十二烷基磺酸钠对多孔银孔尺寸的细化
陆兴,王祥敏,李志强
(大连交通大学 材料科学与工程学院 轨道交通关键材料重点实验室,辽宁 大连 116028)*
0 引言
纳米多孔金属是一种具有高比表面积的新型材料,可以用作催化剂、传感器、驱动器等[1-4].制备纳米多孔金属的主要方法是去合金化法,利用化学腐蚀或电化学腐蚀方法溶解母合金中一种或几种较活泼组元得到纳米多孔金属.目前通过对Au-Ag、Ni-Al、Cu-Au、Pt-Cu、Pt-Si等[5-11]合金体系去合金化制备了不同的纳米多孔金属.采用去合金化方法制备纳米多孔银也有较多研究报道[12-19].然而,制备孔径尺寸为几十纳米的多孔银仍是个难题[14].为了得到孔道、孔带尺寸较小的高比表面积的纳米多孔金属,Li和Balk[20]将表面活性剂加入到腐蚀液中得到了孔道、孔带尺寸仅为5 nm的纳米多孔PdNi膜.十二烷基磺酸钠(SDS)是一种典型的离子型表面活性剂,常作为分散剂制备纳米颗粒,如纳米银粒子.其作用是显著增加纳米颗粒表面电荷的绝对值,形成双电层结构[21-23].本文拟利用SDS加入到0.2m的硫酸溶液中作为腐蚀溶液,将AgZn合金带去合金化制备孔径更细的纳米多孔银.
1 实验方法
母合金所用原材料分别为99.99%的银片、99.80%的锌粒.原料用丙酮、无水乙醇超声波清洗10 min后,用去离子水冲洗,冷风吹干,将其装入型号为JTL-400真空熔炼炉里的石墨坩埚中.真空炉在抽至真空度为5×10-3Pa的状态后,充氩气至0.05 MPa,然后通电感应熔化.当原料全部熔化并搅拌均匀后浇注到钢制锭模中.试样在炉内自然冷却,得到的母合金铸锭直径为φ12.8 mm.铸锭在高真空多功能快速凝固系统中进行喷带.冷却旋转盘直径φ22 cm,喷嘴和铜辊之间间距0.3 mm.调节辊转速1 500 r/min.利用快速冷凝制备Ag-Zn合金条带(宽度1~5 mm,厚几十微米,长几十厘米).INCA能谱仪测定成分.
电化学腐蚀采用LK98BⅡ型电化学工作站,三电极分别为:母合金为工作电极,Pt电极为对电极,饱和氯化钾甘汞电极为参比电极.快淬态Ag32Zn68合金带在加入十二烷基磺酸钠的0.2m硫酸溶液(250 mL)中去合金化,腐蚀电位0.45 V.去合金化后的样品用去离子水清洗,然后用无水乙醇清洗.JSM-6360LV型扫描电子显微镜用于观察合金的组织形貌,利用Smile view软件测量孔和孔带的尺寸.
2 实验结果与讨论
快淬态Ag32Zn68合金带在添加0.2 g SDS的0.2m硫酸溶液(250 mL)0.45 V腐蚀1 200 s 得到纳米多孔银(NPS),能谱分析出只含有很少量的Ag.图1给出了其断面形貌图.NPS呈现出均匀的、双连续的孔道、孔带结构,平均尺寸分别为114 nm和192 nm.
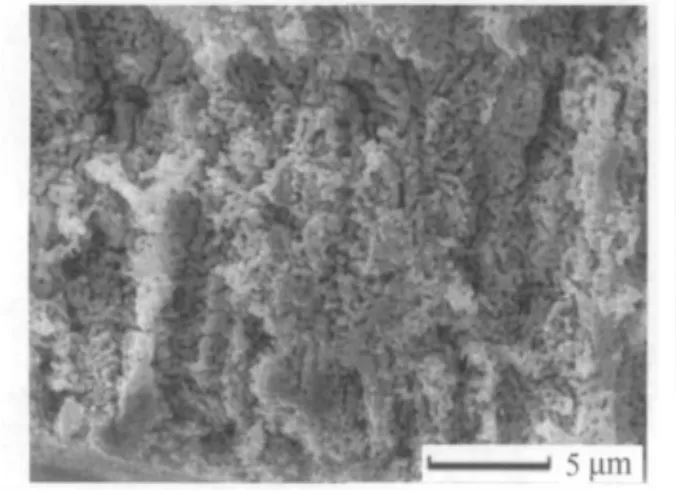
图1 快淬态Ag32Zn68在添加SDS的硫酸溶液中腐蚀1 200 s得到的纳米多孔银的断面形貌
不同腐蚀液中制备的纳米多孔银的表面形貌如图2所示.在0.2m硫酸腐蚀液中,样品表面孔道、孔带的尺寸随着腐蚀时间的延长而粗化,在添加SDS的硫酸溶液中样品表面的孔道和孔带尺寸并没有表现出粗化.图3给出了纳米多孔银的孔道、孔带尺寸和腐蚀时间的关系.没有SDS的腐蚀液中,腐蚀时间对样品表面孔的形成有很大的影响,孔道和孔带尺寸迅速增大.然而,加入SDS的腐蚀液中,当表面Zn原子全部腐蚀掉时(600 s),表面孔道和孔带尺寸没有变化.这表明纳米多孔银形成后SDS的加入能够阻止孔的粗化.去合金化过程中贵金属原子在合金/溶液界面进行表面扩散对多孔的形成起主导主用,对孔道和孔带的尺寸有很大的影响[24-25].Ag原子在硫酸溶液中的表面扩散系数为10-12cm2·s-1,比Au原子在HClO4溶液中的(10-14~10-23cm2·s-1)大很多[14-15].根据 Sieradzki[26]和 Dursun[27]的报道,将多孔银的粗化描述为:

其中,r为在t时刻孔的平均半径;r0为起始孔径;γ为表面能;a为点阵常数;Ds为表面扩散率;k为玻尔兹曼常数;T为绝对温度.根据幂定律,当r大于2r0时,计算Ds时,r0降低7% 作为修正.在目前的报道中,对于最小的孔径73 nm,修正r0对Ds的计算并没有多大的影响,因此本文中用到的r0为1.4 nm.利用式(1)计算去合金化时间为1500 s时的扩散系数 Ds,其中t=1500 s,ro=1.4 ×10-9m,γ =1.302 Jm-2,a =4.09 × 10-10m,k=1.380 6 ×10-23JK-1,T=288 K.得到Ag原子在硫酸溶液中的扩散系数为1.48×10-10cm2s-1,当加入SDS后该值为3.8×10-12cm2s-1.

图2 不同条件下去合金化制备纳米多孔银的表面形貌
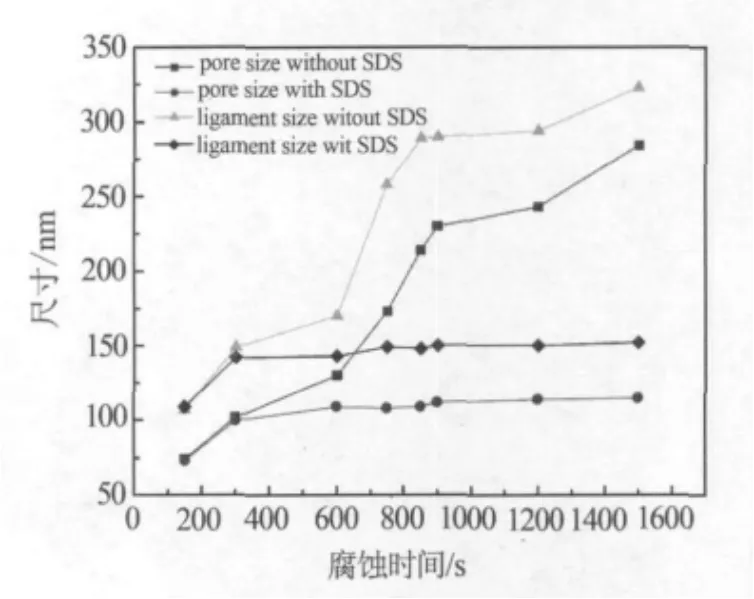
图3 添加表面活性剂后多孔银孔道、孔带尺寸和腐蚀时间的关系
SDS是一种离子型表面活性剂,常用作缓释剂,如对铜、镍、不锈钢[28-30].Fuchs-Godec[29]通过Langmuir曲线计算出表面吸附自由能,认为SDS在0.5m硫酸溶液中的缓蚀作用是由于十二烷基磺酸根离子的在铜表面的静电吸附.实验中用到的SDS的浓度为2.94×10-3mol·L-1,远远低于临界胶束浓度 CMC 至(1.4 ×10-2mol·L-1)[30],溶液中以单分子层分散的十二烷基磺酸根离子是主要的形式.根据 Erlebacher[31]的纳米多孔形成理论,提出SDS减小纳米多孔银尺寸的模型,如图4所示.多孔的形成分为三步:①在凹陷区域,合金的表面(A)暴露在已经形成的富银纳米多孔骨架区域(B),合金表面的Zn原子溶解到溶液(C)中;②随着界面的溶解,表面能增加,银吸附原子释放到表面.这些银吸附原子聚集到Ag团簇(D),或者当Ag孔带(B)相距较远时形成新的团簇(E);③暴露在合金表面的Zn原子溶解到溶液中(F),依此不断循环,孔区域和Ag聚集区域形成.而在我们目前的体系中,十二烷基磺酸根粒子很可能吸附到表面,阻碍银吸附原子的扩散,限制银原子的移动,这和目前研究的多孔形成理论相一致.也就是说,SDS部分阻碍了银吸附原子的扩散,减小表面扩散而使Ag聚集成更小的团簇,使其在原位扩散团聚.
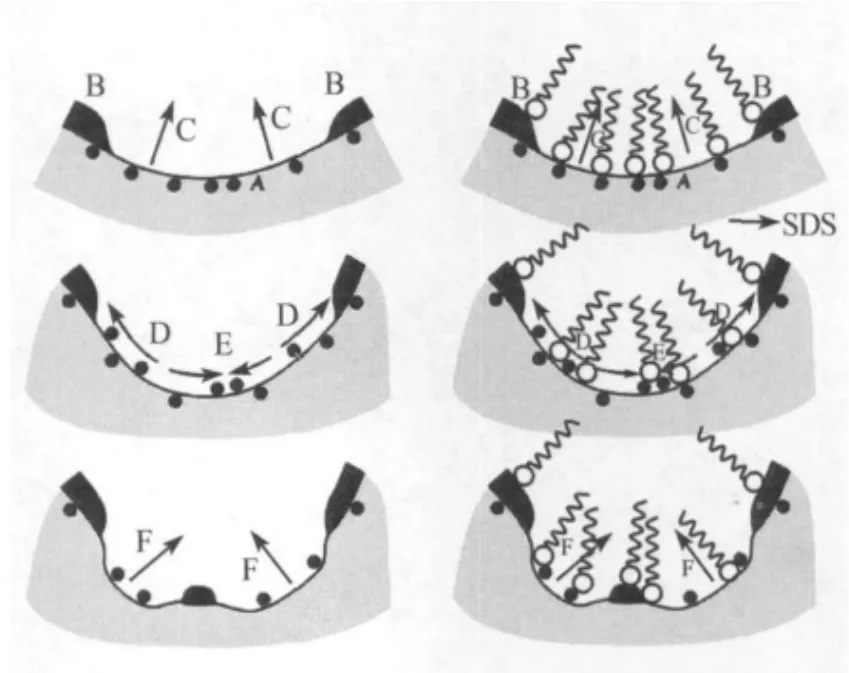
图4 SDS作用和无SDS时多孔形成模型
3 结论
通过将快淬态的Ag32Zn68在0.2m硫酸溶液中0.45 V腐蚀,去合金化得到纳米多孔银.十二烷基磺酸钠加入到腐蚀溶液中可以明显的减小纳米多孔银的孔道、孔带尺寸.这种减小作用是由于当SDS加入0.2m硫酸溶液后吸附在合金表面,Ag原子在的表面扩散系数由1.48×10-10cm2s-1变为3.84×10-12cm2s-1.
[1]BOND GC,THOMPSON DT.Catalysis by gold[J].Catalysis Reviews,1999(41):319-388.
[2]YOU T,NIWA O,TOMITAm,et al.Characterization of platinum nanoparticle-embedded carbon film electrode and its detection of hydrogen peroxide[J].Anal.Chem,2003(75):2080-2085.
[3]JOO SH,CHOI SJ,OH I,et al.Ordered nanoporous arrays of carbon supporting high dispersions of platinum nanoparticles[J].Nature,2001(412):169-172.
[4]RINTOUL MD,TORQUATO S,YEONG C,et al.Structure and transport properties of a porous magnetic gel via x-ray microtomography[J].Physical Review E,1996(54):2663-2669.
[5]LU X,BALK TJ,SPOLENAK R,et al.Dealloying of Au-Ag thin films with a composition gradient influence on morphology of nanoporous Au[J].Thin Solid Films,2007(515):7122-7126.
[6]LU X,BISCHOFF E.,SPOLENAK R.,et al.Investigation of dealloying in Au-Ag thin films by quantitative electron probe microanalysis[J].Scripta Materialia,2007(56):557-560.
[7]ZHANG ZHONGHUA,WANG YAN,QI ZHEN,et al.Generalized fabrication of nanoporous metals(Au,Pd,Pt,Ag,and Cu)through chemical dealloying[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2009(113):12629-12636.
[8]WITTSTOCK A,ZIELASEK V,BIENER J,et al.Nanoporous Gold Catalysts for Selective Gas-Phase Oxidative Coupling of Methanol at Low Temperature[J].Science,2010(327):319-322.
[9]QI ZHEN,ZHANG ZHONGHUA,JIA HAOLING,et al.Alloy composition dependence of formation of porousNi prepared by rapid solidification and chemical dealloying[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009(472):71-78.
[10]PUGH DYLAN V,DURSUN AZIZ,CORCORAN SCAN G.Electrochemical and morphological characterization of Pt-Cu dealloying[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2005(152):B455-B459.
[11]THORP J C,SIERADZKI K,TANG LEI,et al.Formation of nanoporous noble metal thin films by electrochemical dealloying of PtxSi1-x[J].Applied Physics Letters,2006(88):1-3.
[12]YEH FH,TAI CC,HUANG JF,et al.Formation of porous silver by electrochemical alloying/dealloying in a water-insensitive zinc chloride-1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride ionic liquid[J].J.Phys.Chem.B.,2006(110):5215-5222.
[13]LI Y Y,DING Y.Porous AgCl/Ag Nanocomposites with Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Properties[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2010(114):3175-3179.
[14]LI Z,WANG D,LI B,et al.The Dealloying Kinetics of Ag25Zn75 in 0.1m H2SO4[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2010(157):K233-K226.
[15]WANG XIAOGUANG,WANG WEIMIN,QI ZHEN,et al.High catalytic activity of ultrafine nanoporous palladium for electro-oxidation of methanol,ethanol,and formic acid[J].Electrochemistry Communications,2009(11):1896-1899.
[16]SUN YE,BALK T,JOHN.A multi-step dealloying method to produce nanoporous gold with no volume change and minimal cracking[J].Scripta Materialia,2008(58):727-730.
[17]ZHANG JINTAO,LIU PENGPENG,MA HOUYI,et al.Nanostructured porous gold for methanol electro-oxidation[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2007(111):10382-10388.
[18]XU CAIXIA,SU JIXIN,XU XIAOHONG,et al.Low temperature CO oxidation over unsupported nanoporous gold[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2007(129):42-43.
[19]ZHANG W Y,LI Y N,LI G ZH,et al.Fabrication of nanoporous structure silver film by dealloying of Ag-Al alloy and control of pore size.in 5th International Conference on Porous Metals and Metallic Foams[C].Met-Foam 2007,September 5,2008-September 7,2008.2008.Montreal, QC, Canada:DEStech Publications Inc.:325-328.
[20]LI W C,BALK T J.Achieving finer pores and ligaments in nanoporous palladium-nickel thin films[J].Scripta Materialia,2010(62):167-169.
[21]KVITEK LIBOR,PANAĈEK ALES,SOUKUPOVA JANA,et al.Effect of Surfactants and Polymers on Stability and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles(NPs)[J].The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2008(112):5825-5834.
[22]BHUI DK,BAR H,SARKAR P,et al.Synthesis and UV-vis spectroscopic study of silver nanoparticles in aqueous SDS solution[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2009(145):33-37.
[23]CHEN YH,YEH CS.Laser ablation method:use of surfactants to form the dispersed Ag nanoparticles[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2002(197):133-139.
[24]ERLEBACHER JONAH,AZIZ MICHAEL J,KARMA ALAIN,et al.Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying[J].Nature,2001(410):450-453.
[25]ERLEBACHER JONAH.An atomistic description of dealloying porosity evolution,the critical potential,and rate-limiting behavior[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2004(151):C614-C626.
[26]SIERADZKI K,DIMITROV N,MOVRIN D,et al.The dealloying critical potential[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2002(149):B370-B377.
[27]DURSUN A,PUGH D V,CORCORAN S G.Dealloying of Ag-Au alloys in halide-containing electrolytes.Affect on critical potential and pore size[J].Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2003(150):B355-B360.
[28]GUO R,LIU T,WEI X.Effects of SDS and some alcohols on the inhibition efficiency of corrosion for nickel[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2002(209):37-45.
[29]FUCHS-GODEC R,DOLEEK V.A effect of sodium dodecylsulfate on the corrosion of copper in sulphuric acid media[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2004(244):73-76.
[30]PICKERING H W.Characteristic features of alloy polarization curves[J].Corrosion Science,1983(23):1107-1109,1111-1120.
[31]ERLEBACHER JONAH.Dealloying of Binary Alloys:Evolution of Nanoporosity[J].Dekker Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2004,6:893-901.

