锈蚀钢结构连接节点抗震性能研究进展
魏欢欢,雷天奇,郑东东,关晓迪,李涛,万亮婷
重大工程装备
锈蚀钢结构连接节点抗震性能研究进展
魏欢欢1,2,雷天奇3,郑东东2,关晓迪2,李涛4,万亮婷1
(1.杨凌职业技术学院 建筑工程学院,陕西 咸阳 712100;2.西安理工大学 西北旱区生态水利国家重点实验室,西安 710048;3.陕西铁路工程职业技术学院 道桥与建筑学院,陕西 渭南 714099;4.商洛市人民防空办公室,商洛 726000)
基于材料与连接构件层面,总结了近年来国内外既有试验研究及理论分析成果,主要包括腐蚀后的标准试件的单调拉伸、滞回性能退化分析,以及梁柱节点、框架结构的抗震性能研究,并给出了相应的力学性能退化模型,通过进行总结及对比分析后,为复杂环境下工程钢结构给出研究方向,同时也对我国工程结构的设计方法提供理论指导和参考依据。
钢结构;腐蚀;连接节点;单调拉伸;抗震性能;退化模型
随着社会经济的快速发展,人们对结构的功能使用要求明显提高,钢材凭借其自身优势,在水利水电工程、桥梁工程、港口航道和海岸工程等领域取得广泛应用[1-2]。迄今为止,针对工程用钢的安全可靠性,学者们已经展开了大量的研究工作。由于在役承重构件不仅要承担外部荷载作用,还要遭受环境腐蚀性介质的影响,导致有效截面尺寸削减,腐蚀坑处产生应力集中,材料屈服平台减小,力学性能及疲劳寿命降低,最终呈脆性破坏现象[3-5]。从20世纪初期,相关领域的学者对腐蚀环境下的工程钢结构开展了试验研究和理论分析[6]。我国学者通过模拟不同环境下钢材的失效行为,建立了腐蚀损伤演化模型,给出了失效机理及变化规律[7-9]。此外,除了基于极限承载性能失效外,还可能是由于载荷与环境耦合引起的失效[10-11],诸如海洋采油平台倾覆[12]、飞机运行坠落[13]、桥梁连接节点传荷能力丧失[14]、输送管道破裂等[15],腐蚀介质能够降低构件的力学性能,加快裂纹的扩展速率,缩短结构的使用寿命,失效过程具有普遍性和瞬时性[16]。
根据上述存在不足[17],在实际工程中进行了涂层防腐保护措施。现行GB 50017[18]、AISC 360[19]等规范已给出钢结构设计准则,若拟建工程选址在复杂恶劣环境下,此时不再适用。因此,锈蚀钢结构耐久性分析备受各国学者关注,目前为研究领域内亟需解决的工程难题,也是完善结构设计方法的重要选题方向。本文通过介绍相关研究成果,进行梳理、对比及分析后,评估了锈蚀钢结构连接节点的抗震性能,为国产钢材应用及研究提供科学依据。
1 腐蚀研究进展
1.1 腐蚀行为
腐蚀损伤现象涉及土木工程各领域、各方向,在复杂恶劣的环境下,材料表面容易生成不均匀锈坑,形貌发生变化,构件的力学性能退化[20]。一般腐蚀损伤较为严重的主要有海洋环境、工业大气环境及酸雨环境下的在役结构。以海洋环境为例[21],根据腐蚀速率不同,将其划分为5类,分别为大气区、浪溅区、潮差区、全浸区、泥土区。研究结果表明,海洋浪溅区材料的损伤速率最大,为0.3~0.5 mm/a。其中,海洋环境下钢材的腐蚀微观机理如图1所示,腐蚀速率汇总见表1,相关研究成果汇总见表2。
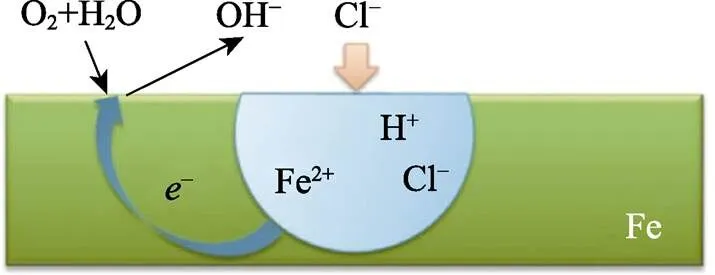
图1 腐蚀机理示意
表1 海洋环境下的钢材腐蚀速率[21]

Tab.1 Corrosion rate of steel in marine environment[21]
表2 腐蚀试验研究汇总

Tab.2 Summary of corrosion test research
1.2 形貌扫描分析
钢结构具有良好的承载性能,在复杂环境下的耐久性较差,目前除了基于材料宏观腐蚀形貌的分析外,更多将借助形貌扫描仪对微观机理进行研究。其中,微面形貌测试方法经过长期发展,由初始的定性测量逐步上升到现阶段的高精度定量测定[28],通过提取材料表面的蚀坑尺寸和分布范围,对腐蚀损伤展开讨论分析,建立腐蚀周期与粗糙度参数的定量关系,为腐蚀机理研究提供依据。
Kacimi等[29]通过SEM扫描结果,得到了镀锌钢材腐蚀损伤的影响因素。Zhang等[30]模拟了海洋环境下EH47高强钢的磨损与腐蚀损伤行为,当溶液含砂量为0.3%(质量分数)时,腐蚀速率受环境的影响最大。刘鹏洋等[31]和张建兵等[32]通过盐雾加速腐蚀试验,模拟了海洋环境下B340LA、WHT1300HF钢材的腐蚀损伤行为,基于XRD仪扫描结果,得到了基体表面微观形貌分布范围、腐蚀速率变化规律与产物化学成分。关于碳钢、低合金钢及高强钢材的腐蚀形貌分析取得了较多成果,但是未能建立各自的腐蚀损伤模型,缺乏可靠的理论指导及科学依据。
2 力学性能研究进展
2.1 材料单调拉伸
国内外学者对腐蚀试件进行了单调拉伸试验研究,得到了力学性能退化规律,主要研究内容见表3。结果表明:随着腐蚀周期的增加,力学性能快速退化;腐蚀损伤导致试件实测数据偏于离散,同一周期各参数存在差异性;不同加速腐蚀方案对钢材力学性能的影响极为明显。
2.2 材料滞回性能
通过对不同强度等级、连接方式和几何参数的研究与对比分析(见表4),得出结论:循环荷载与腐蚀耦合的影响作用大于两者单一行为的损伤累积;随着应力幅值的增加,材料力学性能的退化速率加快;当试件循环受压时,不同腐蚀周期的骨架曲线差异较小,失效行为与腐蚀损伤累积量、分布范围及作用方式等因素相关。
2.3 梁柱节点与框架结构抗震性能
在工程钢结构承重骨架中,梁柱节点作为体系受力和传荷关键区域,通过进行节点梁翼缘削弱,以及局部采用盖板加强的方式,对其抗震性能展开了研究工作[46-47]。但是在役结构体系均与外界腐蚀介质发生接触,节点区域腐蚀剥离损伤相比梁柱构件更为严重,在强震作用时,极易发生整体坍塌。基于上述问题,西安建筑科技大学的研究者们[48-54]对钢材牌号为Q235的锈蚀钢结构梁柱节点的力学性能进行了分析,部分成果见表5。根据研究结果表明:随着节点区域暴露周期增加,滞回曲线逐渐趋于捏缩,抗震性能变弱;若选取不同循环加载方式,对同一腐蚀周期下梁柱节点耗能能力的影响存在较大差异;由于锈蚀率提高,延性退化速率逐渐增大。因此,在研究锈蚀钢结构力学性能的退化规律时,需综合考虑外界环境多因素耦合作用的影响,选择更为适应梁柱连接节点的损伤演化模型。
表3 单调拉伸试验研究汇总

Tab.3 Summary of monotonic tensile test research
表4 循环加载试验研究汇总
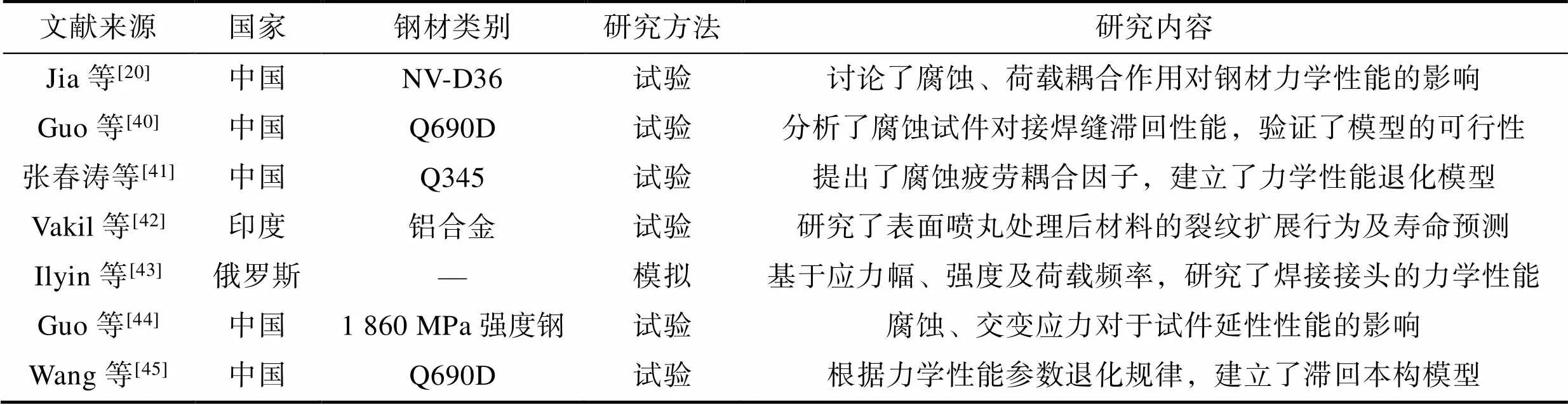
Tab.4 Summary of cyclic loading test research
表5 梁柱节点抗震性能试验研究汇总
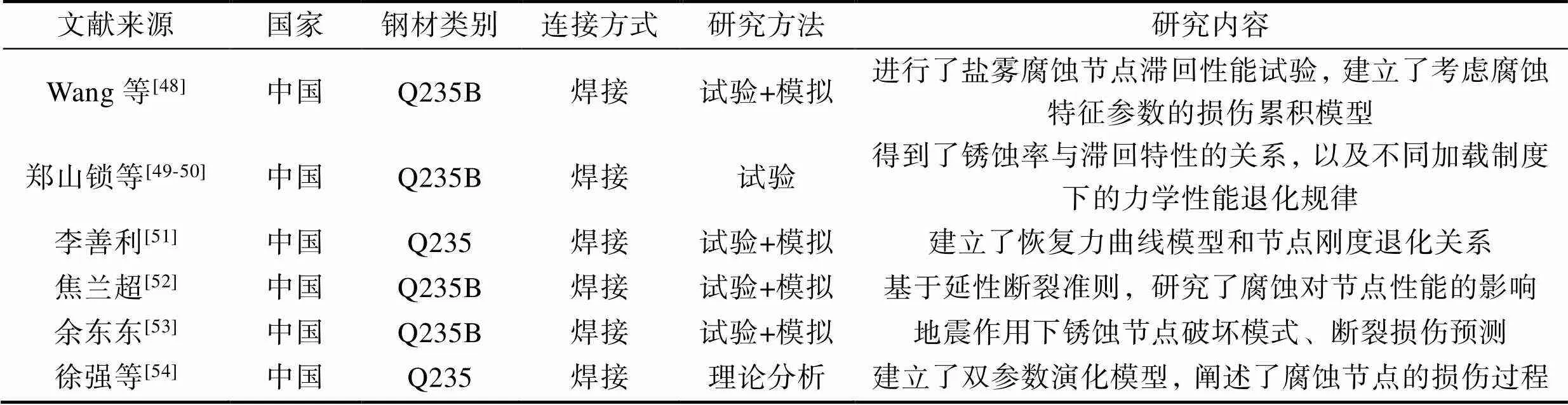
Tab.5 Summary of experimental research on seismic performance of beam-column joints
在锈蚀梁柱节点抗震性能研究的基础上,研究者们对框架结构展开了试验及理论分析[6,55-57],并给出了刚度退化规律,为实际工程应用提供了设计依据。目前主要以碳钢结构分析为主,考虑材料类别可知,针对高强度钢材、低合金钢材梁柱节点的研究较少。此外,国内学者对全焊刚性节点进行了大量的试验研究及理论分析,而关于栓焊连接、全螺栓连接节点滞回性能的研究成果尚处空白,后续应当开展更多类型节点(材料、连接方式、环境介质等)的抗震性能研究,分析其失效机理。
3 结语
1)根据钢结构耐久性研究成果可知,在试验研究分析时,考虑腐蚀因素偏少,加之材料本身存在初始缺陷,对构件及连接节点机理研究的可靠性欠缺,有待更多数据作为支撑保证。
2)随着腐蚀损伤的加剧,材料的力学性能逐渐衰减,后期逐渐趋于平缓。同一周期下,试件实测数据的离散性较大,腐蚀损伤行为存在随机性与不确定性。
3)目前对梁柱全焊节点抗震性能的研究较多,在既有研究基础上,应开展更多连接类型的腐蚀钢结构节点抗震性能分析,为复杂环境工程应用提供理论依据。
4)国内外对各类金属材料、连接构件仍然处于基础研究阶段,尚未取得完备的损伤分析理论。其次,大多主要分析材料层面上力学性能的退化规律,关于钢结构连接节点的成果较少。鉴于目前存在的局限性与不足,通过后续研究工作,给出更为可靠的计算方法。
[1] 史徐行. 高强钢材应用前景研究[J]. 建筑技术开发, 2016, 43(12): 163-164.
SHI Xu-xing. Study on Application Prospect of High Strength Steel[J]. Building Technology Development, 2016, 43(12): 163-164.
[2] 王朝玉. 高强度钢材的发展与应用[J]. 中国金属通报, 2020(10): 9-10.
WANG Chao-yu. Development and Application of High Strength Steel[J]. China Metal Bulletin, 2020(10): 9-10.
[3] GUO Hong-chao, WEI Huan-huan, LI Guo-qiang, et al. Experimental Research on Fatigue Performance of Butt Welds of Corroded Q690 High Strength Steel[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2021, 184: 106801.
[4] GUO Hong-chao, WEI Huan-huan, LI Guo-qiang, et al. Experimental Research on Fatigue Performance of Corroded Q690 High-Strength Steel[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2021, 33(11): 1-10.
[5] 魏欢欢. 湿热周浸环境下锈蚀Q690高强钢对接焊缝疲劳性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2021.
WEI Huan-huan. Research on Fatigue Performance of Butt Welds of Corroded Q690 High Strength Steel in Humid and Hot Immersion Environment[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2021.
[6] 曹琛, 郑山锁, 胡卫兵, 等. 大气环境腐蚀下钢结构力学性能研究综述[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(11): 11162- 11170.
CAO Chen, ZHENG Shan-suo, HU Wei-bing, et al. Review of Research on Mechanical Properties of Steel Structure under Atmospheric Environment Corrosion[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(11): 11162-11170.
[7] 范林, 丁康康, 郭为民, 等. 静水压力和预应力对新型Ni-Cr-Mo-V高强钢腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(6): 679-688.
FAN Lin, DING Kang-kang, GUO Wei-min, et al. Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure and Prestress on Corrosion Behavior of a New Type Ni-Cr-Mo-V High Strength Steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(6): 679-688.
[8] 万金剑. 高强钢A517Gr.Q在模拟海水中的腐蚀行为及机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2017.
WAN Jin-jian. Research on the Corrosion Behaviors and Mechanism of A517Gr.Q Steel in Simulated Seawater[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2017.
[9] 潘兴隆, 张鲁君, 贺国, 等. 舰船内腐蚀海水管路剩余强度预测模型及试验验证[J]. 船舶力学, 2021, 25(2): 202-209.
PAN Xing-long, ZHANG Lu-jun, HE Guo, et al. Prediction Model for Residual Strength of Warship Seawater Pipelines with Internal Corrosion and Test Verification[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2021, 25(2): 202-209.
[10] 李展. 海水中S690钢腐蚀疲劳裂纹扩展行为及拘束效应研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018.
LI Zhan. Corrosion Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior in Seawater and Constraint Effect of S690 Steel[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018.
[11] CHEN Gang, FU Yuan-jie, CUI Yun, et al. Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment on Corrosion Fatigue Behavior of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 127: 461-469.
[12] 佚名. 海洋钻井史上最惨重的九大事故[J]. 石油知识, 2018(5): 30-31.
Nameless. Nine Worst Accidents in the History of Offshore Drilling[J]. Petroleum Knowledge, 2018(5): 30-31.
[13] 李智. 铝合金点蚀坑特征识别及其疲劳寿命预测[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2014.
LI Zhi. Feature Recognition of Corrosion Pits and Fatigue Life Prediction for Pre-Corroded Aluminum Alloy[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2014.
[14] 李英华. 基于长期健康监测的连续刚构梁桥的性能分析与演化规律研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012.
LI Ying-hua. Performance Analysis and Evolution of Continuous Rigid Frame Bridge Based on Long-Term Health Monitoring Health Monitoring[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012.
[15] 侯保荣, 张盾, 王鹏. 海洋腐蚀防护的现状与未来[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(12): 1326-1331.
HOU Bao-rong, ZHANG Dun, WANG Peng. Marine Corrosion and Protection: Current Status and Prospect[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(12): 1326-1331.
[16] ADEDIPE O, BRENNAN F, KOLIOS A. Review of Corrosion Fatigue in Offshore Structures: Present Status and Challenges in the Offshore Wind Sector[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 61: 141-154.
[17] 王从友, 王进东. 岩滩水力发电厂金属结构防腐蚀措施与效果[J]. 人民珠江, 2009, 30(5): 51-53.
WANG Cong-you, WANG Jin-dong. Anti-Corrosion Measures and Effect of Metal Structure in Yantan Hydropower Plant[J]. Pearl River, 2009, 30(5): 51-53.
[18] GB 50017—2017, 钢结构设计标准[S].
GB 50017—2017, Code for Design of Steel Structure[S].
[19] ANSI/AISC 360-16, Specification for Structural Steel Buildings[S].
[20] JIA Zi-yue, YANG Yang, HE Zheng, et al. Mechanical Test Study on Corroded Marine High Performance Steel under Cyclic Loading[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2019, 93: 101942.
[21] 侯保荣. 钢铁设施在海洋浪花飞溅区的腐蚀行为及其新型包覆防护技术[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2007, 28(4): 174-175.
HOU Bao-rong. Corrosion Behavior of Iron and Steel Facilities in the Splash Zone of Ocean Waves and Its New Coating Protection Technology[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2007, 28(4): 174-175.
[22] 刘薇, 王佳. 海洋浪溅区环境对材料腐蚀行为影响的研究进展[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2010, 30(6): 504-512.
LIU Wei, WANG Jia. Environmental Impact of Material Corrosion Research Progress in Marine Splash Zone[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2010, 30(6): 504-512.
[23] 李丽, 苏霄. 1050A铝合金模拟海洋大气环境腐蚀行为的中性盐雾试验[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2014, 35(4): 367-370.
LI Li, SU Xiao. Corrosion Behavior of Aluminum Alloy 1050A during Cyclic Wet-Dry Immersion Test in Simulated Marine Atmospheric Environment[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2014, 35(4): 367-370.
[24] GONG Ke, WU Ming, LIU Guang-xin. Comparative Study on Corrosion Behaviour of Rusted X100 Steel in Dry/Wet Cycle and Immersion Environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 235: 117440.
[25] NEVSHUPA R, MARTINEZ I, RAMOS S, et al. The Effect of Environmental Variables on Early Corrosion of High-Strength Low-Alloy Mooring Steel Immersed in Seawater[J]. Marine Structures, 2018, 60: 226-240.
[26] ELSAADY M A, KHALIFA W, NABIL M A, et al. Effect of Prolonged Temperature Exposure on Pitting Corrosion of Duplex Stainless Steel Weld Joints[J]. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 2018, 9(4): 1407-1415.
[27] XU Wen-hua, HAN En-hou, WANG Zhen-yu. Effect of Tannic Acid on Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in NaCl Solution[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(1): 64-75.
[28] 何宝凤, 丁思源, 魏翠娥, 等. 三维表面粗糙度测量方法综述[J]. 光学精密工程, 2019, 27(1): 78-93.
HE Bao-feng, DING Si-yuan, WEI Cui-e, et al. Review of Measurement Methods for Areal Surface Roughness[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2019, 27(1): 78-93.
[29] KACIMI Y E, GALAI M, ALAOUI K. et al. Surface Morphology Studies and Kinetic Thermodynamic Characterization of Steels Treated in 5.0 M HCl Medium: Hot-dip Galvanizing Application[J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2018, 65(2): 176-189.
[30] ZHANG Hong-mei, LI Yan, YAN Ling, et al. Effect of Large Load on the Wear and Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength EH47 Hull Steel in 3.5wt% NaCl Solution with Sand[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2020, 27(11): 1525-1535.
[31] 刘鹏洋, 周和荣, 但佳永, 等. 中性盐雾腐蚀环境中B340LA钢板的腐蚀周期性研究[J]. 材料保护, 2018, 51(12): 28-32.
LIU Peng-yang, ZHOU He-rong, DAN Jia-yong, et al. Corrosion Periodicity Research of B340LA Steel Plate in Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Environment[J]. Materials Protection, 2018, 51(12): 28-32.
[32] 张建斌, 杨小娟. WHT1300HF高强钢在中性盐雾中的腐蚀行为[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2016, 42(5): 10-13.
ZHANG Jian-bin, YANG Xiao-juan. Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength Steel WHT1300HF in Neutral Salt-Mist Environment[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2016, 42(5): 10-13.
[33] WANG You-de, XU Shan-hua, WANG Hao, et al. Predicting the Residual Strength and Deformability of Corroded Steel Plate Based on the Corrosion Morphology[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 152: 777-793.
[34] GARBATOV Y, GUEDES SOARES C, PARUNOV J, et al. Tensile Strength Assessment of Corroded Small Scale Specimens[J]. Corrosion Science, 2014, 85: 296-303.
[35] APPUHAMY J S, KAITA T, OHGA M, et al. Prediction of Residual Strength of Corroded Tensile Steel Plates[J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2011, 11(1): 65-79.
[36] 龚帆, 齐盛珂, 邹易清, 等. 锈蚀高强钢丝力学性能退化的试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(10): 105-115.
GONG Fan, QI Sheng-ke, ZOU Yi-qing, et al. Experimental Study on Degradation of Mechanical Properties of Corroded High Strength Steel Wire[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(10): 105-115.
[37] 刘洋阳. 基于腐蚀形貌Q690E钢板及焊接接头力学性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.
LIU Yang-yang. Research on Mechanical Properties of Q690E Steel Plate and Welded Joint Based on Corroded Morphology[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019.
[38] 叶继红, 申会谦, 薛素铎. 点蚀孔腐蚀钢构件力学性能劣化简化分析方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2016, 48(12): 70-75.
YE Ji-hong, SHEN Hui-qian, XUE Su-duo. Simplified Analytical Method of Mechanical Property Degradation for Steel Members with Pitting Corrosion[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016, 48(12): 70-75.
[39] PIDAPARTI R M, PATEL R R. Correlation between Corrosion Pits and Stresses in Al Alloys[J]. Materials Letters, 2008, 62(30): 4497-4499.
[40] GUO Hong-chao, WEI Huan-huan, KOU Jia-liang, et al. Mechanical Properties Test of Butt Welds of Corroded Q690 High Strength Steel under the Coupling of Damp-Heat Cycle Dipping[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2021, 111: 102677.
[41] 张春涛, 李正良, 王汝恒. 腐蚀和疲劳耦合作用下Q345角钢拟静力试验研究[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(2): 152-162.
ZHANG Chun-tao, LI Zheng-liang, WANG Ru-heng. Quasi-Static Test of Q345 Equal Angles under the Coupling Action of Corrosion and Fatigue Vibration[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018, 52(2): 152-162.
[42] SINGH V, PANDEY V, KUMAR S, et al. Effect of Ultrasonic Shot Peening on Surface Microstructure and Fatigue Behavior of Structural Alloys[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2016, 69(2): 295-301.
[43] ILYIN A V, FILIN V Y. On the Problem of Quantitative Service Life Assessment for High-Strength Steel Welded Structures under the Effect of Corrosion Medium[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, 14: 964-977.
[44] YAO guo-wen, ZHONG Li, JIANG dong-xia. Experimental Method of Corrosion Fatigue Behaviors for Steel Strand under Corrosive Environment and Cycle Loading[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 578-579: 1424-1429.
[45] WANG Hong. Hysteresis Properties of Corroded High Strength Steel[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2021, 248: 01024.
[46] GUO Hong-chao, MAO Kuan-hong, YU Jin-guang, et al. Experimental and Numerical Study on Seismic Performance Plate-Reinforced and Tapered-Reduced Composite Joints[J]. Structures, 2021, 31: 686-707.
[47] 郭宏超, 周熙哲, 李炎隆, 等. Q690高强钢板式加强型节点抗震性能研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2021, 42(6): 128-138.
GUO Hong-chao, ZHOU Xi-zhe, LI Yan-long, et al. Study on Seismic Behavior of Q690 High Strength Steel Plate Reinforced Joints[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2021, 42(6): 128-138.
[48] WANG Hao, WANG You-de, ZHANG Zong-xing, et al. Cyclic Behavior and Hysteresis Model of Beam-Column Joint under Salt Spray Corrosion Environment[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2021, 183: 106737.
[49] 郑山锁, 王晓飞, 孙龙飞, 等. 酸性大气环境下多龄期钢框架节点抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(10): 20-28.
ZHENG Shan-suo, WANG Xiao-fei, SUN Long-fei, et al. Experimental Research on Seismic Behavior of Multi-Aged Steel Frame Joint under Acidic Atmospheric Environment[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2015, 36(10): 20-28.
[50] 郑山锁, 石磊, 张晓辉, 等. 酸性大气环境下锈蚀钢框架结构振动台试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(11): 77-88.
ZHENG Shan-suo, SHI Lei, ZHANG Xiao-hui, et al. Shaking Table Test of Corroded Steel Frame Structure under Acidic Atmosphere Environment[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(11): 77-88.
[51] 李善利. 一般大气环境下腐蚀钢节点滞回性能试验研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2016.
LI Shan-li. Experimental Study on Hysteretic Behavior of Corroded Steel Joint under General Atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2016.
[52] 焦兰超. 中性盐雾锈损境下锈损钢结构梁柱节点抗震性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017.
JIAO Lan-chao. The Study on Earthquake Resistance of Corroded Steel Beam-to-Column Connections under Neutral Salt Spray Corrosion Environment[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017.
[53] 余冬冬. 酸性大气环境锈损钢框架节点抗震性能试验及理论研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017.
YU Dong-dong. Experimental and Theoretical Analysis on Seismic Behavior of Corroded Steel Frame Joints in Acidic Atmosphere[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017.
[54] 徐强, 郑山锁, 商校瑀. 近海大气环境作用下钢框架节点时变地震损伤研究[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(1): 61-69.
XU Qiang, ZHENG Shan-suo, SHANG Xiao-yu. time-Varying Seismic Damage of Steel Frame Joints Considering Atmospheric Environment[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(1): 61-69.
[55] 高超, 刘建军, 郑逸川, 等. 锈蚀对输电塔角钢力学性能的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2020, 41(8): 32-38.
GAO Chao, LIU Jian-jun, ZHENG Yi-chuan, et al. Effects of Corrosion on Mechanical Properties of Transmission Tower Angle Steel[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2020, 41(8): 32-38.
[56] 徐善华, 张宗星, 李柔, 等. 锈蚀钢框架地震易损性评定方法[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(12): 107-115.
XU Shan-hua, ZHANG Zong-xing, LI Rou, et al. A Method for the Seismic Vulnerability Assessment of Corroded Steel Structures[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(12): 107-115.
[57] 管昌生, 胡国平. 基于ABAQUS的锈蚀平面钢框架数值模拟方法[J]. 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版), 2019, 43(5): 800-804.
GUAN Chang-sheng, HU Guo-ping. Numerical Simulation Method for Corroded Plane Steel Frames Based on ABAQUS[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science & Engineering), 2019, 43(5): 800-804.
Research Progress on Seismic Performance of Corroded Steel Structure Connection Joints
WEI Huan-huan1,2, LEI Tian-qi3, ZHENG Dong-dong2, GUAN Xiao-di2, Li Tao4, WAN Liang-ting1
(1. School of Architectural Engineering, Yangling Vocational & Technical College, Shaanxi Xianyang 712100, China; 2. State Key Laboratory of Eco-hydraulics in Northwest Arid Region, Xi'an University of Technology, Xi'an 710048, China; 3. School of Road, Bridge & Architecture, Shaanxi Railway Institute, Shaanxi Weinan, 714099, China; 4. Shangluo Civil Air Defense Office, Shaanxi Shangluo 726000, China)
Based on the level of materials and connecting components, the results of existing experimental research and theoretical analysis at home and abroad in recent years were summarized. It mainly included the monotonic tensile and hysteretic performance degradation analysis of corroded standard specimen, as well as the seismic performance research of beam-column structural joints and frame structure, and the corresponding mechanical performance degradation model was given. After summarizing and comparative analysis, it gives the research direction for engineering steel structure in complex environment, and at the same time, it also provides theoretical guidance and reference basis for the design method of domestic engineering structure.
steel structure; corrosion; connection joint; monotonic extension; seismic performance; degradation model
TU391;TU511.3
A
1672-9242(2023)01-0097-07
10.7643/ issn.1672-9242.2023.01.014
2021–09–14;
2021-09-14;
2021–11–08
2021-11-08
国家自然科学基金项目(51978571);杨凌职业技术学院2021年自然科学基金项目(ZK21-28)
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (51978571); Yangling Vocational & Technical College 2021 Natural Science Foundation Project (ZK21-28)
魏欢欢(1996—),男,硕士,主要研究方向为高强度钢材钢结构、金属材料疲劳与断裂、耐久性、钢结构高等分析及设计理论。
WEI Huan-huan (1996-), Male, Master, Research focus: high strength steel structure, metal materials fatigue and fracture, durability, steel structure advanced analysis and design theory.
郑东东(1995—),男,博士研究生,主要研究方向为钢结构稳定与疲劳、组合结构、工程结构抗震与加固。
ZHENG Dong-dong (1995-), Male, Doctoral candidate, Research focus: steel structure stability and fatigue, combined structure, engineering structures seismic resistance and reinforcement.
魏欢欢, 雷天奇, 郑东东, 等. 锈蚀钢结构连接节点抗震性能研究进展[J]. 装备环境工程, 2023, 20(1): 097-103.
WEI Huan-huan, LEI Tian-qi, ZHENG Dong-dong, et al. Research Progress on Seismic Performance of Corroded Steel Structure Connection Joints[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2023, 20(1): 097-103.
责任编辑:刘世忠

