Current Cloud Computing Security Concerns from Consumer Perspective
Hafiz Gulfam Ahmad, Zeeshan Ahmad
1.Department of Computer Science, Agriculture University, Faisalabad, Pakistan;2.Bahria University, Islamabad, Pakistan
CurrentCloudComputingSecurityConcernsfromConsumerPerspective
Hafiz Gulfam Ahmad1*, Zeeshan Ahmad2
1.DepartmentofComputerScience,AgricultureUniversity,Faisalabad,Pakistan;2.BahriaUniversity,Islamabad,Pakistan
In recent years cloud computing is the subject of extensive research in the emerging field of information technology and has become a promising business. The reason behind this widespread interest is its abilityto increase the capacity and capability of enterprises, having no investment for new infrastructure, no software license requirement and no need of any training. Security concern is the main limitation factor in the growth of this new born technology.The security responsibilities of both, the provider and the consumer greatly differ between cloud service models.In this paper we discuss a variety of security risks, authentication issues, trust, and legal regularity in cloud environment with consumer perspective.Early research focused only on technical and business consequences of cloud computing and ignored consumer perspective. Therefore, this paper discusses the consumer security and privacy preferences.
cloud computing, security issues, legal regularity
1. Introduction
Cloud services are based on these essential characteristics[1]. a)on demand self-service, b) resource access over the network, c) resource pooling where dynamically reassign the resources, d)resource elasticity and e) characteristic is service measured where resource usage time will be measured.Many SMEs join the cloud computing environment that provide the platform, infrastructure and application as services[2]. Cloud computing is becoming one of the fast growing technology in computing era, that build on the internet and virtualizationtechnologies, infrastructure, platform and software as services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS)[3]. In cloud computing there present three prime layers.
a) System layer which consist ofvirtualized hosts and networks, normally the services deliver are referred as infrastructure as service(IaaS).
b) The platform layer contains virtualized operating system and APIs as platform as service (PaaS)
c) The application layer provide the virtual applications as software as service (SaaS)[4].
In distributed environment, cloud computing is a suitable place for the cyber-attack in any organization[5]. The pioneer of cloud computing vendors, Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) are both well-known examples. While these internet-based online services provide huge amounts of storage space and customizable computing resources. This computing platform eliminates the responsibility of local machines for data maintenance at the same time. As a result, users are at the mercy of their cloud service providers for the availability and integrity of their data. Recent downtime of Amazon’s S3 is an example. In spite of all these hype the enterprise consumer are still reluctant to deploy there business in the cloud, because of security issues such as data privacy and data protection[6]. Cloud computing is agonized from various types of attacks such as, Address Resolution Protocol spoofing, IP spoofing, routing Information Protocol attack, DNS poisoning, Flooding, Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), etc. e.g. DoS attack on the underlying Amazon Cloud infrastructure caused BitBucket.org, a site hosted on AWS to remain unavailable for few hours. Computing Intrusion Detection System (GCCIDS)[7], which is designed to cover the attacks that network and host-based systems cannot detect. Their proposed method used the integration of knowledge and behavior analysis to detect specific intrusions. The paper is focus on the matters related to the security issues of consumer such as provider license and services to consumer on demand. The researcher has tended to focus on virtualization rather than security in cloud computing environment, many issues still prevail.
The paper is structured as follows. Section 2 describes the common security issues in current year that are postured by the cloud providers; section 3 describes the solution for these security challenges; section 4 consists of the conclusion derived out of this discussion.
2.Cloud computing top threats in 2013
There are numerous security threats for cloud computing. New technologies and services, networks, databases, operating system, virtualization, transaction management, and concurrency control are use in cloud computing infrastructure which has not been fully evaluated with respect to security issues. In everyday life especially in computing security is the one of the most important aspects due to sensitivity and data storage in cloud[7]. Management of the data is not fully trustworthy and malicious in loud,denial ofservice compel organization to focus strong attention on these issues[8].The recent top security issues in cloud computing areas follows.
2.1.Trust
One of the major concerns about cloud computing today is the trust between the service provider and the user (customer). In SaaS the client has to depend on the service providerfor security measures, but unfortunately there is no such method that can ensure the user that whether the service provider is trustworthy or not and also it’s difficult to get guarantee that the service will be available whenever the user wants[9]. Hwang et al. proposed a cloud architecture that uses avirtual private network and a secure socket layer, and the model focuses on trust management in provider’s and consumer’s perspective[6]. The only legal agreement between the user and the service provider is that the service level agreement for service quality, priorities, and the responsibilities. This legal document contains all the rules and regulations between both of them, which contains the information that what the service provider is providing and what he is willing to provide[10]. Traditionally SLA have been a contract between a cloud service customer (an enterprise, business, or government agency), and service provider. The expanding value chain, for other services, has made SLAs important for a myriad to have complex relationships between partnerships. Currently there is no clear format for the SLA. However there may be services not documented in the SLAwhich the customer may be unaware off and it may need these services at some later time. In Tab.1, a comparison of the cloud providers in context of the different characteristics from the ACM computing Surveys 2013 is shown.
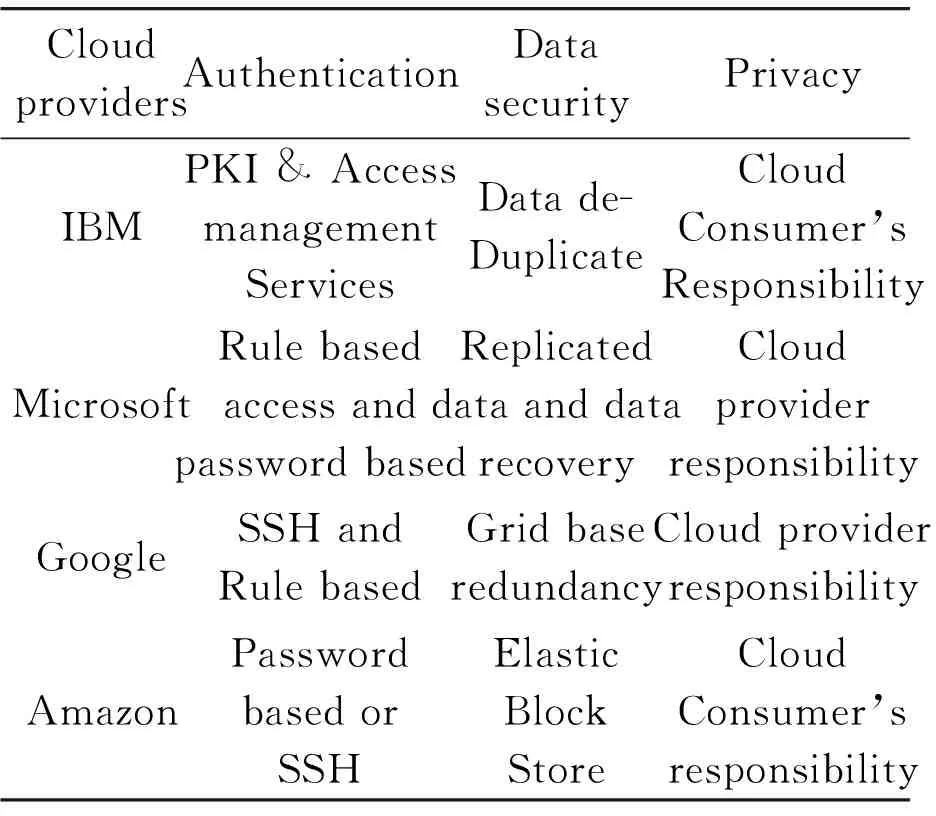
Tab.1 Comparison: cloud service provider in contextof different service trust characteristics
2.2.Confidentiality
Another significant issue in cloud is confidentiality, in which the sensitive data is obtained from the organization or customer and is processed by SaaS application and then stored at the service provider storage data houses. In this whole process, staff of the cloud service provider has an easy access to data so even though encrypted, such data could easily be accessed and tampered. Data confidentiality could be breached unintentionally, due to data remanence. Data remanence is the residual representation of data that have been deleted. In cloud the logical drives are virtually separated and on a single infrastructure there is same hardware shared between multiple users, so there can be some possibility of unwilling disclosure of data. Protection of user account from unauthorized access is needed. The solution can be the use of electronic authentication[11]. Software confidentiality is also important as data confidentiality for overall cloud system security. Software confidentiality enlightens the trust that specific applications or processes will sustain and handle the user’s personal data in a secure way. In a cloud environment the user is required to delegate “trust” to applications provided by the service provider, owning the infrastructure. Software applications interacting with the user’s data must be certified not to introduce additional confidentiality and privacy risks. Unauthorized access can become possible through the exploitation of application vulnerability, cause the issues of data confidentiality. In addition, it is the responsibility of the cloud provider providing secure cloud instances, which should ensure users confidentiality and privacy.
3.Legal regulatory
Currently the legal regulatory landscape for the cloud computing is not static.Cloud computing should be developed in complexlegal and regulatory environments. There are federal, international and even state laws that impose responsibilities to both cloud computing tenants and the providers. Regardless of which side your business is on, you have to consider the legal issues, especially those related to the data you collect, store and process. Laws or regulations typically specify who within an enterprise should be held responsible and accountable for data accuracy and security. New laws have been proposed for both customers and providers of cloud computing, that effect positively in regard of their responsibilities. These phenomena create new challenge that how these laws will be implemented to a wide range of information management. When we discuss the Laws and regulations governing the cloud computing environment, we cannot ignore the latest cyber security bills proposed recently in 2012[12]. There have been many cyber bills proposed, but none was as important as the cyber security act of 2012.Cyber security is a top administration priority for Obama’s second term. His approach to IT security will influence the U.S cloud computing environment over the next four years. This year, in July, senators Joseph Lieberman and Susan Collins proposed the cyber security act of 2012 . The act would have requiredcompanies to voluntary create best practices for the protection of key infrastructures from cyber-attacks.Data breach or intrusion risks are seen to be higher for any company that stores personal information or that operates in the cloud.Glen et al, in their white paper[13], create some practical challenges to understand implementation of laws, regardless of any condition which the cloud computing model is using. In any case of data protection failure, cloud provider may be fine by thecloud tenant, if the cloud customer and provider work in America, Canada or some European country.
3.1.Contractualissues
These are some of the core issues which one must consider at all stages of the contractual process:
Initial due diligence
Contract negotiation
Implementation
Termination(end of term or abnormal)
Supplier transfer
1) Different sector specific laws for cloud computing tenants and providers
To ensure we are in legal compliance, we may want to know more about American laws. In the United States, privacy and security are spread over different industry specific laws and regulations:
2) Health insurance portability and accountability act (HIPAA)
Under HIPAA’s Privacy Rule, an entity may not use or disclose protected health information unless as permitted or required by the rule, or as authorized in writing by the individual affected. HIPAA’s Security Rule complements the Privacy Rule and deals specifically with Electronic Protected Health Information (EPHI).
3) The gramm-leach-bliley act (GLBA)
It has 2 key rules for “financial institutions” for storing data in the cloud: the financial privacy ruleand the safeguards rule. The financial privacy rule requires institutions to notify each customer at the time the relationship is established and annually thereafter about the personal information about them like how it is collected, where that information is kept, with whom is shared, how is used, and how it is protected. The safeguards rule requires financial institutions to develop a written information security plan that describes how the company plans to protect clients’ nonpublic personal information.
4) Family educational rights and privacy Act (FERPA)
FERPA is a federal law that protects student information collected by educational institutions and associated vendors. These institutions must have the student’s consent prior to disclosure of personal data including grades, enrolment status, or billing information. Protection of student information according to FERPA regulations is a key consideration in using cloud-based applications that handle student records. IT administrators must be aware of the information that is passed to a cloud network or application.US-based cloud tenants and providers must consult a plethora of industry-specific laws to determine their legal risks and obligations. But if you don’t adequately protect the information you store, there are some important consequences, like fines or lawsuits which can have devastating consequences for small or midsize businesses.
4.Encryption
The current generation of cloud computing infrastructures does not provide any security against untrusted cloud operators making it unsuitable for storing sensitive information such as medical records, financial records or high impact business data. To address these security holes Microsoft researchers are pursuing various research projects that ranges from theory to practice.
1) Holomorphic cryptography
The most common use of encryption is to provide confidentiality by hiding the plaintext. However, left data useless in the sense that one loses the ability to operate on it. To address this need to design cryptosystems that support a variety of computations on encrypted data covers from general-purpose computationsto special-purpose computations. Research on holomorphic cryptography includes work on fully-holomorphic encryption (FHE), somewhat holomorphic encryption (SHE), searchable encryption, structured encryption, functional encryption and garbled circuits[14].
2) Proofs of storage
Using a proof of storage (also known as a proof of data possession or a proof of retrieveability) a client can verify whether the cloud operator has tempered his data or not. In particular, this can be done without the client, by storing a local copy of the data and without it retrieving any of the data. In fact, the work for the client is negligible no matter how large the data is.
Fig.1 Encryption in cloud
5.Data breaches
When a cloud customer puts its sensitive data into the cloud it is completely reliant on the security and incident response processes of the cloud service provider in order to respond to a data breach. This situation poses many fundamental problems. When an organization handling its own data suffers a breach, it is clear that the organization will be investigating and managing the incident with its own interests as a priority. It has control of its systems and also the data residing therein and can make decisions that protect its own interests from a business and liability perspective.
6.Account and IP Hijacking
There are some standard hacker tricks that cause major headaches for cloud computing companies. One of those is called key logging. Individual user identification and authentication for both Cloud Server Provider and client personnel is essential for access control and accountability.Shared credentials such as user accounts and passwords should not be used in the CSP environment for system administration and maintenance nor should generic or shared accounts be assigned to or used by clients. In cloud service. Compromise of the client’s user-level account in the second environment could therefore result in the attacker hake the account by gaining administrator-level access to the first environment. Client accounts and passwords should be unique for each service, and any account with elevated privilege should be restricted for a specific service or function, and not used for activities or access that do not require such privilege. The other major threat to cloud computing is IP prefix hijacking because of the Defacto protocol of internet domain routing on internet. Many examples for this vulnerability of BGP such as AS27506 prefix hijacking in January 2006 and the famous website YouTube Hijack event in February 2008[13]. Many popular network services unavailable and redirect to other destination.IP prefix hijacking is a serious threat for internet users that can damage the cloud service provider platform[15].
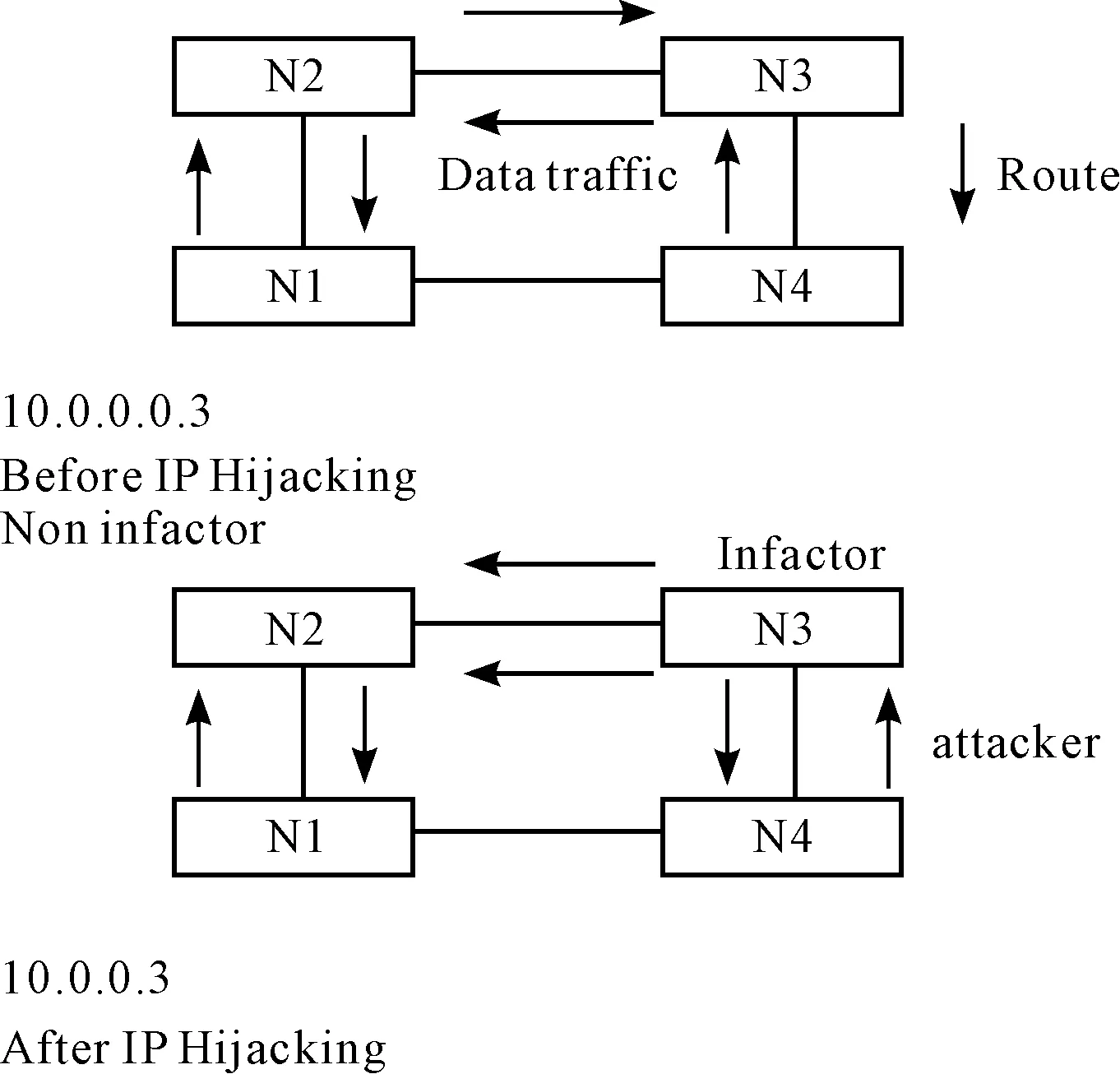
Fig.2 IP Prefix Hijacking
7.Conclusions
There are many advantages of cloud computing but yet many problems needed to addressed and solved. In this paper we have explored the security issues which createhurdles for a lot of potentialconsumers to adopt cloud. The companies offering cloud computing services should have reliable security measures at macro and micro level. Otherwise, they would lose all theirconsumers. It’s in their interest to employ the most advanced techniques to protect their clients’ data. This discussion caters imperative issues,risingin all directions in cloud. There is a demandingneed of designing an integrated solution and then deployed in a cloud to attract the potential users.
[1] Noor T H, Sheng Q Z, Zeadally S. Trust Management of Services in Cloud Environments: Obstacles and Solutions[J].ACM Computing Surveys, 2013.
[2] Subashini S, Kavitha V.A Survey on Security Issues in Service Delivery Models of Cloud Computing[J].Journal of Network and Computer Applications,34(1):1-11.
[3] Gul I, Hussain M.Distributed Cloud Intrusion Detection Model[J]. International Journal of Advanced Science and Technology,2011,34:71-82.
[4] Marston S L, Zhi S,Bandyopadhyay A G.Cloud Computing-The Business Perspective[C]//In 44th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 2011:1-11.
[5] Hwang K,Li D. Trusted Cloud Computing with Secure Resources and Data Coloring[J].IEEEInternet Computing.2010(5):14-22.
[6] Subashini S, Kavitha V.A servey on security issues in service delivery models of cloud computing[J].Journelof Network and Computer Applications,2011(34).
[7] AlZain M, Soh B, Pardede E. A New Approach Using Redundancy Technique to Improve Security in Cloud Computing[J].IEEE,2012.
[8] Bracci F, Corradi A, Foschini L.Database Security Management for Healthcare SaaS in the Amazon AWS cloud[J]. IEEE.2012.
[9] Choudhary V. Software as a service: Implications for investment in softwaredevelopment[J]. International conference on system sciences, 2007.
[10] Weis J, Alves-Foss J.Securing Database as a Service[M]. IEEE Security and Privacy,2011: 49-55.
[11] Dimitrios Z. Addressing cloud computing security issues[J]. Elsevier,2011,28(3).
[12] “The Cyber security act 2013”,http://www.wired.com/images_blogs/threatlevel/2012/02/CYBER-The-Cybersecurity-Act-of-2012-final.pdf data fetch(May 13,2013).
[13] Brunette G. Rich Mogull of Cloud Security Alliance, Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing[M].Cloud Security Alliance December,2009.
[14] Kamara S, Wei L. Garbled Circuits via Structured Encryption, in Workshopon Applied Homomorphic Encryption (WAHC’13), April 2013.
[15] LIU Yujing.Study on IP Prefix Hijacking in Cloud Computing Networks Based on Attack Planning. 2011 International Joint Conference.
2013-09-15
*Hafiz Gulfam, PhD. E-mail:gulfambise@yahoo.com
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.24.001
- 机床与液压的其它文章
- Simulation of Hydraulic Servo System for High-Speed Injection Molding Machine by AMESim
- Research on Pneumatically Actuated 6-DOF Parallel Robot Based on SimMechanics
- Mechanical Amplifier for Giant Magnetostrictive Materials and Piezoelectric Materials
- 基于FANUC-0iTD的刀尖圆弧半径补偿应用研究
- 基于无线的数控机床联网
- 涡流技术在应力检测中的应用

