MRS培养基对幽门螺杆菌具有抑制作用
苗君莅,吴正钧
(光明乳业研究院乳业生物技术国家重点实验室,上海 200436)
Helicobacter pyloriis a spiral-shaped,gramnegative rod that has developed sophisticated strategies to colonize epithelial cells lining the antrum of the stomach and to survive in the acidic environment.It is the causal agent of type B gastritis,peptic ulcers,and gastric cancer.Treatment ofH.pyloriinfection with antibiotics does not always eradicate the organism and causes diarrhea in the host.Also,H.pyloriis becoming resistant to a number of antibiotics.
It has been well documented that probiotic lactic acid bacteria(LAB)can develop antagonistic activity against various human pathogens,and certain LAB may have a role inH.pyloritreatment both through a direct action against the organism and in lessening the clinical side effects associated with antibiotics[1-5].
In these papers,marie-helene coconnier et al.[2]mentioned that the MRS broth adjusted to pH 4.5 showed slight inhibitory activity compared with the LAB-SCS activity on the growth ofH.pylori.The others didn’t mention the inhibition of MRSagainst the growth ofH.pylori[1,3-5],while the MRS was used as a culturing and screening medium for the potential lactobacillus strains.
During thein vitroscreening of lactobacilli antagonistic toH.pylori,it was found that MRS medium(produced by a large companies)showed strong inhibition against the growth ofH.pyloriboth on Columbia agar supplemented with 10%(v/v)sheep serum(FIG 1)and in brain heart infusion(BHI)supplemented with 10%(v/v)sheep serum(Table.1).The inhibition by MRS would lead to false outcome in screening new LAB with activity againstH.pylori.In addition,a significant decrease in the inhibitory activity by MRS was observed when MRS was inoculated LAB without antagonistic effect toH.pylori.In view of it,therefore,it could be used as a suitable medium forin vitroscreening of lactobacilli with potential inhibition effect toH.pylori.
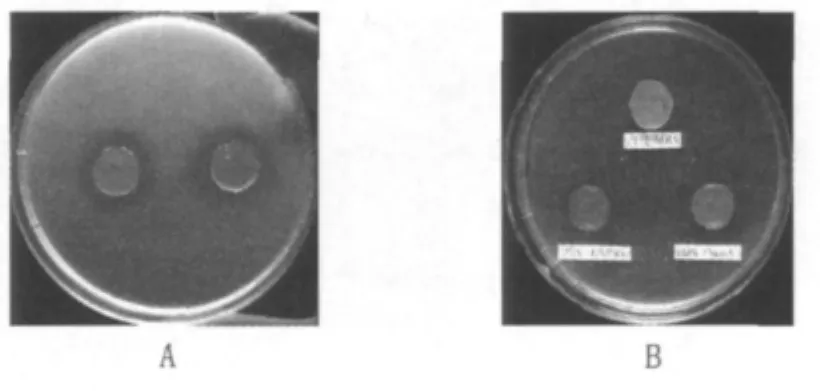
Fig.1 Two-double agar diffusion assay:effect of MRS on the growth of H.pylori on Columbia agar supplemented with 10%(v/v)sheep serum
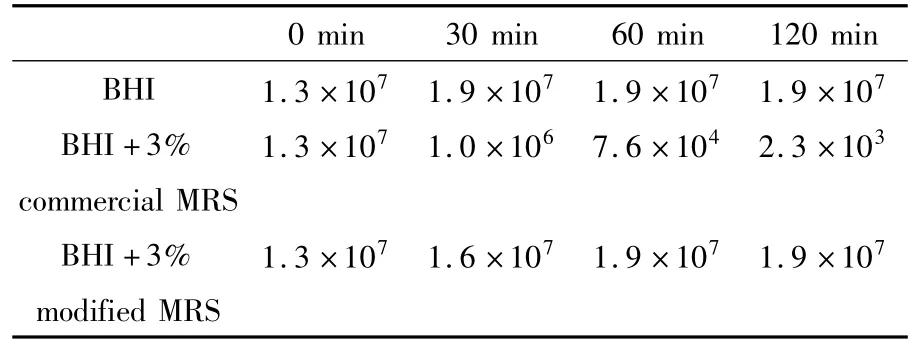
Table1 The comparison of growth inhibition to H.pylori in BHI and BHI+3%(v/v)MRS(pH wasn’t adjusted)(unit:cfu/mL)
So far,it is not clear which ingredient in MRS caused the inhibition againstH.pyloriand why the supernatant of MRS incubated with LAB without antagonistic effect toH.pyloridemonstrated a significant decrease in the inhibitory activity toH.pylori.Therefore,it is strongly suggested that modified MRS or other suitable culture medium which allows good growth of Lactobacillus strains should be usedin vitroscreening of lactobacilli with potential inhibition effect toH.pylori,so that the impact of substrate excluded.
Reference
[1]Bhatia.S.L.,Kochar N.,Abraham P..Lactobacillus acidophilusinhibits growth ofCampylobacter pyloriin vitro[J].Journal of Clinical Microbiology,1989,27(10):2328-2330.
[2]Coconnier MH,Lievin V,Hemery E,et al.Antagonistic Activity againstHelicobacterInfection in vitro and In Vivo by the HumanLactobacillus acidophilusStrain LB[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,1998,64(11):4573-4580.
[3]Graciela L.Lorca,Torkel Wadstrom,Graciela Font de Valdez,et al.Lactobacillus acidophilusAutolysins InhibitHelicobacter pyloriin vitro[J].Curr Microbiol,2001,42(1):39-44.
[4]D.Sgouras,P.Maragkoudakis,K.Petraki,et al.In vitroand In Vivo Inhibition ofHelicobacter pyloribyLactobacillus caseiStrain Shirota[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2004,70(1):518-526.
[5]Long Min,Long Beiguo,Bie Pinghua,et al.Antagonistic Activity againstHelicobacterInfection in vitro by The HumanLactobacillus[J].Chinese Journal of Microecology,2000,12(6):317-319.

