Environmental Security Control of Pharmaceutical Residues and Pathogens
XU Han, WANG Li, USOLTSEV V A
(1.Civil and Environmental Engineering,University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign,Urbana IL61801,USA;2.Environmental& Safety Engineering,Shenyang University of Chemical Technology,Shenyang 110142,China;3.Ural State Forest Engineering University,Yekaterinburg 620100,Russia)
The environmental security(ES)issues is extremely important and timely issues to a country through the world,although the relevant international organizations have not created a definition.The governments thought the ES is able to assure by modifying the current environment protection system because of two reasons.One is whatever the pollution exists is potential influence the ES system.The second pollution control technology is useful tool to insure ES.Several counties,including United States,the Russia,the Commonwealth of independent states,tried to unify an official definition and action for ES,although indicating these countries have respectively created the definition of ES.The inarguable fact is that ES issue is caused by pollution accident whatever the definition of ES is.Currently,the potential risk from the pharmaceutical residues and pathogens in wastewater are concerned because of impacting our human health,growth,coordination,propagation and maturation whenever these are short or long term.Therefore,they are also defined the pollutants of ES.The researches show that the wide range and varied pharmaceutical residues cause endocrine disruption because of the complexity of endocrine systems.According to European Union study,there were 118 substances as potential endocrine disrupters(EDCs)in wastewater from excrements,and also include pathogens[1-2].As the pollutants exited in the wastewater,the harm,injury or disease will occur as a consequence of exposure to a particular hazard.The paper will focus on their ES and control technology from pharmaceutical residues and pathogens in wastewater from ex-crements and their by-side effect to human health,harm or loss of life directly.The review also attempt to represents the contamination from the residues and pathogens and control technology with environmental system security via using new security assessment tools,regulations,protocol and advance biotechnology.
1 Pollution of EDCs from Pharmaceutical Residues
The excrement is one of largest wastewater sources in the world because of vast contamination from human and livestock.The expanded pollution became more intensive and is also growing the much concern of environmental issues due to excessive drainage.The most effective method for their monitoring is the liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry(LC-MS-MS)or(LC-MSn)via using off line solid phase extraction(SPE)which developed to validate 29 multi-class pharmaceuticals including their residues in WWTP(As shown in Fig.1)[3].Others,the manure as a valuable source of nutrients is widely used in the world,but it contains a variety of substances that can negatively affect the environment safety as well.The manure is perceived as a potential source of water and air pollution,which is a variety of substances including trace pharmaceuticals and pesticides,various types of pathogens,nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium,calcium,sodium,sulphur,lead and chloride[4].

Fig.1 LC-ESI-tandem MS analysis of a standard mixture at 1 ng/L
Pharmaceuticals,as veterinary pharmaceuticals(VPs),are special maters,such as sulphonamide,tetracycline,oxytetracyline and tylosin,which were found in surface waters and ground waters from farm areas in world[4].The modern husbandry used them of large amount as physiologically highly active substances to control livestock diseases by medicated feed,injection and external application[5].There is over 13 300 t/a antibiotics used for combating parasites,prevention and treatment of bacterially transmitted diseases,and acceleration of meat production in North A-merica and Europe[5].Due to the difference of the molecular structures and livestock species,as the parent compound,as conjugates,or as oxidation or hydrolysis products of the parent compounds,excretes of livestock also are different.After excretion,these VPs and their metabolites can contaminate the environment,for instance,the veterinary VPs residues mainly reached surface water from runoff of livestock manure fertilizers in soil as if the human medicine compounds discharged into surface water by the release of effluent from sewage treatment systems.The occurrence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds(PACs)have been growing hot spot in the aquatic environment[6].As one of the emerging issues in surface waters and ground waters they have been investigated in worldwide[7].Currently,there are more than 80 compounds,pharmaceuticals and several drug metabolites that have been detected and identified in aquatic environment[5,8].The studies show that some VPs originating from livestock diseases control are not eliminated completely and discharged as contaminants into the receiving waters.Several VPs from various prescription classes have been found in surface waters from the low(μg/L)to the very low(ng/L)concentration range[9].The investigations shows that the carbon disulfide,o-phenylphenol,tetrabrominated diphenyl ether,4-chloro-3-methylphenol,2,4-dichlorophenol,resorcinol,4-nitrotoluene,2,20-bis(4-(2,3-epoxypropoxy)phenyl)propane,4-octylphenol,estrone(E1),17a-ethinylestradiol(EE2),and 17b-estradiol(bE2)existed in surface water[7,10]and the concentration of tetracycline detected in liquid manure-treated agricultural fields is about 10 μg/kg and trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole related with VPs contaminants also detected in a water monitoring programme in the United States directed at waters[11].Another the livestock industry has been identified as a potential source of environmental endocrine disrupter chemicals(EDCs)through the use of PVs,promoters and the production of natural EDCs are excreted in livestock wastes.There are some chemicals which were suspected as EDCs from farm in the Great Lakes basin and natural hormones,such as estrogens,are excreted in animal manures and may also be disruptive to move into surface water.They should affect public health while they reach high concentrations[12].
2 Risk of Pathogens and Nutrient Pollution
Manure also contains countless bacteria,viruses,and parasites.Some of them are pathogenic such as cryptosporidium,giardia and toxoplasma,and they can lead to a variety of diseases and even death like emerging diseases such as foot and mouth disease,mad cow disease,SAS and bird flu.They as zoonotic diseases are found to be transmitted from animals to humans[13].One of transmissive ways is water pollution by ineffective management of livestock manure.Currently,there are not effective and cost efficiency methods completely to removal the spores,cysts,oocysts,ova,larval and encysted stages which lead to emerging zoonotic diseases.A variety of feces-related indicators are used as two common measures of potential contamination of potable water by fecal matter are total coliform bacteria and fecal coliform bacteria.For livestock manure management the methodology needs to be developed to keep a safety environment for human and animals.
Otherwise,eutrophication of surface waters both for inland waters(ditches,rivers,lakes)and coastal waters were caused by high concentration of phosphorus and nitrogen in manures while they as organic fertilizers were extensively and intensively applied,and it results in,for example,explosive growth of algae which causes disruptive changes to the biological equilibrium.The study in a 1987 Quebec showed concentrations of nitrogen in drainage water from corn and barley fields exceeded 40 milligrams per litre into surface waters during the spring and fall[14-15].Beauchemin S obtained the results which total phosphorus concentration in tile drainage water consistently greater than the surface water quality standard of 0.03 mg/L of total P about 1.0~2.0 kg/hm2in Montreal Lowland[16].Concentration of pesticides around 0.1~20 mg/L was detected in waters discharging tile system from New Brunswick[17].Groundwater as important portable water source is being polluted mainly by nitrates.In some areas of Canada,the pollution of groundwater has exceeded the limit of water quality and it is no longer fit to be used as drink-ing water according to present standards[18].
3 Control Technologies for ES from PRs and Pathogens
As mentioned above,the wastewater from excrement drainage can lead to ES issues if it is not effectively been controlled or managed.Many investigations have shown that one of the most difficult environmental challenges,and must face how to manage the pharmaceuticals,pathogens,other chemicals,nutrients and odours associated with municipal wastewater in the developing countries and agricultural industry[19-21].Animal manure is rich in nutrients and organic matter but it often contains rudimental endocrine disrupters(EDs)such as VPs and promoters and pathogens,when the land base area and pollutant retention time is insufficient for the overall volume of swine manure to be spread,there is a risk of groundwater and surface-water contamination.According to sustainable development of livestock manure management,an adequate system should prevent runoff,protect groundwater and surface water,minimize odour and air pollution,and provide sufficient manure storage and treatment unit as shown in Fig.2 and Table 1[22].
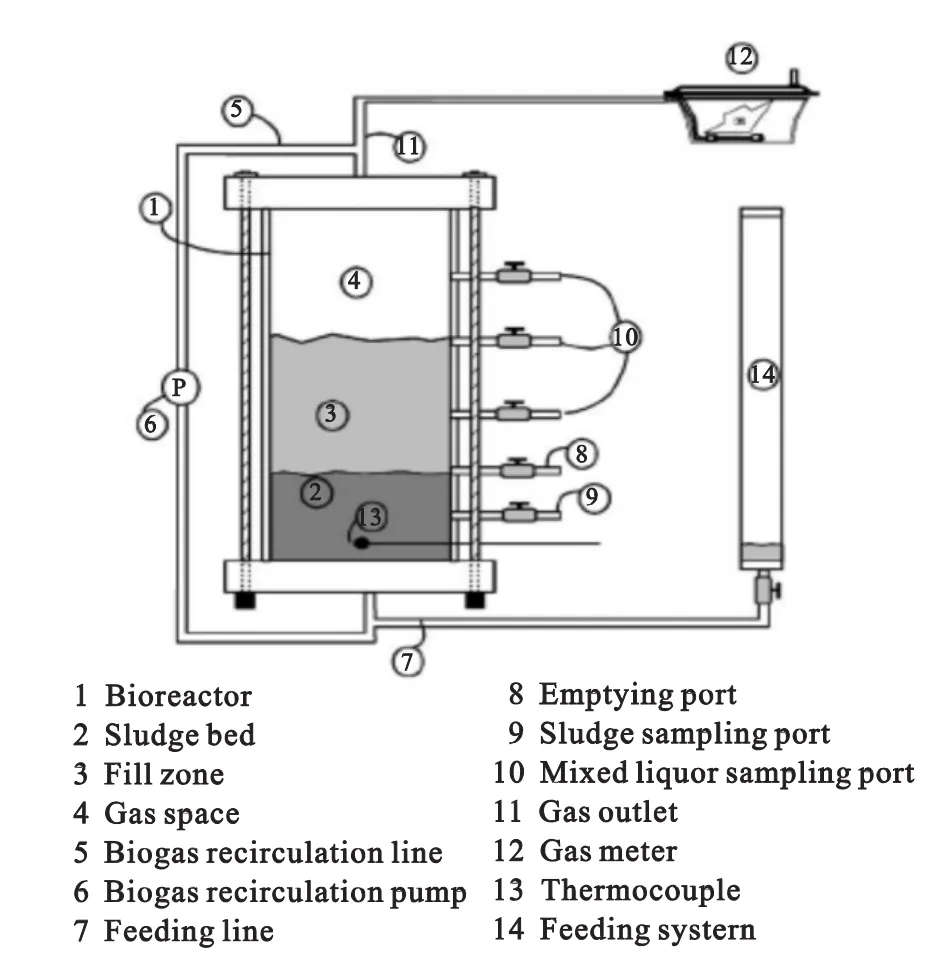
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the bioreactors

Table 1 Indicator and pathogenic microorganisms content of raw manure samples treated effluents
It can be safely applied to the land,and minimize nutrient losses after control.In response to growing concerns and new regulations,there are many treatment technologies to reduce or eliminate the land base required for safety application in manure management during the current time.
Traditional livestock effluent manure disposals use large drainage ditches or lagoons.They are typically dug adjacentto animalconfinement buildings,and lined with clay and/or vinyl material to increase their containment life span.There is a large footprint in lagoon where has 6 to 10 m deep.In many instances lagoons often happen the waste to flow easily across fields into public waterways and seep into aquifers which are threaten portable water supplies and have potential harm from unwanted hormones,PVs,pathogen,nitrate phosphors,ammonia,deadly coliform bacteria and odours[5].Anaerobic and aerobic heating composters were utilized to reduce volume of manure waste and odours[5].Flemming Ingerslev et al studied the fate of antibiotics in scenario in the primary aerobic and anaerobic biodegradability at intermediate concentrations from 50 to 5 000 μmol/L of the antibiotics olaquindox(OLA),metronidazole(MET),tylosiin(TYL)and oxytetracycline(OTC)in a simple shake flask system simulating the conditions in surface waters.The results illustrated the aerobic degradation needed 4~104 days to degrade the four antibiotics,and in absente of oxygen the degradation was significantly slower[23].Another recently published study showed that the degradation rate of tetracycline in liquid manure is approximately 50%in 5 months[5].In a screening of 62 pig slurry samples 9 samples were found positive for tetracycline with amounts of 5 to 24 mg/L.Masse D I,et al obtained the results that the PVs of tylosin,lincomycin,tetracycline,sulphamethazine,peniciline and carbadox were degraded in sequencing batch reactors(SBRs).The presence of penicillin and tetracycline in swine manure reduced 25%and 35%methane production,respectively,and others did not have noticeable adverse effects,but removal radios and the fate of residual PVs was not studied in this research[24].The treatment systems were studied to reduce odours by the anaerobic process[11,18,25].
Mechanical processes often use in manure treatment,which are solid-liquid separation like strainers,rollers,screws,and centrifuges are used for partial liquid-solid separation as pre treatment units,and they are cost effective volume reduction.Reverse osmosis process is membrane filtration under a high pressure gradient and allows separation of elements as small as ions:nitrates,phosphates,ammonia nitrogen,and potassium,pathogen and PVs,but it may be too costly for farmers.Advanced processes as Table 2[24]have represented the high efficiency for removal the EDCs,but whether releasing by-products or not have not studied to show the side-effects because their estrogenic activities higher than their precursors[23-24].
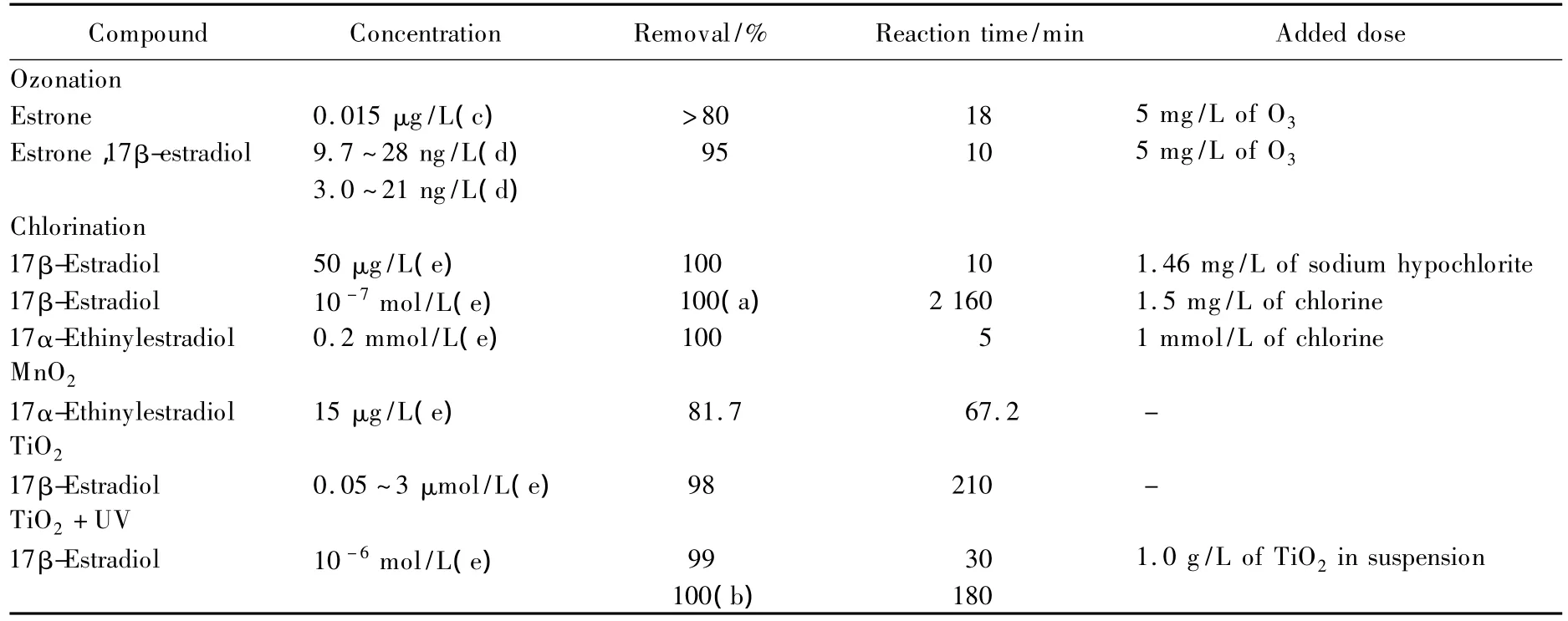
Table 2 Removal of estrogens by advanced treatment processes
Natural systems can contribute to manage wastewater from manures.Soil filter is discussed as on-site wastewater effluent soil absorption and treatment systems in joint AS-NZ standards(AS/NZS 1547∶2000).The research was shown the organic bio-layer on effluent infiltration soil surface significantly affected the saturated conductivity through the effluent/soil interface.Cation exchange capacity is important parameter to design it.The stable soils need to have m(Ca)/m(Mg)>0.5 and minimum unsaturated depth is about 400 mm.The soils unsuited to treat wastewater if they had low cation exchange capacity or poor nutrient retention capacity.The design loading rate and long term acceptant rate values need further to study to avoid collapses of soil structure overestimate soil capacity[25].Drip irrigation had used by low sub-surface drip irrigation.It can take advantage of value of nutrients to enhance vegetable site and landscape.The natural peat as biomedia was reported in wastewater on-site treatment.For nursery runoff from manure fertiliser application soils it should provide very useful information to improve soil filter capacity[23-24].The low pressure pipe geo-textile system was utilized to treat effluent from septic tank.The results were significant,but the fate of PVs and pathogens need to study[23,25].
4 Conclusions
ES is a very important topic related with environmental pollution and its control,and many investigations showed that the ES issues have been caused by the pharmaceutical residues and pathogens in wastewater from all kinds of excrements seriously.From mentions above,mono-method is very difficulty to solve the problem due to pollutants complexities.To avoid surface waters and ground waters pollution from these pollutants we need to find the sustainable solution for ES issues from the wastewater.Currently underway and continuously to critical review of past and recent advances in reducing methods of PVs and pathogens from wastewater have been done.The review have mentioned the methods to assess and control the potential environmental and public health risks pollutants and pathogens,such as tetracycline,sulphonamide,oxytetracyline,tylosin and Cryptosporidium,Giardia and Toxoplasma,associated with on-site treatment servicing.Secondary wastewater treatment system significantly reduced the concentration of EDCs according to the literature,but almost all the studies only analyzed the estrogens in wastewater treatment system influent and effluent,and so assumed that the difference was adsorbed in sludge because of no publication to date and prove the mechanism.DNA fingerprinting and chips as useful analysis tools can monitor the potential pathogens and viruses to avoid their contamination.All studies are not enough to insure ES from the pollution because the epidemiological data have given the evidence of a possible relationship between chemical exposure and harmful observed effects.The sustainable solution would be interesting to look further into investigation and achievement in the future.
[1] Servos M R.Review of the Aquatic Toxicity,Estrogenic Responses and Bioaccumulation of Alkylphenols and Alkylphenol Polyethoxylates[J].Water Qual Res J Can,1999,34:123-177.
[2] Spengler P,Körner W,Metzger J W.Substances with Estrogenic Activity in Effluents of Sewage Treatment Plantsin Southwestern Germany.1.Chemical Analysis[J].Environ Toxicol Chem,2001,20(10):2133-2141.
[3] Johannes Tolls.Sorption of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in Soils:A Review[J].Environ.Sci.Technol,2001,35(17):3397-3406.
[4] Gaynor J D,Tan C S,Drury C F,et al.Runoff and Drainage Losses of Atrazine,Metribuzin and Metolachlor in Three Water Management Systems[J].Journal of Environmental Quality,2002,31(11):300-308.
[5] Thomas Heberer.Occurrence,Fate,and Removal of Pharmaceutical Residues in the Aquatic Environment:a Review of Recent Research Data[J].Toxicology Letters,2002,131(1/2):117-124.
[6] Esperanza M,Suidan M T,Nishimura F,et al.Determination of Sex Hormones and Nonylphenol Ethoxylates in the Aqueous Matrixes of Two Pilot-scale Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants[J].Environ Sci Technol,2004,38:3028-3035.
[7] Crowe A S,Ptacek C J,Rudolph D L,et al.Landfills and Waste Disposal.In Threats to Sources of Drinking Water and Ecosystem Health in Canada[R].Burlington:National Water Research Institute,2001:51-56.
[8] Slifkoa T R,Smithb H V,Rosea J B.Emerging Parasite Zoonoses Associated with Water and Food[J].International Journal for Parasitology,2000,30(12/13):1379-1393.
[9] Sheahan D A,Brighty G C,Daniel M,et al.Estrogenic Activity Measured in a Sewage Treatment Works Treating Industrial Inputs Containing High Concentrations of Alkylphenolic Compounds-acase Study[J].Environ Toxicol Chem,2002,21:507-514.
[10] Beachemin S,Simard R R,Bolinder M A,et al,Prediction of Phosphorus Concentration in Tile-drainage Water from the Montreal Lowland Soils[J].Canadian Journal of Soil Science,2003,83:73-87.
[11] Hamblin P F,He C.Numerical Models of the Exchange Flows between Hamilton Harbour and Lake Ontario[J].Can.J.Civil Eng,2003,30(1):168-180.
[12] Ministry of the Environment.Environmental Monitoring and Reporting Branch.Drinking Water in Ontario[M].Toronto:Queen's Printer for Ontario,2000:20-45.
[13] Feddes J.Design and Its Effects on Odour Management[R].Etobicoke:EPA Press.,1998:15-16.
[14] Baronti C,Curini R,D'Ascenzo G,et al.Monitoring Natural and Synthetic Estrogens at Activated Sludge Sewage Treatment Plants and in Areceiving River Water[J].Environ Sci Technol,2000,34:5059-5066.
[15] United States Department of Agriculture,Soil Conservation Service.Agricultural Waste Management Field Handbook[M].Washington:DC,1992.
[16] Caroline Côte,Daniel I Massé,Sylvain Quessy.Reduction of Indicator and Pathogenic Microorganismsby Psychrophilic Anaerobic Digestion in Swine Slurries[J].Bioresource Technology,2006,97(4):686-691.
[17] Rubin A R.On-site Wastewater Treatment-what are Some Option-some Opportunities[R].Australia:On-site'03 Armidale,2003.
[18] Desbrow C,Routledge E J,Brighty G C,et al.Identification of Estrogenic Chemicals in STW Effluent.1.Chemical Fractionation and in Vitro Biological Screening[J].Environ Sci Technol,1998,32(11):1549-1558.
[19] Cooper A D,Stubbings G W F,Kelly M,et al.Improved Method for the On-line Metal Chelate Affinity Chromatography-high-performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Tetracycline Antibiotics in Animal Products[J].Chromatogr.A,1998,81(1/2):312-326.
[20] Auriol M,Filali-Meknassi Y,Tyagi R D,et al.Endocrine Disrupting Compounds Removalfrom Wastewater,a New Challenge[J].Process Biochemistry,2006,41(3):525-539.
[21] USEPA.On-site System Manual[M].Washington:United States Environmental Protection Agency,2003.
[22] Arcand Y,Talbot P,Robitaille L.Peat Biofilter:an Innovative System Based on a Conventional Approach[R].Jekyll Island:National Onsite Wastewater Recycling Association Press.,1999:211-218.
[23] Crites R,Tchobanoglous G.Small and Decentralized Wastewater Management Systems[R].Boston:McGraw-Hill,1998.
[24] Gaynor J D,Tan C S,Drury C F,et al.Runoff and Drainage Losses of Atrazine,Metribuzin and Metolachlor in Three Water Management Systems[J].Environ.Qual,2002,31:300-308.
[25] Krishnappan B G,Marsalek J.Modelling of Flocculation and Transport of Cohesive Sediment from an On-stream Storm Water Detention Pond[J].Water Res,2002,36(15):3849-3859.

