Research on Tobacco Transformation of Vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit c Gene from Iris lacteal
Wu Duo,Zhou Ai-min,Shi Sheng-feng,Li Shan-shan,and Wang Jin-gang
College of Horticulture,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China
Introduction
V-H+-ATPase is one of the major protein on tonoplast,whose function is to utilize the energy released by ATP hydrolysis in the cytoplasm into the vacuolar H+pump in order to establish transmembrane proton motive force (PMF).PMF has played an important role in plant growth,development and resistance (Ratajczak,2000).The response function of V-H+-ATPase under stress conditions is to ensure that the cells are in normal life activities (Fu et al.,2010).V-H+-ATPase is a multimeric enzyme,composed by two parts of V0and V1.Subunit c encoded by five homologous genes,which is an important part of V0domain,composed by six copies of V-H+-ATPase in the form of ions in and out of the channel,which is the most sensitive subunit in stress (Di,2007).
Tobacco is a model plant in molecular biology.Exogenous gene is transferred into tobacco,and exploring the function through studying and researching its influence on the transgenic tobacco in different stresses and growth processes has already become one of the most direct means in studying gene functions.In this study,the VHA-c gene cloned from the Iris was transferred into tobacco in order to verify its haloduric function,which provided a theoretical basis and practical reference for developing saline alkali land and improving the ecology environment.
Materials and Methods
Materials
The variety of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.) was Longjiang 911,the EHA105 and the VHA-c plant expression vector were supplied by Laboratory of Landscape Plant Breeding of Northeast Agricultural University.The nutrient media involved in the study were as the followings (all the nutrient media were with 0.76% agar and 3% cane sugar).
Nutrient medium of M0: MS,pH=5.80;
Nutrient medium of M1: MS+ NAA 0.1 mg • L-1+6-BA 1.0 mg • L-1,pH=5.80;
Nutrient medium of M2: M1+Km 25 mg • L-1+Amo 100 mg • L-1,pH=5.80;
Nutrient medium of M3: MS+ Km 25 mg • L-1+Amo 100 mg • L-1,pH=5.80.
Methods
Preparation of receptor materials
Soaked the tobacco seeds for 2 h with distilled water.Put the tobacco seeds in 3% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min to sterilize,then washed 5 times with sterile water.After that,put them on the nutrient medium of M0.Until the spires grew to 2-3 cm,removed the leaves,and punched holes along the veins on both sides of the leaf with a diameter of 7 mm.Then put them on the nutrient medium of M1adaxial side down for 2-3 days.When the cut of leaf discs began to intumescentia,the infection could be carried out.
Genetic transfermation mediated by agrobacterium
Transgenic tobacco was generated using an agrobacte rium-mediate method according to the Plant Genetic Engineering (Wu,2001).
PCR analysis of resistance plant
Used the total length primers of VHA-c gene cloned by Fu et al.(2010) and the PCR reaction conditions to proceed PCR analysis of resistance plant.Analyzed with 1% agarose gel electrophoresis after reaction.
Gene function verification of VHA-c from Iris lacteal
Each selected transgenic tobacco line was employed for NaCl tolerance testing.Well-watered plants were treated with 0.7% (w/v) NaCl for 7 days.Five strains selected from each line were used to drought stress.Selected five plants from each line for drought stress.The leaves from the plants cultuered after 0 day,1 day,4 days and 7 days,respectively were harvested for the analysis of superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity,peroxidase (POD) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) content.The SOD activity,the POD activity and the MDA content of each sample was measured according to the method as previously described in Phytophysiology Experimental Technique (Hao et al.,2001).
Results
Regeneration of resistance plant of Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.
Transgenic tobacco was generated using an agrobacterium-mediate method.The plants were precultured in MS medium with 0.1 mg • mL-1NAA and 1.0 mg • mL-16-BA for 2 days.Subsequently,the plants which were transferred to the new MS medium supplemented 0.1 mg • mL-1NAA,1.0 mg • mL-16-BA,25 mg • L-1Km and 100 mg • L-1Amo were co-cultured at 25℃ under light for 2-3 days and placed into new medium every 7-10 days until the adventitious shoots appeared,which could last for about 20-25 days.When the kanamycin-resistant adventitious shoots grew to about 3 cm in length,we cut them and then transferred them to the M3rooting medium for rooting.We could obtain the VHA-c 70 strains by domesticated transplanting the plants until their roots were developed (Fig.1).The transgenic strains were conducted PCR detection until they grew strong enough.
PCR analysis of resistance plant
The result of agarose gel electrophoresis showed that plasmid pBI-121 and some transgenic lines amplified the purpose strap about 495 bp,while the DNA of untransformed plants and water as negative control had not amplified the purpose strap (Fig.2),which initially proved VHA-c subunit gene had been integrated into the tobacco genome.Total 48 strains of tobacco regenerated plants were identified,in which 22 were positive plants,and the PCR detection of the positive rate was 45.83%.

Fig.1 Plant regeneration of Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.

Fig.2 PCR analysis of resistant plants
Gene function verification of VHA-c from Iris lacteal
Analyses of MDA levels in transgenic and normal plants
Malondialdehyde (MDA) was derived from the breakdown of polyunsaturated fatty acids and related esters.Measured the plasma,and the MDA provided an index of lipid peroxidation.Drought,high-salt,heavy metal,SO2and NO could cause the increase of active oxygen radicals of inner plants (Luo et al.,1998).Through the research of Bowler (1992),we could infer that plant in stress conditions,such as hypothermia,drought,and high-salt could enhance the process of peroxidation of membrane lipid.
The test showed that as the time of salt stress prolonged,the MDA content of non-transgenic tobacco showed a rising trend,the MDA content of the GM strains increased firstly,then went down,but finally on the 7th day reached the maximum during the period under stress (Fig.3).Under the stress of NaCl for 1 day,the MDA contents of all other GM strains and the control tobacco went up in various degrees,in which C8,A26and control tobacco had bigger growth in turn;on the 4th day under stress,the MDA content of control tobacco continued to rise,but the MDA content of all the non-transgenic tobacco went down in various degrees,A26had the largest decrease margin;on the 7th day under stress,the MDA content of A3strains which was steady increased rapidly,and became the highest content of all the control strains.
These results showed that the introduction of VHA-c gene into the tobacco could reduce the MDA content under the salt stress,and the ability of membrane lipid oxidation under the salt stress increased accordingly.
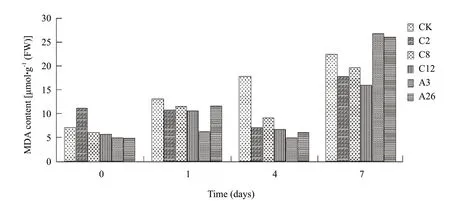
Fig.3 MDA content comparison under NaCl stress at different time of strains
Comparison of the SOD activity between transgenic and normal plants
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) was an indispensable oxygen free radical scavenger in organisms,which could defense oxidative damage of organisms (Diao,1995).The augmentation of the SOD activity could get rid of overweight O2-effectively,in order to maintain normal physiological functions of plants,and increase the resistance of plants at the same time.Compared with normal plants,the SOD activity in transgenic plants was markedly elevated under normal growth conditions (Fig.4).Following salt stress,the SOD activity in both transgenic and normal plants increased;however,the SOD activities in transgenic plants were all higher than those in normal plants,particularly in plants stressed for 4 days,at which time the transgenic lines had significantly higher the SOD activity than the normal plants.These results showed that the expression of VHA-c could increase the SOD activity in transgenic plants,and we could conclude that the viability of plants in versity was improved.

Fig.4 SOD activity comparison under NaCl stress at different time of strains
Comparison of the POD activity between transgenic and normal plants
Peroxidase (POD) was commonly found in plant tissues,whose main function was to eliminate active oxygen intra-cellular induced by salt stress.It also could stop unsaturated fatty acid from peroxidization and maintain stability and integrity of the membrane (Peng et al.,2003).
The test showed that there was no difference in the POD activity between the transgenic plants and normal plants under normal growth conditions (Fig.5).But the POD activity in both normal plants and transgenic plants was increased on 1 and 4 days under the salt stress,although the increase in the POD activity was more marked in the transgenic plants.After 1 and 4 days under salt stress conditions,the POD activity in transgenic plants was much higher than that of normal plants.These results showed that the expression of VHA-c protected the POD enzyme from destroying,and also increased the active oxygen ability of plants,by which the viability of plants was improved fundamentally.

Fig.5 POD activity comparison under NaCl stress at different time of strains
Discussion
Plant salt tolerance and VHA-c gene
When the plants suffered salt stress,ATPase played a role in establishing and maintaining the ions balance.V-ATPase could contribute to the enrichment of the toxic ion in the vacuole to improve the ability of plant resistance to salt stress (Di,2007).It had been observed that the transcription and activity of V-ATPase increased in several plants under the salt stress (Narasimhan et al.,1991).Dupont et al.(1992) had observed a new V-ATPase synthesis under the salt stress;in the mung bean roots treated with the salt stress,V-ATPase activity was 1.7 times of the control as observed by Nakamura et al (1992).The study on the subunit c of the Tortula ruralis showed that the expression level of subunit c increased under the salt stress and salt shock conditions described by Chen et al (2002).
Free radicals of biology suggested by McCord and Frdovich (l969) showed that high activity of protective enzyme made the membrane of the GM strains get less damage under the salt stress.The MDA content increased markly in the GM plants at 7 days under stress,which might be because of the accumulation of redundant Na+.The balance between creation and cleaning of reactive oxygen species was destroyed by the redundant Na+,which caused the damage of membranin and membrane lipid,so the membrane structure was damaged accordingly (Wang,1989).This study proved that salt tolerance of transferred transgenic had been improved than that of the control plants,indicating that VHA-c genes could improve thesalt stress ability of plants.
Molecular analysis of transgenic plants
PCR technology was the most commonly method used for detection of genetically modified plants.The advantage of PCR detection was less demanding of DNA purity,simple operation,and high sensitivity.But a simple PCR detection might mostly get falsepositive clones.The results of the PCR were used to carry on a screening test,then used Southern Blot,Nortthern Blot or quantitative PCR testing methods with the next step.In this study,post-PCR detection of the arrangements would also continue to test the positive plants to determine whether VHA-c gene was transferred into tobacco to further explore the VHA-c gene function.
Conclusions
Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.genetic transformation system was optimized,and the optimal conditions for genetic transformation were determined and the preculture medium was MS+NAA 0.1 mg • L-1+6-BA 1.0 mg • L-1;selected medium was MS+NAA 0.1 mg • L-1+6-BA 1.0 mg • L-1+Km 25 mg • L-1+Amo 100 mg • L-1;25℃ light training;7 -10 days of subculture time.
The plant expression vector of VHA-c was transferred into Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.by the agrobacte-rium-mediate method.There were 22 strains showed masccline and the transformation ratio was 45.83% after PCR detection.Then RT-PCR detection was taken for these 22 masccline strains,18 strains of them sproceeded transcription.
Treated the transgenic tobacco with 0.7% NaCl for 7 days,and the relevant physiological indicators of plants were measured at 0 day,1 day,4 days and 7 days after stress.The results showed that the SOD activity and the POD activity were significantly higher than those of the control in most of the transgenic strains,which reached the maximum on the 7th day under stress.The content of the MDA decreased on the 4th day,while increased sharply at the 7th day,most of them were lower than that of the control,which showed that the salt tolerance of transgenic strains had been enhanced because of the insertion and expression of VHA-c gene.
Narasimhan M L,Binzel M L,Perez-Prat E,et al.1991.NaCl regulation of tonoplast ATPase 70-Kilo-dalton subunit mRNA intobacco cells.Plant Physiol,97: 562-568.
Chen X,Kanokporn T,Zeng Q,et al.2002.Characterization of the V-type H-ATPase in the resurrenction plant Tortula ruralis:accumulation and polysomal recruitment of the proteolipid c subunit in response to salt-stress.J Experimental Botany,53: 225-232.
Di N.2007.Study on the function of subunit c genes of Vacuolar H+-ATPase in Arabidopsis thaliana.Hetao University Journal,4: 2.
Diao Z M.1995.The research and application prospeccts of superoxide dismut.Qin Hai Science,2(1): 1-7.
Dupont F M.Cooke D T,Clarkson D T.1992.Transport and receptor proteins of plant membranes.Plunum Press,New York.
Fu H J,Zhou A M,Che D D,et al.2010.Cloning and sequence analysis of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase subunit c family from Iris lactea.Crops Magazine,3: 60-64.
Hao Z B,Cang J,Xu Z.2001.Theory and technology of plant physiology(B).Harbin Publishing Company,Harbin.pp.190-205.
Luo L X,Sun T H,Jin Y H.1998.Accumulationof superoxide radical in wheat leaves under cadmium stress.Environmental Science Journal,18: 595-599.
McCord J M,McCord Ju,Fridovich I,et al.1969.Dismutase: superoxide an eunction function for erythrocuprein (Hemocuprein).J Biol Chem,244: 6049-6055.
Nakamura Y,Kasamo K,Sakata M,et al.1992.Stimulation of the extrusion of protons and H+-ATPase activities with the decline in pyrophosphatase activity of the tonoplast in intact mung bean roots under high NaCl stress and its relation to external levels of Ca2+ions.Plant cell Physiol,33: 139-149.
Peng Y,Zhang C L,Shen Q R,et al.2003.Effects of two phenolic acids on seed germination and activities of some emzymes in cucumber seedlings under salt stress.Nanjing Agric Univ Sinica,26(l): 33-36.
Ratajczak R.2000.Structure,function and regulation of the plant vacuolar H+-translocating ATPase.Biochim Biophys Acta,14(65): 17-36.
Wang B S.1989.Biological free radicals and membrane damage of plants.Plant Physiology Communications,2: 12-16.
Wu N H.2001.Principles of gene engineering.2 ed.Science Publishing Company,Beijing.pp.172-173.
 Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年3期
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)2012年3期
- Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Regulatory Network of Transcription Factors in Response to Drought in Arabidopsis and Crops
- Comparison of Net Photosynthetic Rate in Leaves of Soybean with Different Yield Levels
- Multiplex PCR System Optimization with Potato SSR Markers
- Analysis on Combining Ability for Characters of Male Sterile Lines in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
- Study on Mutant Induction of Gladiolus by in vitro Culture of Petals
- Genome-wide Analysis of Ovate Family Proteins in Arabidopsis
