鞘内注射p-MPPF对异氟烷镇痛作用的影响
马 涛,袁力勇,王 丹,戴体俊,郭忠民,张励才
异氟烷(isoflurane,Iso)镇痛作用突出,理化性质稳定,全麻效能高,对呼吸循环影响小,毒性低,是临床上广泛应用的吸入麻醉药(inhaled anesthetics)。但Iso的麻醉机制目前尚未明确,在诸多麻醉作用中,镇痛作用是最重要、最基本的作用之一。目前认为Iso的镇痛部位主要在脊髓,可能与脊髓甘氨酸(Glycine,Gly)、谷氨酸(Glutamic acid,Glu)、神经元烟碱(neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine,nACh)和肾上腺素 α2等受体有关[1-8]。研究发现[9],脊髓中不同的 5-羟色胺(5-Hydroxytryptamine,5-HT)受体亚型介导了5-HT对伤害性信息的调制,其中,脊髓5-HT1A受体与疼痛的关系密切[10-13]。目前,关于Iso的镇痛作用与脊髓5-HT1A受体的关系罕见文献报道。
本研究以小鼠腹腔注射(intraperitoneal injection,ip)Iso建立镇痛模型,观察鞘内注射(intrathecal injection,it)5-HT1A受体的拮抗剂p-MPPF(4-Fluoro-N-(2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)1-piperazinyl]ethyl)-N-(2-pyridinyl)benzamide dihydrochloride)对Iso镇痛作用的影响,以分析此作用与脊髓5-HT1A受体的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物 清洁级昆明种小鼠,体质量(20±2)g,由徐州医学院实验动物中心提供。
1.2 实验药品和仪器 药品:Iso,鲁南贝特制药有限公司,批号:080908;p-MPPF,Sigma公司,用人工脑脊液(artificial cerebral spinal fluid,aCSF)稀释成所需浓度;冰醋酸,上海建信化工有限公司试剂厂,批号:XK13-2010942。仪器:HH-42型快速恒温数显水箱(常州国华电器有限公司);YLS-6B智能热板仪(淮北正华生物仪器设备有限公司);微量进样器(上海医用激光仪器厂);FA1104电子天平(杭州汇尔仪器设备有限公司)。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 甩尾法[14]小鼠♀♂各半。将快速恒温数显水箱加热到48℃ ±0.5℃。在小鼠尾巴的下1/3做一标记,把标记以下尾巴浸入水中,记录鼠尾自进入水中到甩出水面的时间即甩尾潜伏期(tail-flick latency,TFL)。给药前,每只小鼠测TFL两次,间隔5 min,将TFL<3 s或>6 s的小鼠淘汰,取两次的平均值作为基础TFL。各小鼠第2次给药后测定5、12、20、27、35 min 的 TFL,最长观察时间为15 s。
1.3.2 热板法[14]均为♀小鼠。将YLS-6B智能热板仪调至55℃,用药之前测小鼠自放到热板上到舔后足的时间,即热板痛阈(pain threshold in hotplate test,HPPT)2 次,间隔10 min,挑选 HPPT 在 10~20 s之间的小鼠,取两次的平均值作为基础HPPT。第 2 次给药后测定 5、15、25、35 min 的HPPT。
1.3.3 醋酸扭体法[14]小鼠♀♂各半,第2次给药5 min后ip 1.0%冰醋酸0.1 ml·10 g-1致痛,观察各组小鼠15 min内的扭体次数(writhing times,WTs)。
1.3.4 鞘内注射[15]以左手掌心压住鼠身,拇、中二指按压骶骨两侧固定,食指按在双骶骨前缘连线正中点皮肤上(可触知L6棘突)指示进针点,右手持微量注射器与脊柱上方成20°角与 L5-6间隙进针,针尖进入一侧棘突与横突间组织后减成10°角仔细缓慢推进,以鼠尾出现突然侧向运动为成功标志。缓慢注药,注射容积为5 μl,注射持续5 s,留针 10 s。
1.4 实验分组和给药方法 每种方法60只小鼠随机分为6组,分别为:Control组,Iso镇痛组(Iso组),单用工具药组:M6组、M3组,合用药组:Iso+M6组、Iso+M3组,每组10只小鼠。Control组:ip NS0.1 ml·(10 g)-11 min 后 it aCSF;Iso组:ip Iso(热板法和扭体法:0.3 ml·kg-1,甩尾法:0.4 ml·kg-1)1 min后 it aCSF;M6组、M3组:ip NS 1 min后it 6 μg 或 3 μg p-MPPF/只;Iso+M6组、Iso+M3组:ip Iso 1 min 后 it 6 μg 或 3 μg p-MPPF/只。
2 结果
2.1 甩尾法 单独it p-MPPF对小鼠TFL无明显影响(vs Control组,P >0.05),见 Tab 1。ip Iso后产生明显镇痛作用(P<0.01);it 6 μg p-MFFP在5、12、20、27、35 min时使小鼠 TFL 缩短(vs Iso组,P <0.01),可恢复到接近用药前水平(P>0.05);it 3 μg p-MFFP也能使TFL缩短(vs Iso组,P<0.01或P<0.05),不如大剂量p-MFFP作用明显,见Fig 1。
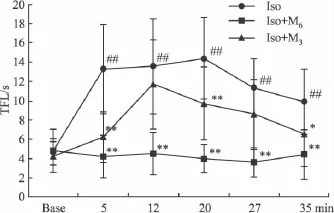
Fig 1 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPFon TFL in isoflurane treated mice
2.2 热板法 单用p-MPPF组的HPPT和Control组相似(P>0.05),见Tab 2。ip Iso镇痛作用明显且可持续35 min之久(P<0.01);it 6 μg p-MPPF在5、15、25、35 min 时使小鼠的 HPPT 降低(vs Iso组,P<0.01),与用药前差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);it 3 μg p-MPPF也可使 HPPT降低(vs Iso组,P <0.01或P<0.05),但不如大剂量p-MPPF作用明显,见Fig 2。
Tab 1 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPF on TFL in mice(tail-flick test,¯ ± s,n=10)
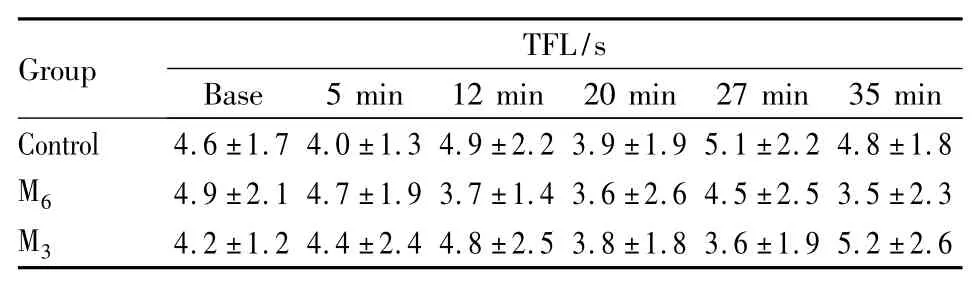
Tab 1 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPF on TFL in mice(tail-flick test,¯ ± s,n=10)
Group TFL/s Base 5 min 12 min 20 min 27 min 35 min Control 4.6 ±1.7 4.0 ±1.3 4.9 ±2.2 3.9 ±1.9 5.1 ±2.2 4.8 ±1.8 M6 4.9 ±2.1 4.7 ±1.9 3.7 ±1.4 3.6 ±2.6 4.5 ±2.5 3.5 ±2.3 M3 4.2 ±1.2 4.4 ±2.4 4.8 ±2.5 3.8 ±1.8 3.6 ±1.9 5.2 ±2.6
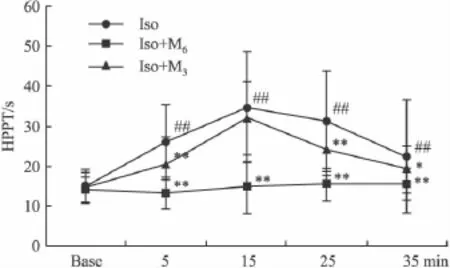
Fig 2 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPFon HPPT in isoflurane treated mice
Tab 2 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPFon HPPT in mice(hot-plate test,¯±s,n=10)
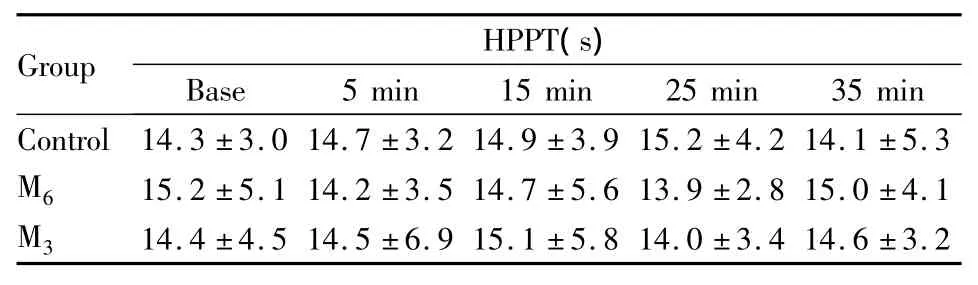
Tab 2 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPFon HPPT in mice(hot-plate test,¯±s,n=10)
Group HPPT(s)Base 5 min 15 min 25 min 35 min Control14.3 ±3.0 14.7 ±3.2 14.9 ±3.9 15.2 ±4.214.1 ±5.3 M6 15.2 ±5.1 14.2 ±3.5 14.7 ±5.6 13.9 ±2.8 15.0 ±4.1 M3 14.4 ±4.5 14.5 ±6.9 15.1 ±5.8 14.0 ±3.4 14.6 ±3.2
2.3 醋酸扭体法 与Control组相比,ip Iso镇痛作用明显(P<0.01)而单独it p-MPPF对小鼠15 min内的WTs影响不大(P>0.05);it 6 μg p-MPPF使小鼠 WTs增加(vs Iso组,P <0.05);it 3 μg p-MPPF对 WTs无影响(vs Iso组,P >0.05),见 Fig 3。
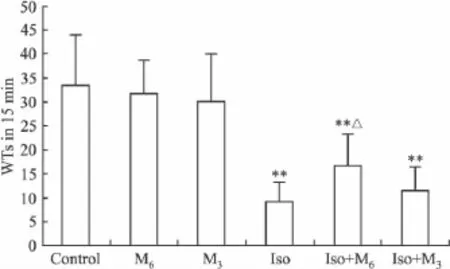
Fig 3 Influence of intrathecal injection of p-MPPFon WTs in isoflurane treated mice
3 讨论
甩尾反射的中枢在脊髓[14]。预实验中我们发现,甩尾法中ip 0.4 ml·kg-1Iso虽可产生一定的镇静作用,但对脊髓反射活动影响很小,因此与另外两种方法(热板法和扭体法)使用的Iso剂量有所不同。实验中选用的工具药p-MPPF是高选择性的5-HT1A受体的拮抗剂,比p-MPPI活性更强。在预实验中,单独it p-MPPF的剂量达到 12.5 μg/只,除 1只小鼠有尿失禁现象外,其它小鼠自主活动正常,无兴奋、惊厥现象。逐渐降低p-MPPF剂量至6 μg/只,仍可明显拮抗Iso的镇痛作用,故本研究中工具药 p-MPPF it最高剂量为6 μg/只。
分布于脊髓的5-HT1受体亚型主要有5-HT1A、5-HT1B、5-HT1C和 5-HT1D受体,研究发现[13],脊髓背角神经元上的5-HT1A受体与伤害性信号传导过程密切相关。在甩尾实验[10]、福尔马林实验[11]和电刺激实验中[12],it 5-HT产生的镇痛作用均可被5-HT1A受体阻断剂削弱或取消;it或脊髓微电泳5-HT1A受体激动剂也呈现出明显的抗伤害效应[16]。在福尔马林致痛实验中,对乙酰氨基酚的镇痛作用也被5-HT1A受体的阻断剂取消[13]。本研究结果表明,Iso体表抗伤害作用能够被it p-MPPF所拮抗,说明脊髓5-HT1A受体参与Iso镇痛过程,而且这种拮抗作用呈现出一定的剂量依赖关系。在扭体实验中,大剂量p-MPPF(6 μg)能拮抗Iso的镇痛作用,小剂量p-MPPF(3 μg)无作用,与其他两种方法实验结果对比,拮抗强度减弱。这可能与体表物理刺激和腹腔化学刺激的痛反射途径不同有关。脊髓5-HT1A受体可能是Iso对体表热刺激产生镇痛作用的重要靶位,而与Iso对抗内脏化学刺激作用关系不大。
与以上结果不同,另一些研究显示[17],it 5-HT1A受体激动剂8-OH-DPAT和Buspirone可明显增强小鼠的甩尾反射,提示5-HT1A受体介导了痛觉的易化效应。这可能是由于给药方式、用药剂量、工具药的特异性以及观察指标和实验过程等的差异引起的。诚如Grasshoff所言[18],疼痛的产生及调控是涉及多部位多机制的复杂过程,因此吸入麻醉药镇痛作用的具体受体机制还有待进一步研究。
[1] 陈 䶮,李惠萍,戴体俊,等.士的宁敏感的甘氨酸受体对吸入麻醉药催眠和镇痛作用的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2007,23(5):604-7.
[1] Chen Y,Li H P,Dai T J,et al.Effects of strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor on the hypnotic and analgesic effects of inhalation anesthetics[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2007,23(5):604 -7.
[2] 杭黎华,戴体俊,曾因明.鞘内注射NMDA拮抗吸入麻醉药的镇痛作用[J].中国药理学通报,2005,21(9):1062 -5.
[2] Hang L H,Dai T J,Zeng Y M.Effects of intrathecal injection of NMDA on the analgesia of inhalation anesthetics[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2005,21(9):1062 -5.
[3] 杭黎华,邵东华,杨映红,等.AMPA对吸入麻醉药催眠、镇痛作用的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2007,23(12):1571 -5.
[3] Hang L H,Shao D H,Yang Y H,et al.Effcets of AMPA on the hypnotic and analgesic effects of inhalation anesthetics[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2007,23(12):1571 -5.
[4] 闫 肃,戴体俊,曾因明.鞘内注射烟碱对异氟烷、七氟烷镇痛作用的影响[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2008,14(6):352 -5.
[4] Yan S,Dai T J,Zeng Y M.Effects of intrathecal injection of nicotine on the analgesic actions of isoflurane and sevoflurane[J].Chin J Pain Med,2008,14(6):352 -5.
[5] 闫 肃,戴体俊,曾因明.神经元烟碱受体与异氟烷、七氟烷催眠和镇痛作用的关系[J].中国药理学通报,2008,24(3):318-22.
[5] Yan S,Dai T J,Zeng Y M.Relationship between neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and the hypnotic and analgesic effects of isoflurane and sevoflurane[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2008,24(3):318-22.
[6] 张 虹,彭春龙,姜梦露,等.鞘内注射育亨宾对异氟烷镇痛作用的影响[J].徐州医学院学报,2008,28(10):664 -6.
[6] Zhang H,Peng C L,Jiang M L,et al.The effect of intrathecal injection with yohimbin on the analgesia of isoflurane[J].Acta Acad Med Xuzhou,2008,28(10):664 -6.
[7] 马 涛,戴体俊,王 丹,等.异氟烷体表抗伤害作用与脊髓α2受体的关系[J].中国医药导报,2009,6(36):17 -9.
[7] Ma T,Dai T J,Wang D,et al.The relationship between the surface antinociceptic effects of isoflurane and α2adrenoceptors in spinal cord[J].China Med Herald,2009,6(36):17 -9.
[8] 闫 肃,戴体俊,程 伟.全身麻醉药镇痛作用受体机制的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2008,24(10):1272 -5.
[8] Yan S,Dai T J,Cheng W.Research progress on receptor mechanisms of analgesia of general anesthetics[J].Chin Pharmacol Bull,2008,24(10):1272 -5.
[9] Calejesan A A,Chang M H,Zhuo M.Spinal serotonergic receptors mediate facilitation of a nociceptive reflex by subcutaneous formalin injection into the hindpaw in rats[J].Brain Res,1998,798(1 -2):46-54.
[10]Xu W,Qiu X C,Han J S.Serotonin receptor subtypes in spinal antinociception in the rat[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,1994,269(3):1182-9.
[11]Korzeniewska I,P'|a'znik A.Influence of serotonergic drugs on restraint stress induced analgesia[J].Pol J Pharmacol,1995,47(5):381-5.
[12]Nadeson R,Goodchild C S.Antinociceptive role of 5-HT1Areceptors in rat spinal cord[J].Br J Anaesth,2002,88(5):679 -84.
[13]Gjerstad J,Tjolsen A,Hole K.The effect of 5-HT1Areceptor stimulation on nociceptive dorsal horn neurones in rats[J].Eur J Pharmacol,1996,318(2 -3):315 -21.
[14]宋必卫,徐叔云,马传庚,等.镇痛药物实验法[M]//徐叔云,卞如濂,陈修主编.药理实验方法学.3版,北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:882-95.
[14]Song B W,Xu S Y,Ma C G,et al.Experimentations of analgesic drugs[M]//Xu S Y,Bian R L,Chen X,chief editor.Emethodology of pharmacological experiment.3rd ed,Beijing:People's Sanitation Press,2002:882 -95.
[15]Hylden J L,Wilcox G L.Intrathecal morphine in mice:a new technique[J].Eur J Pharmacol,1980,67(2 -3):313 -6.
[16]Millan M J,Seguin L,Honore P,et al.Pro-and antinociceptive actions of serotonin(5-HT)1Aagonists and antagonists in rodents:relationship to algesionmetric paradigm[J].Behav Brain Res,1996,73(1-2):69-77.
[17]Alhaider A A,Wilcox G L.Differential roles of 5-Hydroxytryptamine1Aand 5-Hydroxytryptamine1Breceptor subtypes in modulating spinal nociceptive transmission in mice[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,1993,265(1):378-85.
[18]Grasshoff C,Rudolph U,Antkowiak B.Molecular and systemic mechanisms of general anaesthesia:the multi-site and multiple mechanisms'concept[J].Curr Opin Anaesthesiol,2005,18(4):386-391.

