一种改进的有限反馈准正交空时编码方案
韩 冲, 张效民, 李通旭, 陈 瑜
一种改进的有限反馈准正交空时编码方案
韩 冲1, 张效民1, 李通旭1, 陈 瑜2
(1. 西北工业大学 航海学院, 陕西 西安, 710072; 2. 浙江大学 城市学院, 浙江 杭州, 310015)
针对广义正交空时编码利用反馈信道改善系统性能时, 由于反馈量的增加导致复杂度较高而失去空时码自身优势的问题, 提出了一种改进的有限反馈准正交空时分组编码(QOSTBC)方案, 该方案在对编码矩阵对角化重构的同时引入了等效子信道适度旋转设计。结合水声信道模型理论和仿真分析表明, 该方案在峰均功率比、实数乘、实数加计算复杂度等方面有较为明显的改进, 同时进一步提高了系统的信道容量, 降低了系统误码率。
空时编码; 准正交空时分组编码; 信道增益; 误码率
0 引言
在多输入多输出(multiple input multiple output, MIMO)无线系统中, 空时编码是一种能够提高数据传输可靠性的有效带宽传输技术[1]。正交空时分组码以其特殊的正交结构来保证全分集, 同时能够实现简单的线性(如最大似然)译码, 从而成为诸多空时编码中最具吸引力的编码方式之一。最具代表性的正交空时分组编码(orthogonal space- time block codes, OSTBC)是由lamouti提出的双发射天线方案。随后, 大量文章如文献[2]~ [4], 对该方案提出了改进方法, 然而由于其系统自身构造特点使得该类OSTBC具有较低的编码速率(在大于2个天线情况下, 不高于3/4)。

基于此, 笔者提出了一种基于有限反馈的广义正交空时编码方案。该编码将各部分正交空时分组码的各支路信号角度适度旋转, 然后对该编码矩阵进行对角化重构, 使得重构后的编码矩阵具有正交性, 从而使得系统在提升性能的基础上降低了系统译码复杂度, 实现译码更加简单。仿真结果分析验证了该方案较前述QOSTBC方案有更好的性能指标。
1 系统模型
在块衰落信道下, 假设一个MIMO传输系统具有个发射天线和个接收天线[11]。接收端信号矩阵

针对编码矩阵, 本文提出了改进QOSTBC的系统模型, 如图1所示。

图1 广义空时编码系统模型

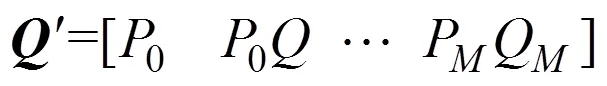
其中,为对角方阵, 且
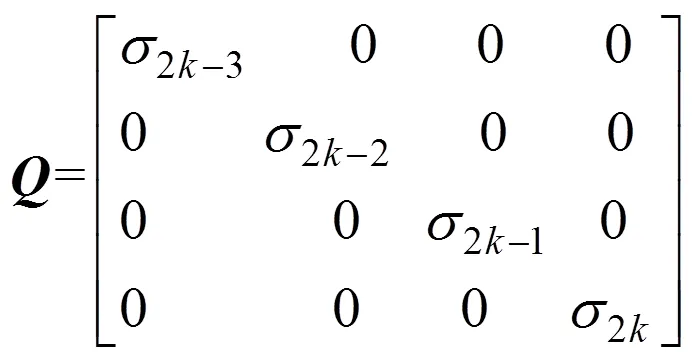
2 改进算法原理
假设在每个传输时隙内信道保持不变, 即在块衰落信道下, 对式(1)变换所得接收信号表示为




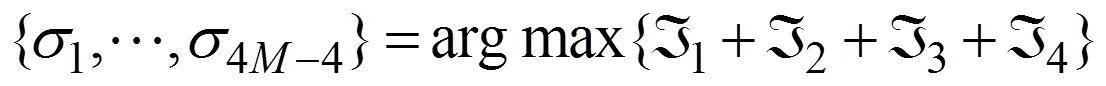

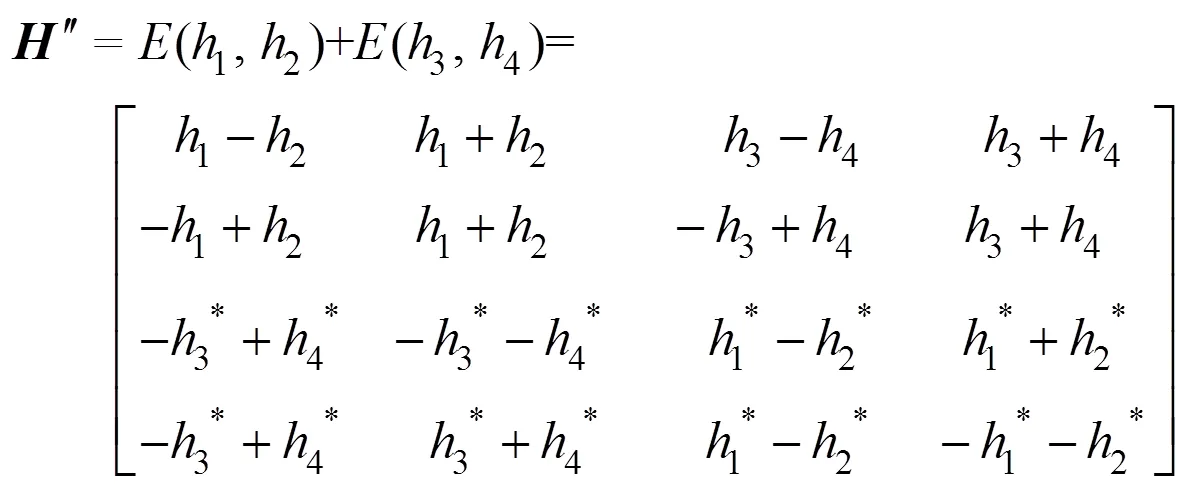
由式(10)可知

假设接收端有个天线, 则对于任意接收天线上的信号进行信道匹配滤波, 得
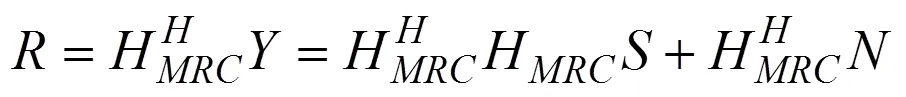


由上述可知, 改进的算法实现对于接收端的分组线性译码, 避免了最大似然(maximum likelihood, ML)等大运算量的译码算法, 降低了系统复杂度。
3 仿真结果与分析


表1 水声信道模型参数
且
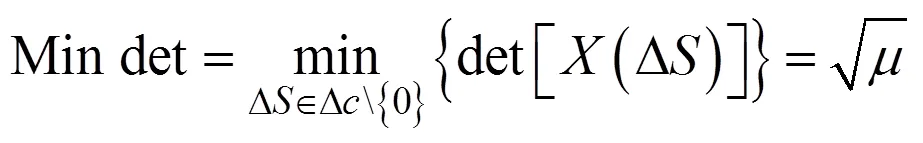
对比试验的仿真参数统一设定为8PSK调制、发射天线数目为4、接收天线数目为1。由表2可知, 改进方案的峰均功率比为2.71, 相对于其他经典算法较低。根据Mindet的结果, 仅有文献[14]中的算法与改进算法具有较高的编码增益。从算法复杂度的结果可知, 由于文献[13]~[15]所用算法的数乘与数加运算中都与发射天线数的3次方成正比, 而正交空时码与改进算法的复杂度与发射天线数成单次幂线性关系, 因而改进算法相对文献[13]~[15]具有较低的计算复杂度。

表2 算法性能对比结果
图2给出了5种空时编码方案的误码率性能仿真对比结果, 仿真采用发射天线数目为8, 2个扩展空时编码器。由图2可知, 文献[13]~[15]算法, 由于在水声多径衰落信道下分集增益与编码增益无法满足最大化, 故在图中表现为, 误码率(bit error ratio, BER)曲线斜率比较平坦。由图中可以看出, 本文提出的改进算法比其他算法信噪比低4 dB以上。与此同时, 虽然改进算法引入了适当的反馈信息, 但对其他几个算法繁琐的运算复杂度而言, 该改进算法总体上还是显著优于其他算法性能。

图2 算法误码率性能对比结果
4 结束语
基于编码矩阵对角化理论与等效子信道适度旋转设计, 本文针对传统空时编码编码增益低、译码复杂度较高的问题, 结合水声信道多径衰落特性, 提出了一种有限反馈准正交空时码。它在对编码矩阵对角化重构的同时, 引入等效子信道适度旋转设计, 使得整个系统复杂度在引入有限反馈量的条件下得到了明显的降低, 缓解了译码阶段的压力; 与此同时, 由于子信道适度旋转相应的角度, 增加了系统的等效信道增益, 从而提升了系统的性能。随后将准备海上试验验证算法的实用性、有效性, 并开展可靠性研究。
[1] 王国珍, 刘毓. 无线通信系统中的MIMO空时编码技术[J]. 现代电子技术, 2011, 34(19): 31-33.
Wang Guo-zhen, Liu Yu. MIMO Space-time Coding Tech- nology in Wireless Communication System[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2011, 34(19): 31-33.
[2] To D, Choi J, Kim I. Error Probability Analysis of Bidire- ctional Relay Systems Using Alamouti Scheme[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2010, 14(8): 758-760.
[3] Liu J, Zhang J K, Wong K M. Full-diversity Codes for MISO Systems Equipped with Linear or ML Detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(10): 4511-4527.
[4] Guo X, Xia X G. On Full Diversity Space-time Block Co- des with Partial Interference Cancellation Group Decod- ing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(10): 4366-4385.
[5] Sirianunpiboon S, Calderbank A R, Howard S D. Bayesian Analysis of Interference Cancellation for Alamouti Multiplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 54(10): 4755-4761.
[6] Zhang W, Xu T, Xia XG. Two Designs of Space-time Block Codes Achieving Full Diversity with Partial Inter- ference Cancellation Group Decoding[J]. IEEE Transac- tions on Information Theory, 2012, 58(2): 747-764.
[7] Naguib A F, Seshadri N, Calderbank A R. Applications of Spacetime Block Codes and Interference Suppression for High Capacity and High Data Rate Wireless Systems[C]// Asilomar Conf. Signals, Systems and Computers, 1998: 1803-1810.
[8] Guo X, Xia X G. Corrections to “On Full Diversity Space- time Block Codes with Partial Interference Cancellation Group Decoding”[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2010, 56(10): 3635-3636.
[9] Damen M O, Abed-Meraim K, Belfiore J C. Diagonal Algebraic Space-time Block Codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2002, 48(3): 628-636.
[10] Geover Rohan, Su Wei-feng, Pados D A. An 8*8 Quasi Orthogonal STBC From for Transmissions over Eight or Four Antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2008, 7(12): 4777-4785.
[11] Simon M, Alouini M. Digital Communication over Fading Channels[M]. Wiley-IEEE Press, 2005.
[12] Eslamifar M, Chin W, Yuen C, et al. Performance Analysis of Two-way Multiple-antenna Relaying with Network Coding[C]//Vehicular Technology Conference Fall(VTC 2009-Fall), 2009 IEEE 70th, 2009: 1-5.
[13] Sezgin A, Altay G, Paulraj A. Generalized Partial Feedback Based Orthogonal Space-time Block Coding[J]. IEEE Transactions Wireless Commun, 2009, 8(6): 2771- 2775.
[14] Fazel F, Jafarkhani H. Quasi-Orthogonal Space-Frequency and Space-Time-Frequency Block Codes for MIMO OFDM Channels[J]. IEEE Trans on Wireless Communi- cations, 2008, 7(1): 184-192.
[15] Janani M, Nosratinia A. Efficient Space-time Block Codes Derived from Quasi-orthogonal Structures[J]. IEEE Tran- sactions Wireless Comun, 2007, 6(5): 1643-1646.
(责任编辑: 杨力军)
An Improved Scheme for Limited Feedback QOSTBC
HAN Chong,ZHANG Xiao-min, LI Tong-xu,CHEN Yu
(1. College of Marine Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi′an 710072, China; 2. College of City, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310015, China)
The quasi orthogonal space-time block code(QOSTBC) scheme uses feedback channel to improve system performance. Because the increase in amount of feedback results in higher complexity, the space-time code loses its own advantage. In this paper, an improved limited feedback QOSTBC scheme is proposed based on the diagonalizti- on reconstruction of encoding matrix and the adequate rotation of equivalent sub-channels. Combining the theory of un- derwater acoustic channel model and the simulation analysis, it shows that the proposed scheme is significantly improved in such parameters as peak power ratio, computation complexity of real numbers multiplication and real numbers addition. In addition, the system complexity is reduced, the equivalent channel gain is increased, and the bit error rate of system is lowered. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed scheme.
space-time coding;quasi orthogonal space-time block code(QOSTBC); channel gain; bit error rate
TJ630.34; TN911.7
A
1673-1948(2014)03-0189-05
2013-10-31;
2014-01-02.
西北工业大学基础研究基金(JC20110210).
韩 冲(1983-), 男, 在读博士, 主要研究方向为宽带MIMO高速通信.

