EXT2基因突变引起的多发性骨软骨瘤的遗传学及表型分析*
钟良英, 丁红珂, 袁 萍, 裴元元, 王一鸣, 黄玮俊
(中山大学中山医学院医学遗传学教研室,广东 广州 510080)
EXT2基因突变引起的多发性骨软骨瘤的遗传学及表型分析*
钟良英, 丁红珂, 袁 萍, 裴元元, 王一鸣, 黄玮俊△
(中山大学中山医学院医学遗传学教研室,广东 广州 510080)
目的: 对2个多发性骨软骨瘤(multiple exostoses)小家系中的先证者进行致病基因EXT1和EXT2编码序列的突变检测,寻找致病性突变。方法应用PCR扩增EXT1和EXT2基因的编码区及外显子-内含子交界区,对产物进行直接测序。在50个正常对照中进行新发现突变位点的PCR测序分析,以排除多态性。结果家系1的先证者检测到1个EXT2基因的已知突变c.668Ggt;C(p.Arg223Pro),该错义突变使精氨酸变成脯氨酸;家系2的先证者于EXT2基因中检测到1个国际数据库中尚未报道的新突变c.950delT(p.Phe317SerfsX15),患者父母均未检测到此突变,故此突变为一个denovo突变。该突变引起开放阅读框架移位,提前引入终止密码子,导致蛋白质分子的截断,即部分exostosin结构域和全部glyco-transf-64结构域的丢失。结论本文发现的EXT2基因的新生及已知突变是引起本研究中多发性骨软骨瘤患者发病的分子机制,可用于临床的分子诊断。
外生骨疣,多发性遗传性; 基因,EXT1; 基因,EXT2;denovo突变
多发性骨软骨瘤(multiple exostoses)是一种常染色体显性遗传性的骨发育障碍疾病,接近80%的患者有阳性家族史[1]。主要表现为长骨近骨骺端多发性良性外生性骨疣[2],常常累及腿、前臂以及手[3],导致骨骼畸形,如前臂缩短和弯曲等,患者常有不成比例的身材矮小[4,5]。多发性骨软骨瘤还可能会引起一些并发症,如由于邻近组织、血管、神经、肌腱受压导致的关节运动受限和疼痛等。 该病在人群中的发病率约1/50 000,男性多见,男女之比约为1.5∶1[6],有0.5%-5%的患者可能恶变为软骨肉瘤或者骨肉瘤[5,7,8]。
在遗传学上,多发性骨软骨瘤虽然具有异质性(genetic heterogeneous),但超过70%的病例是由已克隆的致病基因EXT1(exostosin-1,MIM ID 608177)[9]和EXT2(exostosin-2,MIM ID 608210)[10]的突变所致[11],大多数的致病性突变主要是引起编码蛋白质的截断[12]以致功能域的丧失,从而导致野生蛋白的功能丧失。
本研究收集到2个多发性骨软骨瘤小家系,我们对家系中的先证者进行了EXT1和EXT2 基因编码区及外显子-内含子交界区的突变筛查,现将结果报道如下。
材 料 和 方 法
1材料
1.1主要试剂和仪器 (1)试剂:dNTPs (上海生工生物工程有限公司)、Taq DNA聚合酶(晶美生物有限公司)、DL2000 marker (TaKaRa大连宝生物公司)、SAP酶 (TaKaRa大连宝生物公司)、ExoⅠ(TaKaRa大连宝生物公司)、BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit (Applied Biosystems)、Goldview DNA染料(北京赛百胜生物有限公司)、血液基因组提取试剂盒(天根有限公司)等。(2)仪器:GeneAmp PCR system 9700(Applied Biosystems)、东盛龙PCR仪(东盛创新生物科技有限公司)、Biometra PCR仪、凝胶成像分析仪(UVP)、Beckman Coulter DU730 nucleic acid/protein analyzer、Eppendorf centrifuge 5415R、Sartorius 纯水仪、3730XL DNA analyzer(Applied Biosystems)等。
1.2病人资料 本研究收集了2个小家系(图1)。家系成员均经过详细的临床检查,患者还经过相应部位的X光检查。多发性骨软骨瘤的诊断按国际通用标准[13]。家系1中的先证者及父亲和家系2中的先证者被诊断为患者,余家庭成员健康。
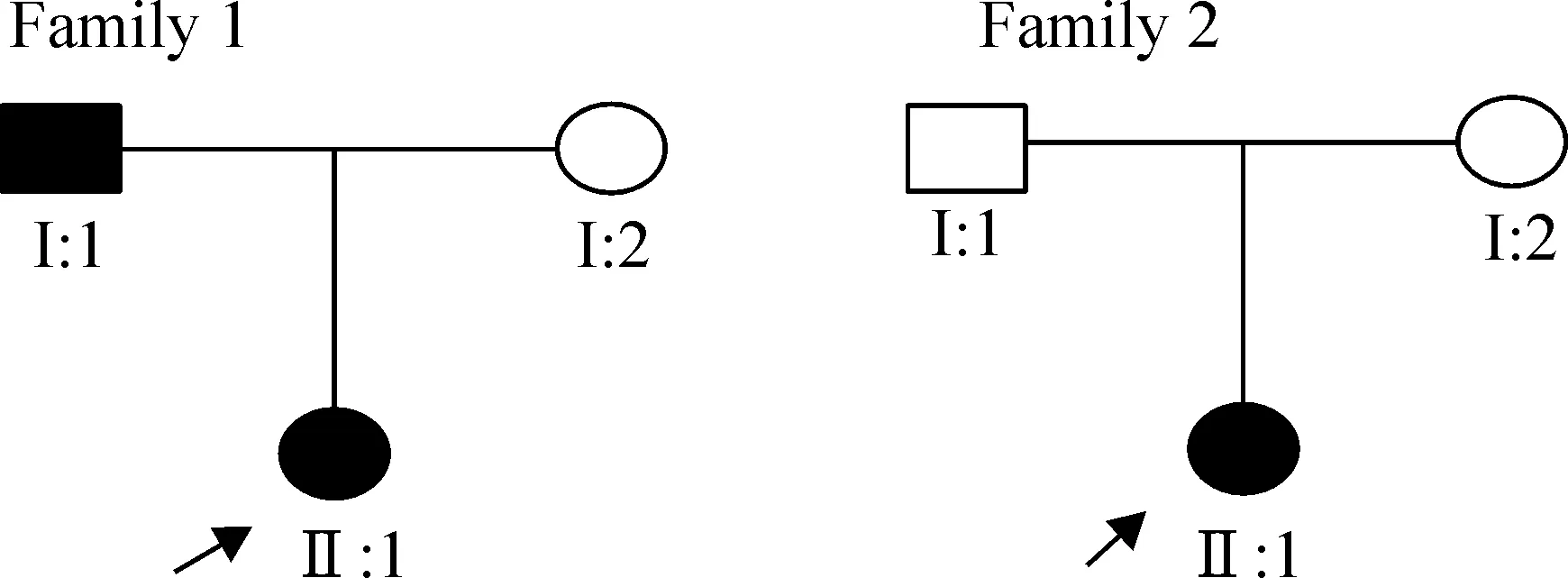
Figure 1.Pedigrees of families with multiple exostoses.Filled circles and squares denote affected family members.Arrows indicate probands.
2方法
2.1DNA提取 取外周血200 μL,按天根血液基因组小量抽提试剂盒(天根生化,北京)要求抽提DNA。
2.2引物设计及PCR扩增 从数据库UCSC Human Genome Browser (http://genome.ucsc.edu) (NCBI36/hg18)提取EXT1和EXT2 基因的序列,引物序列与文章[13]所有序列相同,见表1。进行PCR扩增,反应体系为30 μL:10×PCR缓冲液3 μL、25 mmol/L MgCl22 μL、2 mmol/L dNTP混合物3 μL、3.2 μmol/L上、下游引物各1.5 μL、Taq DNA聚合酶1 μL、DNA模板1 μL,灭菌ddH2O补足体积至30 μL;反应条件:94 ℃预变性3 min;94 ℃ 30 s、引物特异性温度退火1 min、72 ℃ 45 s,35个循环;72 ℃ 10 min。

表1 EXT1和EXT2基因扩增引物
2.3PCR产物测序及突变鉴定 对PCR产物直接进行测序分析:(1)测序预反应:SAP酶0.6 μL、、ExoⅠ 0.15 μL、10×buffer 0.3 μL 、PCR产物1 μL、灭菌ddH2O 0.95 μL,反应条件:37 ℃15 min,85 ℃15 min。(2)测序PCR反应:预反应混合液3 μL,BigDye 0.3-0.8μL,测序引物1 μL(3.2 μmol/L),补足ddH2O组成10 μL 反应体系进行测序PCR。扩增程序:98 ℃ 2 min;96 ℃ 10 s,50 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 4 min,30个循环。(3)测序PCR产物纯化及上机:3 mol/L 醋酸钠 (pH 5.2)和无水乙醇沉淀测序产物,再用75%乙醇洗涤1次,加10uL灭菌ddH2O溶解2-4 h;纯化产物95 ℃变性5 min,立即冰浴3 min,使其保持单链状态;转移至3730XL DNA analyzer上进行毛细管电泳。(4)测序结果鉴定:应用软件 Sequence Scanner 1.0(Applied Biosystems)对测序结果进行分析判读。(5)将所得突变进行遗传命名并与数据库比对:本文参考人类基因组变异协会(Human Genome Variation Society,HGVS)所制定的序列变异命名法则(http://www.hgvs.org/mutnomen);捕获的遗传突变与人类基因组突变数据库(HGMD,http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php)进行比对并查询PubMed上已发表的文章确定所检突变是否是新突变。其中EXT2基因中发现的突变根据以下参考序列命名:GenBank NM_207122.1 和 GenBank NP_997005。
结 果
1病人临床表现
家系1先证者,2岁,X光显示为左腓骨上段点状骨疣突起及左股骨下段的点状骨疣突起,见图2A、B;家系2先证者,19岁,X光显示为右桡骨下段条状骨疣突起及左右股骨下段伞状骨疣突起,见图2C、D。
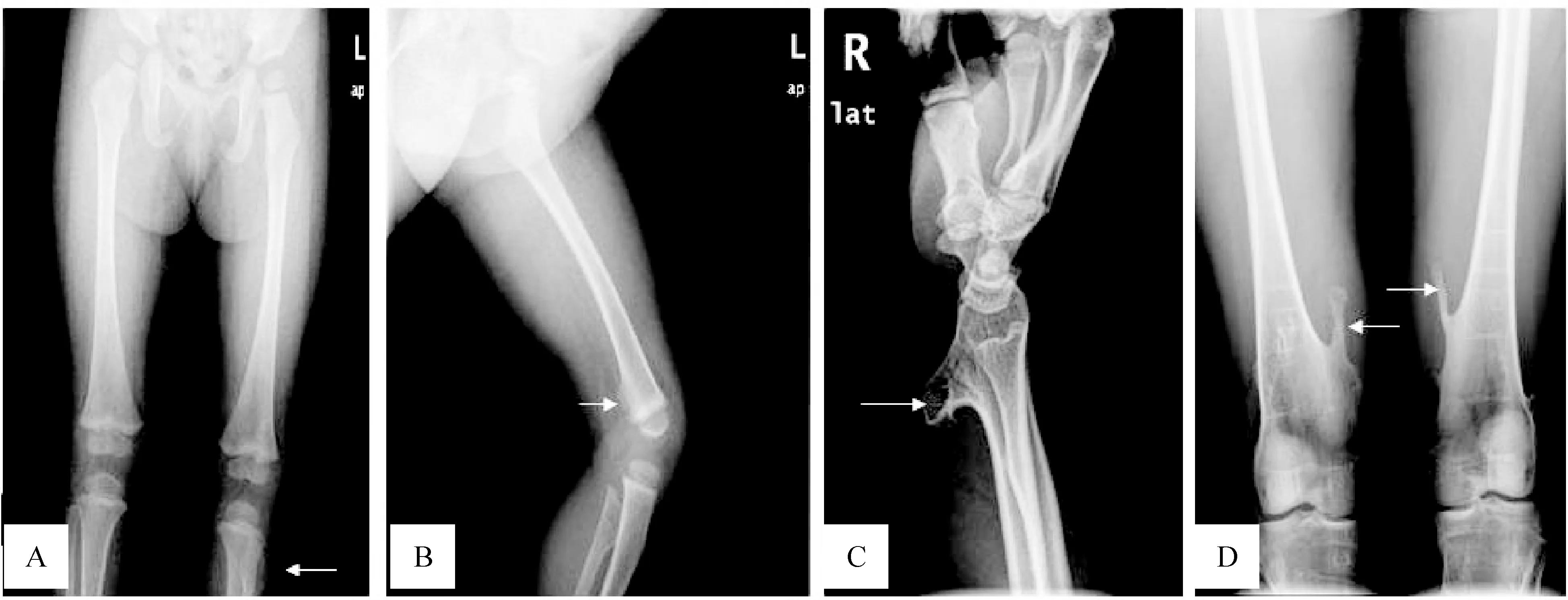
Figure 2.Radiographs of the two probands in the two families.The affected positions were indicated by the arrows.A,B: legs of family 1 proband,showing the dot-like exostoses on the left upper fibula (A) and small supernumerary bone on the distal femur (B); C,D: radiograph of family 2 proband,showing the lower radius growing with the strip exostosis (C) and umbrella protruding bone on the distal femur (D).
2突变筛查结果
2.1家系1 先证者测序结果显示,在EXT1基因的编码外显子及其侧翼序列未发现突变,在EXT2基因发现1个已知突变:c.668Ggt;C (p.Arg223Pro),见图3。
2.2家系2 先证者测序结果显示,在EXT1基因的编码外显子及其侧翼序列未发现突变,在EXT2基因发现1个新突变:c.950delT (p.Phe317SerfsX15),见图4C。该突变造成开放阅读框架的移位,在肽链第331位引入终止密码子,从而使3’端388 个氨基酸丢失,丧失了编码蛋白的部分exostosin结构域及全部glyco-transf-64结构域,见图5。这一突变在人类基因组突变数据库(HGMD,http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php)中未见记录,故为一新生突变。其父母均不带有此突变点,见图4A、B。50个正常对照中也没有发现该突变。
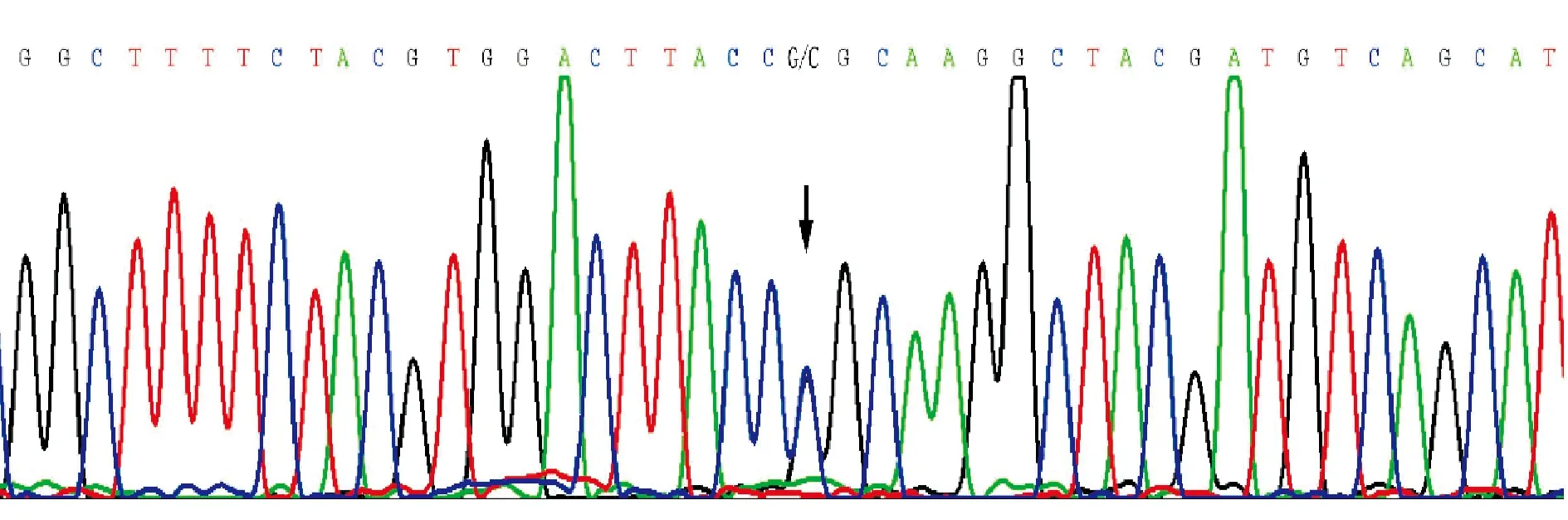
Figure 3.The sequencing result shows the mutation detected in family 1 proband.The arrow denotes the Ggt;C heterozygous change.
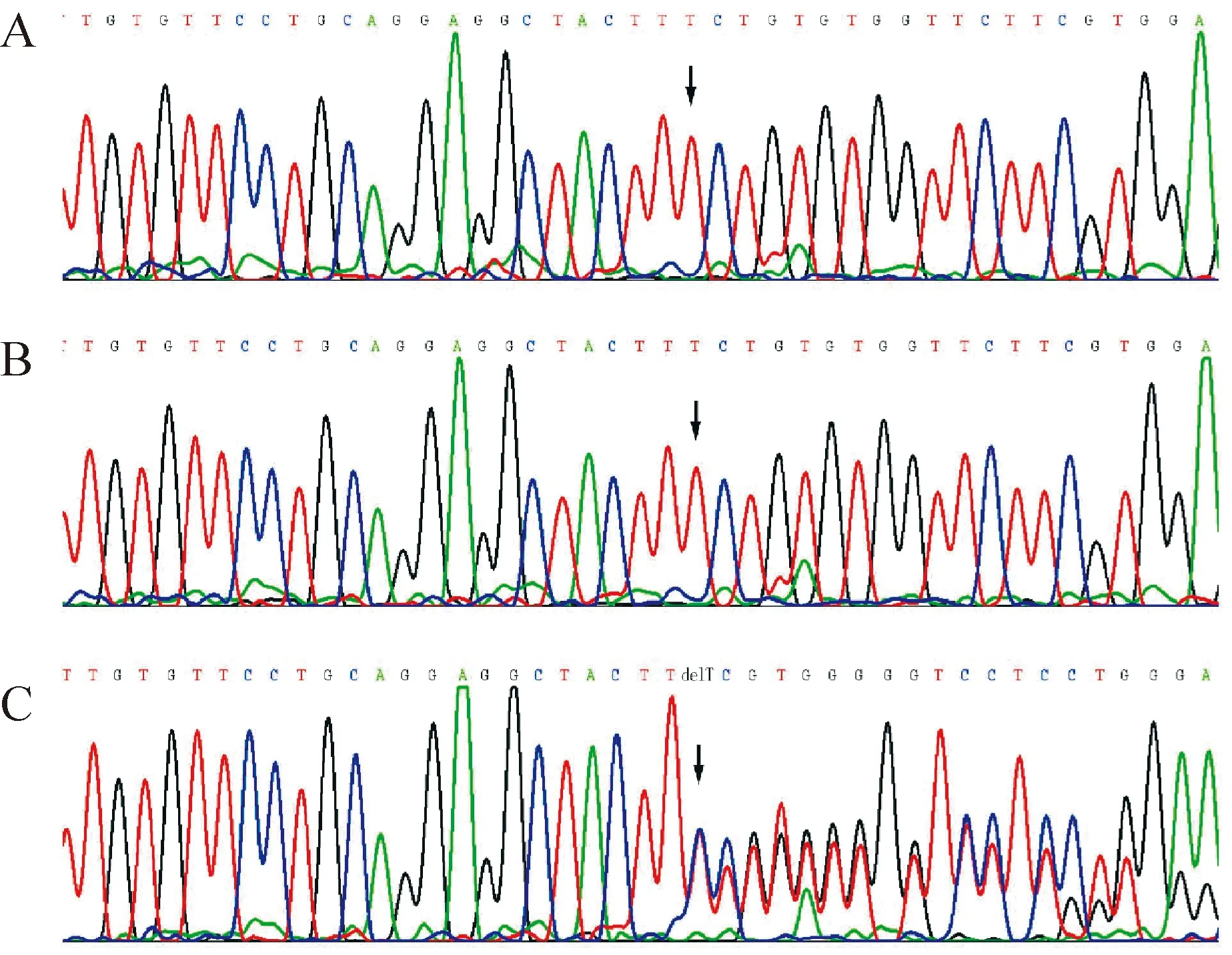
Figure 4.The sequencing results show the de novo mutation in family 2.A: the arrow indicates that the mutation was absent in the proband’s father.B: mother of the proband also had no mutation shown by the arrow.C: the de novo mutation was detected in the proband,which was one basepair T deletion causing the frameshift.
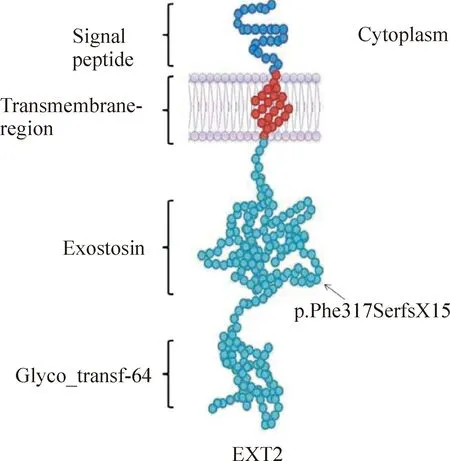
Figure 5.Structural model of the wild EXT2 has four domains: signal peptide,transmembrane region,exostosin and glyco_transf-64[13].Arrow denotes the truncating point of the mutant p.Phe317SerfsX15,which would result in the loss of part of the exostosin and the whole glyco-transf-64.
讨 论
目前基因突变检测已普遍应用于基础和临床研究[14]。本文对2例多发性骨软骨瘤患者进行了EXT1和EXT2基因的突变筛查。通过对PCR产物直接测序的方法,在2个患者中均发现了EXT2基因的突变,家系1的先证者为1个已知突变c.668Ggt;C (p.Arg223Pro),家系2的先证者为1个新生突变c.950delT (p.Phe317SerfsX15),数据库(http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php)检索证明该突变为一个国际上未被报导的新突变。
p.Arg223Pro使突变位点由精氨酸变成脯氨酸,氨基酸的性质发生了从碱性到非极性疏水性的改变[15];患者的临床表型为长骨一端的点状骨疣。该突变在本课题组先前另一多发性骨软骨瘤患者中也有报道[13],提示p.Arg223Pro可能为引发多发性骨软骨瘤的突变热点;p.Phe317SerfsX15使突变位点由苯丙氨酸变成了丝氨酸,氨基酸性质从非极性疏水性变为极性中性,并且由于碱基的缺失导致了密码子的框移,在突变位点后第15个密码子处出现终止密码从而使编码的蛋白质发生截断。根据已报道文献中的蛋白质结构预测,c.950delT(p.Phe317SerfsX15)应该位于exostosin结构域[13],其结果是导致该结构域的部分以及glyco-transf-64结构域的完全丢失,而5’端氨基酸部分(5’ transcript)则会因无义介导的降解(non-sense mediated decay)而降解[16],最终导致整个蛋白质的功能几乎完全丧失;该患者的临床表型为长骨一端的长条状骨疣,较之家系1先证者的症状更加明显,其父母体格检查时未发现异常,但没有做相应的X-光片检查,从阴性的突变筛查结果,可以推测其父母应该属于非患者,同时也说明该患者的突变是新生突变(denovomutation),50个正常对照的筛查也排除了多态性的可能,因此本研究所发现的EXT2新生突变是引起多发性骨软骨瘤的致病性突变。
至今,报道的EXT1基因致病突变有200多个,EXT2基因致病突变有将近100个,这些突变随机分布于整个基因的前2/3编码区[17]。这些突变主要是引起蛋白质发生截断而致病[12],但在中国患者当中由错义突变而致病的现象似乎并不是非常罕见[13]。EXT1和EXT2蛋白都在硫酸乙酰肝素的合成中催化肽链的延长[18,19]。EXT1/EXT2所形成的异源低聚复合物具有的糖基转移酶活性要比单独存在的EXT1或EXT2的活性高得多[20],因此不论是EXT1或者是EXT2的突变都可以影响硫酸乙酰肝素的合成,使正常的骨骼发育信号受到干扰从而导致骨软骨瘤的发生[1]。
总之,本研究对2例多发性骨软骨瘤患者进行了EXT基因的突变筛查,在EXT2基因中,家系1的先证者检测到1个已知突变,家系2的先证者找到1个新生突变,这一发现丰富了EXT2基因的致病性突变谱,并为进一步探索本病的分子机制、分子诊断以及表型-基因型的相关关系研究提供了有力的数据。
[1]Vanita V,Sperling K,Sandhu HS,et al.NovelEXT1 andEXT2 mutations in hereditary multiple exostoses families of Indian origin[J].Genet Test Mol Biomarkers,2009,13(1): 43-49.
[2]Solomon L.Hereditary multiple exostosis[J].Am J Hum Genet,1964,16: 351-363.
[3]Peterson HA.Multiple hereditary osteochondromata[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1989,(239): 222-230.
[4]Hennekam RC.Hereditary multiple exostoses[J].J Med Genet,1991,28(4): 262-266.
[5]Wicklund CL,Pauli RM,Johnston D,et al.Natural history study of hereditary multiple exostoses[J].Am J Med Genet,1995,55(1): 43-46.
[6]Bovée JV.Multiple osteochondromas[J].Orphanet J Rare Dis,2008,3: 3.
[7]Legeai-Mallet L,Munnich A,Maroteaux P,et al.Incomplete penetrance and expressivity skewing in hereditary multiple exostoses[J].Clin Genet,1997,52(1): 12-16.
[8]Gigante M,Matera MG,Seripa D,et al.Ext-mutation analysis in Italian sporadic and hereditary osteochondromas[J].Int J Cancer,2001,95(6): 378-383.
[9]Cook A,Raskind W,Blanton SH,et al.Genetic heterogeneity in families with hereditary multiple exostoses[J].Am J Hum Genet,1993,53(1): 71-79.
[10]Wuyts W,Ramlakhan S,Van Hul W,et al.Refinement of the multiple exostoses locus (EXT2) to a 3-cM interval on chromosome 11[J].Am J Hum Genet,1995,57(2): 382-387.
[11]Wuyts W,Van Hul W.Molecular basis of multiple exostoses: mutations in theEXT1 andEXT2 genes[J].Hum Mutat,2000,15(3): 220-227.
[12]Wuyts W,Van Hul W,De Boulle K,et al.Mutations in theEXT1andEXT2 genes in hereditary multiple exostoses[J].Am J Hum Genet,1998,62(2): 346-354.
[13]Pei Y,Wang Y,Huang W,et al.Novel mutations ofEXT1 andEXT2 genes among families and sporadic cases with multiple exostoses[J].Genet Test Mol Biomarkers,2010,14(6):865-872.
[14]吴文辉,肖隆斌,汤友珍,等.K-ras基因突变与结直肠癌生物学行为的关系[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25 (11):2159-2162.
[15]Shi YR,Wu JY,Tsai FJ,et al.An R223P mutation inEXT2 gene causes hereditary multiple exostoses[J].Hum Mutat,2000,15(4): 390-391.
[16]Bernard MA,Hall CE,Hogue DA,et al.Diminished levels of the pupative tumor suppressor proteinsEXT1 andEXT2 in exostosis chondrocytes[J].Cell Motil Cytoskeleton,2001,48(2):149-162.
[17]Li H,Yamagata T,Mori M,et al.Association of autism in two patients with hereditary multiple exostoses caused by novel deletion mutations of EXT1[J].J Hum Genet,2002,47(5): 262-265.
[18]Lind T,Tufaro F,McCormick C,et al.The putative tumor suppressorsEXT1 andEXT2 are glycosyltransferases required for the biosynthesis of heparan sulfate[J].J Biol Chem,1998,273(41): 26265-26268.
[19]Kitagawa H,Shimakawa H,Sugahara K.The tumor suppressor EXT-like geneEXTL2 encodes an α1,4-N-acetylhexosaminyltransferase that transfersN-acetylgalactosamine andN-acetylglucosamine to the common glycosaminoglycan-protein linkage region.The key enzyme for the chain initiation of heparan sulfate[J].J Biol Chem,1999,274(20): 13933-13937.
[20]McCormick C,Duncan G,Goutsos KT,et al.The putative tumor suppressorsEXT1 andEXT2 form a stable complex that accumulates in the Golgi apparatus and catalyzes the synthesis of heparan sulfate[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2000,97(2): 668-673.
MutationsofEXT2geneinpatientswithmultipleexostoses
ZHONG Liang-ying,DING Hong-ke,YUAN Ping,PEI Yuan-yuan,WANG Yi-ming,HUANG Wei-jun
(DepartmentofMedicalGenetics,ZhongshanSchoolofMedicine,SunYat-senUniversity,Guangzhou510080,China.E-mail:wonrich@yahoo.com.cn)
AIM: To investigate the mutations ofEXT1 andEXT2 genes in the probands of 2 families with multiple exostoses.METHODSAll coding exons and exon-intron boundaries ofEXT1 andEXT2 genes were amplified by PCR.The PCR products were sequenced.Fifty normal subjects were also sequenced for the novel mutation inEXT2.RESULTSA known mutation c.668Ggt;C (p.Arg223Pro) inEXT2 gene was detected in family 1,the missense mutation replaced arginine with proline at codon 223.A novel mutation c.950delT (p.Phe317SerfsX15) inEXT2 was detected in the proband of family 2.This mutation was undetectable in her parents,indicating adenovomutation.This mutation caused the shift of open reading frame,thus introducing a premature termination and resulting in truncation of the 388 amino acids at the C terminus,wiping out part of the exostosin domain and the whole glyco-transf-64 domain of the protein.CONCLUSIONOur results show that the mutations c.668Ggt;C (p.Arg223Pro) and c.950delT (p.Phe317SerfsX15) inEXT2 gene indicate the molecular mechanism for the development of multiple exostoses in the families.The results can be used for molecular diagnosis.
Exostoses,multiple hereditary; Genes,EXT1; Genes,EXT2;denovomutation
1000-4718(2011)05-0980-05
R363
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2011.05.028
2011-01-10
2011-03-21
广东省自然科学基金资助项目(No.10151008901000003)
△通讯作者 Tel:020-87332027;E-mail: wonrich96@yahoo.com.cn

