Abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type
LI Shu, WAN Lei, LIU Jian, HUANG Chuan-bing, CHEN Ying-ying, LI Fang-ze, HU Sai-sai, CHENG Jing
1.Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
2.Department of Rheumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type.Methods:The 30 healthy individuals included in the method were from the Physical Examination Center of Anhui Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and the 60 rheumatoid arthritis patients included were from the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine.The disease activity score of patients with rheumatoid arthritis was evaluated using VAS score and DAS28 score, joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome score were evaluated using graded quantification method, immune inflammation indicators were detected using relevant instruments, inflammatory cytokines were detected using ELISA method, macrophage markers were detected using FCM method, and pathway gene expression was detected using RT-qPCR; Evaluate the predictive effect of circ-CBLB and miR-486-5p on disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis using ROC curves.Results: (1) miR-486-5p,CD14+CD86+, ESR, CRP, RF, Anti CCP Ab, IL-6, TNF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-The levels of circ-CBLB, CD14+CD163+, IL-4, and IL-10 were significantly higher than those of healthy individuals; (2) The expression level of circ-CBLB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is positively correlated with CD14+CD163+, and negatively correlated with miR-486-5p and CD14+CD86+; The expression level of miR-486-5p is negatively correlated with CD14+CD163+and positively correlated with CD14+CD86+; There is a negative correlation between CD14+CD86+and CD14+CD163+; ESR is negatively correlated with circ-CBLB, and positively correlated with miR-486-5p, CD14+CD86+, CRP; CRP is negatively correlated with circ-CBLB, CD14+CD163+, and positively correlated with CD14+CD86+, ESR; (3) The expression level of circ-CBLB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is negatively correlated with joint tenderness, morning stiffness, lack of qi and lazy speech, and postprandial abdominal distension score; The expression level of miR-486-5p is positively correlated with the scores of joint tenderness and decreased appetite.(4) The ROC curve shows that in terms of circ-CBLB,ESR, CRP, VAS, and DAS28 AUC are 0.662 (P=0.032), 0.658 (P=0.035), 0.516 (P=0.830),and 0.791 (P=0.000), respectively.In terms of miR-486-5p, ESR, CRP, VAS, and DAS28 AUC were 0.566 (P=0.385), 0.511 (P=0.883), 0.592 (P=0.223), and 0.727 (P=0.003), respectively.Conclusion: The abnormal expression of circ CBLB and miR-486-5p in peripheral blood mononuclear cell of patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type is related to inflammatory polarization markers, immune inflammation, disease activity, joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis, and the low expression of circ CBLB and high expression of miR-486-5p have certain predictive value for disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis.
1.Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease dominated by arthritis and infiltration of immune cells[1-2].Macrophages participate in the occurrence and development of rheumatoid arthritis.Macrophages show different phenotypes and functions under different factors, namely M1 and M2 macrophages.Macrophages in the body's internal and external blood, synovium and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis tend to M1 type inflammatory Macrophage polarization polarization[3].After polarization, M1 macrophages secrete a large number of Inflammatory cytokine such as interleukin series, tumor necrosis factor, chemokines, etc., activate fibroblasts and Osteoclast,trigger a series of inflammatory reactions, and cause damage to articular cartilage.The imbalance mechanism of “inflammatory polarization” in rheumatoid arthritis is related to abnormal activation of circular RNA (circRNA), small RNA (miRNA), and signaling pathways[4].Therefore, studying the “inflammatory polarization” of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of circRNA/miRNA is of great significance[5].In the early stage, our research team screened differentially expressed circRNAs by extracting Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis,using high-throughput gene sequencing[6], and found circ by circRNAs gene sequencing and combining with GEO database_ The differential expression of 0066715 (CBLB) is relatively large, and circ was found through RNA hybRid prediction_ 0066715 and miR-486-5p have potential sites, so this study selected both.At the same time, our research team found in the early stage that the traditional Chinese medicine syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis presents the characteristics of spleen deficiency, dampness, and phlegm stasis.Spleen deficiency plays an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.The aim of this study is to investigate the abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type.The following report is presented:
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 General Information
The 60 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were from the outpatient and inpatient departments of the Rheumatology Department of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, and 30 healthy people (HC) were from the Physical Examination Center of Anhui Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and the enrollment time was from January 2021 to December 2021.This study was implemented after being approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine (2019AH-12), and all the participants signed informed consent.
2.2 Diagnostic criteria for Western medicine
Referring to the 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR)and the 1987 ACR revised classification standards and scoring system for rheumatoid arthritis[8].Diagnose based on a detailed medical history inquiry, physical examination, and necessary auxiliary examinations of the patient.
2.3 Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Standards
According to the “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Combined with Syndrome”[9], the traditional Chinese medicine syndrome type is spleen deficiency and dampness excess syndrome.Main symptoms: Pain and swelling of limb joints,weakness and numbness of limbs, emaciated body, dull complexion,and muscle atrophy.Secondary symptoms: loss of appetite, lack of appetite, and loose stools.Tongue appearance: The tongue is light red with white and greasy fur; Pulse: The pulse is deep and thin.
2.4 Inclusion criteria
(1) Those who meet the above classification criteria; (2) The patient signs an informed consent form; (3) Age range from 18 to 75 years old; (4) In patients with active disease, the 28 joint disease activity score (DAS28) was greater than 2.6.
2.5 Exclusion criteria
(1) Merge with other serious diseases such as respiratory,cardiovascular, and hematological systems; (2) Patients with severe joint deformities; (3) Having mental illness; (4) Take glucocorticoid and other Immunosuppressive drug at least 4 weeks before the start of the study.
2.6 Main instruments, equipment and reagents
Flow cytometry (CytoFLEX, Beckmann Company); Fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument (PIKOREAL-96, Thermo Company);Enzyme marker (RT-6000, Lei Shu Company); Centrifuge(JW3021HR, Jiawen Company); Fully automatic biochemical analyzer (7600-020, HITACHI company); Fully automatic blood analyzer (Sysmex K-4500, HITACHI company); Full automatic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer (Vital Monitor-20, ELECTA company).
2.6.2 Main reagents
CD14-FITC (Biotechnology, B328962); CD86-PE-Cyanine5(Biotechnology, B326934); CD163-APC (Biotechnology, B326936);Chloroform (Shanghai Su Yi 20190227); Anhydrous ethanol(Shanghai Guangnuo 20210914); Isopropanol (Shanghai Guangnuo 20210716); Trizo (Life technologies, 350508); DEPC-H2O (Gene Rheumatoid Arthritis y Biotech, 2107G20); Novostart SYBR qPCR SuperMix Plus (novoprotein, 05229413); ELISA kit (Wuhan Gene Beauty, GR2021-06); PrimeScript ™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA ERAser (TaKa rheumatoid arthritis, AL21115A).
2.7 Observation indicators and methods
2.7.1 Immune inflammation related indicators
Collect 3 mL of fasting forearm venous blood from the included subjects using a blood sedimentation tube (black tube), and detect the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) using a fully automated ESR analyzer; Biochemical indicators C-reactive protein (CRP),Rheumatoid factor (RF), anti cyclic Citrulline peptide antibody (Anti CCP Ab, After all specimens are collected, they will be tested using a fully automated biochemical analyzer.
2.7.2 Inflammatory cytokines
Collect 5 mL of forearm venous blood from the included subjects using a biochemical tube (yellow tube), coagulate at low temperature between 3 ℃ and 5 ℃, centrifuge at 4000 r/min for 15 min, separate the serum, and store it in a refrigerator at -80 ℃.After all samples are collected, use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect serum interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-6, IL-10, and tumor necrosis factor in the same batch-α Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, TNF-α)Horizontal.
2.7.3 M1 and M2 Macrophage polarization markers
Flow cytometry was used to detect M1 and M2 Macrophage polarization markers CD86 and CD163.Method: Use a heparin anticoagulant tube (green tube) to collect 1ml of venous whole blood.Human M1 and M2 macrophages were expressed by adding 10 μL of fluorescent labeled mouse anti human CD14-FITC, CD86-PE-Cyanine5, and CD163-APC monoclonal antibody reagents.They were thoroughly mixed and reacted in a refrigerator at 4 ℃for 30 minutes.Centrifuge at 1 500 r/min for 5 min and remove the supernatant.PBS resuspended cells were detected by flow cytometry,and the results were analyzed using Flow Jo 7.6.1 software.
2.7.4 Channel related indicators
RT qPCR was used to detect the expression of related genes in PBMCs of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls.The specific steps refer to the instructions, and the relevant primers are as follows (Table 1).
2.7.5 Disease Activity Related Indicators
Visual Analogue Scales (VAS) and DAS28 scores[10].The low activity range of rheumatoid arthritis diseases is (2.6<DAS28<3.2),medium activity is (3.2<DAS28<5.1), and high activity is(DAS28>5.1).The higher the score, the higher the disease activity.
2.7.6 Joint Symptoms and Spleen Deficiency Syndrome Points
Referring to the “New Chinese Medicine”[11], the quantification standard for joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome points[12]: Joint symptoms include joint pain, joint swelling, joint tenderness, and morning stiffness.The spleen deficiency syndrome is characterized by fatigue, decreased appetite, postprandial bloating,and loose stools.According to the grading of no, mild, moderate,and severe degrees, joint symptoms are scored 0, 3, 6, and 9 points respectively, and spleen deficiency syndrome is scored 0, 2, 4, and 6 points respectively.
2.8 Statistical methods
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS23.0 statistical software.The measurement data is described using mean plus minus standard deviation (), t-test is used for inter group comparison, and Pearson test or Spearman test is used for correlation analysis.take =0.05 and P<0.05 are statistically significant differences.
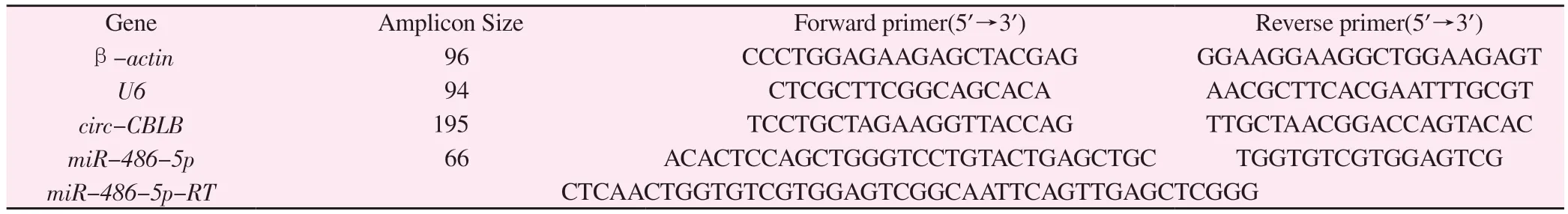
Tab 1 Relevant primers
3.Results
3.1 Changes in immune inflammation indicators in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
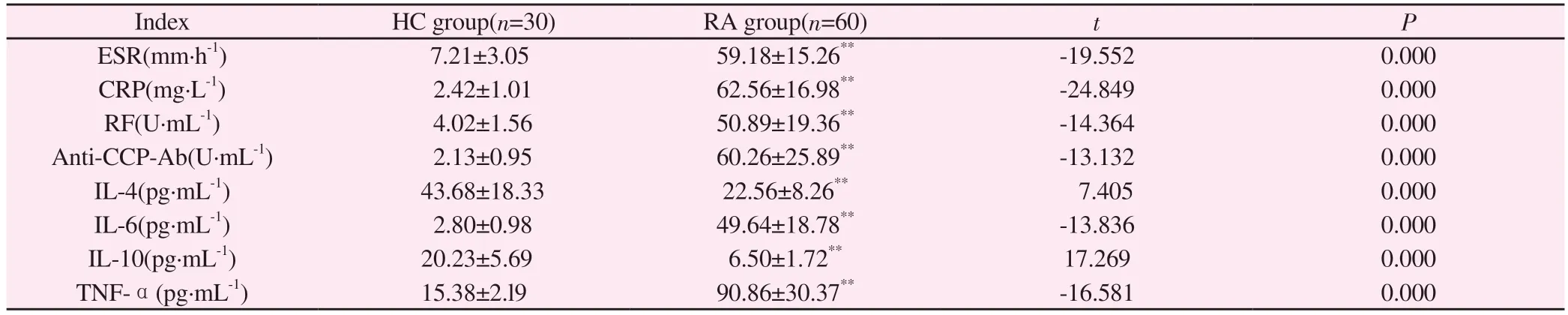
Compared with healthy individuals (Table 2), the inflammatory immune indicators ESR, CRP, RF, Anti CCP Ab, pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, and TNF in the rheumatoid arthritis group- The level increased with statistical significance (P<0.01), while the levels of anti-inflammatory factors IL-4 and IL-10 significantly decreased with statistical significance (P<0.01).
Tab 2 Changes of immune inflammatory indexes in RA patients(±s)
Tab 2 Changes of immune inflammatory indexes in RA patients(±s)
Note: Compared with healthy individuals, ** P<0.01
Index HC group(n=30) RA group(n=60) t P ESR(mm·h-1) 7.21±3.05 59.18±15.26** -19.552 0.000 CRP(mg·L-1) 2.42±1.01 62.56±16.98** -24.849 0.000 RF(U·mL-1) 4.02±1.56 50.89±19.36** -14.364 0.000 Anti-CCP-Ab(U·mL-1) 2.13±0.95 60.26±25.89** -13.132 0.000 IL-4(pg·mL-1) 43.68±18.33 22.56±8.26** 7.405 0.000 IL-6(pg·mL-1) 2.80±0.98 49.64±18.78** -13.836 0.000 IL-10(pg·mL-1) 20.23±5.69 6.50±1.72** 17.269 0.000 TNF-α(pg·mL-1) 15.38±2.l9 90.86±30.37** -16.581 0.000
3.2 Changes in pathway gene expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
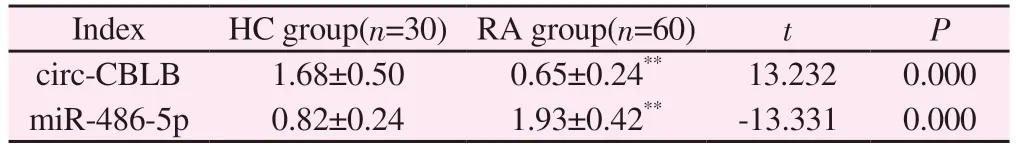
Compared with healthy individuals (Table 3, Figure 1), the expression level of circ-CBLB in the rheumatoid arthritis group decreased significantly (P<0.01), and the expression level of miR-486-5p increased significantly (P<0.01).

Fig 1 Comparison of expression levels of circ-CBLB and miR-486-5p in two groups
Tab 3 Comparison of expression levels of circ-CBLB and miR-486-5p in two groups(±s)
Tab 3 Comparison of expression levels of circ-CBLB and miR-486-5p in two groups(±s)
Note: Compared with healthy individuals, ** P<0.01
Index HC group(n=30) RA group(n=60) t P circ-CBLB 1.68±0.50 0.65±0.24** 13.232 0.000 miR-486-5p 0.82±0.24 1.93±0.42** -13.331 0.000
Tab 4 Comparison of expression levels of polarizing markers of macrophages between two groups(±s, %)
Tab 4 Comparison of expression levels of polarizing markers of macrophages between two groups(±s, %)
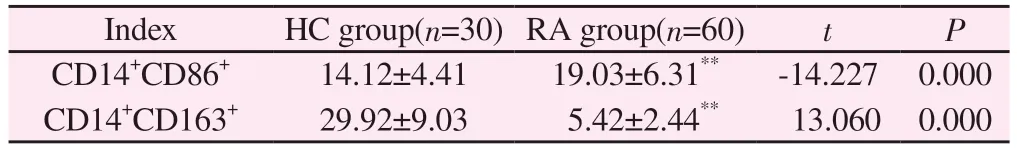
Note: Compared with healthy individuals, ** P<0.01
Index HC group(n=30) RA group(n=60) t P CD14+CD86+ 14.12±4.41 19.03±6.31** -14.227 0.000 CD14+CD163+ 29.92±9.03 5.42±2.44** 13.060 0.000
3.3 Changes of expression level of Macrophage polarization polarization markers in rheumatoid arthritis patients
Compared with healthy individuals (Table 4, Figures 2 and 3), the expression level of CD14+CD86+in the rheumatoid arthritis group was significantly increased, with a statistically significant difference(P<0.01).The expression level of CD14+CD163+was significantly decreased, with a statistically significant difference (P<0.01).
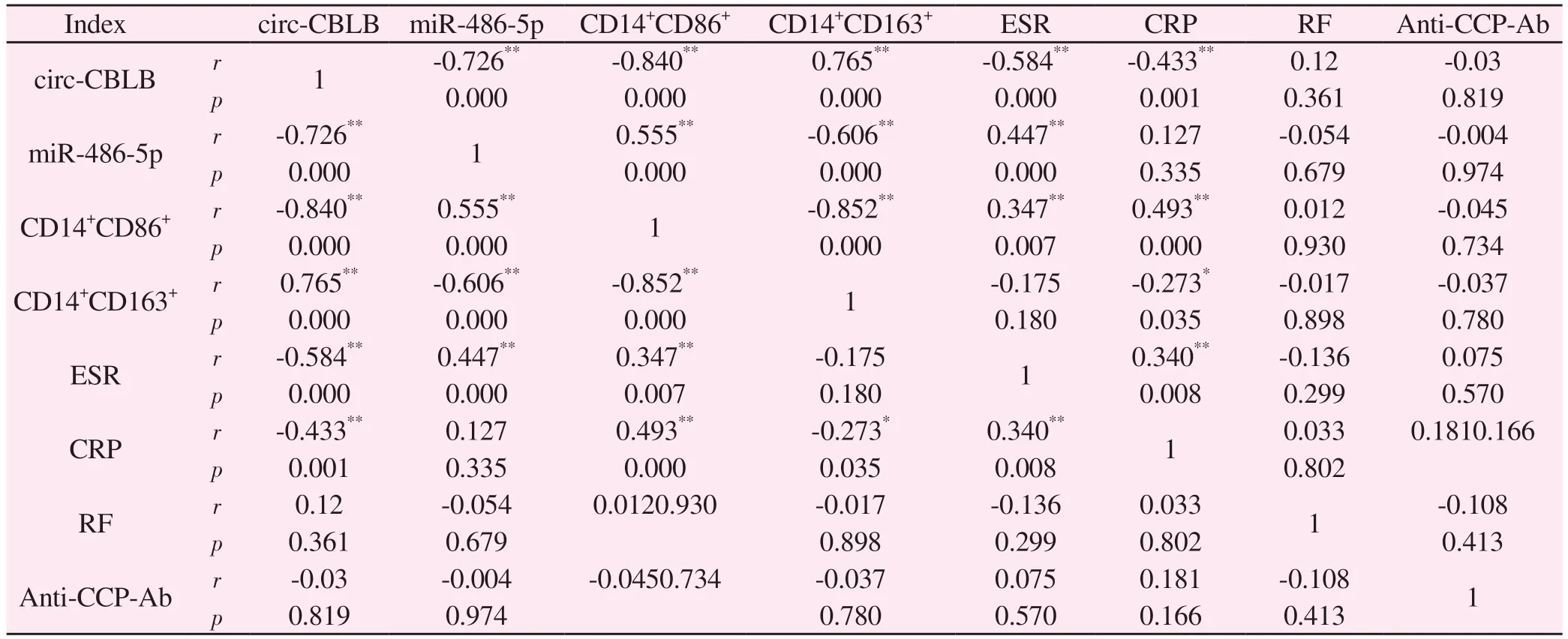
Tab 5 Correlation between circ-CBLB, miR-486-5p, CD14+CD86+, CD14+CD163+ and immune inflammation related indexes
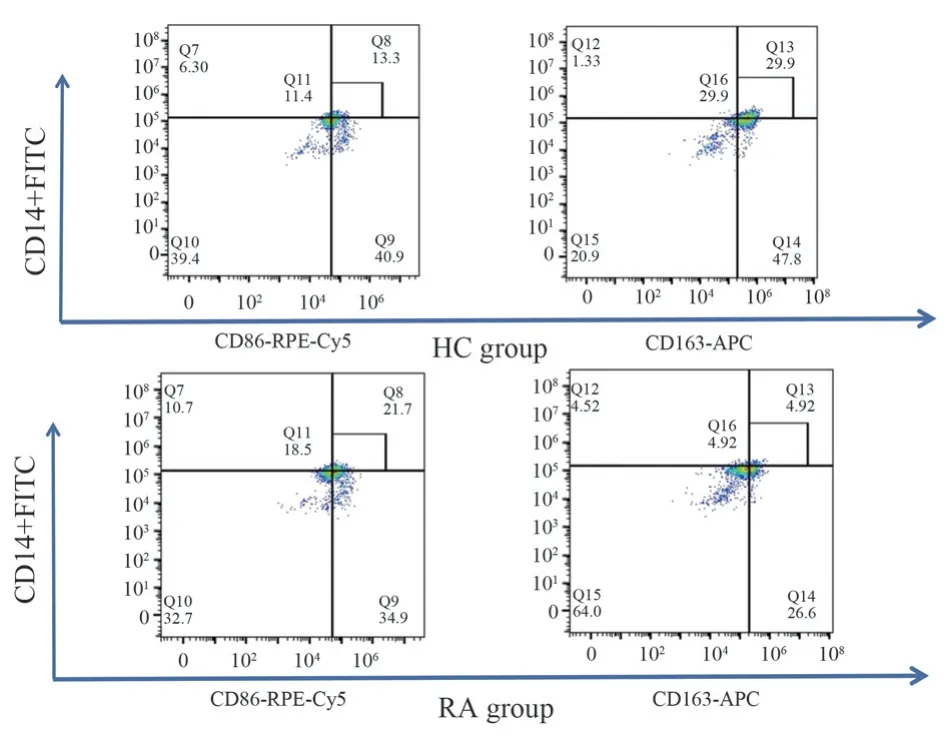
Fig 2 Flow cytometry of CD14+CD86+ and CD14+CD163+ in two groups
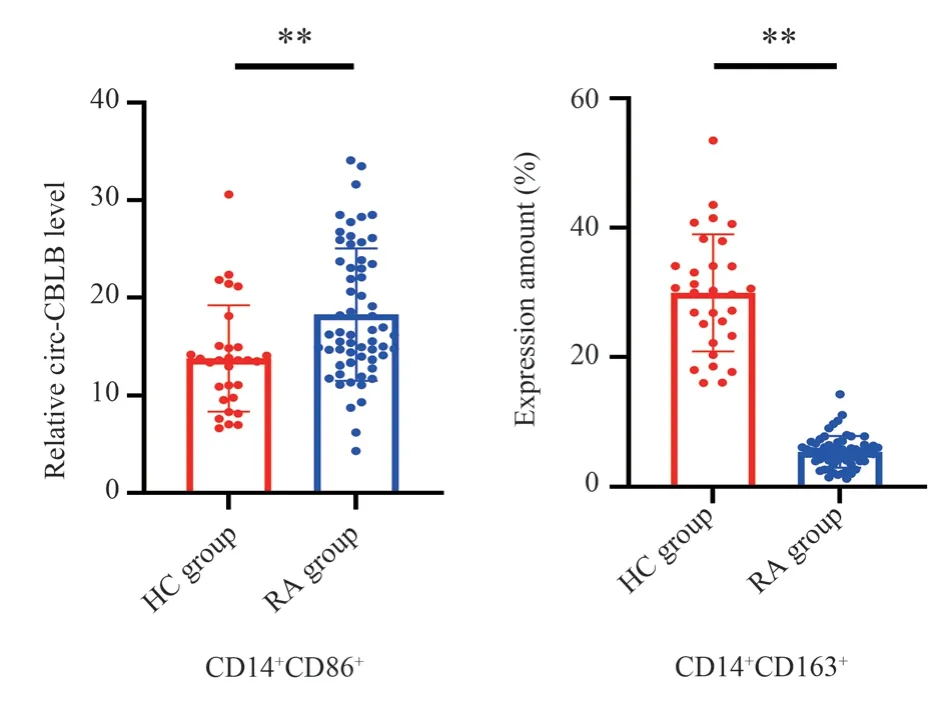
Fig 3 Comparison of expression levels of macrophage polarization markers between the two groups
3.4 Correlation between pathway genes, inflammatory polarization markers, and immune inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
The correlation results showed (Table 5) that the expression level of circ-CBLB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis was positively correlated with CD14+CD163+(P<0.01), and negatively correlated with miR-486-5p and CD14+CD86+(P<0.01); The expression level of miR-486-5p was negatively correlated with CD14+CD163+(P<0.01), and positively correlated with CD14+CD86+(P<0.01); There is a negative correlation between CD14+CD86+and CD14+CD163+(P<0.01); ESR was negatively correlated with circ-CBLB (P<0.01), and positively correlated with miR-486-5p, CD14+CD86+, CRP (P<0.01); CRP was negatively correlated with circ-CBLB, CD14+CD163+(P<0.05, P<0.01), and positively correlated with CD14+CD86+, ESR (P<0.01).
3.5 Correlation between pathway genes and joint symptoms,spleen deficiency syndrome scores in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
The correlation results show (Table 6) that the expression level of circ-CBLB in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is negatively correlated with joint tenderness, morning stiffness, lack of qi and lazy speech, and postprandial abdominal distension (P<0.05,P<0.01); The expression level of miR-486-5p is positively correlated with joint tenderness and decreased appetite (P<0.05).
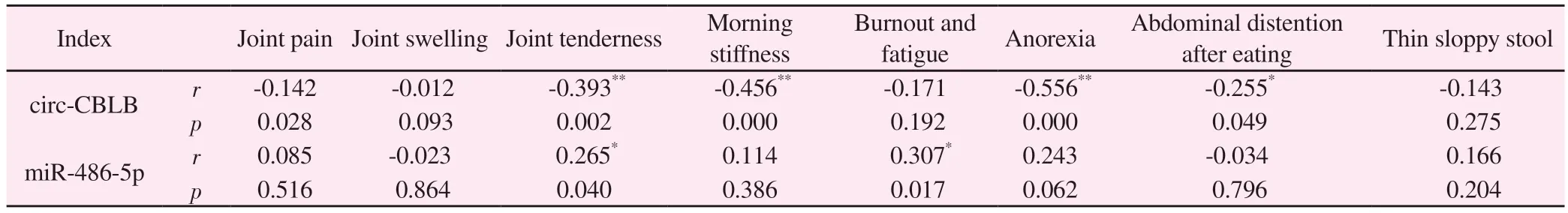
Tab 6 Correlation between pathway genes and joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome score in RA patients
3.6 Relationship between expression levels of pathway genes and disease activity related indicators in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Circ-CBLB is 1 below the average, 2 above the average, and 1 and 2 correspond to ESR, CRP, VAS, DAS28, respectively.miR-486-5p is opposite to circ-CBLB.The results showed that in terms of circ-CBLB (Figure 4), ESR, CRP, VAS, and DAS28 AUC were 0.662(P=0.032), 0.658 (P=0.035), 0.516 (P=0.830), and 0.791 (P=0.000),respectively.In terms of miR-486-5p (Figure 4), ESR, CRP, VAS,and DAS28 AUC were 0.566 (P=0.385), 0.511 (P=0.883), 0.592(P=0.223), and 0.727 (P=0.003), respectively.The results indicate that low levels of circ-CBLB expression and high levels of miR-486-5p expression may have certain predictive value for disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
4.Discussion
The clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis include joint swelling, morning stiffness, pain, and other symptoms.Its molecular mechanism is the disruption of cytokine networks such as pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors[13],leading to an increase in joint inflammation and the occurrence of these symptoms.The traditional Chinese medicine syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis presents the characteristics of “spleen deficiency and dampness excess, phlegm stasis and obstruction”.Spleen deficiency “plays an important role in the pathogenesis of”Bi syndrome “, with the following five specific effects: ① The spleen loses circulation and turns into phlegm due to the stagnation of water and liquid.② Insufficient spleen circulation, biochemical deficiency, and deficiency of qi and blood Poor temper, weak external guard, and susceptibility to dampness and drowsiness The accumulation of dampness leads to the formation of blood stasis over time, which hinders the smooth circulation of qi and blood,resulting in phlegm dampness and blood stasis.Eventually, phlegm and blood stasis merge, causing joint pain, swelling, lingering, and even joint deformation due to obstruction of meridians and joints Dampness is often mixed with cold and heat, causing cold stagnation and invading the meridians, causing blood circulation to slow down or even stagnate; Heat evil circulates into the bloodstream, causing blood circulation to become stagnant and stagnant; Qi deficiency and inability to promote blood circulation result in poor blood flow and long-term accumulation of blood stasis.Phlegm dampness and blood stasis intermingle over time, resulting in phlegm and blood stasis,and joint obstruction.The results of this study show that compared with healthy individuals, the pro-inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF in rheumatoid arthritis patients with spleen deficiency and dampness excess type- As the level increases, the levels of anti-inflammatory factors IL-4 and IL-10 significantly decrease.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease with the main pathological characteristics of synovial inflammation, cartilage and bone destruction[14].However, at present, the disease lacks effective early diagnosis and treatment, and misdiagnosis and mistreatment will lead to serious disability, and eventually lead to early death.CircRNA is a new type of endogenous expression ncRNA,which is formed through Covalent bond, has high stability, and is closely related to the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases[15-18].CircRNA, compared with other cerRNAs, binds more closely with miRNAs with corresponding binding sites, thus affecting the expression and function of its downstream target genes.Therefore, it is also called “super sponge” [19].The crosstalk between circRNA and miRNA has also been confirmed to be involved in the physiological and pathological processes of rheumatoid arthritis[20].Its mechanism is that circRNA competitively binds to miRNA, thereby participating in the regulation of downstream genes in synovial tissue and PBMC.The results of this study show that compared with the healthy group, the expression level of circ-CBLB gene in PBMC of patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type is abnormally down regulated,and the expression level of miR-486-5p gene is abnormally upregulated.The Receiver operating characteristic results show that the low level of circ-CBLB and the high level of miR-486-5p expression have certain predictive value for the disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis.
The “inflammatory polarization” of rheumatoid arthritis is also called “Macrophage polarization”.Macrophages can produce a variety of Inflammatory cytokine and chemokines to participate in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis[21].The number of macrophages in synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis significantly increases.Macrophages have strong heterogeneity and plasticity in their functions[22].Macrophages can be divided into M1 macrophages and M2 macrophages according to their phenotype and function[23].M1 macrophages can secrete a variety of Inflammatory cytokine and express CD80, CD86 and other molecules, which can promote the development of inflammation, accelerate the degradation of extracellular matrix and apoptosis.M2 macrophages secrete antiinflammatory cytokines and express molecules such as CD206 and CD163, exerting anti-inflammatory effects.During the development of rheumatoid arthritis disease, multiple factors will break the M1/M2 macrophages in Dynamic equilibrium, causing imbalance in the number and proportion, leading to the continuous increase of M1 macrophages, thus intensifying the inflammatory response[24-25].The results of this study show that the expression level of circ-CBLB in rheumatoid arthritis patients with spleen deficiency and dampness excess is positively correlated with CD14+CD163+, and negatively correlated with miR-486-5p and CD14+CD86+; The expression level of miR-486-5p is negatively correlated with CD14+CD163+; In terms of immune inflammation, CD14+CD86+is positively correlated with inflammatory markers ESR and CRP, while CD14+CD163+is negatively correlated with CRP.At the same time, the correlation between joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome in patients with spleen deficiency dampness type rheumatoid arthritis shows that the expression level of circ-CBLB is negatively correlated with joint tenderness, morning stiffness, lack of qi and lazy speech, and postprandial abdominal distension; The expression level of miR-486-5p is positively correlated with joint tenderness and decreased appetite.
In conclusion, the abnormal expression of circ-CBLB and miR-486-5p in Peripheral blood mononuclear cell of patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type is related to inflammatory polarization markers, immune inflammation,disease activity, joint symptoms and spleen deficiency syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis, and the low level expression of circ-CBLB and high level expression of miR-486-5p have certain predictive value for disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis.
Authors' contribution
Li Shu: Responsible for building the overall framework of the article, conducting data statistical analysis, and writing the article;Wan Lei: Responsible for conceptualizing the ideas of the article;Liu Jian and Huang Chuanbing: responsible for providing technical guidance for inspection; Chen Yingying and Li Fangze: responsible for purchasing experimental materials and testing indicators; Hu Saisai and Cheng Jing are responsible for collecting and organizing clinical data.
All authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年17期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年17期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on the regulation mechanism of non-coding RNA on ankylosing spondylitis
- Anesthetic effect of phenobarbital sodium on female BALB/c mice
- Research progress of TCM regulation of Cajal interstitial cells in the treatment of functional Gastrointestinal diseases
- Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone on neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model by regulating NLRP3 inflammatory bodies
- Effect of Astragalus-hawthorn on ovarian reproductive function and inflammatory mechanism of action in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Effect of estrogen pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol-Metaanalysis
