花鲈类胰岛素生长因子-1基因的全长cDNA分离与表达分析*
钱 焜,温海深,迟美丽,倪 蒙,张冬茜,丁玉霞
(中国海洋大学水产学院,山东 青岛266003)
花鲈(Lateolabraxjaponicus),俗称七星鲈、鲈鱼、寨花等,广泛分布于我国、朝鲜和日本沿海,因其肉质鲜美,颇受广大消费者喜爱。它适温范围广,在我国南北方皆可养殖;其适盐性也强,海水和淡水均可养殖。因此,是我国重要的网箱与池塘养殖经济鱼类之一[1]。国内外关于花鲈的研究包括生态学、繁殖生理学、营养生理学、摄食行为学、遗传育种等,尤其以养殖领域研究的最全面[1-3],包括亲鱼培育、海水网箱养殖、工厂化育苗、淡水养殖技术等,但是对于分子生理学,特别是类胰岛素生长因子(IGF)信号系统的研究却未见报道。
IGF信号系统是一个进化上较为保守的信号途径,该信号系统由 2个配体(IGF-l,IGF-2)、2 个受体(IGF-1R,IGF-2R)和6个IGF结合蛋白(IGF-binding proteins,IGFBPs)组成。研究表明,该信号系统对于调节生物体内胚胎发育和分化、以及维持成体稳态有重要作用[4-5]。IGF-1是一种在结构和功能上与胰岛素相关的多肽,除了具有产生胰岛素代谢作用外,人类的IGF-1具有多种生物学效应,包括激发细胞分裂和分化,抑制蛋白质降解和细胞凋亡,作为内分泌因子来调节生长过程等[6-8]。许多研究结果表明,肝脏是IGF-1主要的分泌器官[9],但IGF-1不仅在肝脏中表达,在一些其他的器官中也有表达,而且大都是通过自分泌和旁分泌方式释放[10-11]。IGF-1前肽由信号肽、B、C、A、D结构域和E肽6部分组成,成熟肽由B、C、A和D区4个结构域构成[12]。自20世纪末以来,硬骨鱼类中如:斑马鱼(Daniorerio)[13-14]、牙鲆(Paralichthysolivaceus)[15]、金头鲷(Sparusaurata)[16]等,已得到了IGF-1cDNA部分和全长基因序列,揭示了IGF-1在进化过程中的保守性。
本文利用逆转录聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)和cDNA末端快速扩增法(RACE)克隆得到了花鲈IGF-1基因cDNA全长序列,并对其氨基酸结构进行了比对分析,采用荧光实时定量PCR技术对花鲈脑、垂体、心脏、鳃、胃、盲肠、肠、头肾、肾脏、肝脏、性腺(雄)、脾脏和肌肉等13种器官的IGF-1mRNA的表达水平进行了分析,填补了花鲈IGF家族在分子生物学方面的空白,旨在为该基因时空表达特征及具体生理功能提供基础数据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
花鲈于2010年11月采自青岛市市南区南山水产品市场。鱼体重(1 196.7±16.8)g,体长(43.6±1.2)cm。解剖后迅速取出脑、垂体、心脏、鳃、胃、盲肠、肠、头肾、肾脏、肝脏、性腺、脾脏和肌肉13个组织保存于-80℃超低温冰箱中备用。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 总RNA提取和cDNA第一链合成 按照Tr-izol Reagent试剂盒说明书提取花鲈各组织总RNA,利用Biodropsis BD-1000核算测定仪测定RNA的浓度以及OD260/OD280,并用普通琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测RNA完整性。利用DNaseⅠ去除基因组DNA,测定RNA浓度。cDNA第一链利用M-MLV反转录酶来合成。
1.2.2 引物设计 参考点带石斑鱼(Epinepheluslanceolatus)、金头鲷(Sparusaurata)、大马哈鱼(Oncorhynchusketa)等亲缘关系较近鱼种的IGF-1氨基酸序列,用CODEHOP网站在线设计简并引物[17],根据克隆得到的片段设计5′特异性引物(IGF-1 5端),以及用于进行巢式PCR的3′特异性引物(IGF-1 3端A和IGF-1 3端B)(引物情况见表1)。
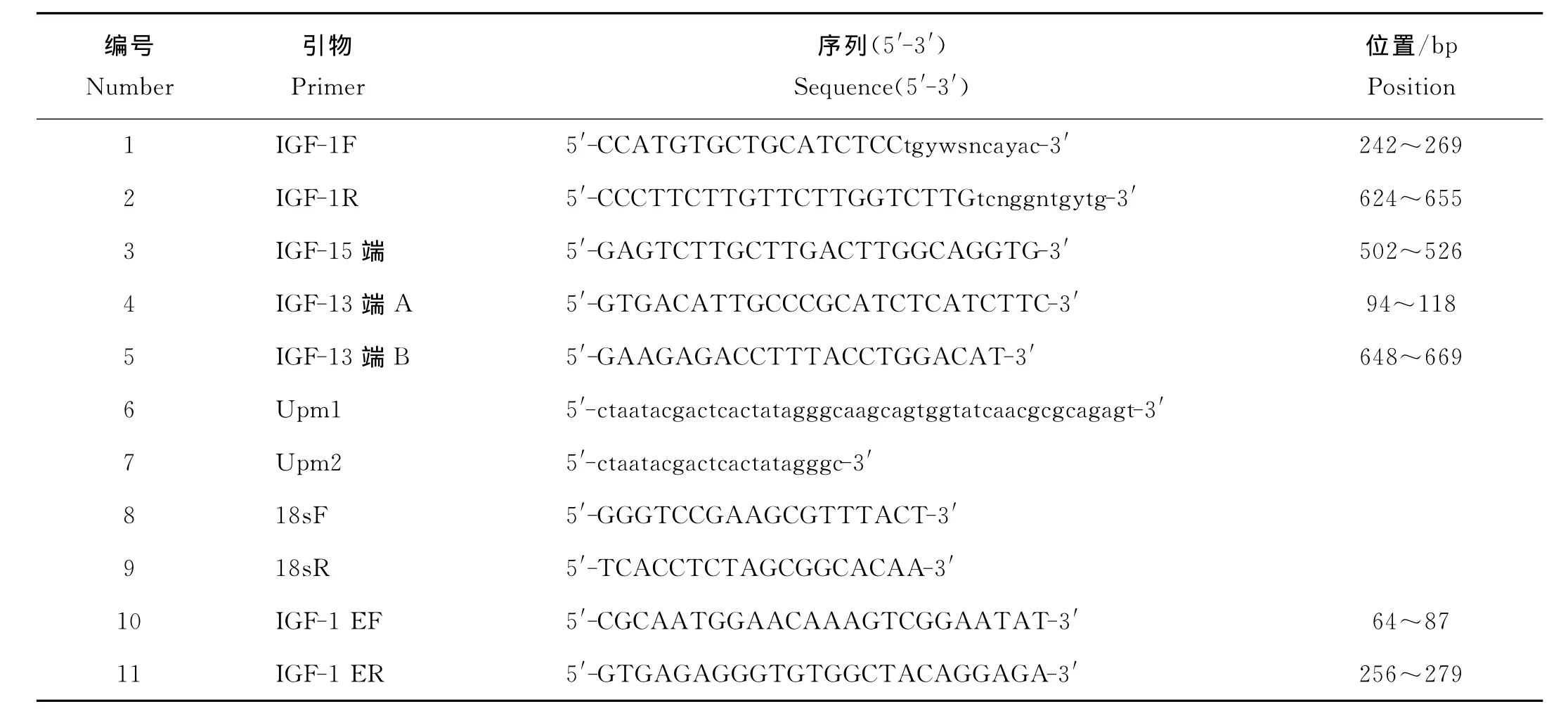
表1 引物序列及其位置Table 1 Nucleotide sequences and positions of oligonucleotide primers
1.2.3 花鲈IGF-1片段克隆 片段克隆反应按照TaKaRaTaqTM说明书进行。PCR反应程序如下:94℃预变性5min;Touchdown PCR:94℃30s,69℃30s,72℃30s,循环数为10,退火温度下降到59℃;94℃30s,59℃30s,72℃30s,循环数为30个;72℃延伸10min。PCR产物用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测;目的片段产物利用 TIANgel Midi Purification kit进行凝胶回收;连接pEASY-T1载体;转化到Trans1-T1感受态细胞;固体培养基37℃过夜培养;挑菌;菌体PCR检测;送交北京华大基因科技公司进行测序。
1.2.4 花鲈IGF-1cDNA 5′端和3′端的克隆 根据SMARTTM RACE cDNA Amplification Kit说明书,分别扩增IGF-1 5′端和3′端序列。5′端PCR反应程序如下:94 ℃ 预变性5min;94 ℃30s,63.5 ℃30s,72℃40s,循环数为40;72℃延伸10min。3′端克隆以IGF-13端A和IGF-1 3端B引物进行巢式PCR,第一个PCR反应以IGF-1 3端A为引物,PCR反应程序如下:94℃预变性5min;94℃30s,64.5℃30s,72℃40s,循环数为40;72℃延伸10min。第二个PCR反应以IGF-1 3端B为引物,PCR反应程序如下,94℃预变性5min;4℃30s,56℃30s,72℃40s,循环数为40;72℃延伸10min。胶回收及后续步骤同片段克隆。
1.2.5 序列分析 花鲈IGF-1cDNA全长在 NCBI上进行BLAST分析;利用DNAMAN推测开放阅读框;利用Signal P 3.0server分析信号肽;利用Scratch程序预测二硫键,利用Clustal X软件和MEGA 4软件对21种动物IGF-1氨基酸序列进行多重比对并采用Neighbor-Joining法(1 000runs,Amino:p-distance)构建系统进化树[18]。
1.2.6 IGF-1mRNA各组织的荧光实时定量PCR以肝脏组织RNA(浓度为500ng/μL)为模板按Prime-Script?RT reagent Kit with gDNA eraser(Perfect Real Time)的说明书进行反转录,cDNA按10倍稀释5个梯度,按照 SYBR Green Premix Ex TaqTM (Tli RNaseH Plus)试剂盒配制反应液,在 Roche LightCycler480实时定量PCR仪上进行PCR反应。采用三步法,内参基因18s的反应程序为:预变性:94℃30s;94℃5s,58℃20s,72℃40s,循环数为40;溶解步骤。目的基因的反应程序为:预变性:94℃30s;94℃5s,58℃20s,72℃40s,循环数为40;溶解步骤。根据结果制作标准曲线,确定扩增效率合理。提取3尾成鱼脑、垂体、心脏、鳃、胃、盲肠、肠、头肾、肾脏、肝脏、性腺、脾脏和肌肉13个组织的mRNA,反转录得到的cDNA模板依照上述步骤进行实时定量PCR反应。
2 结果
2.1 花鲈IGF-1cDNA全长序列
IGF-1基因cDNA全长包含873bp的碱基,其中5′端非编码区190bp,3′端非编码区128bp,编码区555bp,编码185个氨基酸(见图1)。序列已经提交到NCBI数据库,GenBank No.:JQ327805.1。其中信号肽区域包含44个氨基酸,B区30个,C区10个,A区21个,D区7个,E区74个。成熟肽存在CysB6、CysB18、CysA6、CysA7、CysA11和 CysA20六个半胱氨酸残基。多序列比对结果显示在编码区内存在IGF-1与IGF-1受体和结合蛋白结合的保守的氨基酸序列(见图2)。
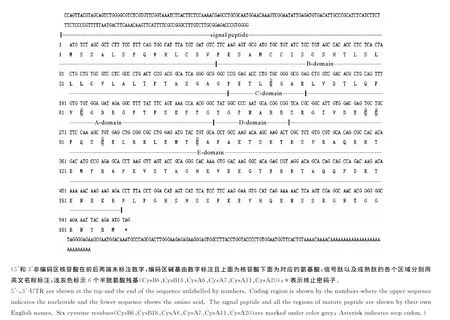
图1 花鲈IGF-1全长及氨基酸序列Fig.1 The cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of Lateolabraxjaponicus IGF-1
在NCBI上对花鲈IGF-1推测的氨基酸进行多序列比对发现其与鳜鱼IGF-1(Sinipercachuatsi)相似度最高为98%,与鞍带石斑鱼(Epinepheluslanceolatus)、加州鲈(Micropterussalmoides)、牙鲆(Paralichthysolivaceus)相似度为97%,与鲫鱼(Carassiusauratus)和鲤鱼(Cyprinuscarpio)相似度为69%,与人类的IGF-1(Homosapiens)相似度为60%,与金仓鼠(Mesocricetusauratus)相似度为50%,与原鸡(Gallus gallus)相似度为53%。各个功能区域间比对发现,B和A区域保守性较高,C区域次之,而与D和E区域保守性最差(见图2)。
对花鲈和其他21种脊椎动物IGF-1氨基酸序列进行系统进化树(Neighbor-joining法)分析(见图3)结果显示,此进化树分为三大分支,分别为鱼类IGF-1分支、鸟类及中华鳖IGF-1分支和哺乳动物IGF-1分支,而花鲈IGF-1氨基酸属于硬骨鱼类IGF-1分支且与加州鲈(Micropterussalmoides)、鳜鱼(Sinipercachuatsi)等鱼类的IGF-1分类地位最为接近。

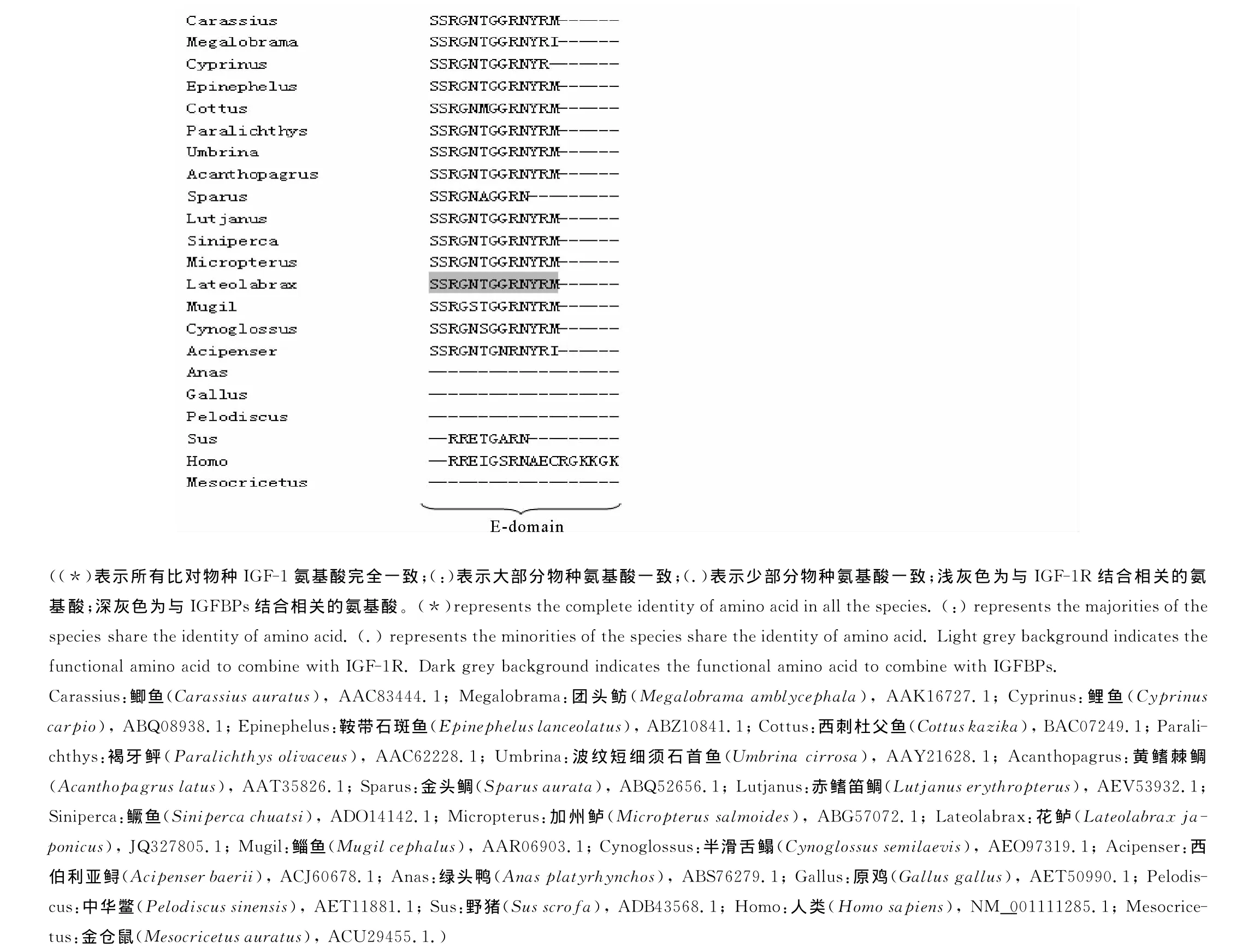
图2 脊椎动物IGF-1氨基酸序列比对Fig.2 Multiple sequence alignment of vertebrate IGF-1amino acid sequences
2.2 花鲈IGF-1组织表达
利用荧光实时定量PCR检测了梯度稀释的肝脏样本,由标准曲线(见图4A、B)可知,花鲈IGF-1基因和内参基因18s扩增效率均符合要求,可进行定量试验。
对花鲈不同组织IGF-1基因和18s进行实时定量实验,分别进行3组重复,采用2-ΔΔCt法并以心脏作为对照因子计算不同组织IGF-1mRNA表达的相对定量结果(见图5)。结果显示,花鲈IGF-1mRNA在肝脏的转录水平最高;肠、盲肠、肌肉、脾脏表达次之;而在鳃、垂体、性腺、胃、肾脏、脑、头肾、心脏表达量较低。
3 讨论
3.1 花鲈IGF-1cDNA的克隆及其序列分析
本研究首次克隆得到了花鲈IGF-1cDNA全长序列,参照人和其它脊椎动物的IGF-1结构,分析认为该基因可形成3对二硫键,对维持IGF-1的空间结构起重要作用[19]。多序列比对分析结果显示B区(86.3%~97%)和 A 区(82%~100%)保守性较高,而C区(36%~100%),D区(29%~100%)和 E区(33%~100%)则在各物种之间有一定得差异。B区和A区在不同物种中的高度保守性归结于他们各自包含与结合蛋白和受体结合的功能性序列[20-21]。
氨基酸序列比对分析发现花鲈IGF-1与鳜鱼(Sinipercachuatsi)IGF-1相似度最高,为98%,与鞍带石斑鱼、加州鲈、牙鲆相似度为97%,与鲫鱼,鲤鱼相似度为69%,与人类的相似度为60%,与金仓鼠(Mesocricetusauratus)相似度为50%,与原鸡相似度为53%,IGF-1在不同鱼类间的高度保守性暗示着其在进化过程中始终保留着主要的功能结构,但是根据自身的身体条件以及生长环境的影响也发生了一定的变异。另外,与其他亲缘关系较近的鱼类相比,花鲈IGF-1氨基酸序列在D结构域有1个碱基缺失,具体原因有待进一步研究。根据Shamblott等[22]的研究结果按照E肽类型可以推断花鲈IGF-1基因序列应属于IGF-1 Ea-4亚型,与加州鲈、鳜鱼、褐牙鲆等大部分海水鱼相同。而鲫鱼、团头鲂(Megalobramaamblycephala)、鲤鱼、西伯利亚鲟(Acipenserbaerii)等淡水鱼的IGF-1基因则属于IGF-1Ea-2亚型。
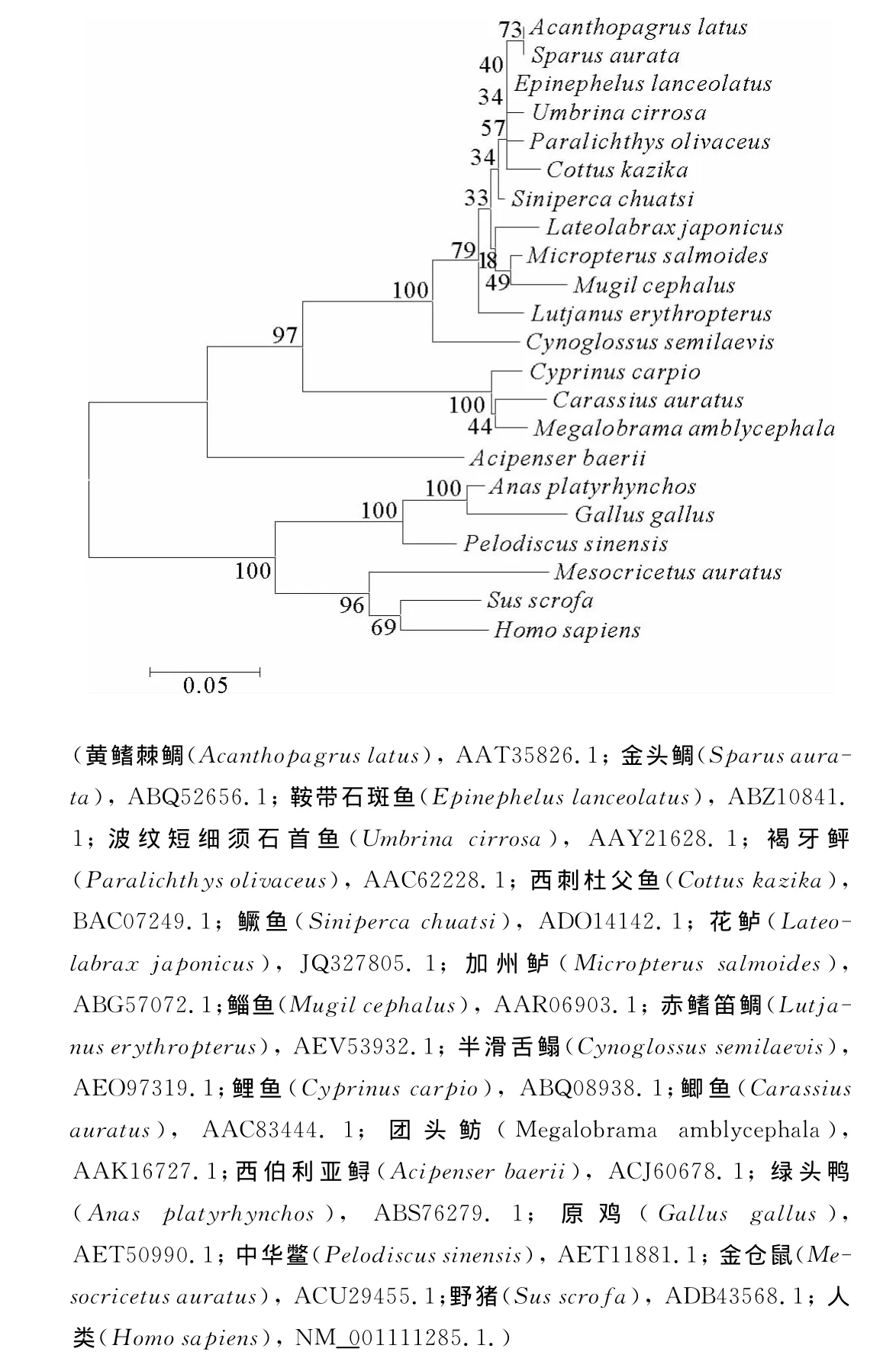
图3 脊椎动物IGF-1的NJ系统进化树Fig.3 NJ phylogenetic tree of vertebrate IGF-1
根据花鲈与其他21种脊椎动物IGF-1氨基酸序列构建脊椎动物NJ系统进化树可以看出,花鲈IGF-1与鳜鱼,加州鲈,褐牙鲆等鱼类的IGF-1分聚一支,说明花鲈IGF-1属于鱼类IGF-1大家族,而进化树分析结果也体现了海水鱼与淡水鱼IGF-1在进化上的差别,哺乳动物、鸟类和两栖类聚为另一支,物种间亲缘关系与其传统地位一致。
3.2 花鲈IGF-1cDNA的空间表达
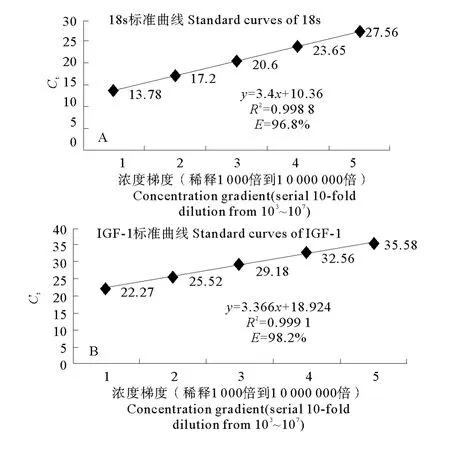
图4 IGF-1和内参基因18s的标准曲线图Fig.4 The standard curves of L.japonicus IGF-1and 18sgene
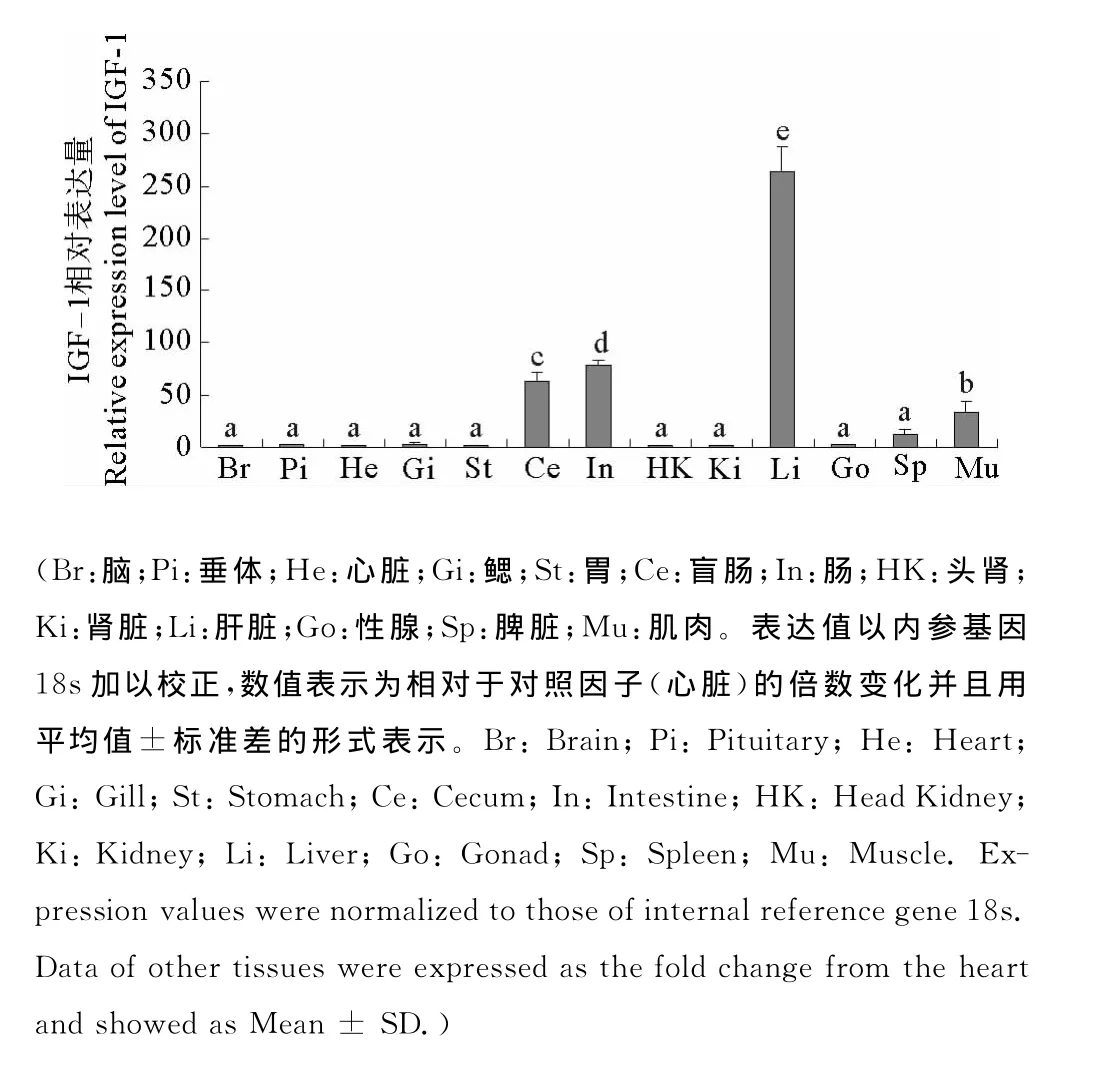
图5 花鲈各组织IGF-1mRNA的相对表达量Fig.5 Relative expression levels of IGF-1mRNA in different tissues of L.japonicus
本研究利用荧光实时定量PCR检测了花鲈成鱼13个组织中IGF-1mRNA的相对表达水平,结果显示其在肝脏表达量最丰富,是心脏的150多倍,这与其他鱼类关于IGF-1mRNA转录水平的研究结果一致,如:金头鲷[23],银大麻哈鱼[24-25],河鲈[26],鲤鱼[27-28],日本鳗鲡[29],尼罗罗非鱼[30],波纹短须石首鱼[31],舌齿鲈[32-33],塞内加尔鳎[34],说明在花鲈体内肝脏对于IGF-1的合成与分泌起着重要的作用。在不同物种中肝脏IGF-1表达量的不同可能归因于物种差异,还与其他的一些参数如生长因子、细胞因子、年龄、体重、营养条件、环境温度和盐度有关,同时也与个体的生长发育时期有很大的联系[35-38]。IGF-1自分泌和旁分泌的作用方式对于相应的器官有着特异性功能[39-40]。研究结果显示在花鲈成鱼的肠和盲肠中的相对表达量是心脏的50多倍,由于鱼类后肠具有渗透调节作用[41],这就暗示着IGF-1在花鲈渗透压调节过程中可能会起到重要的作用。此外,在肌肉中检测到了相对较高的表达量,这可能是由于IGF-1参与由 Ras-MEK-ERK信号通路调节的骨骼肌卫星细胞的增殖与分化,并且在鱼类生长过程中IGF-1也参与到了由 PI3K-AktmTOR 信号通路的调控过程[42-43]。
[1]张美昭,高天翔.花鲈亲鱼人工培育与催产技术研究[J].青岛海洋大学学报:自然科学版,2001,31(2):195-200.
[2]张春丹,李明云.花鲈繁殖生物学及繁育技术研究进展[J].宁波大学学报(理工版),2005,18(3):400-403.
[3]林意斌,薛阿民.花鲈养殖技术[J].河北渔业,2008(1):30.
[4]Duan C,Ding J,Schlueter P J,et al.A zebra view of the insulinlike growth factor signaling pathway [J].Aeta Zoolsiniea,2003,49:421-431.
[5]Duan C,Xu Q.Roles of insulin-like growth factor(IGF)binding proteins in regulating IGF actions[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2005,142(1-2):44-52.
[6]Humbel R E.Hormonal Proteins and Peptides[J].New York:CH Academic,1984,12:57-79.
[7]Lowe W L.Biological action of the insulin-like growth factors[J].In:LeRoith D,editor.Insulin-Like GrowthFactors:Molecular and Cellular Aspects.Boca Raton,FL:CRC Press,1991,1:49-85.
[8]Parrizas M,LeRoith D.Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibition of apoptosis is associated with increased expression of the bcl-xl gene product[J].Endocrinology,1997,138:355-365.
[9]Kajimura S,Uchida K,Yada T,et al.Stimulation of insulin-like growth factor-I production by recombinant bovine growth hormone in Mozambique tilapia,Oreochromismossambicus[J].Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,2001,25(3):221-230.
[10]Reinecke M,Collet C.The phylogeny of the insulin-like growth factors[J].International Review of Cytology,1998,183:1-94.
[11]Reinecke M,Zaccone G,Kapoor B G.Insulin-like growth factor I and II in fish[J].Fish Endocrinology,2006,1:87-130.
[12]Reinecke M,Bjornsson B T,Dickho V W W,et al.Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factors in fish:where we are and where to go[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2005,142(1/2):20-24.
[13]Ayaso E,Nolan C M,Byrnes L.Zebrafish insulin-like growth factor-I receptor:molecular cloning and developmental expression[J].Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2002,191:137-148.
[14]Maures T,Chan S J,Xu B,et al.Structural,biochemical,and expression analysis of two distinct insulin-like growth factor I receptors and their ligands in zebrafish [J].Endocrinology,2002,143:1858-1871.
[15]Nakao N,Tanaka M,Higashimoto Y,et al.Molecular cloning,dentification and characterization of four distinct receptor subtypes for insulin and IGF-I in Japanese flounder,Paralichthysolivaceus[J].Endocrinology,2002,173:365-375.
[16]Perrot V,Moiseeva E B,Gozes Y,et al.Ontogeny of the insulinlike growth factor system (IGF-I,IGF-II,and IGF-1R)in gilthead seabream(Sparusaurata):expression and cellular localization[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,1999,116:445-460.
[17]陈彩芳,温海深,何峰,等.程序化设计的简并引物克隆半滑舌鳎CYP17基因[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版,2009,39(6):1213-1218.
[18]Kumar R S,Tamura K,Nei M.MEGA3:Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment[J].Briefings in Bioinformatics,2004,5(2):150-163.
[19]Hober S,Forsberg G,Palm G,et al.Disulfide exchange olding of insulin-like growth factor-I [J].Biochemistry,1992,31:1749-1756.
[20]Zhang W,Gustafson T A,Rutter W J,et al.Positively charged side chains in the insulin-like growth factor-1Cand D-regions determine receptor binding specificity[J].Journal of Biology Chemistry,1994,269:10609-10613.
[21]Magee B A,Shooter G K,Wallace J C,et al.Insulin-like growth factor I and its binding proteins:a study of the binding interface using B-domain analogues[J].Biochemistry,1999,38:15863-15870.
[22]Shamblott M J,Chen T T.Age-related and tissue-specific levels of five forms of insulin-like growth factor mRNA in a teleost[J].Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology,1993,2(6):351-361.
[23]Duguay S J,Lai-Zhang J,Steiner D F,et al.Developmental and tissue-regulated expression of IGF-I and IGF-II mRNAs inSparus aurata[J].Molecular Endocrinology,1996,16:123-132.
[24]Duan C,Duguay S,Plisetskaya E.Insulin-like growth factor I(IGF-I) mRNA expression in coho salmon,Oncorhynchus kisutch:tissue distribution and effects of growth hormone/prolactin family proteins[J].Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,1993,11:371-379.
[25]Pierce A L,Dickey J T,Larsen D A,et al.A quantitative realtime RT-PCR assay for salmon IGF-I mRNA and its application in the study of GH regulation of IGF-I gene expression in primary culture of salmon hepatocytes[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2004,135:401-411.
[26]Jentoft S,Aastveit A H,Andersen O.Molecular cloning and expression of insulin-like growth factor-I(IGF-I)in Eurasian perch(Percafluviatilis):lack of responsiveness to growth hormone treatment[J].Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,2004,30:67-76.
[27]Tse M C,Vong Q P,Cheng C H,et al.PCR-cloning and gene expression studies in common carp(Cyprinuscarpio)insulin-like growth factor-II [J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2002,(1575):63-74.
[28]Vong Q P,Chan K M,Cheng C H.Quantification of common carp (Cyprinuscarpio)IGF-I and IGF-II mRNA by real-time PCR:differential regulation of expression by GH [J].Endocrinology,2003,178:513-521.
[29] Moriyama S,Yamaguchi K,Takasawa T,et al.Insulin-like growth factorI of Japanese eel,Anguillajaponica:cDNA cloning,tissue distribution,and expression after treatment with growth hormone and seawater acclimation [J].Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,2006,32:189-201.
[30]Caelers A,Berishvili G,Meli M L,et al.Establishment of a realtime RT-PCR for the determination of absolute amounts of IGF-I and IGF-II gene expression in liver and extrahepatic sites of the tilapia[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2004,137:196-204.
[31]Patruno M,Maccatrozzo L,Funkenstein B,et al.Cloning and expression of insulin-like growth factors I and II in the shi drum(Umbrinacirrosa)[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology part B:Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2006,144:137-151.
[32]Terova G,Rimoldi S,Chini V,et al.Cloning and expression analysis of insulin-like growth factor I and II in liver and muscle of sea bass(Dicentrarchuslabrax,L.)during long-term fasting and refeeding[J].Fish Biology,2007,70:219-233.
[33]Patruno M,Sivieri S,Poltronieri C,et al.Real-time polymerase chain reaction,in situ hybridization and immunohistochemical localization of insulin-like growth factor-I and myostatin during development ofDicentrarchuslabrax(Pisces:Osteichthyes)[J].Cell Tissue Research,2008,331:643-658.
[34]Funes V,Asensio E,Ponce M,et al.Insulin-like growth factors I and II in the soleSoleasenegalensis:cDNA cloning and quantitation of gene expression in tissues and during larval development[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2006,149:166-172.
[35]Duan C.Nutritional and developmental regulation of insulin-like growth factors in fish[J].Nutrition,1998,128:306-314.
[36]Meton I,Caseras A,Canto E,et al.Liver insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA is not affected by diet composition or ration size but shows diurnal variations in regularly-fed gilthead sea bream(Sparusaurata)[J].Nutrition,2000,130:757-760.
[37]Larsen D A,Beckman B R,Dickhoff W W.The effect of low temperature and fasting during the winter on metabolic stores and endocrine physiology (insulin,insulin-like growth factor-I,and thyroxine)of coho salmon,Oncorhynchuskisutch[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2001,123:308-323.
[38]Gabillard J C,Weil C,Rescan P Y,et al.Effects of environmental temperature on IGF1,IGF2,and IGF type I receptor expression in rainbow trout(Oncorhynchusmykiss)[J].General and Comparative Endocrinology,2003,133:233-242.
[39]Reinecke M,Collet C.The phylogeny of the insulin-like growth factors[J].International review of cytology-a survey of cell,1998,183:1-94.
[40]Reinecke M,Zaccone G,Kapoor B G.Insulin-like growth factor I and II in fish[J].Fish Endocrinology,2006,1:87-130.
[41]Bern H A,McCormick S D,Kelley K M,et al.Insulin-like growth factors“under water”:role in growth and function of fish and other poikilothermic vertebrates[J].Modern concepts of insulin-like growth factors,1991,1:85-96.
[42]Rommel C,Bodine S C,Clarke B A,et al.Mediation of IGF-1-induced skeletal myotube hyper trophy by PI(3)K/Akt/mTOR and PI(3)K/Akt/GSK3pathways[J].Nat Cell Biol,2001,3:1009-1013.
[43]Castillo J,Johnsen-Ammendrup I,Codina M,et al.IGF-I and insulin receptor signal transduction in trout muscle cells[J].Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol,2006,290:1683-1690.

