Research on the Regulatory Framework of Advanced Therapies in the European Union and the United States
Wulan Qiqige,Yang Yue,Huang Zhe
(1.School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China;2.School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China)
Abstract Objective To study the regulatory framework of advanced therapies in the European Union and the United States,and to provide reference for the regulation of cell-and gene-based therapeutic products in China.Methods The legal and regulatory documents,annual reports,work information and related literature published on the websites of the FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA) were reviewed to analyze the regulatory models of advanced therapies in the European Union and the United States.Results and Conclusion the United States and the European Union have carried out a lot of work in the classification standards of advanced therapies,policy formulation and accelerated listing procedures.Therefore,they have established a relatively mature regulatory system.China can learn from their experience and continuously improve the regulatory system to help the sustainable development of gene and cell therapy industry.
Keywords: advanced therapy;gene therapy product;cell therapy product;European Union;USA
With the rapid development of biotechnology,the types of advanced treatment products change dramatically.They have shown good prospects in the treatment of major refractory diseases such as malignant tumors,infectious diseases,and autoimmune diseases.So,they become an important means of human intervention in diseases[1].In the European Union and the United States,advanced therapies are regulated as biological products,but the specific classification is different.The European Union advanced therapies include four categories:gene therapy,somatic therapy,tissue engineering therapy,and combined advanced therapy.Combined advanced therapy is the combination of the above therapies and medical devices,which will not be introduced in detail in this paper.Advanced therapies in the United States cover two major categories of products,namely gene therapy and cell therapy.Advanced therapy is different from chemical drugs and general biological products.The complexity of preparation process,in vivobiological characteristics,safety risks,individualized application and other characteristics of different types of products are totally different from other chemical drugs.The construction of supervision system brings many challenges and uncertainties[2].Based on clarifying the classification standards of various products of advanced therapy in the European Union and the United States,this paper studies the regulatory system to provide a reference for optimizing the regulatory path in China.
1 Related concepts and classification criteria of advanced therapy
1.1 Concept and classification of gene therapy products
The standards for defining gene therapy in the European Union and the United States are roughly the same: The product must be a biological product containing “recombinant nucleic acid” (the term used in the European Union) or “genetic material” (the term used in the United States),and increase,manipulate or modify human gene expression through its mechanism of action.
In the European Union,gene therapy must meet the following standards: (1) The product complies with the Directive 2003/63/EC and must be biological products;(2) The product must contain recombinant nucleic acid;(3) The recombinant nucleic acid should be of biological origin,independent of the source of the carrier system used;(4) Recombinant nucleic acids are used in humans to regulate,repair,replace,add or delete gene sequences;(5) Recombinant nucleic acids should be directly involved in the therapeutic,preventive or diagnostic effects of products[3].
The requirements for gene therapy in the United States are as follows: (1) The product meets the definition of “biological product” in Section 351 of the “Public Health Services Act (PHSA)”;(2) The product must be suitable for the prevention,treatment or cure of human diseases;(3) The product functions by transcribing or translating the transferred genetic material or by specifically changing the host (human)gene sequence;(4) Products can function through the following mechanisms: Replacing pathogenic genes with healthy genes,inactivating pathogenic genes,or transferring new or modified genes into the body[4].
Different from the United States,one of the standards of European Union gene therapy is that the recombinant nucleic acid should have biological source,independent of the source of the vector system used.In these two regions,products belonging to gene therapy must be used for the prevention and treatment of human diseases.However,the United States does not take disease diagnosis as the standard of such products,and the definition of biological products in the United States does not regard diagnosis as the purpose of products according to the PHSA[5].In the European Union,products for the treatment or prevention of infectious diseases,even if they meet all the above standards,do not belong to the scope of gene therapy,but are classified as vaccines[3].Therefore,the exclusion criteria for classifying the product as gene therapy in two regions are directly related to the use of the product.
1.2 Concept and classification of cell and tissue therapy products
The classification of human cell and tissue therapy products in the European Union and the United States is different.In the European Union,somatic therapy products and tissue engineering products are classified according to the main action mechanism of active substances and the intended use of products.In the United States,as an advanced therapy,tissue therapy products belong to somatic cell therapy products.
The European Union somatic cell therapy products and tissue engineering products have the same inclusion criteria,which means the cells or tissues of the products must be engineered.The difference between them mainly lies in the use of the products.Product engineering must at least meet any of the following criteria: (1) Cells or tissues have been substantially manipulated;(2) The function of cells or tissues in the receptor is different from that in the donor,which is for non-homologous use.In terms of use,somatic cell therapy products treat,prevent or diagnose diseases through the pharmacological,immunological or metabolic effects of their cells or tissues,while tissue engineering products are used to regenerate,repair or replace human tissues.In addition,products composed of engineering cells or manipulation cells that induce regeneration,repair or replacement in natural tissues by secreting paracrine factors also meet the definition of tissue engineering products[3].
In the United States,according to the relevant regulations of the PHSA,human cells,tissues,cellular or tissue-based products (HCT/Ps) are divided into low-risk products (PHSA 361) and high-risk products (PHSA 351) according to the level of risk.FDA manages biological products in accordance with the requirements.Such products shall meet any of the following conditions: (1) Operation beyond the minimum limit;(2) Non homologous use;(3)Having systemic effects;(4) Metabolic activities dependent on living cells play their main functions(except autologous cells,allogeneic cells of firstdegree relatives and germ cells)[6].Human somatic cell therapy products that meet the above criteria belong to advanced therapy,but in the United States,there is no tissue-based advanced therapy product category,which falls under the terminology of cell therapy.The definition and inclusion criteria of human somatic cell therapy products include the following contents[7]: (1) Giving human autologous,allogeneic or xenogeneic living cells;(2) Its production involvesin vitroreproduction,amplification,selection or pharmacological treatment of cells,or other changes in their biological characteristics,which belongs to“operation beyond the minimum”;(3) Used to treat,diagnose or prevent diseases.
2 Regulatory organizational structure for advanced therapy in the European Union and the United States
The European Union and the United States both adopt a risk-based,single track regulatory model dominated by the drug regulatory authorities[8],and there are special committees within the drug regulatory authorities responsible for the review of advanced therapies.
In 2001,European Medicines Agency (EMA)established a Gene Therapy Working Party (GTWP)and then a Cell-Based Product Working Party (CPWP)in 2005 to help EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) deal with scientific issues related to gene and cell therapy products.The two working groups,in cooperation with CHMP and its Biological Working Party (BWP),developed the first ATMP guideline in Europe and contributed to the formulation of technical requirements for ATMP.In 2009,according to Regulation (EC) No 1394/2007,EMA established the Committee for Advanced Therapies (CAT),which is composed of member representatives of all Member States and their alternate members,of which five CAT members are also CHMP members,so as to ensure appropriate cooperation and information exchange between the two committees.There are representatives of doctors and patient organizations in CAT,and these members are nominated by EC[9].CAT is responsible for the classification procedure of advanced therapies,evaluating the quality,safety,and effectiveness of advanced therapies,and tracking the scientific progress in this field.The main responsibility of the committee is to prepare the review comments of advanced therapy applications to support the final recommendations of CHMP and submit them to EMA for approval[10].Regulatory organizational structure for advanced therapy in the European Union is shown in Fig.1.
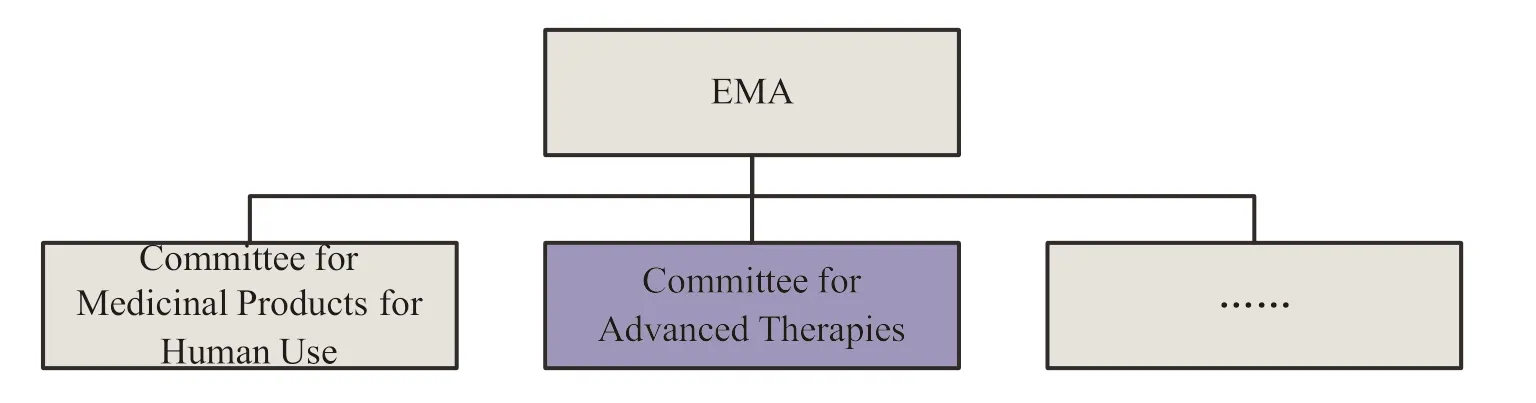
Fig.1 Regulatory organizational structure for advanced therapy in the European Union
In 1974,the National Institutes of Health(NIH) established the Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RAC) to provide NIH with scientific,safe,and ethical suggestions for designing nucleic acid research.After that,the responsibilities of RAC were expanded to include the approval and discussion of human gene therapy.The FDA began to regulate gene therapy in 1990.The dual supervision of NIH-RAC and FDA led to repeated work.In October 2018,Francis S.Collins,then president of NIH,and Scott Gottlieb,director of FDA jointly wrote an article proposing to limit the role of RAC in the evaluation of gene therapy,which should be supervised by FDA independently.The role of RAC should be defined as the emerging technology advisory committee[8].At present,the Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)of FDA regulates all kinds of biological products and the Office of Tissues and Advanced Therapies (OTAT)has been established responsible for products such as cell,gene and tissue therapy.Regulatory organizational structure for advanced therapy in the United States is shown in Fig.2.

Fig.2 Regulatory organizational structure for advanced therapy in the United States
3 Regulatory laws and regulations for advanced therapy in the European Union and the United States
The improved regulatory framework for drugs and biological products in the European Union and the United States is also applicable to advanced therapy.However,considering the particularity of such products and the purpose of encouraging the development of advanced therapy industry,the European Union and the United States have formulated and implemented a number of new regulations for advanced therapy,which formed a relatively perfect legal system composed of laws,regulations and guidelines.
The European Union regulates drugs for human use in accordance with Directive 2001/83/EC and Regulation (EC) No 726/2004.Directive 2004/23/EC stipulated the quality and safety standards for donation,acquisition,screening,treatment,preservation,storage and distribution of human tissues and cells.In 2007,based on the integration of previous relevant regulations,Regulation (EC)No 1394/2007,regulations on advanced therapeutic medical products were promulgated,and the CAT was established accordingly.The regulation provides an overall framework for the supervision of advanced therapies for products expected to be listed in the European Union Member States.In addition,in 2009,Directive 2009/120/EC revised Directive 2001/83/EC to update the definition of advanced therapy and detailed scientific and technical requirements[11].The European Union advanced therapy regulatory system is detailed in Table 1.

Table 1 The European Union legal system for advanced therapies
The drug regulatory framework in the United States consists of two main acts: The “Federal Food,Drug,and Cosmetic Act (FD&CA)” and the PHSA.These two acts provide the FDA with the legal basis for the regulation of human drugs,biological products,and devices.
Based on the principle of risk management,the PHSA divides human cells and tissues into two categories: Low-risk products (PHSA 361) and highrisk products (PHSA 351).Low risk products do not adopt the supervision mode of drugs.They only need to register their cell product institutions and products with FDA,do not need to apply for pre-market review,and accept FDA inspection regularly.High risk products are regarded as advanced therapies and biological products.In addition to institutional and product registration,they also need to comply with the management requirements of biological products and submit an investigational new drug (IND) and biological license application (BLA) to FDA.Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations (21 CFR) details how FDA implements the activities defined in PHSA and FD&CA.In addition,FDA also communicated with other management departments,enterprises and research institutions in the field of advanced therapy,formed a series of guidelines on product preparation,quality control and clinical trials,and successively issued more than 30 relevant regulations and guidelines[1].The United States advanced therapy regulatory system is detailed in Table 2.

Table 2 The United States legal system for advanced therapies
4 Accelerated procedures for the listing of advanced therapies in the European Union and the United States
In order to make advanced treatment products enter the market as soon as possible,the European Union and the United States have launched accelerated development plans and established procedures to speed up the listing of products.
In March 2016,to speed up and optimize the development of European Union priority medicines,EMA launched the priority medicines (PRIME)program.The definition of priority medicines is that these drugs have obvious treatment advantages compared with existing therapies or may be beneficial to patients who have no other treatment options and can meet unmet medical needs.
PRIME uses the acceleration tools in the European Union regulatory framework (such as scientific recommendations,conditional approvals and accelerated evaluation) to optimize the development path of priority drugs.Scientific suggestion is the formal communication with EMA,through which the applicant can obtain the feedback and suggestions of EMA on the development project,so as to ensure the generation of the data required to obtain the marketing license.Conditional approval and accelerated review procedures can make the application for marketing license of products accepted,reviewed and approved as soon as possible,and help patients obtain drugs as soon as possible.Once approved by PRIME,EMA will take a series of measures to continuously communicate with the enterprise and follow up the enterprise’s research and development process[11].
FDA has developed four accelerated marketing procedures for all chemical and biological products for the treatment of serious diseases: Fast track,breakthrough therapy,priority review and accelerated approval.In addition to the above acceleration policies,to promote the research and development of regenerative medicine therapy and accelerate the review,so as to solve the unmet medical needs of patients with serious diseases,FDA has formulated an accelerated policy for regenerative medicine therapy,which is recognized as regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT).The FD&CA 506 (g)(8) stipulates that regenerative medicine therapy includes cell therapy,gene therapy,therapeutic tissue engineering products,human cells and tissue products,and combinations of the above types[12],so,advanced therapy is eligible for RMAT recognition.
As of October 14,2021,the European Union CHMP had received 375 PRIME determinations,96 applications had been approved,227 applications had not been approved,and most of the applications(202) were submitted by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)[13].FDA received 173 applications for recognition of advanced therapies in regenerative medicine,of which 64 were approved,100 were rejected and 8 were withdrawn[14].It can be seen that PRIME and RMAT have encouraged many enterprises to apply for advanced therapy,but the threshold for qualification is relatively high.
5 Thinking and enlightenment
The European Union and the United States started early in the field of gene and cell therapy products and gradually formed a relatively perfect regulatory system.In recent years,China has become one of the countries with the largest number of clinical research on gene and cell therapy products.We have accumulated some experience in basic research and clinical transformation and application,and a number of relevant normative documents and industry guidelines have been issued and implemented.However,China’s regulatory framework for cell and gene therapy products still needs to be improved.Combined with China’s national conditions and referring to foreign experience,it is suggested that the supervision of gene and cell therapy in China should further clarify the product division standards,improve the legal system,make the responsibilities of regulators clear,optimize the review and approval procedures,and strengthen the protection of intellectual property rights,which will promote the healthy and orderly development of gene and cell therapy industry.
5.1 Defining the product division standard
In 2020,in order to cooperate with the implementation of the newly revised “Provisions for Drug Registration”,the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) organized and issued the“Requirements for Registration Classification and Application data of Biological Products”,which made it clear that gene and cell therapy products belong to therapeutic biological products.However,there are no clear requirements on how to divide gene and cell therapy products and specific standards,which is not conducive to the research and development of product,but also may reduce the review efficiency of regulators.
Combined with the international requirements for gene and cell therapy product standards,relevant departments should actively organize experts in the industry to discuss and clarify the division standards of gene and cell products based on China’s condition,which not only ensures the stability and consistency of supervision,but also promotes the healthy and orderly development of the industry.
5.2 Improving the legal system
In recent years,although China has issued a series of relevant regulations to build a sound framework to promote the research and development of gene and cell therapy products,the current regulatory system still does not meet the national regulatory requirements.Therefore,the regulation of gene and cell therapy products lacks superior legal basis.From the regulatory experience of the United States and the European Union,China should improve the legal system and establish a regulatory framework composed of laws,regulations and guidelines.It is suggested to revise the laws related to drug supervision,clarify the legal basis of gene and cell therapy products so that there are laws to follow.Meanwhile,the participation of relevant parties should be strengthened.The government should timely formulate and release guidance documents to cover the whole life cycle,all links and different levels of gene and cell therapy products.Besides,these policies can guide the research and development of enterprises and make the supervision of gene and cell therapy products more scientific and standardized.At the same time,the legal system should also be in line with international standards in the process of building,so as to promote the global development of Chinese gene and cell therapy products.
5.3 Clarifying the responsibilities of regulators
After the medical chaos in the field of gene and cell therapy products in the past few years,China is gradually strengthening the supervision of clinical research of gene and cell therapy.However,at present,the supervision responsibilities between the NMPA and the National Health Commission of People’s Republic of China (NHC) are not very clear.
On the one hand,pharmaceutical enterprises can obtain the marketing license with the approval of the NMPA according to the clinical trial evidence of gene and cell therapy products,which is called registration system.On the other hand,the NHC takes gene and cell therapy products as medical technology and implements the filing system of clinical trials.However,the effectiveness and safety of gene and cell therapy products reviewed only by the NHC may not meet the standards required by international guidelines,as in most cases,the approval of marketing applications for such therapies requires more safety and effectiveness data than clinical research applications.Therefore,pharmaceutical enterprises may not have the incentive to invest in expensive clinical trials in the later stage.As a result,while the number of clinical trials registered with clinicaltrials.gov in China is the same as that in the United States,the number of products actually registered in the NMPA is much lower.In addition,clinical trials of gene and cell therapy products require patients with serious diseases.With low public awareness and participation,it is difficult to recruit enough subjects for clinical trials,and clinical studies conducted by medical institutions will further deprive pharmaceutical companies of clinical resources.
Therefore,the responsibilities of the NMPA and the NHC in the supervision of gene and cell therapy products should be clarified,and the logical differences between drug supervision and technical supervision should be clarified as well.The two departments should also establish a scientific cooperation mechanism and coordinate arrangements to solve the problem of large differences in product quality standards under the registration system and filing system based on the patient-centered principle.The government can unify the quality requirements of gene and cell therapy products under the dual track system,improve the research and development enthusiasm of enterprises,and promote the transformation and application of medical technology to drugs.
5.4 Optimizing review and approval procedures
The “Provisions for Drug Registration”promulgated in 2020 introduced a number of accelerated registration procedures for drugs to facilitate patients’ access to new therapies for serious or life-threatening diseases,including breakthrough therapies,conditional approvals,priority review approvals and special approvals.However,China has not yet issued relevant policies and regulations on orphan drugs used for the treatment of rare diseases,and patients with rare diseases have poor access to medication.Therefore,China should establish an accelerated orphan drug program for patients with rare diseases,encouraging the development of drugs for rare diseases to better meet the needs of patients.
In addition,as gene and cell therapy products are complex,and the phase III trial is difficult,it is not suitable to carry out the research in a randomized controlled manner.For such therapies,fiexible clinical trial design should be adopted,alternative endpoints and single arm test data should be allowed to support the product listing,which can speed up the product listing process and ensure the safety of the product by strengthening post-authorization safety surveillance.
- 亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Enlightenment and Suggestions on the Construction of Information Platform and Processing Mechanism of Drug Shortages in Developed Countries to China
- Investigation on the Current Situation of China’s DTP Pharmacy and Suggestions for Its Development
- Study on the Management of Chronic Diseases in American and British Community Pharmacy
- lnfluence and Suggestions on Trial lmplementation Measures for Early Settlement Mechanism of Drug Patent Disputes
- Enlightenment of COVID-19 Treated by Botanical Drugs on the Development of Drugs for Rare Diseases in China
- Research on Liposomal Irinotecan in Combination with 5-FU/LV for Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma

