玉米免耕播种机振动特性及对排种器排种性能的影响
张红梅 张晨明 朱晨辉 祝英豪 李志杰 李鹏昌

摘要:為研究玉米免耕播种机振动特性以及振动对排种器漏播指数和重播指数的影响,搭建一套由振动加速度传感器、电荷放大器、USB采集卡组成的播种作业振动测试系统,在玉米免耕播种机免耕地表作业时进行振动测试采集播种作业的振动信号。因田间工作环境复杂,使用经典滤波法中的IIR滤波器滤除所采集振动信号中其他高频干扰信号,对田间采集振动信号进行时域分析,均方值作为时域分析指标值。结果表明:振动加速度均方根随着作业速度和旋耕机转速的增加呈线性增加,旋耕机转速和作业速度是引起玉米免耕播种机振动的主要因素,影响顺序为:旋耕机转速>作业速度。使用二次积分法对田间采集信号进行分析,得出播种机作业时最大振动位移为16.004mm,对振动信号进行频域分析,使用直接法求出功率谱密度。结果表明:玉米免耕播种机振动频率主要在0~100Hz之间,频率分布与旋耕机转速影响较大。根据田间振动信号所得工作参数搭建振动试验台,以播种机振动频率、振动幅值、作业速度为试验因素,合格指数、漏播指数为评价指标进行3因素3水平响应面试验。结果表明:作业速度、振动幅值和振动频率对合格指数和漏播指数影响较为显著。各因素对合格指数影响顺序为:振动幅值、作业速度、振动频率;各因素对漏播指数影响顺序为:振动幅值、振动频率、作业速度。研究结果可为降低玉米免耕播种机振动和优化指夹式排种器提供理论参考。
关键词:玉米免耕播种机;指夹式排种器;振动;时频分析;排种性能
中图分类号:S223
文献标识码:A
文章编号:2095-5553 (2024) 05-0001-08
收稿日期:2022年8月31日 修回日期:2022年12月5日*基金项目:河南省现代农业产业技术体系玉米全程机械化专项(HARS—22—02—G4)
第一作者:张红梅,女,1977年生,河南驻马店人,博士,教授;研究方向为智能农业装备技术。E-mail: hmzh86022625@sina.com
通讯作者:朱晨辉,男,1989年生,河南开封人,博士,讲师;研究方向为农业机械化及其自动化。E-mail: zhuchenhui@126.com
Analysis of vibration characteristics of corn no-till seeder and
its influence on seed metering performance
Zhang Hongmei, Zhang Chenming, Zhu Chenhui, Zhu Yinghao, Li Zhijie, Li Pengchang
(College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, 450002, China)
Abstract:
In order to study the vibration characteristics of maize no-tillage seeder and the influence of vibration on the leakage index and reseeding index of the seeder, a vibration test system composed of vibration acceleration sensor, charge amplifier and USB acquisition card was set up. A vibration test was carried out to collect the vibration signal of the sowing operation during the no-tillage surface operation of the corn no-till planter. Due to the complex working environment in the field, the IIR filter in the classical filtering method was used to filter out other high-frequency interference signals of the collected vibration signals. The time domain analysis was carried out on the vibration signals collected in the field, and the mean square value was used as the time domain analysis index value. The analysis results showed that the root mean square of vibration acceleration increased linearly with the increase of operating speed and rotational speed of rotary tillage, and the rotational speed and operating speed of rotary tillage were the main factors that caused the vibration of corn no-till planter. The order of influence was: rotary tillage speed > working speed. Through using the quadratic integration method to analyze the collected signals in the field, it was concluded that the maximum vibration displacement of the planter was 16.004 mm. The vibration signal was analyzed in the frequency domain, and the power spectral density was obtained by the direct method. The results showed that the vibration frequency of the corn no-till planter was mainly between 0-100 Hz. The frequency distribution and rotary tillage speed had a great influence. According to the working parameters obtained from the field vibration signal, a vibration test bench was built, and the vibration frequency, vibration amplitude and working speed of the seeder were used as test factors, and the pass index and missed seeding index were used as evaluation indicators to conduct a three-factor and three-level response surface test. The analysis results showed that the working speed, vibration amplitude and vibration frequency had significant effects on the pass index and missed broadcast index. The order of the influence of each factor on the qualification index was: vibration amplitude, working speed and vibration frequency, the order of each factor on the missed seeding index was: vibration amplitude, vibration frequency and working speed. The research results of this paper can provide theoretical reference for reducing the vibration of maize no-till seeder and optimizing the finger clip seed feeder.
Keywords:
corn no-tillage seeder; finger-clip seed metering device; vibration; time-frequency analysis; seeding performance
0 引言
玉米免耕播种机在田间地表的不平度、机具的振动载荷、拖拉机行走速度等多种因素导致了玉米的均匀性与合格指数降低[1, 2]。
近几年,国内外学者对振动对播种性能的影响进行了研究。张涛等[3]通过对田间作业时免耕播种机排种器振特性测试与分析,运用离散元软件模拟了玉米种群的运动规律。王奇等[4]建立免耕播种机的振动特性模型,求解其稳态振动响应。Liu等[5]采用正交试验的方法对播种机振动特性进行研究,结果表明播种机作业前进速度为7km/h时振动较大。廖宜涛等[6]通过振动台架试验发现吸种负压和振动频率对气力式排种器合格指数影响较大。黄与霞等[7]通过振动试验,得出振动幅值、作业速度与振动频率对勺轮式排种器播种质量的影响。
玉米免耕播种机在开沟器前增加了圆盘锯齿开沟器装置,作业时振动对播种质量影响较大。本文以带旋耕刀的免耕播种机作为研究对象,通过对整机工作原理及结构的分析,采集播种机实际田间工作时的振动信号进行振动的影响因素分析,并在实验室搭建振动试验台,探究各因素对指夹式排种器播种质量的影响,为改进播种机整体结构和优化指夹式排种器提供理论依据。
1 免耕播种机结构和工作原理
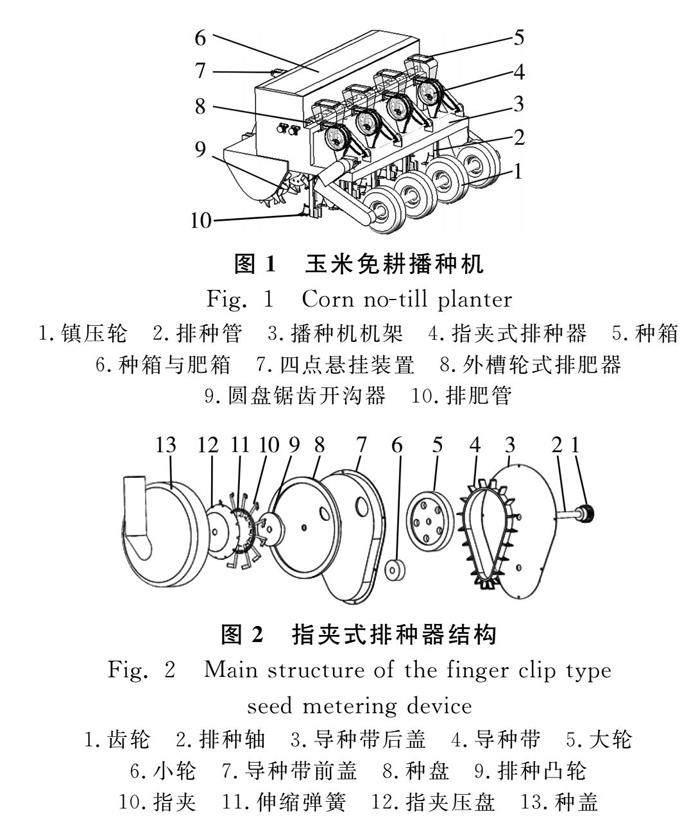
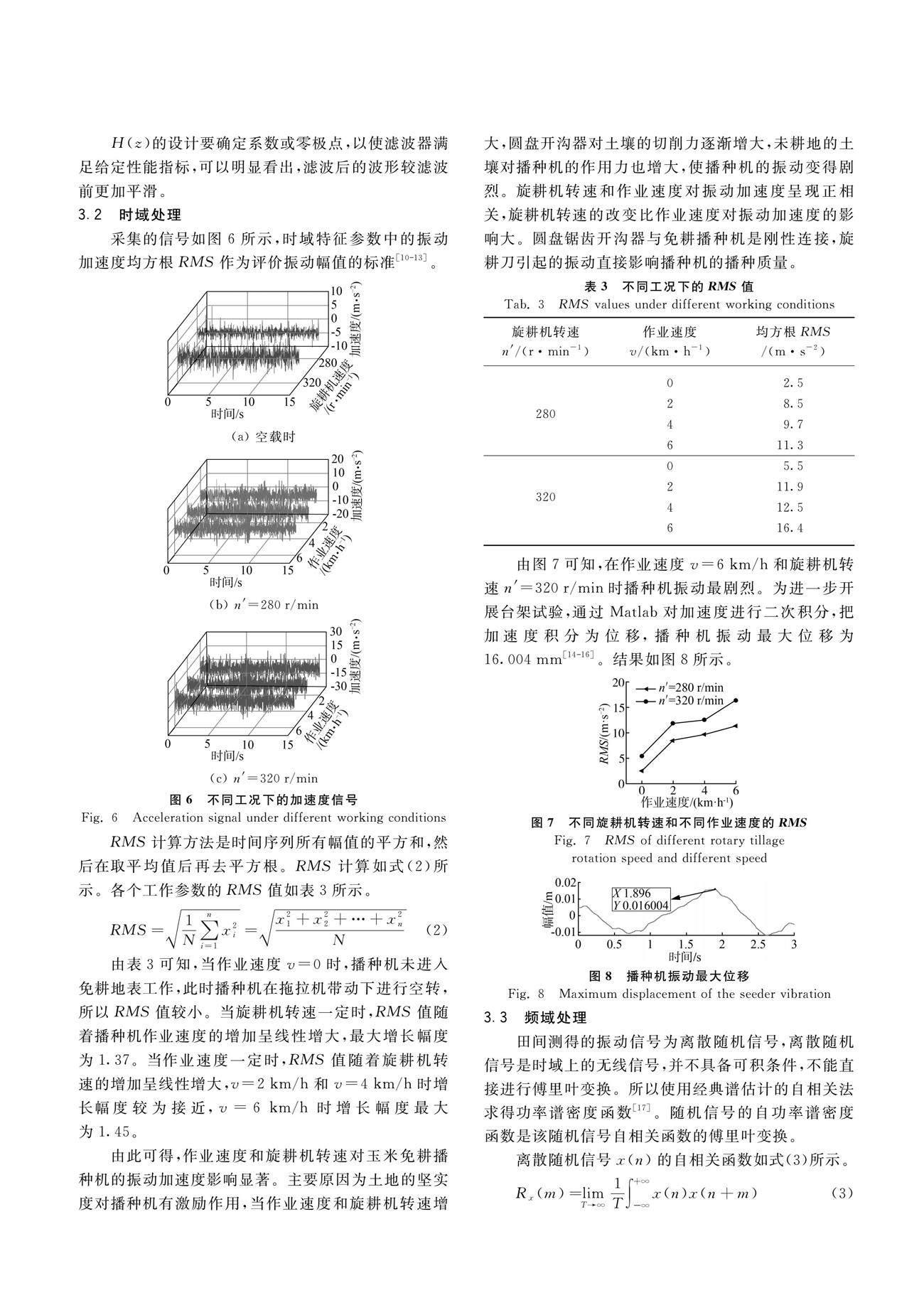
玉米免耕播种机如图1所示。主要由机架、旋耕装置、播种排肥装置和覆土镇压装置组成,由四点悬挂和万向节联轴器与拖拉机相连。旋耕装置采用了圆盘锯齿开沟器,通过内翻刀和外翻刀形成一定夹角,将残留的秸秆进行二次粉碎翻到背垄上,使种子着床到净土上,保证种子出苗率。播种装置是由种箱和肥箱、排种器和排肥器、输种管、开沟器组成。图2为指夹式排种器结构。
2 免耕播种机田间测试
1) 机具与地表相关参数。2021年6月12日在河南省周口市商水县河南农业大学商水试验田进行田间测试,前茬作物为小麦,土壤特质为潮土,拖拉机选用CHERY RC1004 4×4轮式拖拉机,机具与地表相关参数见表1。
2) 测试方法。本次振动测试试验使用单向电荷型加速度传感器,灵敏度为100.08mV/g,加速度可测范围为-50~+50g,采样率设置为1000Hz(采样时间间隔为0.001s),PC计算机的DAQ软件控制数据采集过程[8]参数如表2所示。
3) 试验方案。本次振动测试选用加速度传感器[9],固定在种箱后方,如图3所示。因机械式排种器作业速度最佳在2~6km/h之内,作业速度v选择2km/h、4km/h、6km/h,拖拉机转速选择1500~2300r/min。旋耕机转速n′选择280~320r/min。
通过更换拖拉机不同挡位调整作业速度和旋耕机转速,在拖拉机带动免耕播种机平稳工作时开始测试,采集15s的振动数据。每种工况下进行5次重复试验,后续振动信号由Matlab进行滤波和时频分析,振动测试现场如图4所示。
3 振动信号处理
3.1 滤波处理
在实际采集过程中,因大田工作环境复杂所以数据采集的振动信号包含了很多的噪声部分,使用经典滤波法中的IIR滤波器对信号进行滤波处理,减少干扰信号对真实数据的影响[8]。
IIR滤波器结构带有反馈环路,又称为递归型滤波器。IIR滤波器的N阶差分方程如式(1)所示。
根据回归曲线和表中的数据可得,影响合格指数的顺序为:振动幅值、作业速度、振动频率;漏播指数的顺序为:振动幅值、振动频率、作业速度;为探究试验指标和各因素的影响关系,使用响应面法求解各因素之间的交互关系。固定一个因素为0水平。得到另外两因素响应面如图11所示。
作業速度和振动幅值对合格指数有交互作用。当振动幅值一定时,合格指数随着作业速度的增加而降低,且降低趋势逐渐增大;当作业速度一定时,合格指数随着振动幅值的增加而降低,且降低趋势逐渐减小的。振动幅值分别与作业速度和振动频率对漏播指数有交互作用。当振动幅值一定时,漏播指数随着作业速度的增大而增大,且上升趋势逐渐增大的;漏播指数随着振动频率的增大而增大的,且上升趋势逐渐增大;当作业速度和振动频率一定时,漏播指数随着振动幅值的增大而增大的,且上升趋势是平稳增大的。图12为通过延迟摄影功能拍摄漏种现象。
根据各因素对合格指数和漏播指数的影响结果分析可得,对比无振动和振动条件下,振动的增加会使合格指数明显减小。对比三因素发现振动幅值是影响合格指数和漏播指数的主要因素,振动幅值的增加会使合格指数和漏播指数减小趋势增大。主要原因为:种子运动过程中受到重力、离心力、摩擦力和振动所给的竖直力的作用,当振动幅值增大时,种子所受的垂直加速度增大,使种子从指夹中脱落,产生漏播现象。如何使种子在振动条件下不脱落,是优化排种器结构的有效途径。试验结果为指夹式排种器优化提供理论依据。
5 结论
1) 搭建一套玉米免耕播种机振动测试系统,在免耕播种机工作时进行振动测试,并采集振动数据,分析不同作业速度和不同旋耕机转速信号。结果表明,旋耕机转速和作业速度对振动加速度影响较显著,旋耕机转速的振动加速度均方根最大增大倍数为1.45,作业速度的振动加速度均方根最大增大倍数为1.37,旋耕机转速比作业速度对播种机振动更显著。通过对振动加速度二次积分,播种机最大振动位移为16.004mm。
2) 不同工况下频域分析结果表明,免耕播种机的振动频率分布在0~100Hz,振动频率分布与旋耕机转速有关,与作业速度影响较小,旋耕刀振动基频为28.02~31.98Hz,二倍频为56.04~63.96Hz,三倍频为84.06~95.94Hz。在旋耕装置与播种机主体之间增加减震装置是降低播种机振动的有效途径。
3) 搭建振动试验台并开展排种器振动试验,把作业速度、振动幅值、振动频率作为主要试验因素,合格指數、漏播指数作为试验指标进行三因素三水平响应面试验。通过二次回归正交组合试验可得,作业速度、振动幅值和振动频率对合格指数和漏播指数影响显著。合格指数影响顺序为:振动幅值、作业速度、振动频率;漏播指数的顺序为:振动幅值、振动频率、作业速度。为优化指夹排种器关键部件,减小排种器漏播情况提供理论支撑。
参 考 文 献
[1] 伊力达尔·伊力亚斯, 朱思洪, 徐刚, 等. 拖拉机前桥悬架参数匹配及其对振动特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(10): 29-36.
Yilidaer·Yiliyasi, Zhu Sihong, Xu Gang, et al. Front axle suspension parameters match and its impact on vibration characteristics of tractor [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(10): 29-36.
[2] 程远盛, 李晓勤, 孙帅帅, 等. 田间长波路面不平度表达和分级的新方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(11): 180-188.
Cheng Yuansheng, Li Xiaoqin, Sun Shuaishuai, et al. A new method for expression and classification of long wave road surface unevenness in field [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(11): 180-188.
[3] 张涛, 刘飞, 赵满全, 等. 基于离散元的排种器排种室内玉米种群运动规律[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(22): 27-35.
Zhang Tao, Liu Fei, Zhao Manquan, et al. Movement law of maize population in seed room of seed metering device based on discrete element method [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(22): 27-35.
[4] 王奇, 朱龙图, 李名伟, 等. 指夹式玉米免耕精密播种机振动特性及对排种性能的影响 [J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(9): 9-18.
Wang Qi, Zhu Longtu, Li Mingwei, et al. Vibration characteristics of corn no-tillage finger-type precision planter and its effect on seeding performance [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(9): 9-18.
[5] Liu Y Q, Zhao M Q, Liu F, et al. Vibration test and analysis of no-tillage planter on the maize stubble surface [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 1061-1062: 788-793.
[6] 廖宜涛, 齐天翔, 廖庆喜, 等. 气力式油菜精量联合直播机振动特性及对排种性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(5): 1184-1196.
Liao Yitao, Qi Tianxiang, Liao Qingxi, et al. Vibration characteristics of pneumatic combined precision rapeseed seeder and its effect on seeding performance [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(5): 1184-1196.
[7] 黄与霞, 韩丹丹, 韩哲, 等. 振动对勺轮式排种器排种性能的影响试验[J]. 河南农业大学学报, 2021, 55(5): 896-905.
Huang Yuxia, Han Dandan, Han Zhe, et al. Experiment on the influence of vibration on the seeding performance of the scoop-wheel seed meter [J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University, 2021, 55(5): 896-905.
[8] 高志朋, 徐立章, 李耀明, 等. 履带式稻麦联合收获机田间收获工况下振动测试与分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(20): 48-55.
Gao Zhipeng, Xu Lizhang, Li Yaoming, et al. Vibration measure and analysis of crawler-type rice and wheat combine harvester in field harvesting condition [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(20): 48-55.
[9] 耿令新, 李康, 庞靖, 等. 基于时频和功率谱密度的移栽机振动特性测试与分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2021, 37(11): 23-30.
Geng Lingxin, Li Kang, Pang Jing, et al. Test and analysis of vibration characteristics of transplanting machine based on time frequency and power spectral density [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(11): 23-30.
[10] 高文英, 林静, 李宝筏, 等. 秸秆深埋还田机振动特性分析与结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 970-980.
Gao Wenying, Lin Jing, Li Baofa, et al. Vibration characteristics analysis and structural optimization of straw deep bury returning machine [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 970-980.
[11] Ku E. Field-scale evaluation of parameters affecting planter vibration in single seed planting [J]. Measurement, 2021, 184(109959).
[12] 赵瑞堃. 基于MATLAB的FIR和IIR数字滤波器的设计[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2012.
Zhao Ruikun. FIR and liR digital filter designing based on MATLAB [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2012.
[13] 桂水榮, 陈水生, 万水. 基于路面一致激励车桥耦合非平稳随机振动分析[J]. 振动·测试与诊断, 2018, 38(5): 908-915, 1077.
Gui Shuirong, Chen Shuisheng, Wan Shui. Analysis of non-stationary random vibration of vehicle-axle coupling based on uniform excitation of road surface [J]. Vibration·Testing and Diagnosis, 2018, 38(5): 908-915, 1077.
[14] 徐庆华. 试采用FFT方法实现加速度、速度与位移的相互转换[J]. 振动·测试与诊断, 1997(4): 30-34.
Xu Qinghua. Try to use FFT method to realize mutual conversion of acceleration, velocity and displacement [J]. Vibration·Test and Diagnosis, 1997(4): 30-34.
[15] 林楠, 李东升, 李宏男. 基于零初值的测试加速度积分速度与位移的方法[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2016, 46(6): 602-614.
Lin Nan, Li Dongsheng, Li Hongnan. Novel integration method of measured acceleration to velocity and displacement based on zero initial condition [J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2016, 46(6): 602-614.
[16] 王体强, 王永志, 袁晓铭, 等. 加速度积分位移方法影响因素与可靠性研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2021, 17(S1): 82-88, 107.
Wang Tiqiang, Wang Yongzhi, Yuan Xiaoming, et al. Influencing factors and reliability study on double integral of acceleration measurement for displacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2021, 17(S1): 82-88, 107.
[17] 姚艳春, 杜岳峰, 朱忠祥, 等. 基于模态的玉米收获机车架振动特性分析与优化[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(19): 46-53.
Yao Yanchun, Du Yuefeng, Zhu Zhongxiang, et al. Vibration characteristics analysis and optimization of corn combine harvester frame using modal analysis method [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(19): 46-53.
[18] 散鋆龙, 杨会民, 王学农, 等. 振动方式和频率对杏树振动采收响应的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(8): 10-17.
San Yunlong, Yang Huimin, Wang Xuenong, et al. Effects of vibration mode and frequency on vibration harvesting of apricot trees [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(8): 10-17.
[19] 韩万水, 马麟, 院素静, 等. 路面粗糙度非一致激励对车桥耦合振动系统响应影响分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2011, 44(10): 81-90.
Han Wanshui, Ma Lin, Yuan Sujing, et al. Analysis of the effect of inconsistent stimulus of surface roughness on vehicle-bridge coupling vibrations [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(10): 81-90.
[20] 姜鑫銘. 玉米免耕播种机精确播种关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
Jiang Xinming. Study on key technologies of precision seeding for maize no-tillage planter [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
[21] Hostens I, Anthonis J, Kennes P, et al. PM—power and machinery: Six-degrees-of-freedom test rig design for simulation of mobile agricultural machinery vibrations [J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 2000, 77(2): 155-169.

