浐灞国家湿地公园,西安,陕西,中国
景观设计:西安建筑科技大学/西安建筑科技大学城市规划设计研究院
Landscape Design: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology/Institute of Urban Planning and Design of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology
浐灞国家湿地公园,西安,陕西,中国
Chan-ba National Wetland Park, Xi’an, Shanxi, China, 2013
景观设计:西安建筑科技大学/西安建筑科技大学城市规划设计研究院
Landscape Design: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology/Institute of Urban Planning and Design of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology

1 公园南入口人工湿地景观/The artificial wetland of the south entrance area

2 夕阳下的观鸟塔/The Bird watching tower under the sunset
圈层与流动
西安浐灞国家湿地公园位于西安城市东北之隅,灞河入渭河口,用地西南边界将紧临城市建设区。按自然条件和人为干预程度,由两河河床向城市建设方向,设置4个“圈层递进”层级,由此构成8个湿地类型、20个景观区和11个功能区。河口水流交汇地段具有明显的方向感,加之季节性降雨、地势平坦的特点,以“流动汇集”的理念,构成水系、植物群落、道路、人工地形等系统的空间形态布局,表现了西北半干旱、半湿润地区河口型湿地景观的保育、恢复与营造。
水系和植物
根据水源规划3大水系,灞河取水主要用于恢复区;未来污水处理厂的中水用于中心人工湿地区,建设场地雨水作为补充;渭河取水用于远期北侧林溪荒地自然恢复区。总用水量按全年最少8次换水计算,并设置枯水期和暴雨期的水系调控,确保节约用水。植物群落包含了滩地野生、旱地节水、田园作物以及城市绿化等群系。结合不同湿地类型规划了9类陆生及湿生种植生境群落,3类水生种植生境群落。
地域自然条件,决定了多样的“旱湿地”生境营造途径。建成半年来,时至枯水期,水位下降,滩涂裸露,保育恢复区水系完整,人工可调控水系功能初显。此时植物群落处于生长初期及冬季“荒芜”期,呈现了这片土地的自然本性。1)
传统意义的景观设计,表现了人们的审美追求在空间外在秩序的表达,是一种征服;自然表现在物种群落依托物质生存环境条件下的自生演替、栖息漂移的规律,是一种自由。我们致力于寻找表达自然内在秩序的景观营造途径。(刘晖,徐鼎黄)
注释:
1) 西北地区人工生境营造研究受国家自然科学基金项目资助,51278410
The Circle structure and flowing pattern
Chan-ba National Park is located in the northeast corner of Xi'an where the Ba River joins the Wei River. Bordered by urban construction on the south and west sides, the Park has been organized into four "progressive circles"-marking a journey from the nature to the city, eight wetlands areas, 20 scenic areas and 11 functional zones. In response to the area's rainy season, the flat site and its directional bias, the theme of "Flowing and Gathering" was chosen to organize the water systems, plants communities, circulation, topography and "dried" wetland habitats.
Water and planting system
The water system as a whole uses water from three different sources. Water from the Ba River supports the Recovery area; gray-water from the wastewater treatment plant supplies the center and its constructed wetland; water from the Wei River supplies the moorland streams at the north of the site. The water control system was designed for both dry and flood season criteria. At a minimum it is refreshed eight times annually. The planted areas include native, dry land, farm and urban species. There are nine habitat for terrestrial hygrophilous vegetation and three for aquatic vegetation in the park.
The park is weathering its first winter. In this dry season the level of wetland water has decreased in this dry season and the controlled water system is active for the first time.1)
The representation of the nature
王祥见老道所言非虚,一时间有些害怕,急忙问道:“要是真的如道长所言,该如何消弭此劫呢?”他也是看了不少古装剧,临时拼凑起的台词和老道士倒是很搭调。
The traditional landscape design, like that of historical gardens, always composed space according to man's aesthetic demands-as a kind of conquest. But nature is about inhabitation, the drift and evolution of species and communities in relation to habitat. It is kind of free. Today we are looking for ways to represent these natural internal orders in landscape design.
Notes:
1) The research on the Habitat-site Modeling of the Chan-ba Wetland Park is supported by the NSFC, 51278410
项目信息/Credits and Data
客户/Client:西安浐灞生态区管委会
项目主持/Principal in Charge:刘晖(项目前期:控规调整、修规、核心保护区景观设计项目负责人),董芦笛(项目后期:公园精致区、野趣区景观设计方案及施工图设计项目负责人)
设计团队/Design Team:董芦笛,徐鼎黄,杨建辉,陈磊,吕琳,李莉华(项目前期:西安建筑科技大学城市规划设计研究院与西安建筑科技大学建筑学院);刘晖,许舸强,徐鼎黄,高鹏飞,王晓利,陈磊,郑邦毅(项目后期:西安建筑科技大学建筑学院与沃易森建筑景观设计有限公司)
用地面积/Total Area:798.2hm2
建成区面积/Built Area:317.7 hm2(包括一期灞河河滩湿地自然保育区、灞河左岸堤内核心恢复区,以及二期精致区和野趣区)
项目过程/Project Phase:国家林业局审批立项,2008;总体规划等各类规划设计成果编制,2008-2011
图纸制作/Drawing:徐鼎黄
摄影/Photos: 桑磊(Fig 1,3,6,9-12),徐鼎黄(Fig 2),李莉华(Fig 8)

3 核心恢复区冬季湿地景观/The wetland of the recovery area in the winter
评论
鲍威:当人们置身于大尺度景观规划当中,可感知尺度与总图尺度相距甚远,这对设计而言一般是很难把握的。此案在对大尺度自然景观生态科学治理的前提下,适当地引入人工景观,比较成功地将两个不同尺度与性质的设计有机结合在一起。景观建筑元素尤以观鸟塔暧昧的形式为亮点,人们在自然的超尺度下找到了可以联系自身的物体。
阙镇清:8大类湿地叠加11大功能区,以水过程联系并与两河及城市开发区整合,根据河口汇流形态规律形成自然演替的骨架。自然表达的设计旨归,强调自然生境的保育、恢复和人工营建,遵循最小干扰的宗旨。设计师依托生态学知识,做好湿地的医生或护理员,剩下的一切交给自然和时间。在城市化快速杀伐自然生态系统的今天,我们尤其需要更多的自然解放者,而非征服者!
Comments
BAO Wei:When presented with large scale landscape planning, it's always hard to synchronize the scale of human experience with the scale of the master plan.This project successfully integrates these two scales by introducing adequate artificial landscape features on the premise that large scale natural landscape ecology would be well managed. The formal ambiguity of the bird watching tower is the highlight of the project. It helps people find something to relate to in the megascale landscape.
QUE Zhenqing:In this park, eleven major functional areas overlap with eight categories of wetlands connected via water system. According to the principle of minimal interference on nature, the designers focused their efforts on the conservation, restoration and artificial re-construction of natural habitats only. Acknowledged with theories of modern ecology, designers act as good doctors or guardians of the wetlands. Except the eco-restoration design, they just leave the wetlands to live its life through into a landscape. Today, as rapid urbanization is threatening natural ecosystems throughout the nation, we do need many more liberators of nature than conquerors of nature!
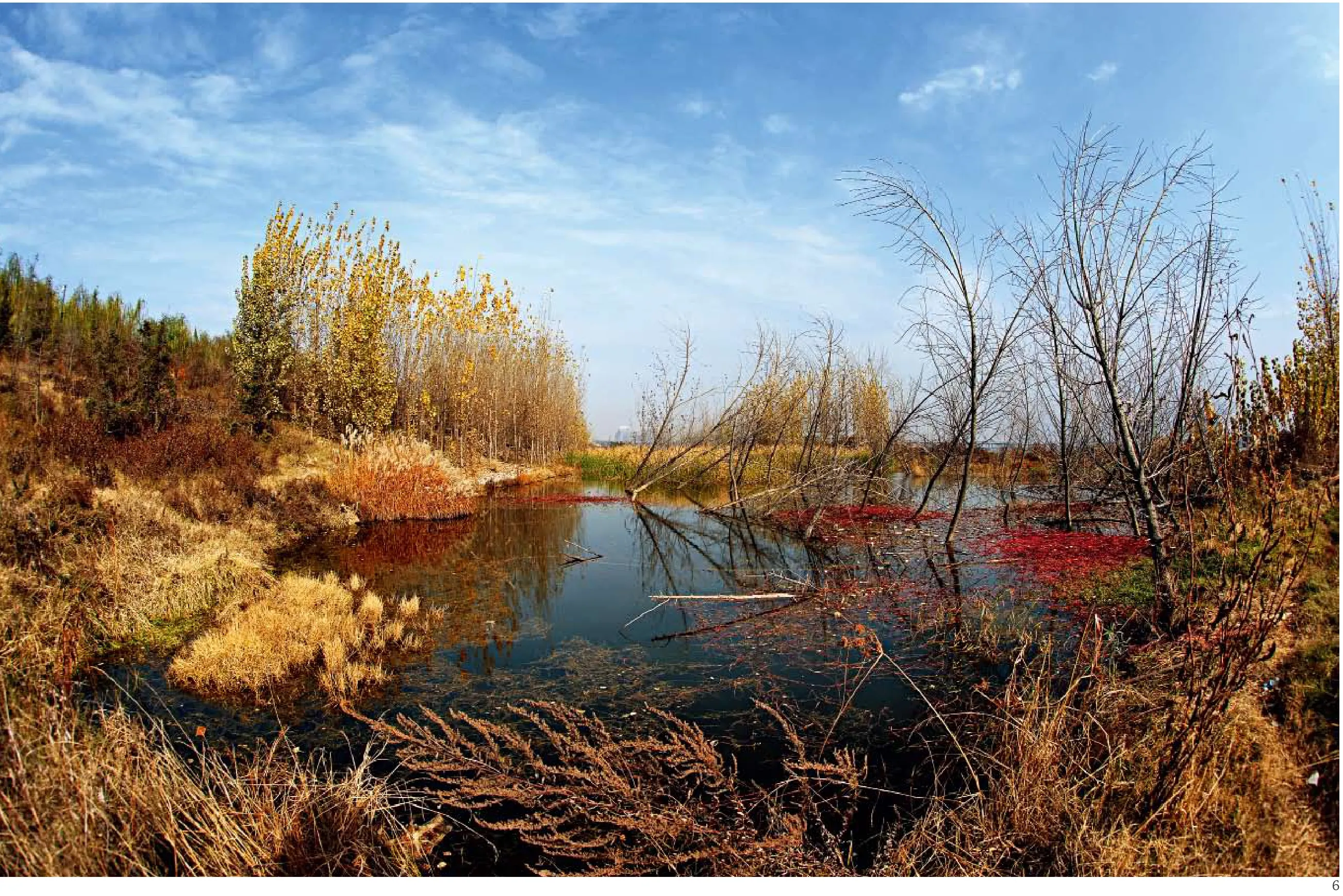
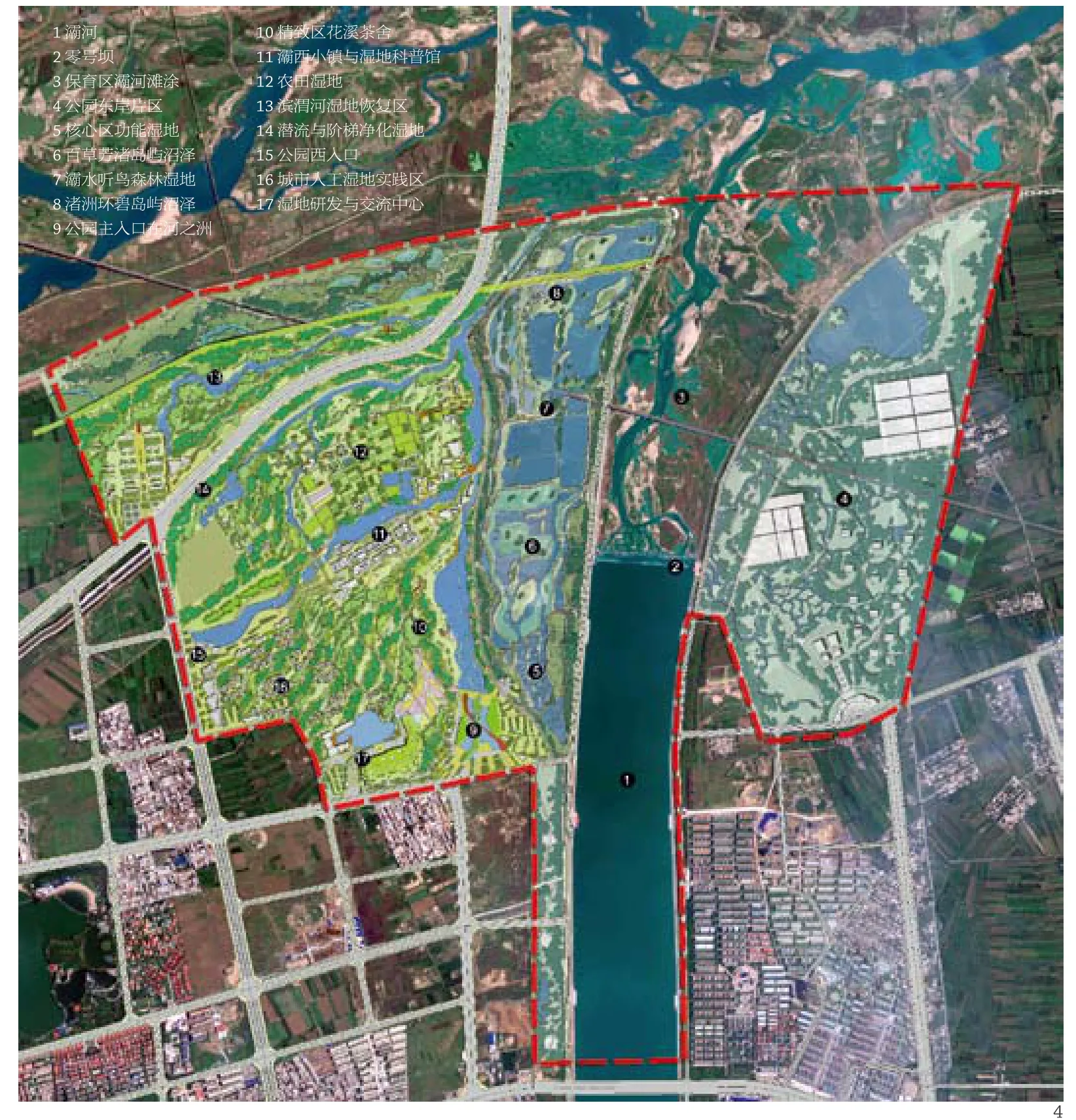
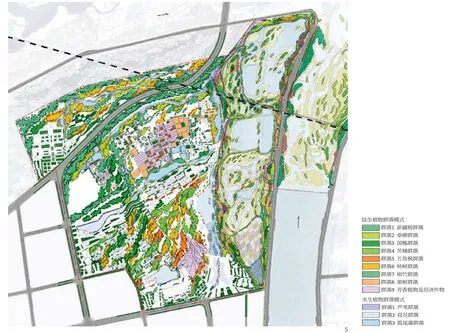



4 西安浐灞国家湿地公园规划总平面/The master plan of the wetland park5 植物种植群落分布图/Distribution of the plants communities6 河滩保育区湿地植物景观/The plants of the conservation area7 湿地类型分布图/Distribution of the wetlands8 各种野生及人工植物群落/The different wild and artificial plants communities

10 保育区灞河滩涂冬季景观/The conservation area of the Ba River bed

11 观鸟塔和过冬的候鸟。核心恢复区水位下降,滩涂裸露/The Bird watching tower and the wide birds. It shows the decreased water lever.
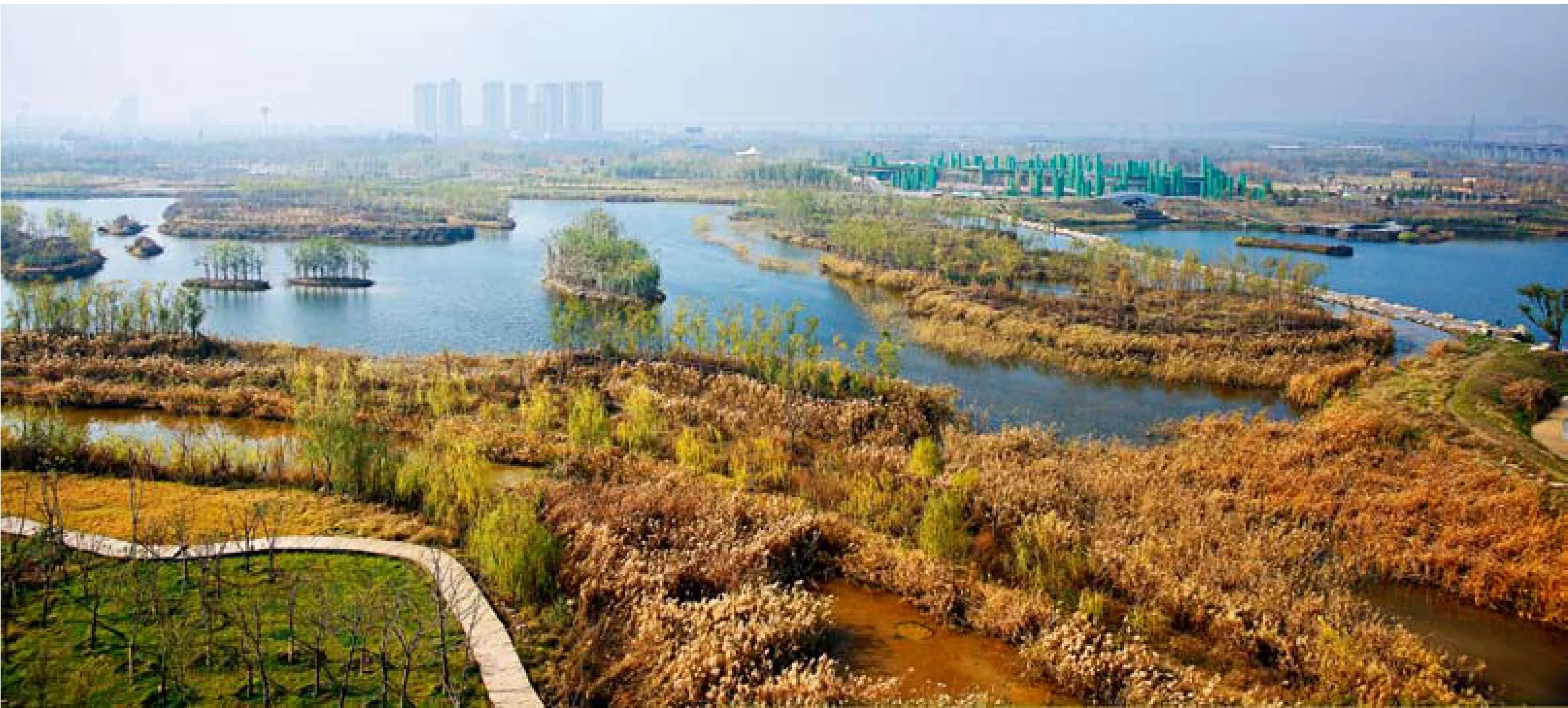

12 观鸟塔上向西鸟瞰已建成的核心恢复保育区/The bird view of the core recovery area form the Birding tower
book=2,ebook=43
——美丽的家园

