A New Flavonoid Glycoside from Polygonum capitatum
Lei HE, Yan LIN, Minghui HE, Bo TU
1. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550025, China; 2. Engineering Research Center of Chronic Disease Prevention and Treatment of Authentic Medicinal Materials for Institutions of Higher Education in Guizhou Province, Guiyang 550025, China
Abstract [Objectives] To discover novel compounds with significant anti-inflammatory activity in the alcohol extract of Polygonum capitatum. [Methods] Firstly, a new flavonoid glycoside,capitaone B (1), was isolated from the ethyl acetate extract from P. capitatum, and then 27 compounds were screened using NO anti-inflammatory activity model. [Results] Four compounds, such as kaempferol (12), 1,2, 6-trigalloyl-β-d-glucose (15), catechin (16) and β-sitosterol (26), could significantly inhibit LPS-induced NO production in macrophages, with IC50 values of 15.31, 8.43, 6.92 and 5.72 μM, respectively. [Conclusions] The chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of P. capitatum were preliminarily studied, and the results provide a theoretical basis for further research on the action mechanism of subsequent anti-inflammatory active compounds of P. capitatum.
Key words Polygonum capitatum, Chemical composition, Anti-inflammatory activity
1 Introduction
Miao medicinePolygonumcapitatum, which is the dried whole grass or above-ground part ofPolygonumcapitatumBuch.-Ham.ex D. Don of Polygonaceae, is mainly distributed in the southwest of China. It was first reported in theAnnalsofTraditionalChineseMedicineofGuangxi[1], and is now recorded in theQualityStandardofTraditionalChineseMedicinalMaterialsandEthnicMedicinalMaterialsofGuizhouProvince(2003 edition)[2]and theStandardofTraditionalChineseMedicinalMaterialsofHunanProvince(2009 edition)[3]. In theChineseHerbalMedicineofGuangxi[4], it is recorded that it has the effect of detoxification and diminishing inflammation, and is mainly used in the treatment of dysentery, skin ulcers, and unidentified swelling poison. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that it has the function of clearing heat and damp, promoting blood circulation and relieving pain, and is often used in the treatment of dysentery, heat strangury, blood strangury, stone strangury, rheumatic arthralgia, trauma, mumps, eczema, pyelonephritis, cystitis, urinary calculi and other diseases[5].
P.capitatummainly contains flavonoids, lignin, phenols and other compounds[6-7], and these components have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antioxidant and anti-tumor biological activities[7-10]. Among them, phenolic acids and flavonoids have significant activities. We found that the alcohol extract of Miao medicineP.capitatumhas strong anti-inflammatory activity in previous systematic studies[11-14]. Therefore, in order to further develop and utilize this medicinal plant, 27 compounds were isolated from the alcohol extract of Miao medicineP.capitatum, one of which was a new compound. Then, 27 chemical components were screened by using the NO anti-inflammatory activity model to find the monomer compounds with significant anti-inflammatory activity in the alcohol extract.
2 Instruments and reagents
Main instruments included YMC-Pack ODS-A column (5 μm, 10 mm× 250 mm, YMC Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan), Nexus 470 FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Nicolet NEXUS 470 FT-IR, Nicolet Inc., Madison, WI, USA), Aglient 1260 high performance liquid chromatograph (Agilent Corporation, USA), semi-preparative liquid chromatograph (Cypress Technology Co., Ltd.), ultra-high performance liquid chromatocl-ion trap time-of-flight high resolution mass spectrometry (Shimadzu UPH-IT-TOF, Shimadzu Corporation, Japan), 600M superconducting nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (BPUKER 600M NEO NMR, Bruker GMBH, Germany), column chromatography silica gel (100-200 mesh or 200-300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical Plant), Sephadex LH-20 gel (Pharmacia Company), thin layer chromatography silica gel GF254(Yantai Jiangyou Silica Gel Development Co., Ltd.), electronic balance (Shanghai Zhuojing Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., BSM-220), carbon dioxide cell incubator (Sanyo, Japan), ultra-clean workbench (Sujing Antai, Suzhou), Multiskan enzyme-linked immunometric meter (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Finland), Tyrosinase (1:250, trypsin) (Gibco, Maryland, USA), DMEM medium, fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Hyclone, Utah, USA), nitric oxide (NO) detection kit (Biyuntian, Jiangsu), and positive drug curcumin (Nanjing Zelang Medical Technology Co., Ltd.). All other reagents are analytically pure reagents.
3 Medicinal materials and sample preparation
P.capitatumwas collected from Qianxi County, Bijie City, Guizhou Province in October 2020, and was identified as a dry whole grass ofP.capitatumby the members of the research group by using ITS sequence for DNA barcode analysis according to its traits[15]. The medicinal materials were crushed into coarse powder after being dried, and soaked in 95% ethanol twice for 10 d each time. They were soaked in 75% ethanol once for 10 d. After the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, the extract was dispersed with distilled water, and then extracted with ethyl acetate. The filtrate was concentrated under vacuum and reduced pressure to obtain its ethyl acetate extract.
The ethyl acetate extract repeatedly flowed through silica gel column chromatography, polyamide column chromatography, LH-20 column chromatography, and a new compound capitaone B (1) was obtained after semi-preparative liquid phase purification. In addition, the 26 compounds used in this study were obtained from the ethyl acetate extract in the previous stage. Details of these 27 compounds are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Information of the 27 compounds from Polygonum capitatum
4 Structural identification of the new compound
Compound 1 was obtained as a yellow amorphous powder. Based on13C NMR data and HR-ESI-MS spectrum, its molecular formula was determined to be C32H32O16. The degrees of unsaturation of compound 1 was 13, and the molecular ion peak wasm/z673.084 2[M+H]+in the HR-ESI-MS spectrum (Calcd. for C32H32O16, 672.084 2). First of all, The 1H NMR data (Table 1) of compound 1 showed signals for aromatic protons at[δH7.53 (1H, d, J=2.4 Hz,H-2′ ), 6.83 (1H, d, J=8.4 Hz, H-5′ ), 7.67 (1H, brs, H-6′ ), 6.41 (1H, d, J=1.8 Hz, H-8), 6.20 (1H, d, J=1.8 Hz, H-6), 5.39 (1H, d, J=7.8 Hz, H-1′′′′), 3.57 (1H, t, J=8.4 Hz, H-2′′′′), 3.37 (1H, m, H-3′′′′), 3.65 (1H, d, J=2.8 Hz, H-4′′′′), 3.31 (2H, m, H-5′′′′), 3.46 (2H, m, H-6′′′)], along with13C-NMR spectrum signals of δC 156.2 (H-2), 133.5 (H-3), 177.5 (H-4), 161.3 (H-5), 98.7 (H-6), 164.4 (H-7), 93.6 (H-8), 156.3 (H-9), 103.9 (H-10), 116.0 (C-2′), 144.9 (C-3′), 148.6 (C-4′),115.2 (C-5′), 122.1 (C-6′), 101.8 (C-1′′′′), 71.2 (C-2′′′′), 73.2 (C-3′′′′), 68.0 (C-4′′′′), 75.9 (C-5′′′′), and 60.2 (C-6′′′′). According to the signal analysis described above and the literature[16]. The skeleton structure of quercetin 3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside was confirmed. Furthermore, the 1H NMR spectrum showed the presence of one 1,3,4,5-tetrasubstituted phenyl group[δH7.73 (1H, d, J=3,5.4, H-2′′), 7.66 (1H, brs, H-6′′)], and one butyl ester[δH 4.22 (2H, t, J=6.6, H-2′′′), 1.64 (2H, brs, H-3′′′), 1.37 (2H, brs, H-4′′′), 0.91 (2H, t, J=9.6, H-5′′′)], and the HMBC spectrum showed that H-2′′ (δH7.73, 1H, brs) correlated with C-6′′ (δC131.8) and C-1′′′ (δC 167.0), and H-6′′ correlated with C-5′′ (δC156.2). It was noteworthy that the mass spectral data and downfield chemical shifts of C-4′ (δC148.5) and C-1′′ (δC156.2) supported the linkage of 1,3,4,5-tetrasubstituted phenyl groups to C-4′. Meanwhile, C-4′′ (δC131.6), and C-5′′ (δC156.2) provided the presence of a hydroxyl group at C-4′′ and C-5′′. Further, the 1H-NMR spectrum showed signals of[δH 4.22 (2H, t, J=6.5 Hz), 1.64 (2H, m), 1.38 (2H, m), 0.91 (3H, t, J=7.4 Hz)], and also the HMBC correlations from H-2′′′ (δH4.22) to C-1′′′ (δC167.0), C-3′′′ (δC30.0), and C-4′′′ (δC18.7) respectively indicated that the n-butyl unit was attached in C-3′′. The resolved structures were also confirmed in the 1H-1H COSY spectrum. Thus, compound 1 was identified as quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside -4′-gallic butyl ester and was named capitaone B. The key HMBC and 1H-1H COSY correlations for compound 1 are shown in Fig.1. NMR data of compound 1 are shown in Table 2.
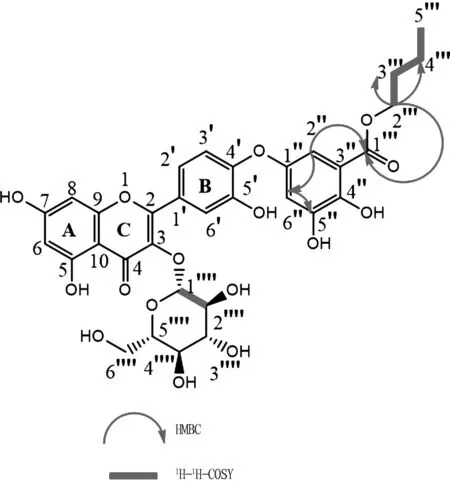
Fig.1 Key HMBC and 1H-1H COSY correlations for compound 1

Table 2 NMR data of compound 1 (1H: 600 MHz, 13C: 150 MHz, DMSO-d6)
5 Anti-inflammatory activity
5.1 Screening of anti-inflammatory activity of NOThe mouse mononuclear macrophage RAW264.7 model was used to screen anti-inflammatory activityinvitro. RAW264.7 cells were cultured until logarithmic growth stage, and then 100 μL of cell suspension (1×105cells/mL) was added to each well. The cells were cultured for 24 h in an incubator containing 5% CO2at 37 ℃. Afterwards, 1 μg/mL of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and 10 μM ofP.capitatummonomer compound (without serum) were added to each well, and 1 μL/mL of DMSO was added to the blank control group, while 10 and 20 μM of compounds were added to the positive control group. Each group had 3 multiple wells. Finally,ODvalue was measured with an enzyme-linked immunometric meter at 540 nm, and Gris reagents I and II were added respectively to calculate the inhibition rate of NO release. In the period, 50 μL of culture medium supernatant was absorbed and transferred to a new 96-well plate for operation.
5.2 ResultsAmong the 27 compounds ofP.capitatum, four compounds (12,15,16, and26) could significantly inhibit LPS-induced NO production in macrophages, and the inhibition rate reached more than 30% at 10 μM concentration (the inhibition rate of curcumin in positive control was 13.5% at 10 μM and 44.8% at 20 μM). The more active compounds were steroidal compounds, mainly including Stigmast-5-en-3-O-β-D-glucoside (15) and β-sitosterol (26), with inhibition rates of 39% and 45% at 10 μM, respectively. In addition to monomer compounds, the inhibitory effect of ethyl acetate extract ofP.capitatumon NO at 25 and 50 μg/mL was also evaluated (with inhibition rates of 17% and 51.4% at 25 and 50 μg/mL), which is consistent with the screening results of the anti-inflammatory activity of monomer compounds. Among all the active compounds, kaempferol (12) and β-sitosterol (26) showed strong anti-inflammatory activity, withIC50values of 15.31 and 5.72 μM (Fig.2). The inhibitory activity of these two compounds on NO has been reported[16-17], and theirIC50values were basically consistent with those in the previous studies.
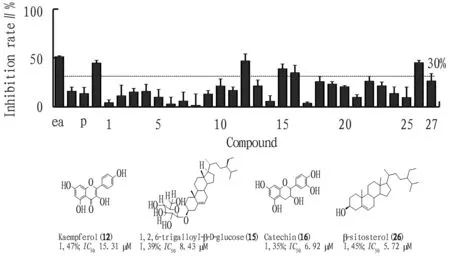
Note: ea. 50 and 25 μg/mL EtOH crude extracts; p. 10 μM, 20 μM positive drug curcumin.
6 Conclusions
In this study, a new flavonoid glycoside was isolated from the ethyl acetate extract ofP.capitatum, and 27 compounds in the extract were used for screening the anti-inflammatory activity of nitric oxide. A total of 4 compounds with significant activity (12,15,16, and26). The results of this study further enrich the material composition ofP.capitatumand lay a certain preliminary foundation for further investigation of substances with anti-inflammatory activity.
- Medicinal Plant的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Plant Hormones on Growth Status and Secondary Metabolism of Houttuynia cordata Thunb.
- Identification of Xunxi Shujin Decoction by TLC
- Preparation of 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol PLGA Nanoparticles
- A Network Pharmacology Study on Active Components and Targets of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium for Treating Keloids
- Pharmacognostic Identification of Hedyotis auricularia and Mitracarpus villosus
- Determination of Salvianolic Acid B in Yiqi Huayu Prescription by HPLC

