The Impact of Population Aging on the Expenditure of Medical Insurance Fund for Urban Workers in China
Wang Shuling,Dou Lele,Shi Hui,Huang Zhe
(School of Business Administration, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China)
Abstract Objective To explore the impact of population aging on the expenditures of medical insurance funds against the background that great changes in population structure influences economic development.Methods Through analyzing the impact of the population aging,the income and accumulated balance of the medical insurance fund,and other related factors on the expenditure of the medical insurance fund,development status of the medical insurance fund for urban employees in China since 2003 was obtained.Stata 16.0 was used to perform multiple linear regression analysis on related factors to determine the correlation between population aging and the change in medical insurance expenditures.Results and Conclusion The factors that have a greater impact on the expenditure of the medical insurance fund are the amount of income from the medical insurance,followed by the number of people over the age of 65 in China and the urban retired employees participating in medical insurance.We should focus on the sustainable development of the urban employee medical insurance fund to deal with the threat of aging.
Keywords: population aging;medical insurance fund expenditure;stata;multiple linear regression
The population is a key factor affecting economic and social development.Since the reform and opening up,China’s population structure has undergone tremendous changes,which also has a great impact on China’s economic development.The 7th Census data published recently shows that the workingage population of China between 15-59 years old has dropped by 6.79% compared to that in 2010.China’s working-age population has declined,and the demographic dividend has also been dropping[1].Demographic factors can affect a country’s economic growth from multiple angles,including the labor market,capital accumulation,economic structure,and social productivity[2].The rapid development of China’s economy is inseparable from the demographic dividend.
But after decades of rapid development,the problem of rapidly increasing population aging has gradually become serious[3].China’s medical insurance system highlights the preferential treatment and care for the elderly in the financing policy settings.In addition,the long-term care insurance system that China has explored and established is also to solve the care problems of senior citizens[4,5].With the rapid development of the aging population,it will inevitably put great pressure on China’s medical system.Social medical insurance in many other countries also has to face a huge fiscal deficit due to the aging problem.Therefore,it is vital to study the impact of population aging on the expenditure of medical insurance funds[6].
1 The status quo of China’s population aging
1.1 The development trend of population aging
As one of the most populous countries,the government’s policy of encouraging childbirth in the last century enabled China to obtain a demographic dividend quickly,which has contributed inestimably to China’s rapid development in recent decades.However,with the fast development of the economy,the change of people’s perceptions and the promotion of the national policy of prenatal and postnatal care,the trend of excessive population growth was significantly alleviated in the past decade[7].Therefore,population growth has transitioned to the stage of low birth rate,low death rate,and low natural growth rate.However,due to the policy of encouraging childbirth,China’s high fertility rate in the 1950s and 1960s caused a sharp increase in the current population aging from 60 to 70 years.As a result,the old-age dependency ratio is getting higher,and the pressure on young people to support the elderly has increased accordingly,which means China enters the aging stage.
When the population over 60 is more than 10% in a country or more than 7% of the population is over 65,it means that this country belongs to the aging one[8].In 2000,the proportion of the population over 65 in China was 7%,so China officially entered an aging society.The change of China’s aging population is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Trend map of China’s aging population
China’s aging population has been on the rise since 2000.From the curve of the proportion of the population over 65 years old,it can be seen that the growth rate of aging population has been increasing year by year,indicating China has entered a stage of aging acceleration.The rapid development of aging will inevitably bring a certain burden to medical expenditures and medical security expenditures.
1.2 Development status of China’s medical insurance fund
1.2.1 Development status of China’s basic medical security
In January 1997,the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council promulgated the “Decision on Health Reform and Development”.In December 1998,the “Decision of the State Council on Establishing a Basic Medical Insurance System for Urban Employees” was promulgated.This indicates that the reform of China’s urban social medical insurance system starts innovation comprehensively.The original publicly funded medical system stops working any more.In 1999,the basic medical insurance system began to reform in some cities of China.Medical insurance fund refers to a special fund collected by the state according to the law.Enterprises,institutions,organizations,and individuals participating in medical insurance should pay a certain amount of medical insurance premiums under a predetermined proportion.It is the basic medical expenses paid by the state to protect the insured during the period of illness.
The number of people participating in medical insurance in China from 1999 to 2020 is shown in Fig.2.This includes the number of people participating in urban employee medical insurance,urban and rural residents’ medical insurance,and the new rural cooperative medical insurance.

Fig.2 Number of people participating in basic medical insurance
Since the establishment of the basic medical insurance system,the number of insured persons in China has increased year by year,and the growth rate at the initial stage has also risen fast,reaching 106.29%.China’s urban employee medical insurance developed early and the system was complete,while urban residents’ medical insurance and new rural cooperative medical insurance developed relatively late.China is currently vigorously developing basic medical insurance,striving to achieve full coverage[9].Therefore,the large increase in the number of insured persons in 2007,2008 and 2017 is mainly due to the large number of urban residents participating in the new rural cooperative medical system.
By the end of 2020,China had 1.361 billion people participating in basic medical insurance.According to the seventh census data,there were 1.411 77 billion people in China by the end of 2020,and the basic medical insurance coverage rate reached 96.4%.It can be seen from Fig.2 that from 2018 to 2020,the number of people insured in China has remained stable and the increase rate is low.Therefore,this will be the normal state of the increase in the number of people insured in the future.
1.2.2 Status quo of China’s urban employees participating in insurance
The number of urban employees participating in basic medical insurance in China reached 0.344 23 billion in 2020,of which 253.98 million were in-service employees and 90.25 million were retired employees.A comparison of the number of employees participating in insurance and the population over 65 in China is shown in Fig.3.

Fig.3 Number of employees insured
China’s basic medical insurance policy for retirees is that they have to pay medical insurance fees for a certain number of years,then they can enjoy medical insurance benefits when they get retired.As shown in Fig.3,the number of insured employees and retired employees in China has increased every year.
1.2.3 Development status of urban employee medical insurance fund
Since 2006,the total amount of funds raised for urban employee medical insurance nationwide has increased from 174.71 billion yuan to 1 562.46 billion yuan in 2020.The amount of expenditure increased from 127.67 billion yuan in 2006 to 1 283.44 billion yuan in 2020.The cumulative balance increased from 175.24 billion yuan in 2006 to 2 532.35 billion yuan in 2020.
The income,expenditure,and balance of the medical insurance fund of urban employees in China have increased sharply in 15 years,as shown in Fig.4.

Fig.4 Income,expenditure and balance of urban workers’ medical insurance fund from 2006 to 2020
2 Regression model
2.1 Variable selection and data sources
Stata 16.0 is used to estimate and test the regression of time series data from 2003 to 2020 in this paper.By analyzing the impact of population aging on the income,expenditure and cumulative balance of the urban employee fund,we can empirically test the impact of the proportion of population aging on the expenditure of urban employee medical insurance funds.
2.1.1 Explained variable:Urban employees’medical insurance fund expenditure(Y)
Based on the income,expenditure and balance of the national basic medical insurance for urban employees from 2003 to 2020 (18 years in total) in the National Bureau of Statistics (Annual Statistical Bulletin) and the China Health Database,we sort out the population aging data.Since the basic medical insurance for urban employees is the first medical insurance system implemented in China,it has been relatively complete and perfect.Therefore,the expenditures of the urban employees’ medical insurance fund are recorded asY.
2.1.2 Explanatory variable:The number of people over 65 years old(β1)
Among many indicators to measure aging,this paper selects 65 years old as the node to calculate the proportion of the elderly population in the total population.Among them,the data for 2020 are the seventh census data,which is more representative.The remaining years are the proportion of the 65-yearold to the total population.Since the increase in the elderly population will increase the corresponding medical insurance costs,there is a correlation between them[10].So,the number of people over 65 years old is used as an explanatory variable and recorded asβ1.
2.1.3 Control variables
(1) Medical insurance fund income (β2).Medical insurance fund expenditure and income are inextricably related.Generally speaking,expenditure needs to be based on income.However,due to its s feature,medical insurance fund may have a special situation of being unable to make ends meet.Therefore,the medical insurance expenditure is taken as a control variable,denoted asβ2.
(2) Cumulative balance of medical insurance fund (β3).The cumulative balance of the medical insurance fund is another important factor affecting medical insurance expenditure.When the medical insurance fund cannot make ends meet,the cumulative balance is the backbone of the medical insurance fund[11],and it is a key force to effectively resist various family medical risks.Therefore,the accumulation of medical insurance funds is regarded as a control variable,denoted asβ3.
(3) Total number of urban employees participating in insurance (β4).The number of urban employees participating in the insurance is the main income of the urban employee medical insurance fund and the premise of the expenditure of the medical insurance.Therefore,the total number of urban employees participating in the insurance is taken as a control variable and recorded asβ4.
(4) Number of retired urban employees participating in insurance (β5).After retirement,the insured urban employee do not have to pay medical insurance fees,but they can enjoy medical insurance benefits.These people are the objects to consume medical insurance fund.Therefore,they are regarded as a control variable,denoted asβ5.
(5) Other factors (ε).The other factors that affect urban employees’ medical insurance expenditures are more complicated,and they are denoted asε.
2.2 Model establishment
According to the setting of explained variables,explanatory variables and control variables in 2.1,the following multiple linear regression model is established:
Among them,αiis the Coef.coefficient,that is,the original number under natural conditions,andεis a discrete variable used to represent the random disturbance term.
2.3 Econometric regression results
Stata 16.0 is used to process the data,and the measurement results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Stata measurement regression results
Among them,cons represents a constant term.From the results,theFstatistic of the regression model is 936.51,and its correspondingPvalue (Prob>F) is 0.000 0,indicating that the regression equation is highly significant.R-squared showsR2=0.997 4,and AdjR2=0.996 4,indicating that the goodness of fit of the equation is good.It follows that the fitting model is:
The reason for the larger perturbation term is that the data base used in this equation is too large.Among them,theβ1coefficient is 0.256 0,which means that for every additional 10 000 people over the age of 65,the medical insurance fund expenditure will increase by 256.0 million yuan.When theβ2coefficient is 0.861 6,it means that for every 100 million yuan increase in medical insurance fund income,the medical insurance fund expenditure will increase by 86.16 million yuan.When theβ3coefficient is 0.097 1,it means that for every 100 million yuan increase in the cumulative balance of the medical insurance fund,the medical insurance fund expenditure will increase by 0.097 1 million.When theβ4coefficient is 0.006 8,it means that every 10 000 urban employees are insured,the medical insurance fund expenditure will increase by 106.8 billion yuan.When theβ5coefficient is 0.168 5,it means that for every additional 10 000 retired urban employees to participate in the insurance,the medical insurance fund expenditure will increase by 168.5 million yuan.
According to the above results,it can be seen that the factors having a greater impact on the expenditure of the medical insurance fund are the amount of income of the medical insurance,followed by the number of people over the age of 65 and the urban retired workers participating in medical insurance.
2.4 Multicollinearity test
The multicollinearity test of the model is as Table 2.
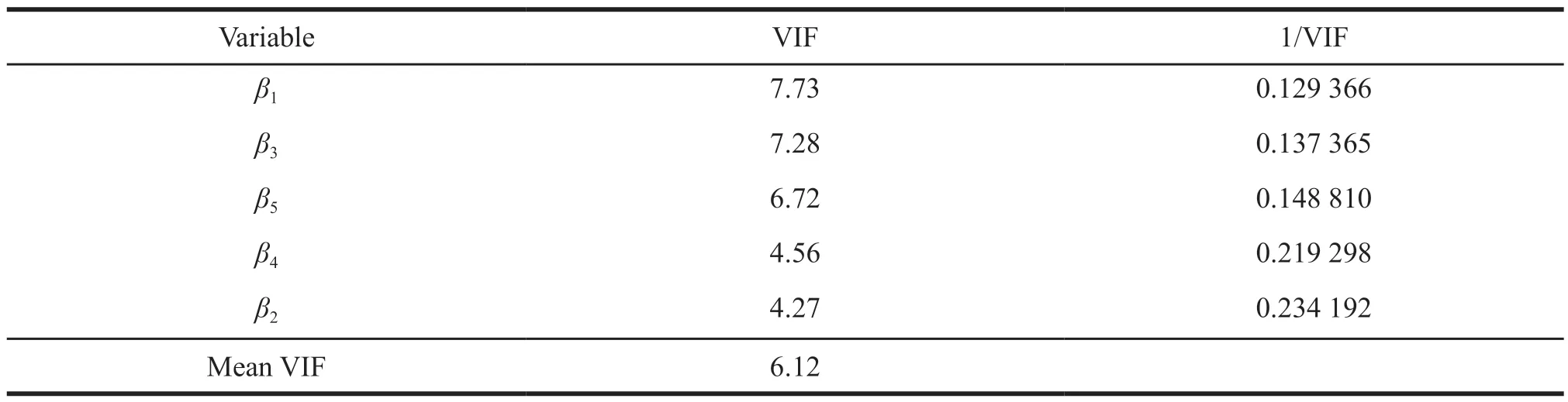
Table 2 Multicollinearity test results
It can be seen that the VIF values of the five variables of the model are all less than 10,and their mean is 6.12.Therefore,the model does not have multicollinearity.It can be seen that the model fits well and can be further tested.
2.5 Test for heteroscedasticity
The test results are as follows:
Breusch-Pagan/Cook-Weisberg test for heteroskedasticity
Ho: Conatant variance
Variables: Fitted values ofy
chi2 (1)=2.82
Prob > chi2=0.092 8
The test results show that thePvalue is greater than 0.05,and the null hypothesis is not rejected.Therefore,the model can be considered as homoscedastic.
3 Thoughts and conclusion
3.1 Focusing on the sustainable development of medical insurance funds
Based on the research results,Chinese aging population has brought severe challenges to the expenditure of the employee medical insurance fund.We should focus on the sustainability of the employee medical insurance fund to deal with the threat posed by the large number of aging population.At the same time,the factor that has a greater impact on the expenditure of the medical insurance is the amount of income of the medical insurance fund.China’s medical insurance has not yet reached a saturated condition,and the government should encourage uninsured people to participate in medical insurance through the introduction of corresponding policies.In terms of improving the sustainability of medical insurance funds,two aspects such as increasing revenue and reducing expenditure can make the contribution to it.
3.2 Actively exploring more appropriate reimbursement of medical insurance fund
Reimbursement of medical insurance fund is a key link in basic medical insurance management and deepening medical insurance reform.Appropriate reimbursement can effectively cut cost to control unreasonable expenditures of medical insurance funds.Compared with developed countries,China has many problems in reimbursement of medical insurance.We should actively explore new methods for diagnosis related groups (DRGs) system.At present,more than 30 countries including the United States and Germany have fully implemented this reimbursement method.Since the new round of medical reform,China is also actively exploring reimbursement based on disease types.
3.3 Vigorously developing the aging services industry and giving full play to the role of this industry
Although the trend of population aging is irreversible,it does not mean that we can only let it go.We should increase the fertility rate and improve the population structure while vigorously developing the aging services industry.Besides,we can incorporate the aging services industry into the local industry development plan,and the local governments should strengthen industry guidance to promote infrastructure construction in elderly care services.Therefore,this group of people will bring economic growth momentum.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Effect of the Policies to Prevent Drug Shortage and Stabilize Drug Prices in Medical lnstitutions
- Research on the Countermeasures for the Development of Biopharmaceutical Industrial Parks in China
- Research Progress in FDA’s Focus Areas of Regulatory Science for Drugs and Suggestions for China
- Hypersensitivity Reaction Caused by Intravenous Gadolinium-based MRI Contrast Agents
- Cost-effectiveness Analysis of lnsulin Degludec and Liraglutide lnjection in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- A Systematic Review of Patient-Reported Outcome Measurement for Psoriasis in Chinese Population

