Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone on neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model by regulating NLRP3 inflammatory bodies
GE Shu-li, DONG Jian-jian, XU Chen-chen, CHENG Nan✉
1.Graduate School, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
2.Affiliated Hospital of the Institute of Neurology, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230061, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the intervention mechanism of Thymoquinone in regulating NLR Family Pyrin Domain Containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome mediated on neuroinflammatory injury of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease.Methods: After establishment of the MPTP-induced PD mouse model, which was randomly divided into control group, control+TQ group, model group and model +TQ group.The effects of TQ on the motor deficits in PD mice were evaluated by open-field test and rotarod test.The effects of TQ on the expression of tyrosine hydroxylase, α-Synuclein and NLRP3 inflammasomes in midbrain of PD mice were determined by Western blot.In vivo, BV-2 cells were induced by lipopolysaccharide and MPP+ to establish neuroinflammation models of Parkinson's disease.The cell supernatant was collected as conditioned medium and acted on human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells to construct PD inflammatory injury model.MTT method determined the optimal concentration of TQ and MPP+ in vitro intervention and the survival rate of cells in each intervention group; SH-SY5Y cells apoptosis was detected by TUNEL.Western blot was used to analyze the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, Caspase-3 proteins in each experimental group.The effect of TQ on the proinflammatory factor interleukin 1β by ELISA.The expression of related proteins NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, IL-1β and Tubulin were detected by Western blot after TQ treatment.Results: Compared with normal group, the motor function of model group was significantly decreased (P<0.01), the motor function of TQ group was significantly increased (P<0.01).In Western blot experiment, compared with normal group, the -Syn level in model group was significantly increased (P<0.01).Compared with model group,TQ significantly decreased the -Syn level of MPTP mice (P<0.01); Compared with model group, TH protein expression was significantly increased after TQ administration (P<0.01).TQ further inhibited the up-regulation of NLRP3, Caspase-1, IL-1β, ASC protein expression in PD mice (P<0.01).MTT detection found that the survival rate of SH-SY5Y cells after 100 μmol·L-1 MPP+ treatment was significantly decreased, SH-SY5Y cells damage can be relieved after TQ treatment.TUNEL staining showed that SH-SY5Y cells treated with MPP+conditioned medium could induce apoptosis, and TQ pretreatment could significantly (P<0.01)reduce the apoptosis rate.Western blotting showed that MPP+ conditioned medium caused the down regulation of Bcl-2/Bax in SH-SY5Y cells, while TQ inhibited the down regulation of Bcl-2/Bax.Meanwhile, MPP+ conditioned medium induced the activation of Caspase-3 in SH-SY5Y cells, and caspase-3 expression was decreased by TQ (P<0.01).ELISA kit showed that TQ inhibited MPP+ induced IL-1β content increases (P<0.01).Western blotting showed that TQ inhibited the protein expression of NLRP3, Caspase-1, IL-1β and ASC of BV-2 cells induced by MPP+ (P<0.01).Conclusion: Thymoquinone can reduce the inflammatory damage of PD model neurons by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in PD model, and thus play a protective role in dopaminergic neurons.
1.Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a central neurodegenerative disease with the death and loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra as its basic pathological change, and it often occurs in middleaged and elderly people clinically[1].China is a country with a large population, and with the increasing aging of the population, the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in China is in a stage of sharp rise, which will bring severe challenges to the whole society [2].The pathogenesis of PD is complex and involves multiple pathways and mechanisms, such as abnormal protein dynamics, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation, which promote the development of PD[3-4].Studies have found that PD neuronal injury is closely related to over-activated microglia[5].Activated microglia produce inflammatory cytokines, and these pro-inflammatory cytokines can aggravate neuronal damage through receptordependent apoptotic pathways in the neuroinflammatory process[6-7].
Thymoquinone (TQ) is isolated from the herb black seed and purified into an effective and active monomer, which has been proven to have anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptosis and other effects[8-9].Previous studies by our research group found that TQ activated the Nrf2 pathway to up-regulate the expression of antiheme oxygenase-1 protein, alleviate cell apoptosis, and delay the occurrence of PD[10].However, these studies have not been able to elucidate the specific therapeutic mechanism of TQ on experimental PD neuroinflammatory injury.This study induced PD mouse models with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-Tetrahydropyridine (MPTP).LPS combined with MPP+to construct PD neuroinflammation model,to observe the effect of TQ on NLRP3 inflammatory and SHSY5Y cell injury, and study the mechanism of TQ in treating PD neuroinflammatory injury.
2.Materials
2.1 Animals
C57BL/6 mice introduced by Hangzhou Ziyuan Laboratory Animal Science and Technology Co., LTD., production license No.: SCXK(Zhejiang)2019-0004, were reared and propagated by specially-assigned people in SPF Laboratory Animal Center.The ambient temperature is controlled at about 25 ℃, normal light,conventional rat feed and free drinking water.The experimental mice required for the experiment were 2-3 months old.The animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences(IACUC19001).
2.2 Cells and drugs
Microglia (BV-2) and human neuroblastoma (SH-SY5Y) cells were purchased from Hefei Miaochu Biotechnology Co., LTD.Sigma (St.Louis, USA) purchased TQ (99% purity, item number MKCC0600),MPP+ ( 98% purity, item number 0000134347), MPTP ( 98%purity, item number SLCJ8770).
2.3 Reagents
MEM culture-medium (Gibco, USA, No.2323185); F-12 culturemedium (Gibco, USA, article No 2277085); Fetal bovine serum(Gibco, item No.2305262RP); ELISA kit (Jianglai Biotechnology Co., LTD., article No.JL18442).NLRP3, Caspase-1 antibody(Abcam, UK, item No.ab263899, ab1872), ASC, IL-1β antibody(Chengdu Zonen Biotechnology Co., LTD., item No.340097,511369), Caspase-3 (Abcam, article No.ab4051), Bcl-2, Bax antibody (Chengdu Zhengneng Biotechnology Co., LTD., article No.381702 and 380709 respectively).TH, alpha-synuclein antibody(CST Company of the United States, product numbers 2792S and 2642S, respectively)
2.4 Experimental apparatus
Super clean table (model SW-CJ-1F): Suzhou Purification Equipment Company; CO2 incubator (Model GOLD-SIMW200IR):SIM Company of USA; Open field experiment video analysis system (Noldus, Netherlands); JLBehv-RRT (Shanghai Jilang Software Technology Co., LTD.); Biotek Epoch2 (Bio Tek Epoch2):BioTEK Instrument Co., LTD.Electrophoresis apparatus (Model Pow-erpac Basic): Bio-Rad (USA) Company; Pure water machine(Model FBZ2001-UP-P): Qingdao Fulham Technology Co., LTD.
3.Methods
3.1 Construction of PD mouse model
The PD mouse model was established by subcutaneous injection of C57BL/6 mice with 30mg·kg-1MPTP for 5 d[11]
3.1 Grouping and administration method
Male C57BL/6 mice were fed for 7 days and randomly divided into control group, control +TQ group, model group, and model +TQ group.(1) C57BL/6J mice in the control group were intraperitoneally injected with equal volume normal saline once a day for 5 consecutive days; (2) Control +TQ group: C57BL/6J mice were intraperitoneally injected with thymoquinone (10 mg·kg-1·d-1) for 5 d.(3) Model group: C57BL/6J mice were injected subcutaneously with 30 mg/kg MPTP for 5 d.(4) Model +TQ group: 60 minutes before MPTP administration, C57BL/6J mice were intraperitoneally injected with TQ (10 mg·kg-1·d-1) for 5 d.
3.2 The motor function of mice was measured by behavioral analysis
(1)Open field test: Evaluation of autonomic behavior in mice.At the beginning of the experiment, the room was kept quiet, and the results of the behavior of the experimental mice were tried to avoid being influenced by human factors.The mice were put into an observation box, recorded continuously for 10 min in a quiet environment, and trained for 3 d.The test was carried out on the fourth day, and the central distance and central time and the side distance and edge time were recorded.
(2)Rotarod test: To evaluate the coordination ability of the limbs of mice.Before the experiment, the mice were trained on the rotary rod at a speed of 5-10 r/min for 5 min, so that the mice could crawl on the rotating shaft.According to the results of the pre-test, the speed was set at 30 r/min for 5 min detection.The mice were trained for 3 d and their time on the rod was recorded on day.Each mouse was tested for 3 times, with an interval of 1 h between each two tests.The average of the results of the 3 tests was taken and recorded in the results of this test.
3.3 Cell culture and passage
BV-2 and SH-SY5Y cells were cultured in a 5%CO2incubator at 37 ℃.The cells grew to a density of about 80% and were passed every 2-3 d.
3.4 Cell conditioned culture
Cell conditioned culture was adopted according to relevant literature[12].BV-2 cells were divided into control group, model group, model +TQ group and positive control group MCC950[13].The control group was not treated; The model group was induced with 0.1 μg/mL LPS[14] for 3h, then replaced with culture medium containing 100 μmol·L-1MPP+for 8h, and the PD neuritis model was established.In the TQ group, the culture medium containing LPS was first cultured for 3 h, and the culture medium containing 0.25 μmol·L-1and 0.5 μmol·L-1TQ was replaced for 12 h, and the culture medium containing 100 μmol·L-1MPP+was abandoned for 8 h.The positive control group was cultured with culture medium containing LPS for 3 h, replaced with culture medium containing 0.1 μmol·L-1MCC950 for 1h, and abandoned culture medium with culture medium containing MPP+for 8 h.After intervention, the original culture medium was replaced with MEM/F12 complete culture medium, treated for 24 h, and SH-SY5Y cells of each group were collected for 24 h.
3.5 The effects of MPP+ and TQ on proliferation of BV-2 and SH-SY5Y cells were detected by MTT
BV-2 and SH-SY5Y cells were placed on 96-well plates with a density of 2×104cells per well.When the cell growth reached 70%,each group was added with the required culture medium of 100 μL.After the treatment time was over, each well was added with MTT solution of 20 μL (dark operation).After being cultured in the incubator of CO2constant temperature incubator for 3 h, each well was added with DMSO solution of 150 μL for 5 min (dark operation).The absorbance OD value of 450 nm was measured by enzyme-labeled instrument.
3.6 Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
The BV-2 cells in good condition were digested, collected and passed through.The normal group, model group and TQ group were cultured in a constant temperature incubator for 24 h.When the cells grew to 90%, intervention was performed.The TQ group was treated with 0.25 μmol·L-1and 0.5 μmol·L-1TQ medium for 12 h, and then treated with 100 μmol·L-1MPP+for 8h.Follow the instructions for ELISA.Absorbance OD (450nm) was measured by enzyme-labeled instrument.
3.7 The apoptosis of cultured SH-SY5Y cells was detected by TUNEL method
SH-SY5Y cell plates were placed in 6-well plates with climbing plates at a density of 5×105cells/mL, and were divided into control group, model group, model +TQ group, and MCC950 group for intervention.After PBS washing, paraformaldehyde was fixed at room temperature for 20 min.TUNEL staining was performed according to kit instructions, and Image J software was used for quantitative analysis.
3.8 The protein expression was detected by Western blot
Mouse midbrain tissues were extracted and cells of each group were digested and collected.RIPA lysate and PMSF mixture were added, and the lysate was mixed for 30 min on the ice bath table every 10 min.Centrifuge at 4 ℃, 12 000 r/min for 30min, take the supernatant, add the protein sample buffer, immediately heat in a water bath at 100 ℃ for 8min, and store in a refrigerator at -80 ℃for later use.The proteins were transferred to the NC membrane after electrophoresis.It was sealed in a rapid sealing solution for 25 min, then added TH, α-Syn, NLRP3, Caspase-1, ASC, IL-1β,Caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax primary antibody at 4 ℃ and incubated overnight (all diluted at 1:1 000), and rinsed in a PBST shaker for 6 times, 5 min/ time.Put NC film (1:10 000) into the second antiliquid, incubate at 37 ℃ for 1.5 h, and rinse with PBST shaker for 6 times, 5 min/ time.Liquid A and B were 1:1 proportioned in the developing working liquid, and the NC film was exposed in the developing instrument compartment, and the image scanning operation was processed by ImageJ software.
3.9 Statistical method
SPSS 23.0 software was used for statistical analysis, and each experimental data was expressed as mean ± standard deviation(±s).Independent sample t test was used for comparison between two groups, and one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between multiple groups.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
4.Results
4.1 Effect of thymoquinone on behavior of PD mouse model
The open-field test results showed that compared with the control group, the central distance and central time decreased in the model group, while the side distance and edge time increased (P<0.01).Compared with model group, the central distance and central time increased in model +TQ group, while the side distance and edge time decreased significantly (P<0.05).(Table 1).
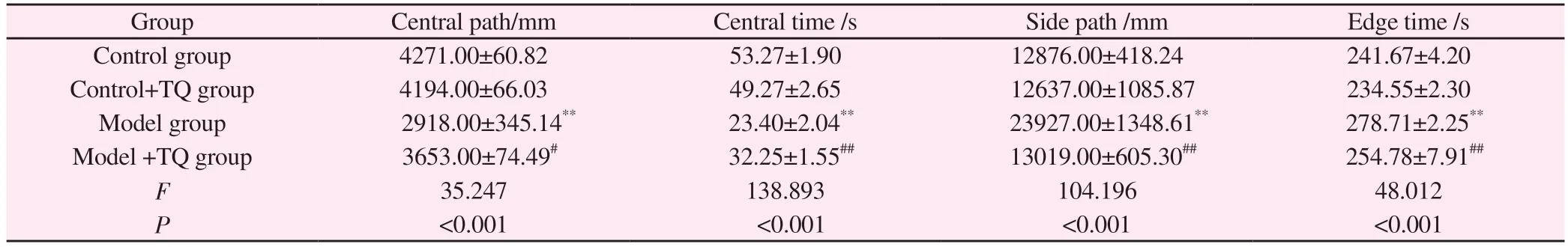
Tab 1 Open field (n=10)
The result of rotating the rod showed that: compared with the control group, the rod time in the model group was significantly reduced (P<0.01); compared with model group, model +TQ group could significantly increase the rod time of mice (P<0.01) (Table 2).
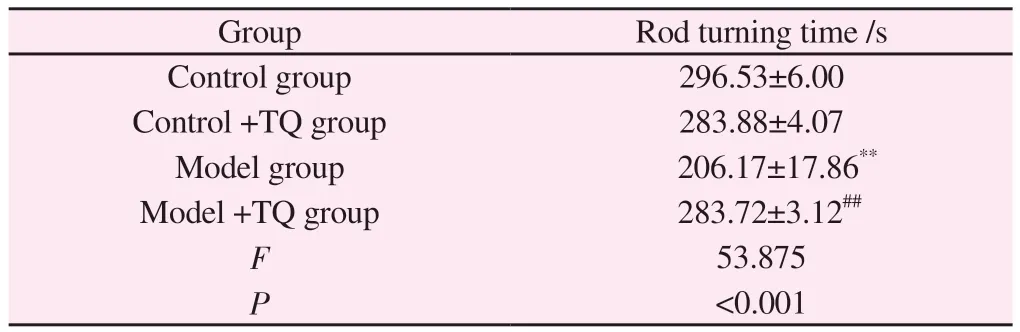
Tab 2 Rotarod experiments(n=10)
4.2 Effect of thymoquinone on dopaminergic neuron loss in PD mouse model
The effect of TQ on Dopaminergic neurons injury induced by MPTP was observed, and the expression of TH and α-Synuclein protein was detected by Western Blot.The results showed that the expression level of TH in model group was significantly decreased(P<0.01), and the TH protein level in model +TQ group could be restored (P<0.01).The expression of α-Synuclein in the model group was significantly increased (P<0.01).In the model +TQ group, the expression of -Synuclein significantly decreased (P<0.01)(Figure 1, Table 3).
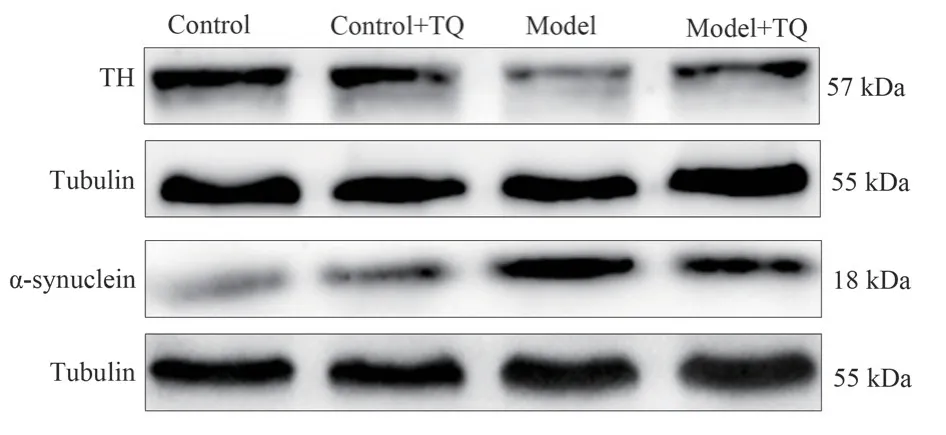
Fig 1 TH, α-Synuclein protein expression in mouse midbrain (n=6)
Tab 3 Comparison of TH and -Synuclein expression in mice of each group (±s,n=6)
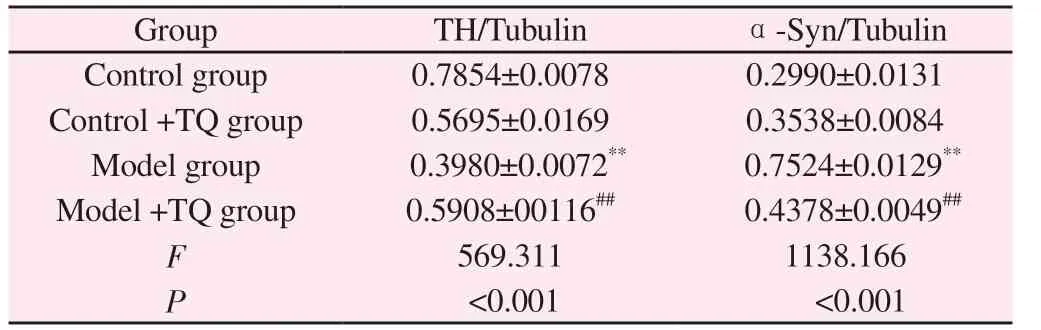
Tab 3 Comparison of TH and -Synuclein expression in mice of each group (±s,n=6)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group,##P<0.01.
Group TH/Tubulin α-Syn/Tubulin Control group 0.7854±0.0078 0.2990±0.0131 Control +TQ group 0.5695±0.0169 0.3538±0.0084 Model group 0.3980±0.0072** 0.7524±0.0129**Model +TQ group 0.5908±00116## 0.4378±0.0049##F 569.311 1138.166 P<0.001 <0.001
4.3 Effect of thymoquinone on the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-related protein in PD mouse model
The results showed that NLRP3, ASC, Caspase1, IL-1β protein expression levels were significantly increased in the model group, and NLRP3 inflammasome protein expression levels were significantly decreased in the model +TQ group compared with the model group (P<0.01, Figure 2 and Table 4).
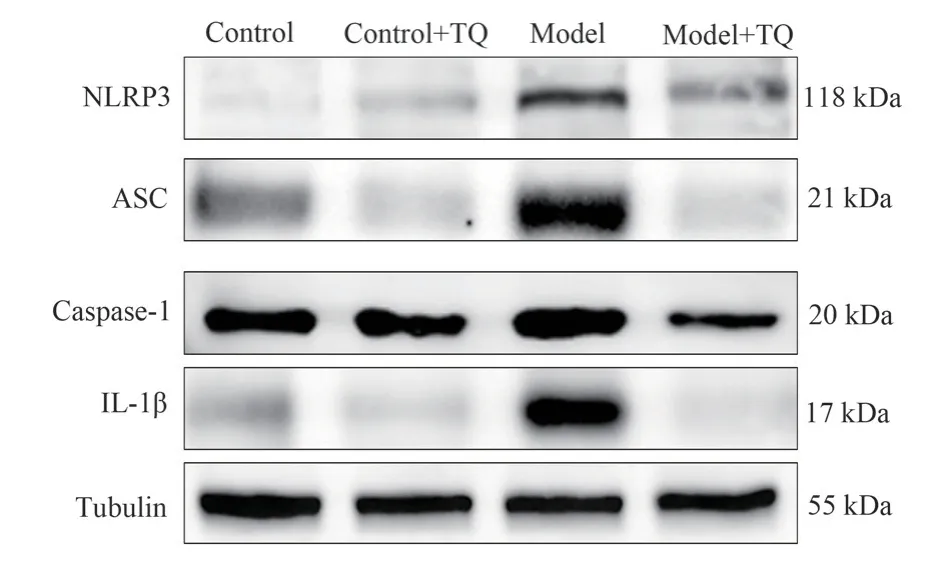
Fig 2 Protein expression of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β in mouse midbrain (n=6)
4.4 Effect of MPP+ on activation of BV-2 cells
Without any intervention, the BV-2 cells remained in an inactive state, with their axons clearly visible and well attached.After adding different concentrations of MPP+, the BV-2 cell surface protrusions gradually contracted, and showed an activated state of enlarged cell body, shorter protrusions, and rounded cell shape (Figure 3).
4.5 Indirect effect of BV-2 cell activation induced by MPP+on SH-SY5Y cell injury
To test whether MPP+ induced SH-SY5Y cell damage at the dose required to activate BV-2 cells, we observed the effect of MPP+onSH-SY5Y cell viability.MTT results showed that MPP+did not cause significant SH-SY5Y cell death in the concentration range of 1~400 mol·L-1(P> 0.05).When MPP+concentration was 100 mol·L-1, a large number of BV-2 cells were activated (Figure 3 and Table 5).When cultured with BV-2 cells and SH-SY5Y cells, 100 mol·L-1MPP+significantly decreased the survival rate of SH-SY5Y cells (P<0.01, Table 6).However, the addition of an equivalent amount of MPP+(without BV-2 cell regulation) directly to SHSY5Y cell culture did not reduce SH-SY5Y cell activity.According to the MTT results, a follow-up experiment was conducted with 100 mol·L-11 MPP+.
Tab 4 Expression of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β proteins in mouse midbrain (±s, n=6)
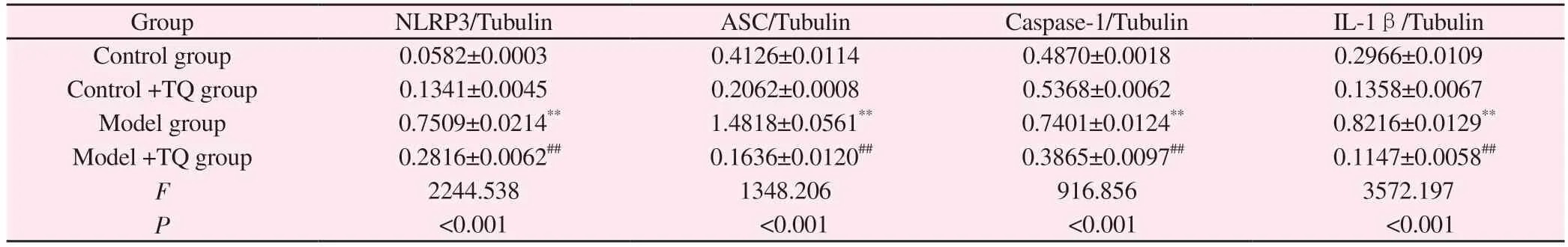
Tab 4 Expression of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β proteins in mouse midbrain (±s, n=6)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group,##P<0.01.
Group NLRP3/Tubulin ASC/Tubulin Caspase-1/Tubulin IL-1β/Tubulin Control group 0.0582±0.0003 0.4126±0.0114 0.4870±0.0018 0.2966±0.0109 Control +TQ group 0.1341±0.0045 0.2062±0.0008 0.5368±0.0062 0.1358±0.0067 Model group 0.7509±0.0214** 1.4818±0.0561** 0.7401±0.0124** 0.8216±0.0129**Model +TQ group 0.2816±0.0062## 0.1636±0.0120## 0.3865±0.0097## 0.1147±0.0058##F 2244.538 1348.206 916.856 3572.197 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001
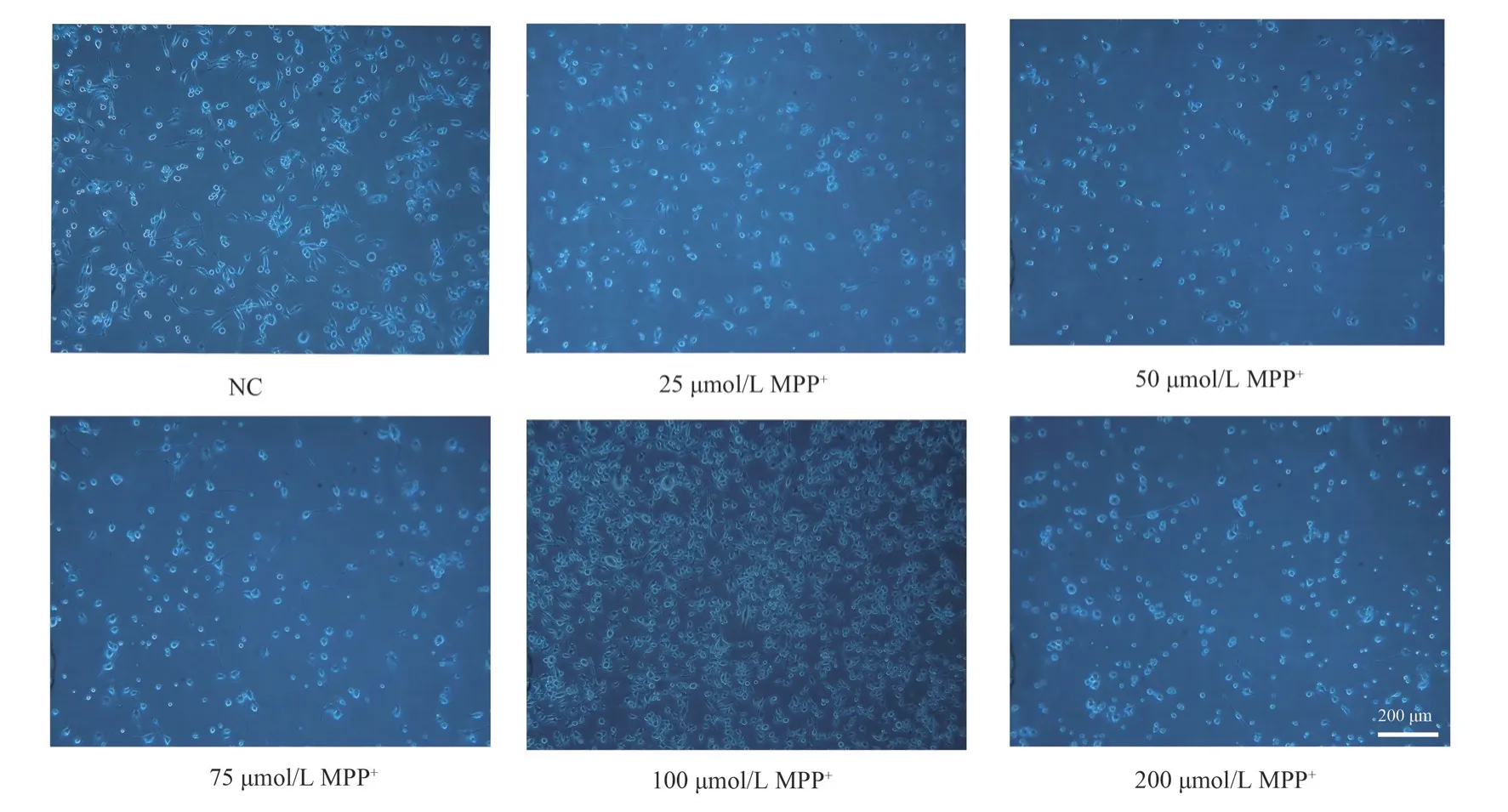
Fig 3 Morphological changes of BV-2 cells under inverted microscope (×200)
4.6 Effect of thymoquinone on injury of conditioned SH-SY5Y cells
After 24 h of conditioned culture of SH-SY5Y cells, the results showed that 0.25 μM and 0.5 μM TQ could significantly reduce the death of SH-SY5Y cells induced by conditioned culture solution(P<0.01, Table 7).Follow-up experiments were conducted with 0.25 μM and 0.5 μM TQ.
Tab 5 Effect of MPP+ on the viability of BV-2 cells and SH-SY5Y cells(±s, %, n=3)
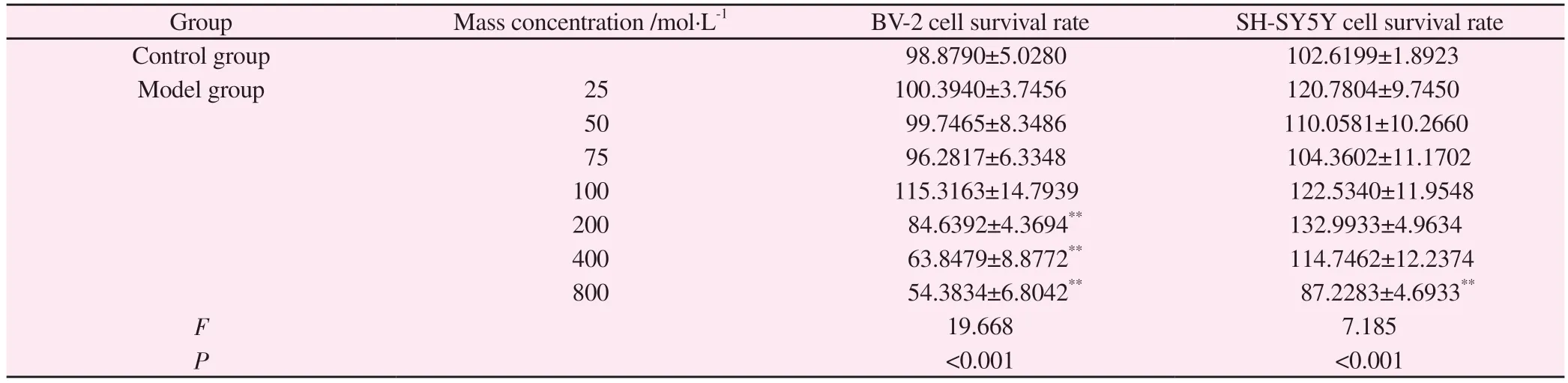
Tab 5 Effect of MPP+ on the viability of BV-2 cells and SH-SY5Y cells(±s, %, n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 BV-2 cell survival rate SH-SY5Y cell survival rate Control group 98.8790±5.0280 102.6199±1.8923 Model group 25 100.3940±3.7456 120.7804±9.7450 50 99.7465±8.3486 110.0581±10.2660 75 96.2817±6.3348 104.3602±11.1702 100 115.3163±14.7939 122.5340±11.9548 200 84.6392±4.3694** 132.9933±4.9634 400 63.8479±8.8772** 114.7462±12.2374 800 54.3834±6.8042** 87.2283±4.6933**F 19.668 7.185 P<0.001 <0.001
Tab 6 Effect of MPP+ on the viability of conditioned SH-SY5Y cells(±s,%)
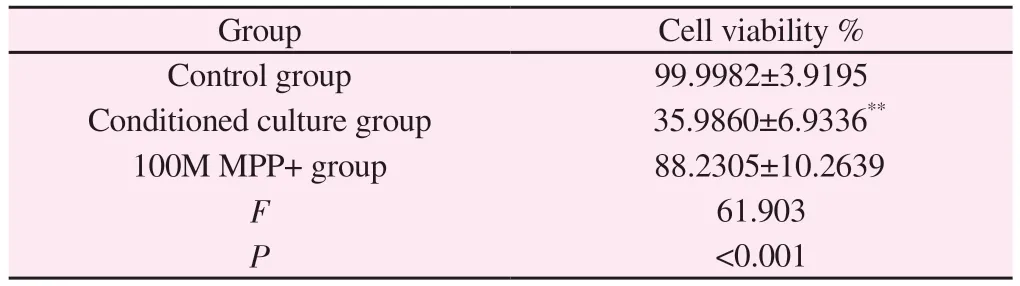
Tab 6 Effect of MPP+ on the viability of conditioned SH-SY5Y cells(±s,%)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01.
Group Cell viability %Control group 99.9982±3.9195 Conditioned culture group 35.9860±6.9336**100M MPP+ group 88.2305±10.2639 F 61.903 P<0.001
Tab 7 Effect of TQ on MPP+-mediated viability of conditioned SH-SY5Y cells(±s, % , n=3)
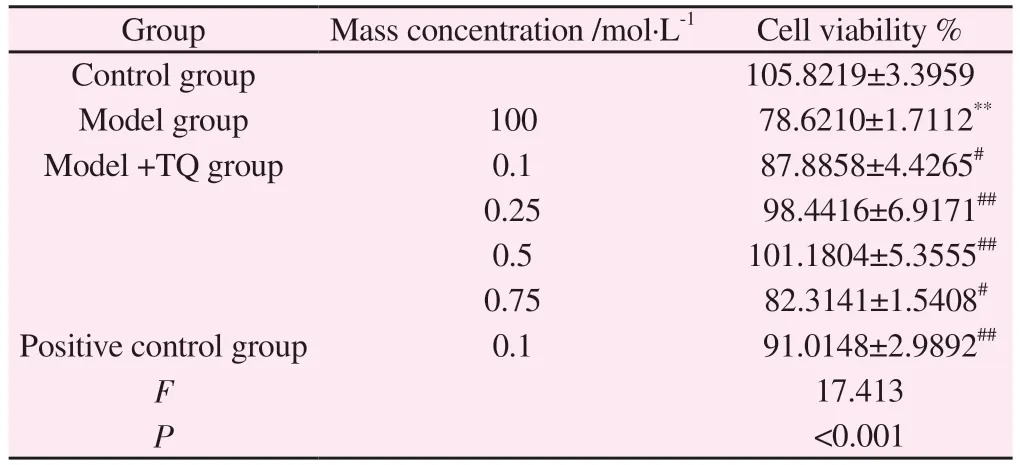
Tab 7 Effect of TQ on MPP+-mediated viability of conditioned SH-SY5Y cells(±s, % , n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group, #P<0.05, ##P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 Cell viability %Control group 105.8219±3.3959 Model group 100 78.6210±1.7112**Model +TQ group 0.1 87.8858±4.4265#0.25 98.4416±6.9171##0.5 101.1804±5.3555##0.75 82.3141±1.5408#Positive control group 0.1 91.0148±2.9892##F 17.413 P<0.001
4.7 Effect of thymoquinone on apoptosis rate of conditioned cultured SH-SY5Y cells
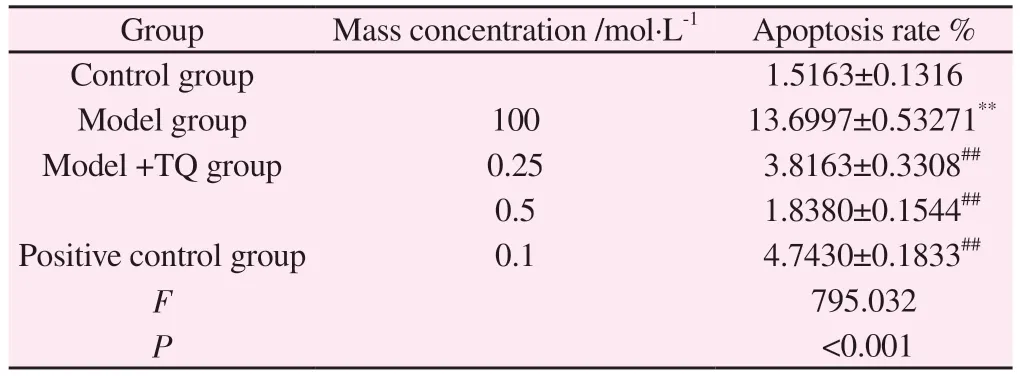
The results showed that the number of apoptotic cells in the model group increased significantly (P<0.01), while the number of apoptotic cells in the model +TQ group and the positive control group decreased significantly (P<0.01, Figure 4, Table 8).
4.8 Effects of thymoquinone on apoptosis-related proteins in cultured SH-SY5Y cells
After MPP+, the expression of Bcl-2/Bax ratio was significantly down-regulated, while TQ could promote the expression of Bcl-2/Bax ratio (P<0.01).At the same time, MPP+promoted the expression of Caspase-3, a key regulatory protein of apoptosis (P<0.01),indicating that activated BV-2 cells had a damage effect on SHSY5Y cells, while TQ significantly inhibited the increase of MPP+induced Caspase-3 after intervention (P<0.01).It was suggested that TQ alleviated the apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells by intervening in the activation of BV-2 cells (Figure 5, Table 9).
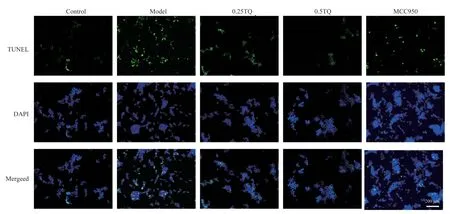
Fig 4 Inhibition of TQ on apoptosis in conditioned SH-SY5Y cells (scale bar 200 μm, n=3)
Tab 8 Effect of TQ on apoptosis rate of SH-SY5Y cells cultured under MPP+conditions (±s, % , n=3)
Tab 8 Effect of TQ on apoptosis rate of SH-SY5Y cells cultured under MPP+conditions (±s, % , n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group, ##P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 Apoptosis rate %Control group 1.5163±0.1316 Model group 100 13.6997±0.53271**Model +TQ group 0.25 3.8163±0.3308##0.5 1.8380±0.1544##Positive control group 0.1 4.7430±0.1833##F 795.032 P<0.001
4.9 Effects of thymoquinone on secretion of inflammatory cytokines in BV-2 cells
ELISA results showed that after treating BV-2 cells with 100 mol·L-1MPP+for 8h, the expression of IL-1β was significantly increased compared with that of control group (P<0.01).Pretreatment with 0.25 μM and 0.5 μM TQ decreased IL-1β levels(Table 10)
Tab 9 Comparison of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 protein expression in SH-SY5Y cells cultured under conditions in each group(±s, n=3)
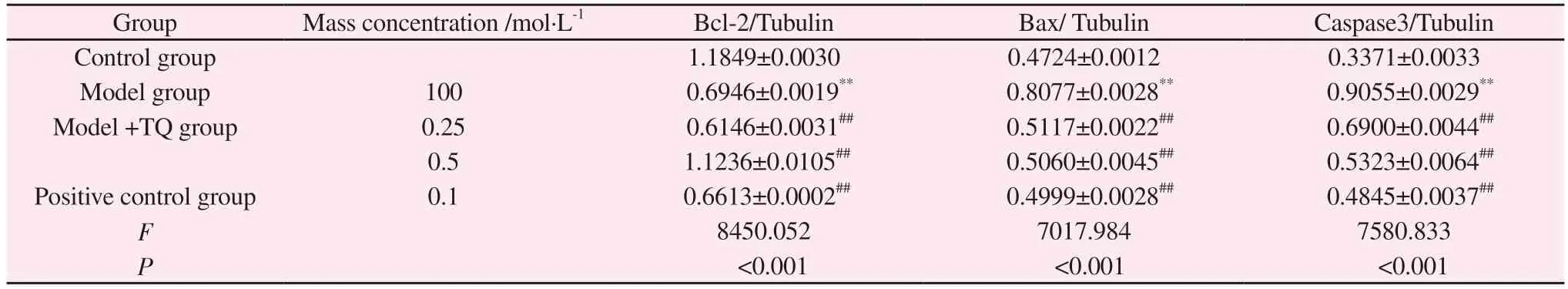
Tab 9 Comparison of Bcl-2, Bax and Caspase-3 protein expression in SH-SY5Y cells cultured under conditions in each group(±s, n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group,##P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 Bcl-2/Tubulin Bax/ Tubulin Caspase3/Tubulin Control group 1.1849±0.0030 0.4724±0.0012 0.3371±0.0033 Model group 100 0.6946±0.0019** 0.8077±0.0028** 0.9055±0.0029**Model +TQ group 0.25 0.6146±0.0031## 0.5117±0.0022## 0.6900±0.0044##0.5 1.1236±0.0105## 0.5060±0.0045## 0.5323±0.0064##Positive control group 0.1 0.6613±0.0002## 0.4999±0.0028## 0.4845±0.0037##F 8450.052 7017.984 7580.833 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001
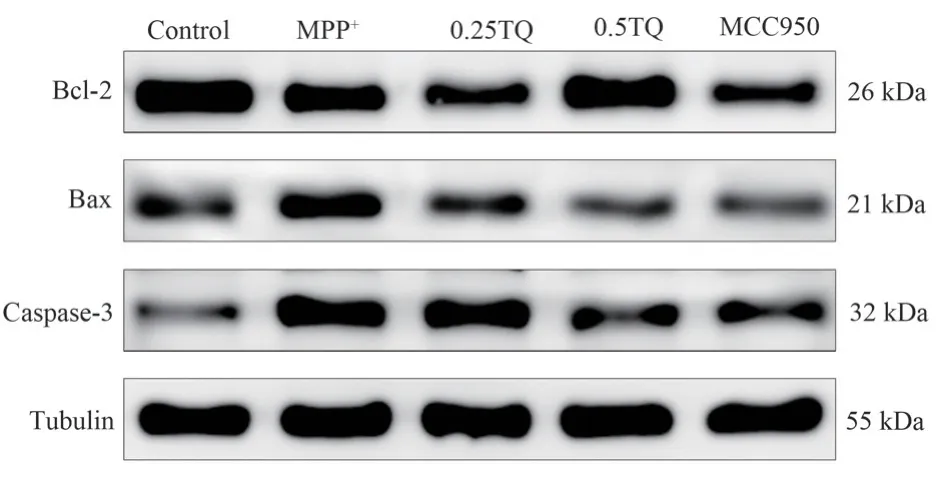
Fig 5 Comparison of Bcl-2, Bax, and Caspase-3 protein expression in SHSY5Y cells cultured with conditions in each group(n=3)
4.10 Effect of thymoquinone on the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-related protein in BV-2 cells.
The results showed that MPP+induced a significant increase in the levels of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β inflammatory signalingpathways in BV-2 cells.NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, and IL-1β inflammatory signaling pathways were significantly inhibited after intervention with 0.25 μM and 0.5 μM TQ (P<0.01, Figure 6,Table 11).
Tab 10 Comparison of IL-1β content in BV-2 cells of each group(±s, n=3)
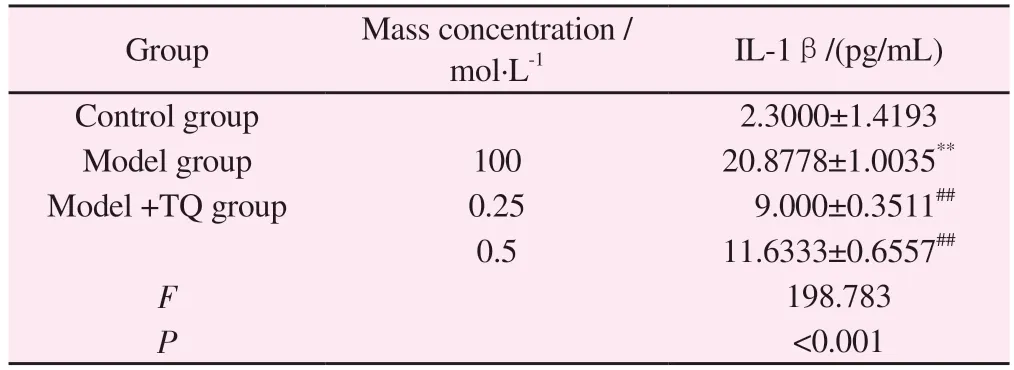
Tab 10 Comparison of IL-1β content in BV-2 cells of each group(±s, n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01;Compared with the model group,##P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 IL-1β/(pg/mL)Control group 2.3000±1.4193 Model group 100 20.8778±1.0035**Model +TQ group 0.25 9.000±0.3511##0.5 11.6333±0.6557##F 198.783 P<0.001
5.Discussion
PD is closely related to neuroinflammation.The inflammatory cytokine TNF-α released by activated microglia can bind to the TNF receptor on neurons and activate the cysteine aspartic protease(Caspase) dependent cascade, accompanied by the activation of toll-like receptor (TLR) and nucleotide-bound oligomerization receptor (NLR).This process aggravates neuroinflammation and leads to neuronal apoptosis[15-16].Studies[17-18] have shown that NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in the substantia nigra region of PD patients and PD animal models, confirming that NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor can significantly alleviate the loss of dopaminergic neurons and improve motor dysfunction in PD mice.Studies have found[19] that during the development of PD,pathological -synuclein can also cause the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, resulting in DA neuron damage.TQ can produce a large number of natural antioxidants by scavenging free radicals and increasing gene transcription[20].TQ can effectively reduce neuronal damage by inhibiting the expression of pre-apoptotic proteins Caspase-3 and Caspase-9[21].TQ also exhibits anti-inflammatory activity by inhibiting LPS-induced IL-6 and inducible nitric oxide(iNOS) inflammatory factors[22].
Tab 11 Comparison of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β expression in BV-2 cells of each group(±s, n=3)

Tab 11 Comparison of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β expression in BV-2 cells of each group(±s, n=3)
Note: Compared with control group,**P<0.01; Compared with the model group,##P<0.01.
Group Mass concentration /mol·L-1 NLRP3/Tubulin ASC/Tubulin Caspase-1/ Tubulin IL1β/Tubulin Control group 0.0508±0.0018 0.1399±0.0051 0.2534±0.0022 0.8796±0.0311 Model group 100 1.3857±0.0057** 0.8607±0.0012** 0.7670±0.0041** 1.6065±0.0068**Model +TQ group 0.25 0.3653±0.0038## 0.2524±0.0044## 0.5083±0.0020## 0.8921±0.0131##0.5 0.3913±0.0119## 0.5591±0.0062## 0.6669±0.0152## 1.1328±0.0315##Positive control group 0.1 0.5067±0.0009## 0.6455±0.0042## 0.4551±0.0036## 1.1954±0.0265##F 19593.593 12539.373 2188.170 455.846 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001
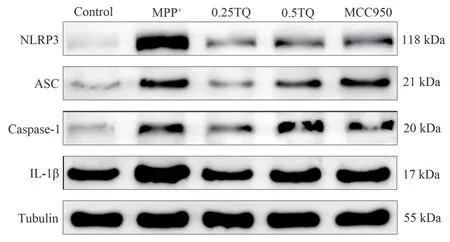
Fig 6 Comparison of NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1 and IL-1β expression in BV-2 cells of each group (n=3)
The results of in vitro experiments showed that TQ could significantly improve the behavior disorder of PD mice, reduce the level of α-Syn and the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-related protein in PD mice, and promote the expression of the characteristic antiboth-protein on the surface of dopaminergic neurons.In vivo,LPS combined with MPP+stimulated BV-2 cells to simulate the pathological environment of PD, and TQ intervention was given.As a common apoptotic gene in the Bcl-2 family, Bax combines with Bcl-2 to form heterodimer, which regulates the activity of Bcl-2.When the expression of Bax increases, Bax/Bcl-2 is up-regulated,and the whole state is in a state of promoting apoptosis, which can promote the expression of Caspase-3[23-24].The experimental results showed that the expression of Bax was significantly up-regulated and the expression of Bcl-2 was down-regulated in PD model.TQ treatment could inhibit the up-regulation of Bax and promote the expression of Bcl-2.Moreover, TQ can also inhibit the up-regulation of Caspase-3 proapoptotic protein expression.After TQ treatment,the level of inflammatory factor IL-1β and the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome-related protein were decreased.These results suggested that after MPP+activated BV-2 cells, a large number of inflammatory cytokines were released, which promoted the release of NLRP3 inflammasome and then activated Bax apoptotic protein, leading to the apoptosis of SH-SY5Y cells.TQ protects SHSY5Y cells by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome,alleviating the neuroinflammatory injury of PD.
In conclusion, TQ can alleviate the damage of dopaminergic neurons in PD mouse model.TQ can reduce the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome and the release of inflammatory factors in BV-2 cells induced by MPP+ intervention, reduce inflammatory response, improve dopaminergic neuron injury, and have a protective effect on PD neuroinflammation.
Authors' contribution
Ge Shuli: designing experiments, analyzing data, writing papers;Cheng Nan: Put forward guidance on the paper; Dong Jianjian, Xu Chenchen: Participated in animal modeling and experimental index detection.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年17期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年17期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on the regulation mechanism of non-coding RNA on ankylosing spondylitis
- Anesthetic effect of phenobarbital sodium on female BALB/c mice
- Research progress of TCM regulation of Cajal interstitial cells in the treatment of functional Gastrointestinal diseases
- Abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type
- Effect of Astragalus-hawthorn on ovarian reproductive function and inflammatory mechanism of action in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Effect of estrogen pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol-Metaanalysis
