Geometric Programming for Nonlinear Satellite Buffer Networks With Time Delays under L1-Gain Performance
Yukang Cui , Yihui Huang , Michael V.Basin , and Zongze Wu
Dear Editor,
This letter concerns the parameter tuning problem for nonlinear satellite buffer networks with communication delays, aiming to optimize their stability properties underL1-gain.We first model the satellite buffer networks by a nonlinear time-delay positive system and propose a novel characterization under which the nonlinear system is asymptotically stable with a prescribedL1-induced performance.Then, the problem of finding the minimum-cost parameters is reduced to geometric programming (GP), which can be resolved by convex optimization efficiently.The flexibility of GP allows simultaneous tuning of parameters in system state, input, and output matrices.A numerical example is presented to illustrate the efficiency of our proposed optimization framework.
Satellite networks are critical for providing communication services to remote rural areas, disaster response teams, and military operations [1].Besides, the emerging concept of integrated sensing and communication (ISC) offers advantages over traditional satellite networks by improving data collection, transmission, and analysis while reducing complexity, power consumption, and cost [2].To reduce the communication delay and loss rate of satellite networks sensing data, buffer management is necessary to store and forward data packets between different components, such as satellites, ground stations, and user terminals.
Before their employment in satellite networks, buffer networks play a critical role in managing data flows to prevent congestion in computer networks and IoT before their use in satellite networks [3].The optimal design of buffer networks has been a hot research topic for several decades, with various studies proposing different models and algorithms for minimizing network congestion and maximizing throughput by tuning their parameters, such as flow size and routing paths [4].One of the earliest studies in this field was conducted in[5], who developed a model for analyzing the performance of buffer networks.Recent research has studied factors influencing network performance, such as packet loss, throughput, and delay.In [6], nonlinear optimal buffer allocation approaches were proposed for quality of service (QoS) assurance in mobile networks.As confirmed by simulations, the proposed methods minimize wasted data traffic and improve resource optimization, leading to improved QoS.
The famous SpaceX’s Starlink project aims to provide high-speed Internet access to remote areas by significantly increasing the number of network satellites.It remains a daunting task to optimize the satellite network at such a massive scale.In this letter, we introduce GP for optimizing the parameters of satellite buffer networks with communication delay and nonlinear characteristics.GP is a nonlinear optimization technique employing generalized posynomials as objective functions and constraints [7].It has been successfully applied in diverse areas, including the chemical industry, network power control [8], and resource allocation [9].GP-based algorithms are efficient and robust in optimizing resource allocation for largescale networks.
This letter introduces a convex optimization framework, specifically GP, to tune the system parameters for nonlinear satellite buffer networks.The main contributions are twofold: 1) A necessary and sufficient criterion is first derived to characterize theL1-gain performance for buffer networks modeled as nonlinear time-delay positive systems; 2) Based on the obtained input-output performance criterion, we prove that the problem of searching the minimum-cost parameters can be reformulated into a GP one and solved by convex optimization efficiently.
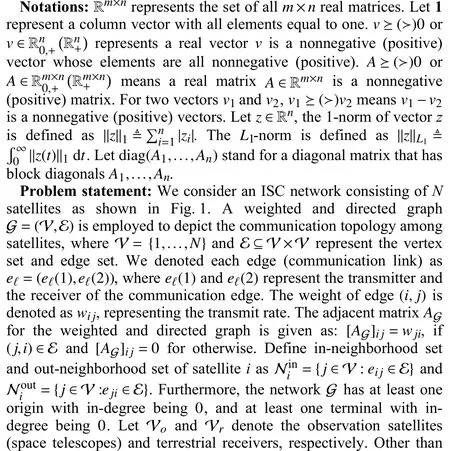

Fig.1.Information flow in satellite buffer networks.



Fig.2.The quantity of optimal source allocations under different γ.The redder the colors, the larger the optimized parameters φi and ψi.
differentγare shown in Fig.2.For scenarios when γ=1.5γ∗, 2γ∗,and 4γ∗, the optimal values of φiandψiare given explicitly.
Conclusion: This letter has studied the parameter tuning problem for nonlinear satellite buffer networks.A fundamental performance characterization is first proposed to guarantee the asymptotic stability of nonlinear systems withL1induced performance.Then, a GP framework is proposed to find the minimum-cost parameters through convex optimization.Finally, the efficiency of the proposed method is demonstrated by a simulation example.
Acknowledgments: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61903258), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515010234), Project of Department of Education of Guangdong Province (2022KTSCX105,2023ZDZX4046), and Shenzhen Natural Science Fund ( Stable Support Plan Program 20231122121608001).
 IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica2024年2期
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica2024年2期
- IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Reinforcement Learning in Process Industries:Review and Perspective
- Communication Resource-Efficient Vehicle Platooning Control With Various Spacing Policies
- Virtual Power Plants for Grid Resilience: A Concise Overview of Research and Applications
- Equilibrium Strategy of the Pursuit-Evasion Game in Three-Dimensional Space
- Robust Distributed Model Predictive Control for Formation Tracking of Nonholonomic Vehicles
- Stabilization With Prescribed Instant via Lyapunov Method
