共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝的纺丝成形
姬洪 宋明根 张玥 陈康 张玉梅


摘 要:为了纺制兼具良好阻燃与力学性能的共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝,在分析高分子量阻燃共聚酯流变特性以及量化不同纺丝温度条件下共聚酯热降解程度的基础上,设计和优化熔融纺丝工艺。对纺制的阻燃工业丝力学性能与阻燃性能进行测试,并采用X-射线衍射和声速纤维取向测量仪对纤维的微细结构进行测试分析。结果表明:相较纯PET,共聚酯熔体黏度较低,温敏性更为明显。采用低的纺丝温度(285 ℃左右),熔体黏度对纺丝压力影响小且热降解程度低,可制备断裂强度为6.75 cN/dtex、极限氧指数(LOI)可达31%的共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝,且其阻燃耐久性突出,实现了良好阻燃性能与力学性能共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝的制备。
关键词:聚酯工业丝;共聚型;阻燃;力学性能
中图分类号:TS102
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1009-265X(2023)04-0056-07
收稿日期:2022-11-24
网络出版日期:2023-02-22
基金项目:高性能纤维及制品教育部重点实验室开放课题(2020)
作者简介:姬洪(1987—),男,山东泰安人,博士,主要从事高性能纤维材料开发与应用方面的研究。
通信作者:张玉梅,E-mail:zhangym@dhu.edu.cn
(Mn>2.5X104,[η]>0.85 dL/g)聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)制备的聚酯工业丝具有强度高、模量大、耐热性能好等优点[1],广泛用于安全带、吊装带、土工布、汽车帘子线、缆绳、传送带等领域[2-3]。但是,PET的极限氧指数(LOI)只有20%左右,在纤维燃烧性能等级划分中属于易燃等级,限制了其应用领域的进一步拓展[4-6]。通过聚合反应将阻燃单体共聚引入聚酯大分子链,可以有效避免阻燃剂在聚酯加工及使用过程中的迁移,与共混添加法相比具有阻燃耐久等优点,是制备阻燃聚酯纤维材料的一种较为理想的方法[7-8]。
采用共聚法制备阻燃聚酯工业丝的技术要求高,由于共聚单体空间位阻、大分子链规整性破坏以及弱键等原因,阻燃共聚酯在固相缩聚反应(SSP)中分子量提升[9]以及在纺丝加工过程中高分子量共聚酯的分子量保持是制备共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝的关键技术。PET在高温加工条件下会发生降解反应,严重影响制品性能与品质[10]。阻燃共聚酯因阻燃单体的引入,其键接结构发生改变,相较于常规PET可能更易发生热解[11-13]。现有共聚型阻燃聚酯工业丝产品其力学性能与阻燃性能难以兼顾 (断裂度6.5 cN/dtex左右,LOI在30%以下),远不能满足特殊的工业应用领域,如用于水龙带、过滤/通风织物和涂层织物等的特定要求[15]。目前高分子量阻燃共聚酯在熔融纺丝过程中的热降解及工艺调控的相关信息未见报道,然而,这对于其热解控制、分子量的保持具有重要意义。另一方面,聚合物熔体流变特性是熔融纺丝加工中的关键参数,不仅受共聚阻燃剂的影响,同時分子量参数的微小变化也会导致其流变特性行为的显著变化。因此为保证纺丝顺利进行以及成纤力学性能,需要对这些材料特性指标予以明确,为相应的工艺提供参数指导。
在以往研究阻燃共聚酯SSP反应并成功制备高分子量共聚酯的基础上[9],本文首先研究纺丝熔融加工条件下高分子量阻燃共聚酯的流变行为,并对纺丝工艺进行相应设计,对纺丝成型过程中共聚酯的热降解程度进行明确,据此优化纺丝工艺,最后对制备的工业丝的性能与结构进行测试、表征和分析。
1 实 验
1.1 实验材料
高分子量聚酯(HPET,特性黏度为(1.050±0.003) dL/g)和高分子量阻燃共聚酯(HFRP,特性黏度为(1.050±0.005) dL/g),均由浙江尤夫高新纤维股份有限公司提供,阻燃共聚酯所采用的阻燃剂为2-羧乙基苯基次磷酸(CEPPA),共聚酯的磷含量为0.006%。
1.2 纺丝试验
以HPET和HFRP为原料,采用纺丝-后牵伸两步法制备聚酯工业丝(P-Y)和阻燃聚酯工业丝(FRP-Y),设计单纤纤度为5 dtex。
熔融纺丝工艺:采用日本ABE公司纺丝机进行纺丝试验,其中喷丝板规格为:孔径为5 mm,孔数为36孔。纺丝试验中螺杆(一区到四区)、管道、计量泵以及箱体温度设置如表1所示。熔体由喷丝板挤出后,经侧吹冷却,通过纺丝甬道后由卷绕机卷绕成筒,卷绕速度为800 m/min。
后牵伸工艺:采用平行牵伸机(苏州特发机电有限公司,TF-100)对熔纺低速卷绕的初生丝进行牵伸。其中工艺参数为: 热盘温度为80 ℃;热板温度为160 ℃,牵伸倍数分别为3.2,3.8,4.2,4.6。
热管牵伸工艺:采用有机高性能纤维温控多级牵伸实验装置(实验室自制装置)对平板牵伸倍率为3.2倍的纤维进行三级热管牵伸,P-Y和FRP-Y两种样品的热牵伸温度如表2所示,总后牵伸倍率为5.8倍。
1.3 测试与表征
1.3.1 特性黏度
参照标准GB/T 14190-2017《纤维级聚酯切片(PET)试验方法》,将干燥充分的样品溶解于苯酚/1,1,2,2-四氯乙烷(50/50,质量比)混合溶剂,溶液浓度为0.50 g/dL。在恒温水浴槽中,温度(25±0.05) ℃下使用毛细管直径0.7~0.8 mm的乌氏黏度计进行特性黏度测定。
1.3.2 燃烧性能测试
LOI值 (极限氧指数)测试中将50根纱线加捻,捻度约20捻/10 cm,制成长约10 cm的绳状样条,参考JIS L1091—1999《阻燃测试E-1法》进行测试;垂直燃烧试验采用极限氧指数(LOI)样条制备方法制备待测样品,参照GB/T 2408—2021 《塑料 燃烧性能的测定 水平法和垂直法》进行燃烧测试。
1.3.3 X-射线衍射实验(XRD)
采用日本理学公司的D/max-2550VB+/PC 型18 kW转靶 X 射线衍射仪进行XRD测试。样品制成粉末状,以消除测试过程中取向对衍射强度的影响。将剪碎后的样品置于样品台上进行测试,其中X射线波长为0.154 nm, 2θ测试范围为 5°~60°。
1.3.4 声速取向
采用东华凯利公司的SCY-Ⅲ型声速取向测试仪,测定声波在纤维中的传播速率,计算纤维的声速取向因子fs。
1.3.5 熔体流变性能测试
将样品120 ℃干燥12 h,含水率低于6×10-5%,采用奥地利安东帕有限公司Physica MCR301旋转流变仪,选取等温恒定剪切速率时间扫描测试模式,25 mm平行板,间距1 mm,剪切速率5 s-1,测试时间0~1800 s。
1.3.6 纤维力学性能测试
采用YG 020B 形单纱强力测试仪,在恒温恒湿环境下(20 ℃/65% RH)对纤维力学性能进行测试,其中测试参数设定:强力测试加持距离200 mm,拉伸速度200 mm/min。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 熔体流变特性
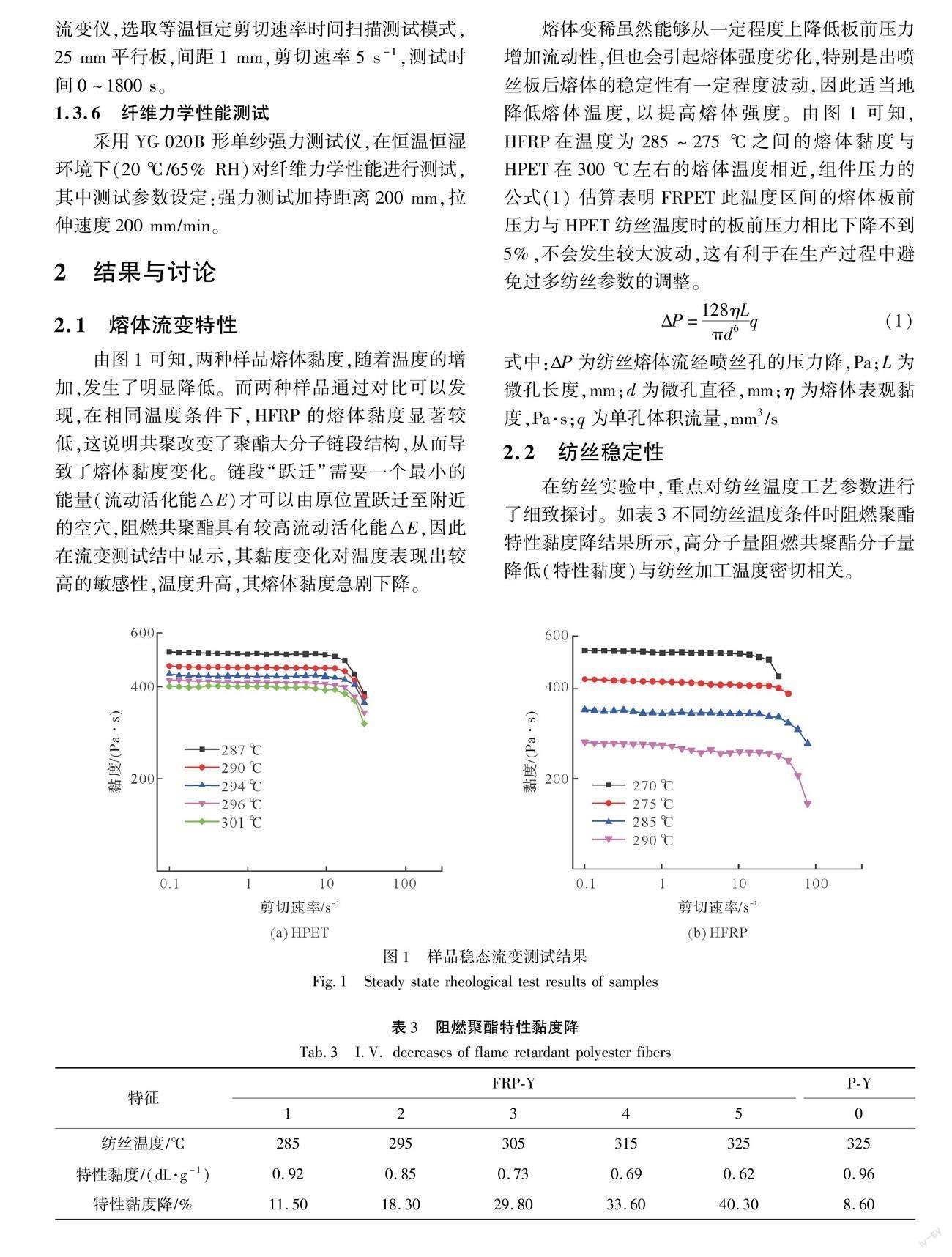
由图1可知,两种样品熔体黏度,随着温度的增加,发生了明显降低。而两种样品通过对比可以发现,在相同温度条件下,HFRP的熔体黏度显著较低,这说明共聚改变了聚酯大分子链段结构,从而导致了熔体黏度变化。链段“跃迁”需要一个最小的能量(流动活化能△E)才可以由原位置跃迁至附近的空穴,阻燃共聚酯具有较高流动活化能△E,因此在流变测试结中显示,其黏度变化对温度表现出较高的敏感性,温度升高,其熔体黏度急剧下降。
熔体变稀虽然能够从一定程度上降低板前压力增加流动性,但也会引起熔体强度劣化,特别是出喷丝板后熔体的稳定性有一定程度波动,因此适当地降低熔体温度,以提高熔体强度。由图1可知,HFRP在温度为285~275 ℃之间的熔体黏度与HPET在300 ℃左右的熔体温度相近,组件压力的公式(1) 估算表明FRPET此温度区间的熔体板前压力与HPET纺丝温度时的板前压力相比下降不到5%,不会发生较大波动,这有利于在生产过程中避免过多纺丝参数的调整。
2.2 纺丝稳定性
在纺丝实验中,重点对纺丝温度工艺参数进行了细致探讨。如表3不同纺丝温度条件时阻燃聚酯特性黏度降结果所示,高分子量阻燃共聚酯分子量降低(特性黏度)与纺丝加工温度密切相关。
在最高纺丝温度305 ℃时,特性黏度由1.05 dL/g降低至0.62 dL/g,黏度降高达40.3%。适当降低纺丝温度后,特性黏度降有所改善,在纺丝温度为280 ℃左右时,在保证纺丝压力在稳定范围内的前提下,此时特性黏度降在10.6%左右的较低水平,特性黏度可以维持在0.93 dL/g左右,基本满足了工业丝对高分子量的要求。并基于此,对此温度下熔纺卷绕成型的阻燃纤维进行进一步的牵伸加工处理。
为获得更高强力,以满足工业丝强力指标要求,对低速卷绕获得的初生丝进一步进行牵伸加工,以获取更高取向与结晶度,达到较高强力。如表4不同牵伸倍率时阻燃聚酯工业丝力学性能测试结果所示,平板牵伸3.2~4.6倍时,纤维强度随着牵伸倍率的提高而增加明显,断裂伸长率随之降低。P-Y与FRP-Y两种样品相比较,发现在相同牵伸倍率时,后者强度始终低于P-Y样品,但是其断裂伸长较高。说明共聚结构对纤维强度影响明显,同时也赋予了纤维良好的可拉伸性。在平板牵伸最高倍率4.6倍时,FRP-Y强度可以达到3.98 cN/dtex,为PET强度的87.8%,而此时的断裂伸长率为21.2%,表明FRP-Y具有进一步牵伸以提高强度的潜力。对此,为进一步提高拉伸倍率,采用热管牵伸工艺,最终在稳定牵伸的情况下,最高倍率可以到达5.8倍,此时FRP-Y强度达到了6.75 cN/dtex (PET的强度为7.20 cN/dtex),实现了阻燃工业丝强度指标要求。
2.3 阻燃聚酯工业丝的结构
聚酯工业丝的优异力学性能取决于其高结晶度、高取向度的微细结构。对于阻燃聚酯工业丝微观结构进行研究,一方面可以明确其结构特征并与力学性能关联,探究其构效关系;另一方面可以在明晰其结构性能关系的基础上,指明高强所需结构特征的调控方向,为进一步的工艺改进具有指导意义。为此对所制备的强力最高的普通聚酯工业丝和阻燃聚酯工业丝的超分子结构进行表征。
P-Y与FRP-Y纤维的一维XRD曲线如图2所示,可以看出两种样品的晶形结构完全一致,说明共聚酯大分子链只有纯聚酯链段才可以嵌入晶格。对其进行进一步数据处理,所得结构参数如表5所示。由表中数据可以看出,FRP-Y纤维的结晶度明显较低,且晶粒尺寸较下,这是由于共聚结构对方大分子链规整性破坏所导致的。此外与P-Y纤维相比,FRP-Y纤维的整体取向(fS)微弱降低,晶区取向(fc)变化不大,但是非晶区取向(fA)较低。如图3聚酯工业丝的结构示意图所示,阻燃共聚单元减少了纯聚酯链段数量并且影响近端纯聚酯链段长度不足難以嵌入晶格导致了超分子结构参数中结晶度下降以及非晶区链段因共聚单元难以拉直取向度较低。
2.4 聚酯工业丝的阻燃性能
选取强力最高的聚酯工业丝样品进行燃烧性能测试结果如表6所示。阻燃聚酯工业丝实际磷含量测试结果为5.9×10-3%左右。极限氧指数(LOI)测试结果显示,FRP-Y纤维样品的LOI可以达到30.9%,表明其具有较好的阻燃性能。为了更全面地表征其燃烧性能,参照塑料测试标准,对其垂直燃烧性能进行了测试。其结果显示,FRP-Y燃烧时间(2 s以内)明显降低,且样品损毁长度为0.7 cm,较P-Y样品(8.1 cm)显著改善。垂直燃烧实验中,FRP-Y表现为难点燃,良好的离火自熄性以及难续燃的优异阻燃性。
3 結 论
阻燃共聚单元的引入可破坏大分子链规整性降低了熔体黏度,影响结晶,同时共聚弱键更易发生降解,基于此优化设计了热解可控的纺丝工艺,降低纺丝温度、降低热拉伸定型温度与增
加定型时间,制得阻燃性能(LOI达30%以上)良好的阻燃聚酯工业丝,拉伸断裂强度在6.75 cN/dtex左右,且水洗牢度性能优异。与普通聚酯工业丝相比力学性能降低的原因是阻燃共聚结构减少了可嵌入晶格链段数量,纤维结晶度和取向度降低。
参考文献:
[1]KOKKALAS D E, BIKIARIS D N, KARAYANNIDIS G P. Effect of the Sb2O3 catalyst on the solid-state postpolycon-densation of poly(ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1995, 55(5): 787-791.
[2]王玉萍.涤纶工业丝行业发展现状及应用研究[J].合成纤维,2011,40(9):1-6.
WANG Yuping. Development situation and application of polyester technical yarn industry[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China, 2011, 40(9):1-6.
[3]CHEN K, YU J, LIU Y, et al. Creep deformation and its correspondence to the microstructure of different polyester industrial yarns at room temperature[J]. Polymer International, 2019, 68(3): 555-563.
[4]姬洪,张阳,陈康,等.基于动力学特性的黑色高强聚酯工业丝研发[J].纺织学报,2020,41(4):1-8.
JI Hong, ZHANG Yang, CHEN Kang, et al. Developing black high-tenacity polyester yarns based on dynamic characteristics[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2020, 41(4): 1-8.
[5]CHEN L, WANG Y. Aryl polyphosphonates: Useful halogen-free flame retardants for polymers[J]. Materials, 2010, 3(10): 4746-4760.
[6]JI H, CHEN K, SONG M G, et al. Effect of flame retardant on the microfine structures and creep behavior of polyester industrial yarns[J]. The Journal of the Textile Institute, 2022, 113(2): 273-280.
[7]姬洪,冯新星,陈建勇,等.芳纶1313/阻燃涤纶混纺纱线的阻燃抗熔滴性能[J].纺织学报,2013,34(4):37-40.
JI Hong, FENG Xinxing, CHEN Jianyong, et al. Flame-retardant and melt-dripping resistant properties of aramid 1313/flame retardant polyester blended yarns[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2013, 34(4): 37-40.
[8]CHEN H B, CHEN L, DONG X, et al. Block phosphorus-containing poly(trimethylene terephthalate) copolyester via solid-state polymerization: Reaction kinetics and sequential distribution[J]. Polymer, 2012, 53(16): 3520-3528.
[9]WANG L S, WANG X L, YAN G L. Synthesis, characterisation and flame retardance behaviour of poly(ethylene terephthalate) copolymer containing triaryl phosphine oxide[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2000, 69(1): 127-130.
[10]JI H, GAN Y,KUMI A K, et al. Kinetic study on the synergistic effect between molecular weight and phosphorus content of flame retardant copolyesters in solid-state polymerization[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020, 137(38): 49120.
[11]JABARIN S A, LOFGREN E A.Thermal stability of polyethylene terephthalate[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 1984, 24(13): 1056-1063.
[12]SATO M, ENDO S, ARAKI Y, et al. The flame-retardant polyester fiber: Improvement of hydrolysis resistance[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2000, 78(5): 1134-1138.
[13]CHANG S J, SHEEN Y C, CHANG R S, et al. The thermal degradation of phosphorus-containing copolyesters[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 1996, 54(2/3): 365-371.
[14]姬洪,宋明根,薛勇,等.高黏阻燃共聚酯的熱解行为及其机理[J].东华大学学报(自然科学版),2022,48(1):12-16.
JI Hong, SONG Minggen, XUE Yong, et al. Pyrolysis behavior and mechanism of flame retardant co-polyesters with high intrinsic viscosity[J]. Journal of Donghua University (Natural Science), 2022, 48(1): 12-16.
[15]王鸣义.高品质阻燃聚酯纤维及其织物的技术进展和趋势[J].纺织导报,2018(2):13-22, 24.
WANG Mingyi. Technological development of high-quality flame-retardant polyester fiber and its fabric[J]. China Textile Leader, 2018( 2): 13-22, 24.
Spinning research of copolymerized flame-retardant polyester industrial yarns
JI Hong1, SONG Minggen1, ZHANG Yue2, CHEN Kang3, ZHANG Yumei2
(1.Zhejiang Unifull Industrial Fiber Co., Ltd., Huzhou 313017, China; 2a.College of Materials Science and Engineering;
2b. Key Laboratory of High Performance Fibers & Products, Ministry of Education, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China;
3.School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China)
Abstract:
Polyester industrial yarns are widely used in the fields of safety belts, rubber reinforcement materials, geotextile, and cables due to their excellent dimensional stability, weather resistance, and mechanical properties. However, the flammability of the polyester limits its further application. With excellent flame-retardant durability, the copolymerized flame-retardant polyester is the ideal method for the flame-retardant modification of polyester industrial yarns. In the process of high-temperature melt spinning, how to restrain the thermal degradation of high molecular weight copolyesters and ensure the appropriate liquidity of melt is the key technology to prepare the copolymerized flame-retardant polyester industrial yarns. Based on the rheological behavior of high molecular weight flame-retardant copolyesters during spinning and melting, the corresponding spinning process was designed, the thermal degradation degree of copolyesters during spinning and forming was determined, and the process parameters were optimized. Polyester industrial yarns with good mechanical properties, flame-retardant properties, and durability were prepared.
The rheological properties of high molecular weight flame-retardant copolyesters at different temperatures were tested by the rotating rheometer. The spinning processing temperature range was defined according to appropriate melt fluidity and stable spinning pressure requirements. At the same time, the thermal degradation of copolyesters was quantified at different spinning temperatures to optimize the melt-spinning process. Then, the thermal drawing processes such as temperature and ratio were designed to improve the mechanical properties of the fibers. The mechanical and flame-retardant properties of the industrial yarns were measured by means of tensile and combustion tests. In addition, X-ray diffraction and sonic orientation equipment were used to analyze and test the crystal and orientation of the fibers. It is found that compared with pure PET, the viscosity of copolyesters melt is lower and the temperature sensitivity is more obvious. When the temperature is between 275 ℃ and 285 ℃, the melt viscosity is similar to that of pure PET spinning temperature. The pressure fluctuation of the spinning pack in this temperature range is small, which is conducive to avoiding excessive adjustment of spinning parameters in the production process. The process was further optimized by choosing a lower spinning temperature (about 285 ℃). The melt viscosity had little influence on spinning pressure and the thermal degradation degree was low (the viscosity dropped to 11.5%). Finally, by multistage hot drawing process, the breaking strength of the flame-retardant industrial yarns prepared by the primary fiber can reach 6.75 cN/dtex, the limit oxygen index (LOI) can reach 31% and the flame-retardant durability is outstanding, which meets the requirements of flame-retardant and mechanical properties of flame-retardant polyester industrial yarns. The results of microstructure analysis show that the copolymerization unit reduces the number of pure polyester chain segments and results in a short length of near-end pure polyester chain segments, which makes it difficult to embed in the lattice and further leads to the decrease of crystallinity and the low orientation of the amorphous chain segment, and the decline of mechanical properties of flame retardant fibers.
Based on the rheological properties and degradation behavior of high molecular weight flame-retardant copolyesters, the key technical factors of processing and molding were studied. The melt spinning process was designed, the drawing parameters were optimized, and the relationship between structural characteristics and mechanical properties of the prepared flame-retardant copolyesters was analyzed. On this basis, the flame-retardant polyester industrial yarns with good mechanical properties and excellent flame-retardant properties and outstanding flame-retardant durability were prepared, which greatly expanded the application of polyester industrial yarns and had certain guiding significance for the development and application of flame-retardant polyester industrial yarns.
Keywords:
polyester industrial yarns; copolymerized; flame retardant; mechanical properties

