Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达及临床意义
逯 强 吴春云 王保仓 刘兰泽 李 勇 王 辉 闫 明
. 骨肿瘤 Bone neoplasms .
Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达及临床意义
逯 强 吴春云 王保仓 刘兰泽 李 勇 王 辉 闫 明
目的Fascin-1 是一种与 F-肌动蛋白结合的 55kDa 细胞骨架蛋白,并参与细胞膜突起的形成及细胞的迁移。目前已知在多种肿瘤细胞中呈现高表达。本研究的目的探讨 fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达及其与相关临床参数之间的关系。方法65 例骨巨细胞瘤患者均来自唐山市第二医院,其中男 30 例,女35 例;平均年龄 35 (9~58 ) 岁。患者平均随访时间 51.5 (12.5~80.0 ) 个月。应用免疫组化检测 65 例骨巨细胞瘤组织中 fascin-1 蛋白的表达情况,并与临床病理数据进行统计学分析。结果65 例骨巨细胞瘤标本中有40 例表现为阳性表达,阳性率为 66.7%,主要表现在细胞浆中。Fascin-1 表达与各种反映肿瘤预后的指标进行相关性研究结果表明,在 36 例良性骨巨细胞瘤患者中有20 例呈阳性表达,占 55.6%,而在27 例侵袭性患者中有19 例呈阳性表达,占 70.3%;在2 例恶变及转移患者均呈阳性表达;对比预后良好的患者,16 例复发患者中10 例呈阳性表达,占 62.5%。统计表明 fascin-1 蛋白的表达与肿瘤分类及预后相关 ( P<0.05 ),而与性别、年龄、肿瘤部位及大小无明显相关 ( P>0.05 )。结论Fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤组织中呈现高表达,可能在骨巨细胞瘤的复发及恶变过程中发挥重要作用,并可能成为我们治疗骨巨细胞瘤的一个新的靶点。
骨巨细胞瘤;骨肿瘤;免疫组织化学;Fascin-1 蛋白
骨巨细胞瘤是常见的原发性骨肿瘤之一,生物 学特点为局部侵袭性生长、易复发和低转移率,国人的发病率为西方国家的2~3 倍,局部侵袭性生长和术后复发比例可高达 40%~50%。但是目前尚缺乏明确反映其复发、转移等生物学行为的组织学指标。
Fascin-1 又称肌动蛋白交联蛋白,是一种编码相对分子质量为 55 000 的细胞骨架蛋白,位于细胞质张力纤维和细胞膜皱褶边缘的丝状伪足、微棘的核心肌动蛋白束中,可促使细胞膜发生结构变化,降低细胞间联系的完整性,从而促进肿瘤细胞侵袭和转移。目前研究表明,在正常上皮细胞中,Fascin-1 常表现为缺失或低表达,而在某些恶性肿瘤中常呈高表达,包括胃癌[1],食管癌[2]、卵巢癌[3]等;并且这种高表达常与一些反映肿瘤侵袭的指标及预后密切相关。
本研究探讨 fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤组织中的表达及其与临床病理、预后指标的关系,以评估其应用价值。
资料与方法
一、一般资料
65 例来自唐山市第二医院 2006 年至 2011 年经手术并经病理证实的骨巨细胞瘤患者,其中男30 例,女 35 例;平均年龄 35 (9~58 ) 岁。患者平均随访 51.5 (12.5~80.0 ) 个月。按照肿瘤直径:<5 cm 者 35 例,≥5 cm 者29 例。按照肿瘤部位:位于胫骨上段者26 例,位于股骨下段者22 例,其它部位者17 例。按照病理分级:良性者病例 36 例,侵袭性者病例27 例,恶性者2 例。按预后:正常者 47 例,复发者16 例,恶变及转移者各1 例( 表1)。所有病例均经2 名以上病理医生确认。
二、试剂
Fascin-1 鼠单克隆抗体购自 Santa Cruz 公司;二抗、三抗为通用型试剂盒。
三、免疫组织化学染色
S-P 法行 fascin-1 免疫组化研究。石蜡标本常规脱蜡水化后,PBS 漂洗,微波抗原修复,室温冷却,过氧化氢酶阻断,加入 fascin-1 单克隆抗体(1∶100 )4 ℃ 过夜,加入二抗,DAB 显色,苏木红复染,封片。以已知的 fascin-1 在乳腺癌组织表达为阳性对照[4],PBS 取代一抗为阴性对照。
四、结果判断
光学显微镜下观察组织标本的染色情况。Fascin-1 定位于细胞浆内,呈棕黄色或棕褐色颗粒。判定标准:参考文献免疫组化评分方法,评定方法如下:-,阴性或<5% 阳性细胞表达;+,5%~25% 阳性细胞表达;++,26%~50% 阳性细胞表达;+++,>50% 阳性细胞表达。-或 + 规定为阴性表达,++ 或 +++ 规定为阳性表达[5]。
五、统计分析
采用 SPSS13.0 软件进行统计学分析,以 χ2检验来评价 fascin-1 表达与临床病理指标的关系。P<0.05 差异有统计学意义。
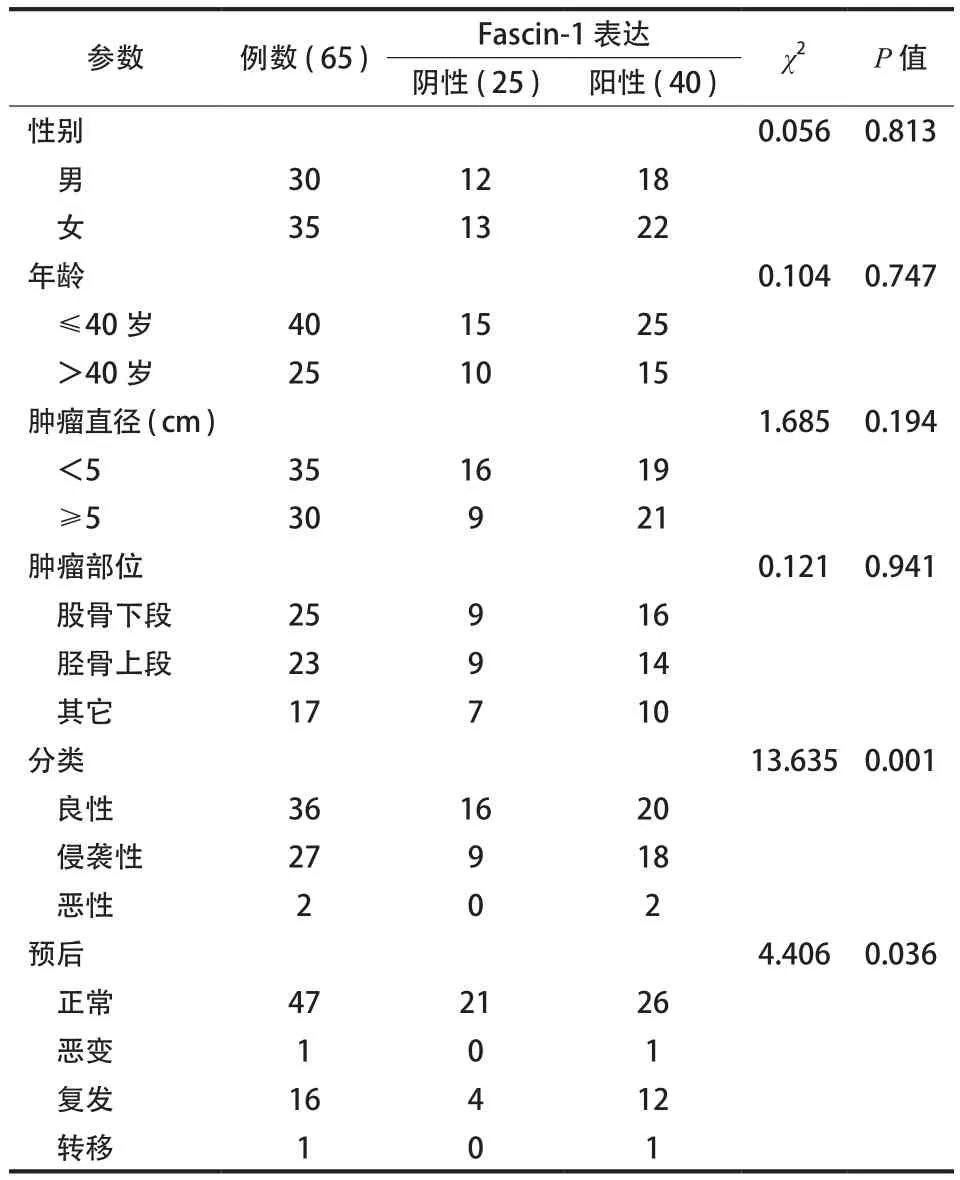
表1 Fascin-1 的表达与临床病理参数的关系Tab.1 The relationship between the expressions of fascin-1 and the clinicopathologic features
结 果
一、Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 ( 图 1a~d )
65 例骨巨细胞瘤标本中有 40 例表现为阳性表达,阳性率为 66.7%,主要表现在细胞浆中,呈棕黄色或棕褐色颗粒。
二、Fascin-1 的表达与临床病理指标的相关性
Fascin-1 表达与各种反映肿瘤预后的指标进行相关性研究结果表明,在 36 例良性骨巨细胞瘤患者中有20 例呈阳性表达,占 55.6%,而在27 例侵袭性患者中有19 例呈阳性表达,占 70.3%;2 例恶变及转移患者均呈阳性表达。47 例预后正常患者中26 例呈阳性表达,16 例复发患者中10 例呈阳性表达,2 例恶性骨肉瘤中均为阳性表达。阳性表达( 图 1c、d );阴性表达 ( 图 1a、b )。综上所述,Fascin-1 蛋白的表达与肿瘤分类及预后相关,而与性别、年龄、肿瘤部位及大小无明显相关 ( 表1)。

图1 Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 ( SP 法 ×200 ):Fascin-1 定位于细胞浆内,呈棕黄色或棕褐色颗粒,-或 + 为阴性表达,++ 或+++ 规定为阳性表达 a:在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 (-),阴性或 <5% 阳性细胞表达;b:Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 ( + ),5% ~25% 阳性细胞表达;c:Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 ( ++ ),26% ~ 50% 阳性细胞表达;d:Fascin-1 在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达 ( +++ ),> 50% 阳性细胞表达Fig.1 Immunohistochemical analysis of fascin-1 expressions in giant cell tumors of bone tissues by SP staining ( ×200 ). Fascin-1 was detected in the cytoplasm, which was light or dark brown. Negative expressions were identified by – or +. Positive expressions were identified by ++ or +++ a: Fascin-1 expressions in giant cell tumors of bone ( – ), no or <5% positive cell expressions; b: Fascin-1 expressions in giant cell tumors of bone ( + ),5%-25% positive cell expressions; c: Fascin-1 expression in giant cell tumors of bone ( ++ ),26%-50% positive cell expressions; d: Fascin-1 expressions in giant cell tumors of bone ( +++ ), >50% positive cell expressions
讨 论
肿瘤的侵袭生长是一个多因素参与、多步骤完成的过程,细胞外基质金属基质蛋白酶 ( MMPs ) 是一蛋白水解酶家族,几乎能降解细胞外基质中各种蛋白成分,能破坏正常的组织学屏障,已知实验证实其与肿瘤发生、侵袭和转移密切相关,而且其高表达与肿瘤的进展及预后密切相关。此外,细胞外基质金属基质蛋白酶诱导因子 ( EMMPIN,CD147 )广泛表达于细胞表面的跨膜糖蛋白,是一种细胞表面黏附分子,介导细胞间的黏附,其高表达有助于癌细胞的浸润、转移。肿瘤细胞表达的 CD147 可刺激肿瘤相关的间质成纤维细胞和内皮细胞产生MMPs,促进肿瘤的浸润、转移[6]。
Fascin-1 是一种运动相关蛋白,其蛋白质编码产物是一种细胞骨架蛋白,存在于细胞质张力纤维和细胞膜皱褶边缘的丝状伪足、微棘的核心肌动蛋白束中。Fascin-1 的过分表达可导致细胞间连接的完整性减少。以前的研究发现 fascin-1 的表达与多种蛋白共相关,包括 EMMPRIN、VEGF、Ezrin、Ki67 等,国内学者[7-8]的研究表明 fascin-1 的表达与金属基质蛋白酶2、9 及 TIMP-1 的表达密切相关[9],而且金属基质蛋白酶2、9 可参与到骨肉瘤的进展中[10-12]。肿瘤细胞固有运动性和侵袭力要求提高肌动蛋白细胞骨架的可塑性,这要通过调节与fascin-1 等肌动蛋白的表达来实现。有研究证明,细胞内 fascin-1 基因的上调表达会导致细胞膜突起增多,细胞间连接发生解离,细胞的运动也相应增加,现有证据表明 fascin-1 蛋白在细胞迁移、细胞黏附以及细胞间信息交流等过程中发挥作用,可以促进肿瘤的迁徙和转移[13]。也是衡量结肠癌、乳腺癌及其它肿瘤不佳预后的独立因素,而且 fascin-1与结肠癌、乳腺癌、前列腺癌的转移率密切相关[14]。上述情况可能提示 fascin-1 蛋白在肿瘤的侵袭、转移过程中扮演多种角色。有可能作为基因治疗的靶点已引起关注。
骨巨细胞瘤在生物学上具有高复发率及低转移率的特点,尽管之前有研究表明,hTERT、p63 在骨巨细胞瘤中高表达并与生存期及复发率相关。目前仍缺少能够准确预测预后的生物学指标。本研究发现 fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤组织中明显表达增高,阳性率达 66.7%,这与其它组织的研究结果基本一致。fascin-1 蛋白的表达与肿瘤分类及预后相关,而与性别、年龄、肿瘤直径及部位无明显相关,P>0.05。我们的研究结果提示 fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤的复发中有重要作用,本组2 例恶性骨巨细胞瘤患者均呈阳性表现,提示 fascin-1 蛋白可能与恶性骨巨细胞瘤的发生发展关系密切。但是,本组恶性骨巨细胞瘤病例较少,还需要进一步总结研究。
目前,关于 fascin-1 基因在肿瘤组织细胞中上调表达的分子机制尚不十分清楚。有研究提示,Fascin-1 基因的蛋白编码产物可能是 c-erbB-2 在细胞骨架上的一种效应蛋白。其在肿瘤细胞中 fascin-1基因的上调表达可能影响 wnt 或类胰岛素生长因子受体1 ( IGF-RI ) 等途径的调节[15]。已知,Rac 和Cdc42 是 fascin-1 的上游调节剂[16-17]。Jayo 等[18]通过 FRET 方法发现活化调节 fascin-1 与 actin 的相互作用,通过 Rho 酶活化这种调节是不依赖 myosin II的活化的,而且不通过 fascin-1 / PKC 复合物的促进来调节。Fascin-1 介导的食管癌细胞的侵袭也同样具有 TGF-β 细胞信号转导通路依赖性。
综上所述,Fascin-1 蛋白在骨巨细胞瘤组织中呈阳性表达,而且阳性表达组有更高的复发率及恶变率,由此推论 fascin-1 蛋白可能在骨巨细胞瘤的复发及恶变过程中发挥重要作用,并可能成为我们治疗骨巨细胞瘤的一个新的靶点。
[1]李凯, 王蓓, 封国生. Fascin、nm23和C-erbB-2蛋白在胃癌中的表达及临床意义. 中华普通外科学, 2009,3(1):14-18.
[2]Zhang H, Xu L, Xiao D, et al. Fascin-1 is a potential biomarker for early-stage oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Pathol, 2006, 59(9):958-964.
[3]Lin CK, Chao TK, Yu CP, et al. The expression of six biomarkers in the four most common ovarian cancers: correlation with clinicopathological parameters. APMIS, 2009, 117(3):162-175.
[4]Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Sarrió D, Honrado E, et al. Prognostic significance of basal-like phenotype and fascin expression in node-negative invasive breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res, 2006,12(5):1533-1539.
[5]Tsai WC, Jin JS, Chang WK, et al. Association of cortactin and fascin-1 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological parameters. J Histochem Cytochem, 2007, 55(9):955-962.
[6]逯强, 吕刚, 王岩峰, 等. CD147在骨肉瘤中的表达及其与临床病理指标的相关性实验研究. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2010,18(7):588-590.
[7]韩跃虎, 杨柳, 黄景辉, 等. CD147、PCNA、VEGF和MMPs在骨巨细胞瘤中的表达及临床意义. 中国骨与关节外科, 2012,5(1):65-71.
[8]李恩民. 细胞骨架结合蛋白Ezrin和Fascin在食管癌中的异常表达与功能及其相关细胞信号转导通路. 中国肺癌杂志, 2009,12(6):54-55.
[9]Onodera M, Zen Y, Harada K, et al. Fascin is involved in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent production of MMP9 in cholangiocarcinoma. Lab Invest, 2009, 89(11):1261-1274.
[10]Korpi JT, Hagstr☒m J, Lehtonen N, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2,-8,-13,-26, and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 in human osteosarcoma. Surg Oncol, 2011,20(1):18-22.
[11]Cho HJ, Lee TS, Park JB, et al. Disulfiram suppresses invasive ability of osteosarcoma cells via the inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression. J Biochem Mol Biol, 2007, 40(6): 1069-1076.
[12]Sun D, Wang X, Zhang H, et al. MMP9 mediates MICA shedding in human osteosarcomas. Cell Biol Int, 2011, 35(6): 569-574.
[13]Li A, Dawson JC, Forero-Vargas M, et al. The actin-bundling protein fascin stabilizes actin in invadopodia and potentiates protrusive invasion. Curr Biol, 2010,20(4):339-345.
[14]Chen L, Yang S, Jakoncic J, et al. Migrastatin analogues target fascin to block tumour metastasis. Nature, 2010, 464(7291): 1062-1066.
[15]Guvakova MA, Boettiger D, Adams JC. Induction of fascin spikes in breast cancer cells by activation of the insulinlike growth factor-I receptor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2002, 34(6):685-698.
[16]Parsons M, Adams JC. Rac regulates the interaction of fascin with protein kinase C in cell migration. J Cell Sci, 2008, 121 (Pt17):2805-2813.
[17]Adams JC, Schwartz MA. Stimulation of fascin spikes by thrombospondin-1 is mediated by the GTPases Rac and Cdc42. J Cell Biol, 2000, 150(4):807-822.
[18]Jayo A, Parsons M, Adams JC. A novel Rho-dependent pathway that drives interaction of fascin-1 with p-Lin-11/Isl-1/Mec-3 kinase (LIMK)1/2 to promote fascin-1/actin binding and filopodia stability. BMC Biol, 2012,10:72.
( 本文编辑:王永刚 )
Expressions and clinical signifcance of fascin-1 in giant cell tumors of bone
LU Qiang, WU Chun-yun, WANG Bao-cang, LIU Lan-ze, LI Yong, WANG Hui, YAN Ming. Department of Spinal Surgery, the second Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan, Hebei, 063000, PRC
ObjectiveFascin-1 is the 55 kilodalton ( kDa ) F-actin-binding cytoskeletal protein, which takes part in the formation of cellular membrane protrusions and cell migration. Fascin-1 is upregulated in several types of carcinomas. To investigate the relationship between the fascin-1 expressions in giant cell tumors of bone and the related clinical parameters.MethodsA total of 65 patients with giant cell tumors of bone were adopted by the second Hospital of Tangshan, including 30 males and 35 females. Their average age was 35 years old ( range:9-58 years ). The average follow-up period was 51.5 months ( range:12.5-80.0 months ). Immunochemistry with digital image analysis was used to determine the fascin-1 protein expressions in histologic sections from the 65 patients. The fascin-1 expressions of 65 tissue samples were detected by immunochemistry. The fascin-1 expressions with the clinicopathologic features of giant cell tumors of bone were assessed.ResultsThe fascin-1 expressions were positive in 40 of the 65 patients with giant cell tumors of bone, and the positive rate was 66.7%. Cytoplasm was the main location. A correlation study was performed between the fascin-1 expressions and various indexes refecting the tumor prognosis. The results showed positive expressions were noticed in20 of 36 patients with benign giant cell tumors of bone ( 55.6% ) and in19 out of27 patients with invasive tumors ( 70.3% ). The fascin-1 expressions were positive in2 patients with malignant and metastatic tumors. Patients with good prognosis were observed. The positive expressions were found in10 out of16 patients with recurrence, accounting for 62.5%. The data above demonstrated that the fascin-1 expressions were signifcantly correlated with the classifcation and prognosis of tumors ( P<0.05 ), but not with the gender, age, tumor location or tumor size ( P>0.05 ).ConclusionsFascin-1 is upregulated in giant cell tumors of bone, which may play an important role in their recurrence and malignant transformation. So fascin-1 could be a new target in the treatment of giant cell tumors of bone.
Giant cell tumor of bone; Bone neoplasms; Immunohistochemistry; Fascin-1 protein
10.3969/j.issn.2095-252X.2014.07.006
R738.1
河北省 2011 年医学科学重点课题资助 ( 20110623 )
063000 唐山市第二医院脊柱二科 ( 逯强,刘兰泽,吴春云 );骨病科 ( 王保仓,李勇,王辉,闫明 )
2013-05-30 )

