Impact of let-7g on Proliferation and Lactation of Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cells
Feng Li,Li Qing-zhang,Cui Wei,and Ding Wei
Key Laboratory of Dairy Science of Education Ministry,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) belong to a class of endogenous single-stranded RNA of about 21-25 nucleotides in length,which can regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level through complementary base pairing binding to target mRNA 3'UTR (3'untranslated region),and caused mRNA cleavage or translational expression (Cai et al.,2009;Chekulaeva et al.,2009;Ma et al.,2010).Thousands of miRNAs have been identified in several species,and the expression of most miRNAs is highly conserved.These miRNAs are involved in regulating a series of important biological processes,such as cell proliferation,differentiation,apoptosis,individual growth and development,and occurrence of disease (Ryusuke et al.,2007).In the present study,let-7 family is one of the most extensive miRNA families.It is originally discovered in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans,where it regulates cell proliferation and differentiation,but subsequent work has shown that both its sequence and function are highly conserved in mammals (Büssing et al.,2008;Roush et al.,2008).This study was conducted to explore a series of biological effects of mouse mammary epithelial cells that let-7g was produced.
Materials and Methods
let-7g target prediction
The algorithms miRanda (http://www.microrna.org/) and TargetScan (http://www.targetscan.org/) (Maziere et al.,2007) were used to predict let-7g that potentially bound to target Tgfbr1.
RNA extraction
Total RNA was isolated from mouse (Harbin Medical University) mammary gland tissue samples or cells by using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen).After extraction,the quality of each RNA sample was checked by using UV spectrophotometer (DU640,Beckman coulter,USA).
Real-time RT-PCR assays for mature let-7g
To quantify the expression of mature let-7g,ABI7500 PCR instrument (Applied Biosystem,USA) was utilized by using Hairpin-itTM miRNAs qPCR Quantitation Kit (Shanghai GenePharma Technology Co.,Ltd.) for real-time RT-PCR.To normalise the expression levels of let-7g,5S rRNA was used as an endogenous control.
Cell culture
Digested female mouse mammary gland tissue of pregnancy with collagenase type I (Gibco) and hyaluronidase at 37℃,then obtained cell pellets which were incubated at 37℃,5% CO2.After three passages,purified mammary epithelial cells were obtained.To observe specific expression of cytokeratin 18 (Acris),confocal microscopy was utilized by using cytokeratin 18 immunofluorescence staining (Bentwich,2005).
Transfection experiment
let-7g inhibitor (Shanghai GenePharma Technology Co.,Ltd.) was transfected into the culture cells using X-tremeGENE siRNA Transfection Reagent (Roche) according to the manufacturer instructions.The negative control (Shanghai GenePharma Technology Co.,Ltd.) was also used as the control.
Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation assays were performed by using CASY®-Technology (Schärfe System,Germany).Briefly,cells grew in plates and incubated for 0,24,36,48 and 72 h,then they were collected and measured the number of viable cells at each time point.
Western blotting
Cells were lysed,sonicated,boiled,and fractionated on a 10% Tris-glycine gels,and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane,which was hybridized with an antibody to TGFβR Ⅰ or GAPDH (Santa Cruze Biotechnology).Optical densities of bands were analyzed by using BandScan4.3.
HPLC
Collected cell secretions and detected β-Casein levels by using HPLC (280 nm;0.8 mL • min-1).Determined β-Casein of the standard under the same condition.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as mean±SD.Comparisons between two groups were performed by t-test.Multiple comparisons were performed by ANOVA.A value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Expression of let-7g in mouse mammary gland development,lactation and involution processes
To detect the differential expression of let-7g by qRTPCR in different developmental stages of mouse mammary gland,tissue samples were obtained in virgin,pregnancy,lactation and involution processes.As observed in mouse mammary gland tissues,let-7g was expressed in every developmental period of mouse mammary gland,according to real-time RTPCR analysis.let-7g expression was the lowest in pregnancy and lower than that in lactation (P<0.05) and involution (P<0.01) significantly;in virgin,let-7g was down-regulated and its expression was significantly lower than that in involution (P<0.05);in lactation and involution,let-7g expression was relatively high,but the difference was not significant (P>0.05),in which involution was the highest expression (Fig.1).Bentwich (2005) showed that let-7g expression presented phase specificity,mammogenesis was relatively strong and let-7g expression was lower during virgin and pregnancy,while let-7g expression increased significantly in the subsequent development process.In addition,Neilson et al.(2007) also proved that miRNAs expression was a dynamic regulatory process in different stages of cell development.
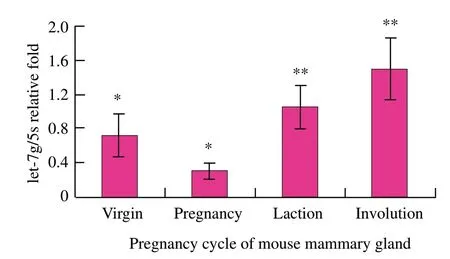
Fig.1 let-7g expression in mouse mammary gland by qRTPCR
Detection of let-7g inhibitor transfection efficiency
To test the transfection efficiency,parallel transfected cells were collected and the mature let-7g levels were measured by real-time RT-PCR.let-7g expression was down-regulated (P<0.01) in mouse mammary epithelial cells (Fig.2).
Detection of TGFβR I protein
To examine whether let-7g was capable of suppressing translation of TGFβR Ⅰ ,mouse mammary epithelial cells were transfected with let-7g inhibitor or the negative control.48 h after transfection,as observed in mouse mammary epithelial cells,TGFβR Ⅰ protein was over-expressed (P<0.01) in the transfected group in comparison with the negative control group according to Western blotting analysis (Fig.3).These results were consistent with the hypothesis that let-7g negatively regulated TGFβR Ⅰ expression at posttranscriptional level,which strongly suggested that let-7g might inhibit TGFβRⅠexpression.
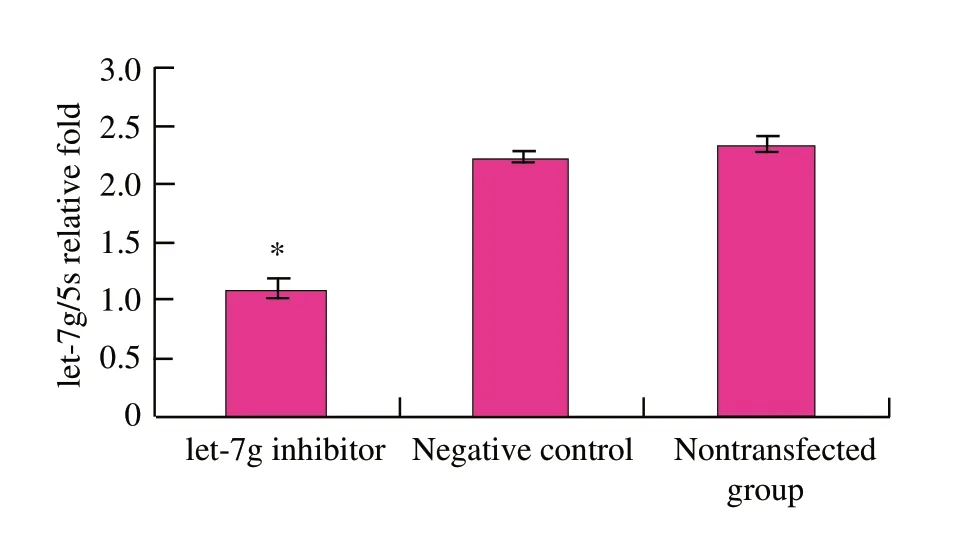
Fig.2 let-7g expression in mouse mammary epithelial cells by qRT-PCR after let-7g inhibitor
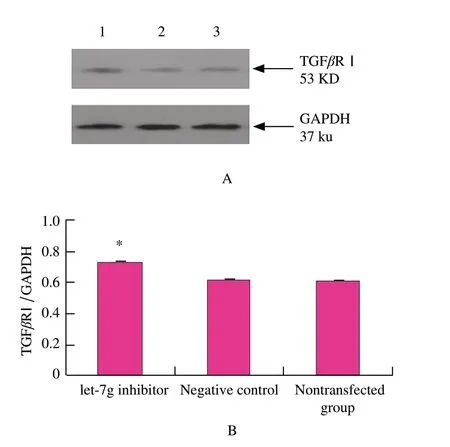
Fig.3 Western blotting analysis of TGFβR I expression change after let-7g inhibitor
Researchers found that TGF-β signaling pathway can regulate cell growth,differentiation,apoptosis,migration and formation of extracellular matrix.TGFβR Ⅰ mediates signal transduction pathway,as a transmembrane receptor in TGF-β signaling pathway,and it is very important for the signal transduction of TGF-β.But transmembrane serine/threonine receptor TGFβRⅠactivates TGFβR Ⅰwhich specifically recognizes and phosphorylates R-Smad proteins (Kathleen et al.,2009;Rojas et al.,2009;Masri et al.,2010).Therefore,phosphorylation of TGFβRⅠ is a key step in signal transduction.
Thus,bioinformatics predictes that let-7g targets Tgfbr1,which associates with mouse mammary gland development and lactation processes closely.Down-regulation of TGFβRⅠexpression that let-7g produced affects the TGF-β signal transduction,and then affects biological processes such as proliferation,differentiation and the expression of milk protein in mouse mammary epithelial cells.Therefore,it is considerable important for researching the regulatory mechanism of TGFβR Ⅰ.
Cell growth trend analysis
To investigate the impact of let-7g on suppressing cell proliferation,mouse mammary epithelial cells were transfected with let-7g inhibitor or the negative control and then subjected them to cell proliferation analysis.0-72 h after transfection,cell count showed a increase (P<0.05) in viable cell levels in the transfected group in comparison with the negative control group (Fig.4).Down-regulation of let-7g enhanced the proliferation of mouse mammary epithelial cells,which suggested that let-7g might inhibit cell proliferation.

Fig.4 Change of mouse mammary epithelial cell curve after let-7g inhibitor
Detection of β-Casein
To investigate the effect of let-7g on β-Casein expression,mouse mammary epithelial cells were transfected with let-7g inhibitor or the negative control,and then subjected them to HPLC analysis.β-Casein expression in mouse mammary epithelial cells was higher (P>0.05) for the transfected group when compared with the control group (Table 1).Therefore,down-regulation of let-7g affected β-Casein expression in mouse mammary epithelial cells.

Table1 Changes of β-Casein contents in mammary epithelial cells
Conclusions
In summary,these results indicated that let-7g showed differential expression in mouse mammary gland at different developmental stages.And also demonstrated that let-7g could negatively regulate the expression of target Tgfbr1 in mouse mammary epithelial cells,and then regulate the cell proliferation and expression of β-Casein by suppressing TGFβRⅠexpression.Further studies are needed to explore the mechanism between let-7g and its target Tgfbr1,and then provide the theoretical foundations for revealing regulatory mechanism and biological function of let-7g.
Bentwich I.2005.Prediction and validation of microRNAs and their targets.FEBS Lett,579(26): 5904-5910.
Büssing I,Slack F J,Großhans H.2008.let-7 microRNAs in development,stem cells and cancer.Trends Cell Biol,14(9): 400-409.
Cai Y M,Yu X M,Hu S N,et al.2009.A brief review on the mechanisms of miRNA regulation.Genomics,Proteomics &Bioinformatics,7(4): 147-154.
Chekulaeva M,Filipowicz W.2009.Mechanisms of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells.Curr Opin Cell Biol,21(3): 452-460.
Kathleen C,Lalae M.2009.Transforming growth factor-βs and mammary gland involution;functional roles and implications for cancer progression.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia,14(2): 131-144.
Ma J B,Huang Y.2010.Post-transcriptional regulation of miRNA biogenesis and functions.Front Biol,5(1): 32-40.
Masri S,Zheng L,Phung S,et al.2010.The role of microRNA-128a in regulating TGFbeta signaling in letrozole-resistant breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res TR,124(1): 89-99.
Maziere P,Enright A J.2007.Prediction of microRNA targets.Drug Discov Today,12(11/12): 452-458.
Neilson J R,Zheng G X,Burge C B,et al.2007.Dynamic regulation of miRNA expression in ordered stages of cellular development.Genes Dev,21(5): 578-589.
Rojas A,Padidam M,Cress D,et al.2009.TGF-β receptor levels regulate the specificity of signaling pathway activation and biological effects of TGF-β.Biochim Biophys Acta,1793(7): 1165-1173.
Roush S,Slack F J.2008.The let-7 family of microRNAs.Trends Cell Biol,18(10): 505-516.
Niwa R,Slack F J.2007.The evolution of animal microRNA function.Curr Opin Genet Dev,17(2): 145-150.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年3期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年3期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Regulatory Network of Transcription Factors in Response to Drought in Arabidopsis and Crops
- Comparison of Net Photosynthetic Rate in Leaves of Soybean with Different Yield Levels
- Multiplex PCR System Optimization with Potato SSR Markers
- Analysis on Combining Ability for Characters of Male Sterile Lines in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
- Study on Mutant Induction of Gladiolus by in vitro Culture of Petals
- Research on Tobacco Transformation of Vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit c Gene from Iris lacteal
