the liver[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2012, 35(4): 852-858.
Comparison of different embolization methods in the treatment of hepatic hemangioma
LI Hui1, DUAN Min2, CAO Jing-qin1
1Department of Invasive Technology, West Region of the First People's Hospital of Ji'ning City, Ji'ning 272000, Shandong Province, China;2Central People's Hospital of Ji'ning City, Ji'ning 272000, Shandong Province, China
CAO Jing-qin. Email: caojingqin8877@sina.com
ObjectiveTo discuss the curative effect and safety of different embolization methods in the treatment of hepatic hemangioma.MethodsClinical data about patients with hepatic hemangioma received treatment in our hospital from 2010 to 2013 were retrospectively analyzed. According to the treatment, enrolled patients were divided into two groups: observe group (Gelatin sponge particles combined with Bleomycin iodized oil emulsion) and control group (simply Bleomycin iodized oil emulsion). The effect of treatment, postoperative complications, hospitalization time, time of getting out of bed and the changes of TBA before and after the treatment in two groups were compared.ResultsA total of 60 patients were retrospectively analyzed, including 30 in control group and 30 in observe group. The effective rate of treatment and the marked effective rate of patients in observe group were better than those in control group. The differences had statistical signif i cance (χ2=6.734, P=0.034), while the differences in the incidence rate of complications had no statistical signif i cance (χ2=0.098, P=0.75). The hospitalization time (t=7.257, P<0.01) and the time of getting out of bed (t=19.39, P<0.01) in observe group were less than those in control group. The differences in the level of TAB had no statistical signif i cance (t=0.073, P=0.94). The level of TAB after treatment for 3 d was lower in observe group than those in control group (t=3.195, P<0.01). There was no statistical difference in alanine, aspartate aminotransferase, albumin, total bilirubin and prothrombin time between two groups.ConclusionPatients in observe group are not only effective and safe, but also have a faster postoperative recovery.
hepatic hemangioma; interventional embolization; gelatin sponge particles; bleomycin lipiodol emulsion
R 445.4
A
2095-5227(2014)12-1217-03
10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2014.12.011
时间:2014-11-13 17:14
http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3275.R.20141113.1714.002.html
肝血管瘤是肝良性肿瘤中较为常见的一种,其中又以海绵状血管瘤最为多见,目前其确切病因还尚未完全明了,考虑与先天发育异常、激素刺激等原因有关[1-2]。其治疗方法多样,包括血管瘤缝扎术、血管瘤切除术、肝动脉栓塞术、肝动脉结扎术、射频治疗等手术及非手术治疗方案[3]。肝血管瘤介入术是目前应用较为广泛的一种方案[4]。本研究针对肝血管瘤常用的两种栓塞治疗方案—明胶海绵微粒+平阳霉素碘化油乳剂与单纯的平阳霉素碘化油乳剂进行比较和分析。
材料和方法
1 研究对象 分析2010年8月- 2013年4月在济宁市第一人民医院介入放射科接受治疗的肝血管瘤患者的临床资料。入组标准:根据患者的症状及影像学证据(B超、CT和磁共振成像MRI等)确诊为肝血管瘤的患者;年龄18 ~ 60周岁;肝、肾、心、肺等重要脏器功能良好,无凝血功能障碍。排除标准:伴有恶性肿瘤患者;伴有高血压、糖尿病等慢性全身性疾病者;伴有严重精神疾患者。入组患者均需签署知情同意书。
2014-04-18
李辉,男,硕士,主治医师。研究方向:外周血管与肿瘤的介入治疗。Email: 13455596668@163.com
曹景勤,男,副主任医师,主任。Email: caojingqin8877@sina.com

