Psychometric Properties of Geometrical Texture Features for Tactile Roughness Sensation of Fabric Surfaces
HU Ji-yong(胡吉永) ,JIANG Rui-tao(姜瑞涛),YANG Xu-dong (杨旭东),DING Xin(丁 辛),WANG Ru-bin(王如彬)
1 Key Laboratory of Textile Science and Technology,Ministry of Education,Donghua University,Shanghai 201620,China
2 College of Textiles,Donghua University,Shanghai 201620,China
3 The Institute for Brain Information Processing and Cognitive Neurodynamics,East China University of Science and Technology,Shanghai 200237,China
Introduction
With the development of Internet and information technology,online shopping becomes the new trend and breaks the structure of retail industry.Nevertheless,online shopping confronts an immense challenge,i.e.,how to make the customers feel the products genuinely which might affect their decisions,like tactile sense[1],particularly for the textiles.The emerging haptic rendering technology is the potential solution for the lack of tactile feelings in online shopping,whereas the knowledge of haptic rendering technology for textiles is not understood,a type of thin-sheet compliant materials.In this study the psychometric characteristics of inherent physical determinants for tactile roughness sensation of fabric was focused on,so as to guide the design for haptic interaction interface of fabric surface textures.
Roughness sensation is one of the basic features constituting the space of tactile texture attributes.Researchers widely concern on the roughness sensation of hard objects with artificial patterns,such as regular gratings,sandpapers[2],and have found out the element amplitude,element size,the interelements spacing and the texture spatial period (TSP)of elements,as their physical determinants.Some scholars have conducted researches on the discrimination threshold and Weber fraction of physical stimulus affecting grating surface roughness sensation.Among the researches by directly touching the grating surface with fingers, Louw found out the discrimination threshold of authentic Gaussian distribution surface (σ:150-240 μm)was 1-8 μm,whatever raised or sunk surfaces;estimated threshold of sine grating surface (TSP:2.5-10 mm)was 0.64-4.99 μm[3-4].Nefs et al.[5]has proved that the discrimination threshold of the sine grating surface amplitude by active dynamic touch can reach 2 μm (amplitude of reference surface is 12.8 μm and TSP is 2.5 mm).The amplitude resolution of surface with TSP 2.5 - 10 mm increases proportionally to the TSP.
The researches above are all about the surfaces of hard objects,few about compliant materials such as fabrics.In order to simulate the tactile roughness sensation of fabric surface textures,the inherent physical stimulus properties for the roughness sensation and their psychometric properties should be firstly studied.We've discovered that the fabric roughness is related to the height and TSP of element in the previous studies[6-7].Moreover,considering the studies on physical determinants for pattern roughness sensation of hard objects as well as the definition of activating stimulus in the haptic rendering device,the surface topography will be firstly Fourier transformed into the spectrogram,and the peak and corresponding wave length will be selected to represent the fabric surface topography.Therefore,four texture feature indexes are selected as the physical stimulus in this study.With respect to the extracted four texture indexes for fabric roughness sensation, the main psychometric properties,i.e.,the discrimination threshold and Weber fraction are explored by the constant stimulus and the paired comparison method.
1 Experiment
1.1 Experimental materials
Thirteen pieces of commercialized clothing fabrics are selected for this experiment.The sample specifications and their texture feature as physical stimulus indexes are listed in Table 1.In Table 1,WD represents weaving density (ends ×peaks/10 cm);SMD represents standard mean deviation;MHA is the maximum harmonic amplitude;HW of MHA is harmonic wavelength of MHA;WS is weaving structure;ITPS is intertexture-patterns spacing;TPW is texture-patterns width;RSR is roughness sensation rank.
1.2 Subjects
As raters,21 students,9 male and 12 female,took part in the sensory experiment,ages between 20 and 30.All of students are right-hand dominant, and have no sensory dysfunction.

Table 1 Fabric specifications and their texture features
1.3 Experimental methods
Before sensory experiments, all of raters read the experimental instructions.Firstly,each of raters will rank the 13 pieces of fabric samples with respect to the stimulus SMD,MHA,HW,and TSP,respectively,in the ascending order.And then the paired experiments are performed,each of raters takes one of the fabrics as the reference fabric and compares it with the others about the roughness sensation.The larger the ranking of the stimulus is,the strong the perceived roughness is.If the subject judges the same as the ranking regarding the degree of roughness by each of four indexes,it's considered correct judgment and recorded as“1”,otherwise,as“0”.The discrimination threshold and Weber fractions with respect to each of 4 texture feature indexes can be calculated by the experimental recordings in the paired comparison experiments.
1.4 Experimental procedures
Put the randomly selected 13 pieces of fabrics into the constant temperature &humidity laboratory for over 48 h.In the first sessions,the rater ranks the 13 pieces by the stimulus SMD in the ascending order.Take No.7 fabric as the reference and compare it with the others one by one.The judgment results will be recorded.Make sure all the fabrics have been compared with No.7 reference fabric.
1.5 Statistical analysis
To calculate the psychometric characteristics, the incremental value of all of physical stimulus is used.For example,the incremental value of SMD is the difference of the compared fabric and the assigned reference one in each session.Because any two fabrics in the experiments above have been compared,we can judge if the comparison results obtained after the change of stimulus are correct or not,based on the results ranking SMD.By fitting the incremental difference to the correct judgment proportion of perceived roughness, the psychometric curve for each of 4 texture features can be obtained.Psychophysical functions were fitted with a cumulative Gaussian function using “psignifit ” software described in Refs.[8 -9].

where the parameter σ is a measure of the 75%discrimination threshold,which is the sensitivity of the subjects to perceive softness differences between two objects;and the parameter μ is a measure of the point of subjective equality,indicating the softness of the test stimulus that is perceived as being equivalent to the reference stimulus.From the psychometric functions we determined the discrimination threshold as the difference in test stimulus between the correct proportion of 0.25 and 0.75.
To observe whether psychometric characteristics vary with the reference samples,two kinds of psychometric curve are fitted.The first kind is that the influence of reference fabric is not considered.Therefore, the each incremental stimulus difference between all of paired samples and the corresponding correct proportion of judgment about the perceived roughness are considered.The second kind is that data points are divided into 7 sets according to 7 reference fabrics and for the same reference fabric,each set is fitted.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Psychometric curves without reference effect
The fitted psychometric curves are plotted in Fig.1,and this chart doesn't consider the effect of reference fabric on roughness judgment.The diagrams in Fig.1 show that the curves are all in the shape of“S”.The scattered points in the Boltzmann fitted curve were adopted to calculate the 75%discrimination threshold of each stimulus.Heller[10]took the sandpaper as the experimental object to study the roughness sensation and found that the subject could discriminate the surface of 2-3 μm the diameter of sand grits.Nefs et al.[5]found that the discrimination threshold of amplitude could reach 2 μm.In this study,the 75% discrimination threshold of SMD stimulus is 0.86 μm,which is smaller than that of hard material.This is because the scholars who study the surface roughness of hard material have selected materials with larger amplitude than that of the materials used in this study.
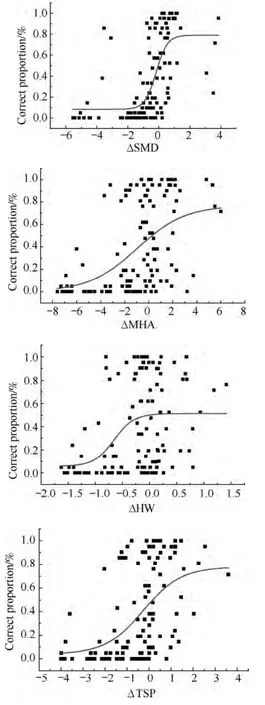
Fig.1 Psychometric curves for different stimulus increments
Morley et al.[11]found that regarding fence with 770 -1 002 μm slot width,Weber fraction was 5% and discrimination threshold was 38.5 -50.1 μm.Nefs et al.[5]found that regarding surface with 2.5 mm spatial period,Weber fraction was 6.4% and discrimination threshold was 0.16 mm.In this paper,when taking TSP as the stimulus,its 75% discrimination threshold is 2.48 mm,larger than that of the hard materials.As the stimulus selected in this study is not single factor variance,there are interactions between the stimuli,which leads to the results above.In addition to this,because fabrics used in this study have many other surface characteristics including thickness of thread,twist,and feather,it's not as sensitive as the hard material surface.Thus the roughness threshold of fabric is larger than that of the hard materials relative to most of clothing fabrics.
As to the other two stimulus of single harmonic component,including the peak and corresponding wave length,the judgment correct proportion is less than 75%.And with the increasing stimulus difference,the correct proportion tends to stay constant.This means that the 75% discrimination threshold of the harmonic wave peak and corresponding wave length cannot be obtained in this experiment.It is hypothesized that the reference stimulus intensity has an effect on the psychometric properties.
2.2 Psychometric features with reference effect
Take Nos.2,5,6,9,11,12,and 13 as the reference fabrics respectively and compare them with the others about the roughness sensation.From the fitted psychometric curves,the derived 75% discrimination thresholds are illustrated in Fig.2,and the abscissa is the fabric sample No.referred to Table 1.

Fig.2 Differential thresholds (75%)of texture features with roughness sensation
From Fig.2 we can see that 75% MHA discrimination threshold is zero in the case of using No.2 as reference fabric;and 75% HW is also zero in the case of using No.6 and No.9 as reference fabrics.This shows that,to some extent,the two stimuli cannot describe the fabric roughness sensation correctly based on the macro geometrical texture features of fabric.These results also indicate that the reference stimulus intensity has a significant effect on the tactile discrimination capability of surface roughness of fabrics.
Weber fraction can be calculated by the discrimination threshold and stimulus value.In Fig.3,with the increasing SMD,MHA,HW,and TSP,the Weber fraction of each stimulus tends to decrease (the abscissa is the reference stimulus intensity).Researches about the surfaces of hard objects also show that Weber fraction changes while the texture height increases.With the increasing TSP,Weber fraction decreases from 11.8% to 6.4%[5].However,in this study on fabrics,Weber fraction scatters widely,and some even reaching 3.70.When taking TSP as the stimulus,the Weber fraction of No.13 fabric is largely different from that of the hard surface.There's one common point of the four diagrams,i.e.,Weber fraction is very high when using Nos.12 and 13 as the reference fabrics.Reasons might be as follows.
(1)When taking one piece of fabric as the reference,data amount is small and it's difficult to fit the psychological physical curve accurately,resulting in the abnormal discrimination threshold and Weber fraction.
(2)Because the stimulus of Nos.12 and 13 is small and 75% discrimination threshold is large,Weber fraction is relatively large.Although the two fabrics have low ranking of medium height,they feel granular strongly and make the subjects think they are rough.For this kind of fabric,according to the known physiological mechanism of human sensing texture roughness,when the TSP of hard material surface is less than 200 μm,the roughness sensation is determined by the vibration sensed by the PC receptor.High frequency can stimulate PC receptor to release action potential within certain range and sense the roughness[12-14].

Fig.3 Weber fraction for different texture feature indexes
For Nos.9,12,and 13 fabrics,stimulus generating the roughness sensation might not be 4 adopted in this study.
Apart from the previous regular surface patterns of hard objects[1],apparently,fabric has complex surface texture features.When human touch fabric surfaces,many texture features harmonically deform to generate different mechanical stimulus and evoke the difference of perceived roughness sensation.Although some previous experimental results showed the alone determinant of surface grating amplitude or width in judging their roughness sensation,the judgment of fabric roughness sensation depend on the complex stimulus from the basic texture features.
3 Conclusions
Inspired by the previous study on the roughness sensation of surface patterns of hard objects,4 geometrical texture features were investigated and their psychometric properties were explored.The differential thresholds of fabric surface roughness and the TSP are different from those on patterns of hard materials,and they are affected by the reference stimulus intensity.And also, our results showed that any single roughness index could not represent the fabric roughness sensation.These results indicate that the delicate tactile roughness sensation of textiles can't be simulated by one dimensional activation stimulus,and their haptic rendering needs deep understanding of the interaction of complex surface geometrical and material properties.
[1]Hollins M,Bensmaia S J.The Coding of Roughness [J].Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology,2007,61(3):184-195.
[2]Picard D, Dacremont C, Valentin D, et al.Perceptual Dimensions of Tactile Textures[J].Acta Psychologica,2003,114(2):165-184.
[3]Kantowitz B H,Roediger III H L,Elmes D G.Experimental Psychology [M].Monterey:Wadsworth Publishing Company,2008:167-198.
[4]Louw S,Kappers A M L,Koenderink J J.Haptic Detection Thresholds of Gaussian Profiles over the Whole Range of Spatial Scales[J].Experimental Brain Research,2000,132(3):369-374.
[5]Nefs H T,Kappers A M L,Koenderink J J.Amplitude and Spatial-Period Discrimination in Sinusoidal Gratings by Dynamic Touch[J].Perception,2001,30(10):1263-1274.
[6]Hu Y J,Hu J Y,Zhao Q,et al.Relationship between Tactual Roughness Judgment and Surface Morphology of Fabric by Fingertip Touching Method[J].Fibers and Polymers,2013,14(6):1024-1031.
[7]Pan D,Hu J Y,Ding X,et al.Fabric Roughness Based on Spectrum Analysis[J].Journal of Donghua University:Natural Science Edition,2012,38(1):6-11.(in Chinese)
[8]Leek M R.Adaptive Procedures in Psychophysical Research[J].Perception &Psychophysics,2001,63(8):1279-1292.
[9]Fründ I,Haenel N V,Wichmann F A.Inference for Psychometric Functions in the Presence of Nonstationary Behavior[J].Journal of Vision,2011,11(6):1-19.
[10]Heller M A.Visual and Tactual Texture Perception:Intersensory Cooperation[J].Perception & Psychophysics,1982,31(4):339-344.
[11]Morley J W, Goodwin A W, Darian-Smith I.Tactile Discrimination of Gratings [J].Experimental Brain Research,1983,49(2):291-299.
[12]Bueno M A, Lamy B, Renner M, et al.Tribological Investigation of Textile Fabrics[J].Wear,1996,195(1/2):192-200.
[13]Bolanowski S J Jr,Gescheider G A,Verrillo R T,et al.Four Channels Mediate the Mechanical Aspects of Touch [J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,1988,84(5):1680-1694.
[14]Hollins M,Risner S R.Evidence for the Duplex Theory of Tactile Texture Perception[J].Perception &Psychophysics,2000,62(4):695-705.
 Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2013年5期
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)2013年5期
- Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Electrospun Small Diameter Tubes to Mimic Mechanical Properties of Native Blood Vessels Using Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone)and Silk Fibroin:a Preliminary Study
- Properties of Scaffold Reinforcement for Tendon Tissue Engineering in vitro Degradation
- Mineralized Composite Nanofibrous Mats for Bone Tissue Engineering
- Promoted Cytocompatibility of Silk Fibroin Fiber Vascular Graft through Chemical Grafting with Bioactive Molecules
- Fatigue Performance of Fabrics of Stent-Grafts Supported with Z-Stents vs.Ringed Stents
- Effect of Media on the in vitro Degradation of Biodegradable Ureteral Stent
