HPLC-MS/MS法检测鸡肉食品中金刚烷胺残留
孙海新,曹立民,林 洪,孙伟红,吕 芳
(中国海洋大学食品科学与工程学院,山东青岛266003)
Influenza A viruses may cause epidemic or even pandemics of severe and fatal acute respiratory diseases in humans and are responsible for enzootic outbreaks in other animal,including pigs and chicken for example[1-3]. As far as many researchers know,there are only two classes of anti-influenza virus drugs. The first classes was the ion channel blockers,including amantadine and rimantadine,which was widely believed as the most effective antiviral drugs against influenza A virus,the other was neuraminidase,including ostaweil and zanamivail,which was believed effective against influenza B virus[4-8]. However,with the widely use against human virus disease and as the treatment or prevent in animal husbandry. The high frequency of resistance to the amantadine has been detected[9-12].Such problem has effected the human optional drugs validity against influenza virus and significantly enhance the possibility of cross infection between animal and human. As the above reason,most countries or world organization of the world,including China,has banned the use of amantadine and rimantadine in animal husbandry[13-14]. On the other hand,many studies has showed the long-term touch with amantadine may produce neurotoxicity, including heteroptics,neurological disorder for example[15]. However,as the lack of anti-virus drugs for substitution,there were still many farmers take amantadine as the preferred drug for the prevention and treatment of virus disease.Although peoples had known amantadine existed in bodies as original shape[16]and also some researcher had reported the detection method of amantadine residue in chicken[17],little researcher had clearly indicated what the residue degree of amantadine was after amantadine been banned in animal husbandry and as a result,the authority could not decide if it was necessary to issued more strict regulation to supervise the procedure of animal. For the above reason,it is necessary to investigate the residue of amantadine in animal product in order to give more information for the decision-maker. Due to these reason,the present study was designed to investigate the residue of amantadine in chicken’s product.
1 Material and methods
1.1 Material and Instruments
Quantum Access Tandom mass spectrometer equipped with Accela HPLC instrument Thermo,US.SIGMA3K15 ultracentrifuge SIGMA,US. SCIENTZ-ⅡD Ultrasonic instrument Scientz,P. R. China.CAV214 electronic balance Ohaus,US. Milin -Q Advantage A10 Water Purification System Milipore,US. 0.45μm and 0.22μm Membrane filter Millipore,US.
Amantadine standards(CAS:665-66-7) were purchased from Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co.,Ltd(Solarbio,China). HPLC-grade solvents including trichloroacetic acid,methanol,ammonium acetate and formic acid were purchased from Tedia Co.,Ltd(TEDIA,US). Sample treatment solutions were mixed with methanol and 1% acetocaustin with the volume ratio 1∶1,then been filtered with 0.45μm and 0.22μm membrane filter.Standard amantadine solutions,at different concentrations(0.5,1.5625,3.125,6.25L,12.5,25,50,100,200ng/mL),were prepared freshly by dilution using the sample treatment solvents followed by been filtered with 0.45μm and 0.22μm membrane filter. The water been used in this whole study was purified using a Mili -Q Advantage A10 Water Purification System.
1.2 Sample collection
Chicken(45 days-old)were purchased,during January to February in 2012,from five farms(30000~60000 chicken in total at every farm)located in east of China. The chicken were killed and totally 103 chicken product samples,including 21 chicken livers,30 chicken wing,30 chicken drumstick and 22 chicken breast,were detected in this study. All these sample were stored under a 4℃ environment before the treatment and were treated within 2 days in order to avoid corruption.
1.3 The pretreatment procedure of chicken product sample
All the samples were respectively eliminate the bone and been minced according to Yun[17]had reported and some sample treatment detail were amended in our study. 2g of each sample were weighed and took into polypropylene tubes(total volume was 50mL). 10mL sample treatment solutions was added into the tubes. The sample tubes was shaken 60s followed by ultrasonication in a ultrasonic instrument for more than 30min(10 seconds for each time followed by an interval of 10 seconds,120 circles). The sample after ultrasonication was centrifuged for 30min at 10000r/min. The supernatant was then decant into another polypropylene tubes(50mL) and determined the final volume as 10mL. Then the supernatants were filtered through 0.45μm syringe filters and successively filtered through 0.22μm syringe filters. Then the filtered solution were stored under 4℃environment for HPLC-MS/MS analysis.
1.4 HPLC-MS/MS conditions
The further isolation of sample solutions were performed using a HPLC-MS/MS with following conditions refer to Torsten Amdt and Yun Huan[17-18].Such instruments was worked according to the following conditions:positive ion mode,C18column of 50mm×2.1mm,(Thermo Hypersil Gold,1.9μm),column temperature of 30℃,sample room temperature of 4℃,sample volume of 10μL. Mobile phase A:0.005mol/L ammonium acetate solution with 0.1% formic acid;mobile phase B:methanol;speed:0.3mL/min;grad elution procedure:eluted with 90% mobile phase A and 10%mobile phase B for 1min,then eluted with 20% A and 80% B for 3 min,and finally eluted with 90% A and 10% B.
The sample flow out from the HPLC column was transferred to mass instrument equipped with an ESI source. The sample solution was performed in the positive ion mode. The electrospray voltage was 4.5kV.The capillary temperature was 300℃. Shealth gas and Aus Gas pressure was 0.28MPa and 10MPa,respectively.The collision energy was showed as Table 1.
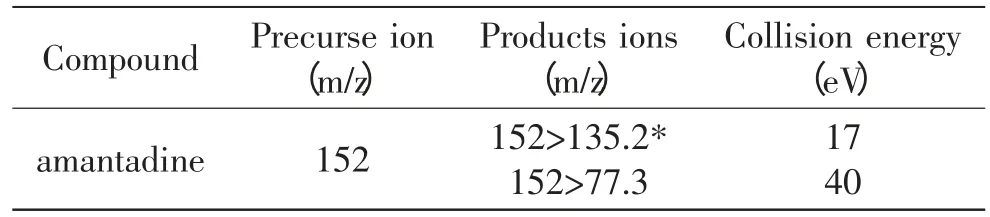
Table 1 MS condition for the amantadine in positive mode
1.5 The determination of LOQ and linear range of method
In this study,the standard solutions prepared as 1.1 had mentioned was firstly monitored with HPLCMS/MS. Then the standard linear equation was build according to the peak area of the monitored product ion as the Y-axis and the standard concentration as the X-axis. The linear range and limit of quantitation(LOQ)values were calculated from the equation and standard curve.
1.6 Analysis of chicken product sample
To investigate the residue of the amantadine in the chicken product been treated. Four groups of sample(chicken livers,wings,drumstick and breasts)were monitored as standard solutions,respectively. Then concentrations of amantadine in the samples were calculated based on standard linear equation.
2 Results and analysis
2.1 The linear range and LOQ of the detection system
The ion chromatographys of amantadine in standard and sample solution were showed as Fig.1,Fig.2. The linear curve of amantadine was build according to the above method. Linear equation was Y=0.4717X+2.4538 with correlation coefficients of 0.995. The linear equation and correlation coefficients was reached the level Yun had mentioned[17]. Then the maximum and minimum concentrations of standard sample were 0.5ng/mL and 200ng/mL,respectively. The quantity detection range was determined from 0.5 to 200ng/mL and the minimum linear detection limit was determined as 0.5ng/mL. Considering the pretreatment procedure of chicken sample showed in 1.3 the LOQ was calculated as 2.5μg/kg.

Fig.1 The ion chromatography of amantadine in standard solution
Fig.2 The ion chromatography of amantadine in chicken wing sample solution
2.2 The amantadine residue in different chicken product
There were totally 103 samples were analyzed during this study,including 21 chicken livers,30 chicken wing,30 chicken drumstick and 22 chicken breast. The results of amantadine residue in these samples were showed in Table 2. The result from Table 2 showed for approximately 18.4% of the total samples could be detected. Among the 21 liver samples,4.8%(1/21) samples were detected positive with the concentration of 5.5μg/kg. Both the chicken wings and drumsticks were detected positive with occurrence of 36.7%(11/30)and 23.3%(7/30)respectively. The concentrations of amantadine in chicken wings were varied from 32.6μg/kg to 92.4μg/kg and in drumsticks the concentration were varied from 11.4μg/kg to 25.3μg/kg. However,there were no positive sample were detected in chicken breast,which indicated chicken breast was not the preferred part in chicken body that be suit to residue. The above result also indicated,among the three kinds of organs with amantadine positive,chicken wing had the highest residue of amantadine compared with chicken drumsticks and chicken livers.
As one detoxification organs,in many consumers’traditional opinion,liver was one of most possible organs,which confers many antibiotic or drugs residue.From this result,it was also very clear to find that liver was not the organs which has the highest residue of amantadine residue. The amantadine residue was highest in chicken wing followed by chicken drumsticks,livers and breasts.
And the most important information we could got from these result was,although amantadine had been banned in animal breeding,there were still illegal use in animal breeding field.
3 Discussion and conclusion
In China,there was little research about the residue of amantadine in chicken or pigs. Although many countries had banned the use of amantadine in animal husbandry,they have not issued standard detection method beside few research article about the detection method of amantadine residue in chicken,human serum[17,19-20]. As a result,there was no standard detection method,which had been adopted in this study. So we mainly adopt the detection method of amantadine residue in chicken or serum,which had been published openly. As some researcher hadreported[8],the chicken sample pre-treatment was totally need more than 3 hours including mechanical disruption, ultrasonic disruption for 30mins,centrifugation with speed of 8000r/min for 10mins and solid phase extraction. However,the above procedure was not suitable for many labs because the solid phase extraction consume much time,consuming labor and solid phase extraction column as well. The most disadvantages of above procedure were it was not suitable for the large quantities of samples detection.So we amended the sample pre-treatment procedure base our lab condition based on such analysis that amantadine was one kind of chemical material with perfect water-solubility and exist with origin structure in vivo. So the water-solubility extraction solution was better than fat-soluble extraction solution in order to avoid the disturb of fattiness in chicken bodies. The ultrasonic treatment was prolonged to 40mins. The centrifugation speed was raised from 8000r/min for 10mins to 10000r/min for 30mins. In order to avoid the solid phase extraction which include wash,elution,weather with nitrogen,re-solution and filter. In this study,before the HPLC-MS/MS analysis,two filter steps was done with 0.45μm filter and 0.22μm filter respectively which assurance the extraction solution with drugs became very clear. The whole sample treatment time was reducing to less than 100mins. The most important was the sample treatment procedure in this study needs not any expensive extraction column and as a result,it reduce the treatment time and easy to be operated as well.
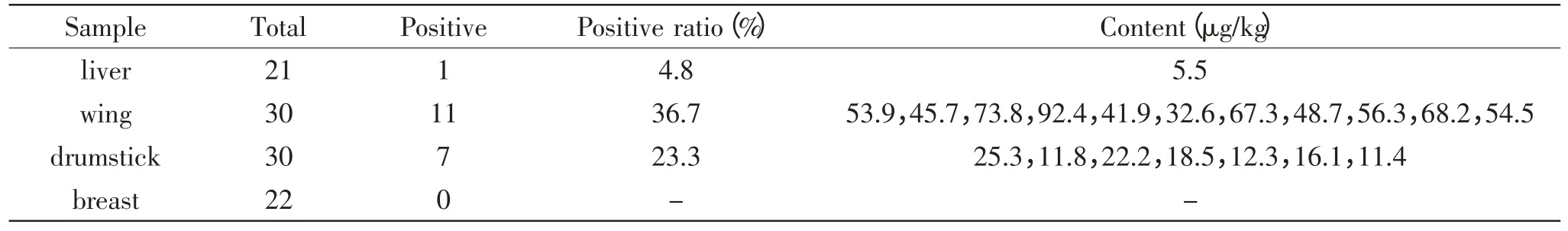
Table 2 The content of amantadine in positive samples
The first and central purpose of this study was to confirm if illegal use of amantadine in chicken breeding was existing or not. The second and subordinate purpose was to approximately investigate or evaluate the degree of amantadine residue in chicken food. The result in this study had presented the first-hand information about the amantidine residue in chicken food and confirmed the use of amantadine in chicken breeding. This was the first step to further supervise the chicken breeding and issued standard detection method according to the concerned rules established by government. And the result was also useful to direct consumer to effectively avoid the possibility of amantadine accumulate from food chain.Further work was needed to supervise the amantadine production,circulation and use. Then developing new succedaneum drugs of amantadine against virus disease infection in animal breeding was necessary.
[1] Michaela Schmidtke,Raland Zell,Katia Bauer,et al.Amantadine Resistance among Porcine H1N1,H1N2,and H3N2 Infl uenza A Viruses Isolated in Germany between 1981 and 2001[J]. Intervirology,2006,49:286-293.
[2] Fatimah S,Dawood,M D,Seema Jain,et al. Emergence of a Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A(H1N1)Virus in Humans[J].The new England Journal of Medicine,2009,360(25):2605-2615.
[3] Rick A Bright,Marie-jo Medina,Xiyan Xu. Incidence of adamantane resistance among influenza A(H3N2) viruses isolated worldwide from 1994 to 2005:a cause for concern[J].Academic Research Library,2005,366:1175-1181.
[4] Frederick G Hayden. Antivirals for influenza:Historical perspectives and lessons learned[J]. Antiviral Research,2006,71:372-378.
[5] Pathumwadee Intharathep , Chittima Laohpongspaisan ,Thanyada Rungrotmongkol. How amantadine and rimantadine inhibit proton transport in the M2 protein channel[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics and Modelling,2008,27:342-348.
[6] Antonios Kolocouris,Christos Zikos,R William Broadhurst.19F NMR detection of the complex between amantadine and the receptor portion of the influenza A M2 ion channel in DPC micelles[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2007,17:3947-3952.
[7] Ri-Bo Huang,Qi-Shi Du,Cheng-Hua Wang,et al. An indepth analysis of the biological functional studies based on the NMR M2 channel structure of influenza A virus[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2008,377:1243-1247.
[8] Jason R Schnell,James J Chou. Structure and mechanism of the M2 proton channel of influenza A virus[J]. Nature,2008,451:591-595.
[9] Kanti Pabbaraju,Kevin C Y Ho,Sallene Wong,et al.Adamantane resistance in circulating human influenza A viruses from Alberta,Canada(1970-2007)[J]. Antiviral Research,2008,79:81-86.
[10] Gui Rong Bai,Mailinee Chittaganpitch,Yuta Kanai,et al.Amantadine- and oseltamivir-resistant variants of influenza A viruses in Thailand[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2009,390:987-901.
[11] Guimei He,Jian Qiao,Changgui Dong,et al. Amantadineresistance among H5N1 avian influenza viruses isolated in Northern China[J]. Antiviral Research,2008,77:72-76.
[12] Michael B,Townsend,James A Smagala,et al. Detection of adamantane-resistant influenza on a microarray[J]. Journal of Clinical Virology,2008,42:117-123.
[13] Frederick G,Hayden M D. Antiviral resistance in influenza viruses-implications for management and pandemic response[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine,2006,354:785-788.
[14] Chittima Laohpongspaisan,Thanyada Rungrotmongkol,Pathumwadee Intharathep,et al. Why amantadine loses its function in influenza M2 mutants:mD simulations[J]. J Chem Inf Model,2009,49:847-852.
[15] Earl Justice Smith. Amantadine-induced psychosis in a young healthy patient[J]. The America Journal of Psychiatry,2008,165:1613.
[16] Wang Ping,Liang Yi-zeng,Chen Ben-Mei,et al.Quantitative determination of amantadine in human plasma by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and the application in a bioequivalence study[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2007,43:1519-1525.
[17] Yun huan,Zhang Zhaohui,Luo Shengliang,et al.Determination of anmantadine residues in food of animal origin by solid-phase extraction/LC-MS/MS[J]. Moderninstrs,2009,6:42-45.
[18] Torsten Amdt,Brunhilde Guessregen,Axel Hohl,et al.Determination of serum amantadine by liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry[J]. Clinical Chimica Acta,2005,359:125-131.
[19] Cui Shuangjin,Feng Fang,Liu Han,et al. New method for high -performance liquid chromatographic determination of amantadine and its analogues in rat plasma[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2007,44:1100-1105.
[20] Tsai-Hui Duh,Hsin-Lung Wu,Chi-Wen Pan,et al.Fluorimetric liquid chromatographic analysis of amantadine in urine and pharmaceutical formulation[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2005,1088:175-181.

