一类指数型三种群差分生态系统的动力学行为





摘要:种群动力学作为生态系统的一个重要分支,日益受到广大学者的关注。单种群及两种群的差分生态系统的研究已取得一些重要成果,但对三种群生态差分系统的研究工作还未见发表。本文研究一类指数型三种群生物差分系统。首先,利用迭代方法及不等式技巧证明了该系统的每一个正解都是持久的和有界的;其次,利用不动点理论证明了该系统正平衡点的存在性;最后,利用线性化理论、Rouche定理及李亚普诺夫稳定性理论获得了确保该生态系统正平衡点渐近稳定的若干充分条件。所得结论推广了参考文献[20-24]中的相应结果。
关键词:生态系统;有界性;持久性;平衡点;稳定性
中图分类号: O241.84 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-2443(2024)04-0306-08
引 言
数学模型已经被广泛研究,因为它们可以描述生物学、生态学、物理学、经济学等领域的许多现实生活问题[1-3]。近年来,随着生物技术的快速发展,生物数学模型受到了数学和生物工作者的广泛关注[4-8]。差分方程作为一种重要的生物数学模型,可用于描述种群生物学中的真实情况[9-10]。最近,人们对指数型差分方程组进行了充分的研究[11-13]。尽管差分方程的形式非常简单,但要彻底理解其解的动力学行为是极其困难的[14-19]。有许多论文与指数型生态差分系统有关,例如,El Metwally等[20]研究了以下单物种差分种群模型
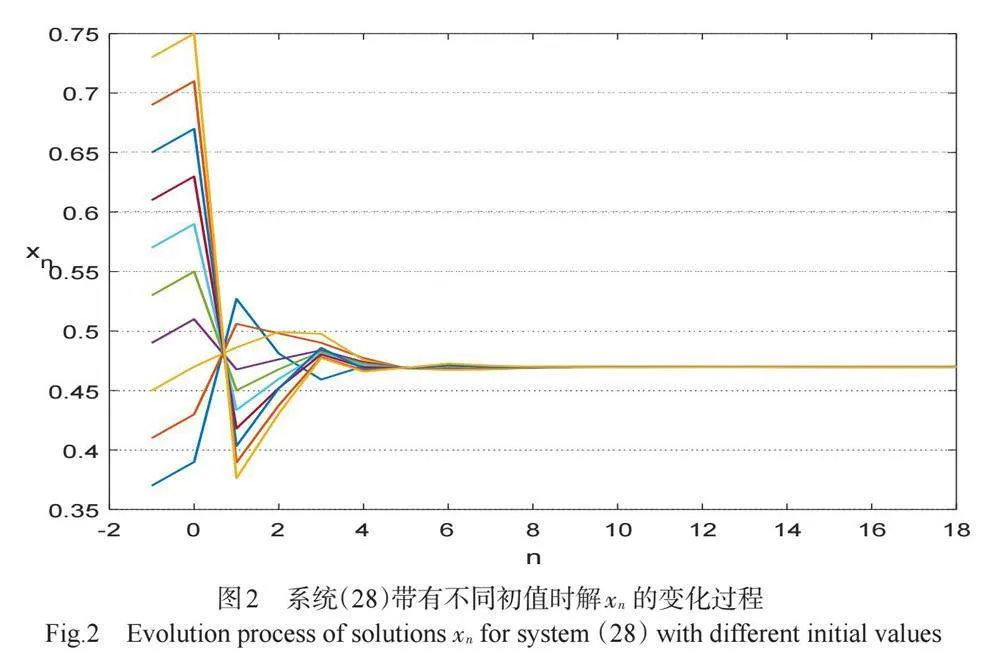
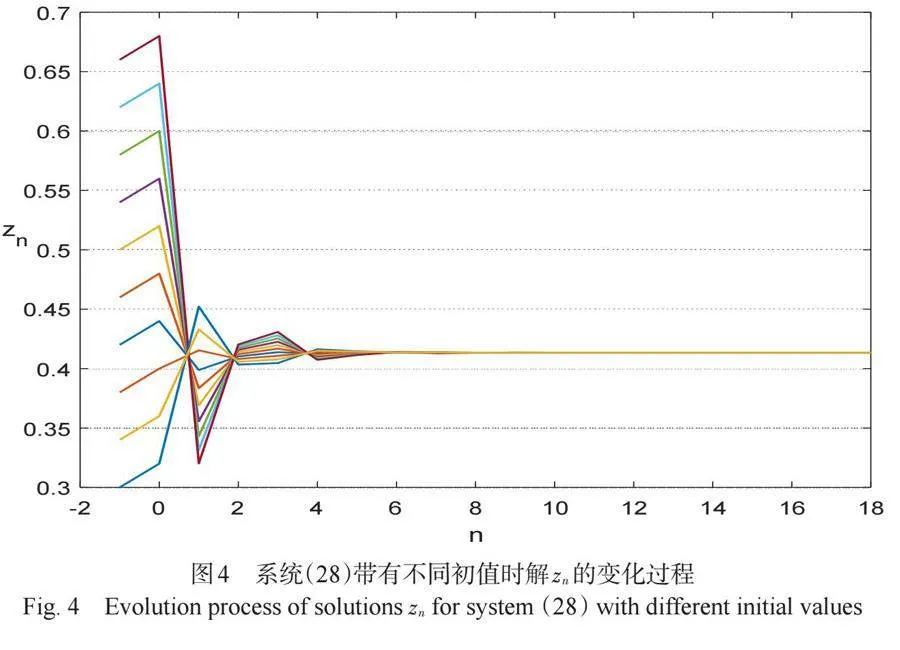
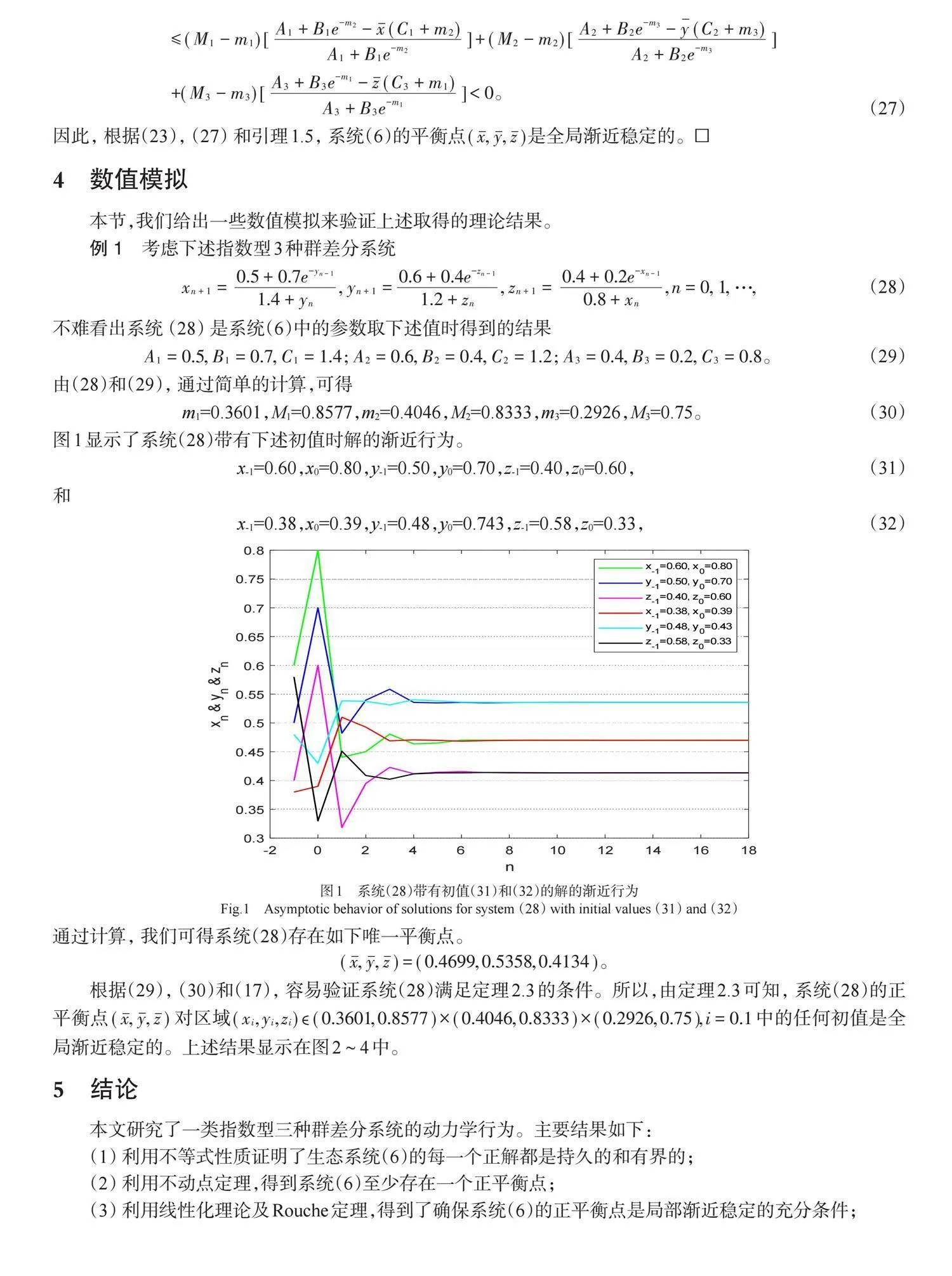
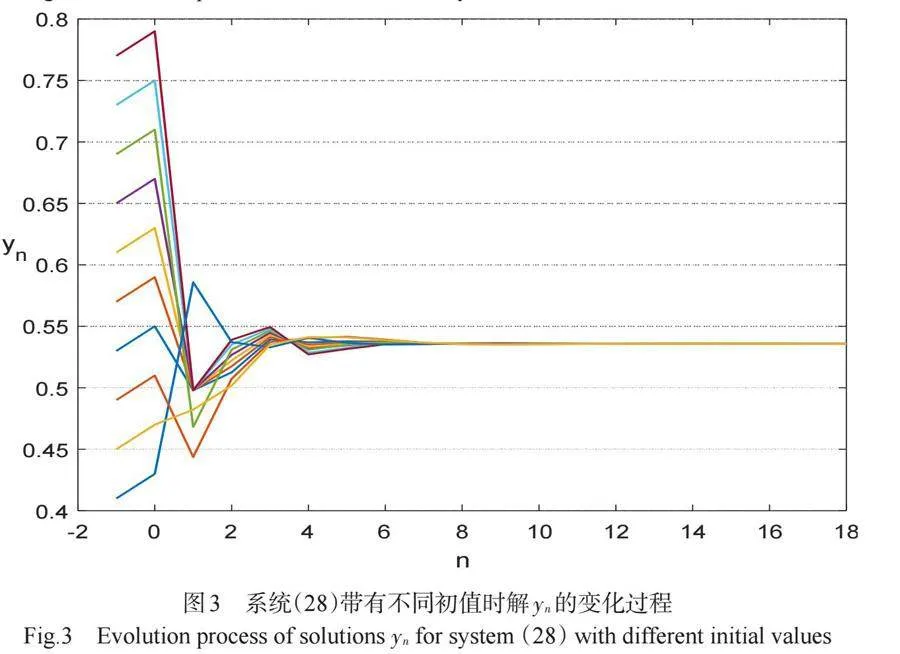
根据(29), (30)和(17), 容易验证系统(28)满足定理2.3的条件。所以,由定理2.3可知, 系统(28)的正平衡点[(x, y, z)] 对区域[(xi,yi,zi)ϵ(0.3601,0.8577)×(0.4046,0.8333)×(0.2926,0.75),i=0.1]中的任何初值是全局渐近稳定的。上述结果显示在图2~4中。
5 结论
本文研究了一类指数型三种群差分系统的动力学行为。主要结果如下:
(1) 利用不等式性质证明了生态系统(6)的每一个正解都是持久的和有界的;
(2) 利用不动点定理,得到系统(6)至少存在一个正平衡点;
(3) 利用线性化理论及Rouche定理,得到了确保系统(6)的正平衡点是局部渐近稳定的充分条件;
(4) 利用李亚普诺夫稳定性定理,得到了确保系统(6)的正平衡点是全局渐近稳定的充分条件;
(5) 通过数值算法验证了所得理论结果的正确性。
所得结论推广了参考文献[20-24]中的相应结果。另外,本文的方法可用于研究类似的多种群差分系统。
参考文献:
[1] BRAUER F,CHAVEZ CC. Mathematical Models in Population Biology and Epidemiology[M].New York:Springer Verlag, 2001:3-47.
[2] WANG C Y, WANG S. Oscillation of partial population model with diffusion and delay[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2009, 22: 1793-1797.
[3] ELSAYEDE M, ALZAHRANI F, ABBAS I, et al. Dynamical behavior and solution of nonlinear difference equation via Fibonacci sequence[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2020, 10: 282-296.
[4] WANG C Y, WANG S, YANG F P, et al. Global asymptotic stability of positive equilibrium of three-species Lotka-Volterra mutualism models with diffusion and delay effects[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2010, 34: 4278-4288.
[5] ZHANG Y J, WANG C Y. Stability analysis of n-species Lotka-Volterra almost periodic competition models with grazing rates and diffusions[J]. International Journal of Biomathematics, 2014, 7(2): Article ID: 1450011.
[6] WANG C Y, LI L R, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Dynamical behavior of a Lotka-Volterra competitive-competitive-cooperative model with feedback controls and time delays[J]. Journal of Biological Dynamics, 2019, 13: 43-68.
[7] VARGAS-DE-LEON C. Global stability of nonhomogeneous coexisting equilibrium state for the multispecies Lotka-Volterra mutualism models with diffusion[J]. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2022, 45: 2123-2131.
[8] CHEN X S, LUO D M. Dynamical analysis of an almost periodic multispecies mutualism system with impulsive effects and time delays[J]. Filomat, 2023, 37: 551-565.
[9] KOCIC V L, LADAS G. Global Behavior of NonLinear Difference Equations of Higher Order with Applications[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1993:1-26.
[10] ELAYDI S. An Introduction to Difference Equations[M]. third ed, New York: Springer, 2005:10-38.
[11] PAPASCHINOPOLUOS G, SCHINAS C J. On the dynamics of two exponential type systems of difference equations[J]. Computational & Applied Mathematics, 2012, 64: 2326-2334.
[12] KHAN A Q, QURESHI M N. Behavior of an exponential system of difference equations[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2014, Article ID: 607281.
[13] KHAN A Q,NOORANI M S M, ALAYACHI H S. Global dynamics of higher-order exponential systems of difference equations[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2019, Article ID: 3825927.
[14] ELSAYED E M. Solutions of rational difference system of order two[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2012, 55: 378-384.
[15] WANG C Y, FANG X J, LI R. On the solution for a system of two rational difference equations[J]. Journal of Computational Analysis and Applications, 2016, 20: 175-186.
[16] TASKARA N, TOLLU D T, TOUAFEK N, et al. A solvable system of difference equations[J]. Communications of the Korean Mathematical Society, 2020, 35: 301-319.
035781a44e85aa2e97927c9f2b468e548f4dc76535e48602d601bd44ca99c2f4[17] WANG C Y, LI J H,. Dynamics of a high-order nonlinear fuzzy difference equation[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2021, 11: 404-421.
[18] JIA L L , WANG C Y, ZHAO X J, et al. Dynamic behavior of a fractional-type fuzzy difference system[J].Symmetry, 2022, 14: Article ID:1337.
[19] JIA L L , ZHAO X J , WANG C Y ,et al. Dynamic behavior of a seven-order fuzzy difference system[J]. Journal of Applied Analysis and Computation, 2023, 13(2): 486-501.
[20] EL-METWALLY H,GROVE E A, LADAS G, et al. On the difference equation [xn+1=α+βxn-1e-xn][J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory Methods and Applications, 2001, 47: 4623- 4634.
[21] WANG W, FENG H. On the dynamics of positive solutions for the difference equation in a new population model[J]. Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Applications, 2016, 9: 1748-1754.
[22] OZTURK I, BOZKURT F, OZEN S. On the difference equation[yn+1=(α+β e-yn)/][(γ+yn-1)][J].Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2006, 181: 1387-1393.
[23] PAPASCHINOPOLUOS G, RADIN M A, SCHINAS C J. Study of the asymptotic behavior of the solutions of three systems of difference equations of exponential form[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2012, 218: 5310-5318.
[24] THAI T H, DAI N A, ANH P T. Global dynamics of some system of second-order difference equations[J]. Electronic Research Archive, 2021, 29: 4159-4175.
[25] SEDAGHAT H. Nonlinear difference equations: theory with applications to social science models[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2003:3-11.
[26] CAMOUZIS ,LADAS E G. Dynamics of third-order rational difference equations: with open problems and conjectures[M]. Boca Raton :Chapman and Hall/HRC,2007:3-28.
On the Dynamic Behavior of a Type of Exponential Three Populations Differential Ecosystem
WANG Chang-you 1, YANG Tao 1, CHEN Hua 2, WANG Qi-yu 1
(1. College of Applied Mathematics, Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu 610225, China;2. College of Marxism, Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China)
Abstract: Population dynamics, as an important branch of ecosystems, is increasingly receiving attention from scholars. Significant achievements have been made in the study of differential ecosystems of single and two populations, but research on differential ecosystems of three populations has not yet been published. In this paper, we study a class of exponential 3 populations biological differential systems. Firstly, we use iterative methods and inequality techniques to prove that every positive solution of the system is persistent and bounded. Secondly, the existence of a positive equilibrium point of the system is proved, using fixed point theory. Finally, using linearization theory, Rouche theorem and Lyapunov stability theory, we provide sufficient conditions for the asymptotic stability of the positive equilibrium point of the ecosystem. The obtained conclusion extends the corresponding results in references [20-24].
Key words: ecosystem; boundedness; persistence; equilibrium point; stability
(责任编辑:马乃玉)

