基于分布鲁棒优化的发电商中长期合同电量分解模型
张少华,刘 帅,王 晛,吴 彪
基于分布鲁棒优化的发电商中长期合同电量分解模型
张少华,刘 帅,王 晛,吴 彪
(上海大学机电工程与自动化学院,上海 200444)
在我国中长期合同交易与现货市场衔接的政策背景下,中长期合同电量必须分解至短时间尺度。针对发电商中长期合同电量的自主分解问题,研究了发电商在现货市场价格严重不确定环境下基于分布鲁棒优化的中长期合同电量分解方法。首先,针对现货价格的严重不确定性,以Wasserstein距离作为分布函数距离测度,构建了现货价格分布不确定性的模糊集。其次,建立了发电商合同分解的分布鲁棒优化模型。以发电商利润最大化为目标,考虑发电商运行约束和合同分解约束,并采用对偶理论等将模型转化为可高效求解的二次规划问题。最后,通过算例仿真并与传统的随机优化和鲁棒优化模型进行对比。结果表明所提模型在处理现货价格不确定性时能有效兼顾发电商合同分解决策的经济性和鲁棒性。
发电商合同分解;现货市场价格不确定性;分布鲁棒优化;对偶理论
0 引言
在电力市场环境下,市场主体签订的中长期合同电量要与现货市场交易电量一同交割,因此中长期合同电量与现货市场交易电量的交易时间尺度必须有效衔接,这需要将中长期合同电量合理分解到短时间尺度,形成分时的合同电力曲线。而且,随着我国电力市场的发展,中长期合同电量交易将趋向于由市场主体直接签订合同电力曲线,或提前定义分解方式,在规定的时间内形成合同电力曲线[1-2]。由于发电商合同电力之外的出力将参与日前或实时现货市场竞争,并按现货市场价格结算,因此,发电商的合同电量分解对其现货市场收益具有重要影响。而且,由于通常需要在现货市场出清之前进行合同分解决策,因此,发电商合同分解决策时对于现货市场价格的预测具有较严重的不确定性[3],如何在合同分解时考虑现货市场价格的严重不确定性,是一个具有理论和现实意义的研究课题。
关于中长期合同电量分解方法,国内外学者已有较多相关研究[4-5]。文献[6-7]从管理者角度出发,分别以各发电厂和机组完成其合同电量的进度一致为目标,构建了基于二次规划的合同电量分解模型。文献[8]以发电商申报的合同分解曲线和最终分解结果差异最小化为目标,提出了合同电量分解法,其中,发电商可申报其所期望的合同电量曲线,但是最终分解结果仍由市场管理者来决定。文献[9]从管理者角度出发,分别以最大化公平性和最小化弃水量为目标,解决枯期和汛期的水电站群月度电量分解问题。文献[10]从电网公司的角度出发,提出以购电费用最小为目标的合同电量分解方法。文献[11]构建了市场管理者以最小化发电商市场力为目标的合同分解模型。文献[12]从管理者角度出发,提出了中长期合约电量分解的二次规划方法,并用于水火电短期多目标调度。然而,以上文献均未考虑现货市场价格等不确定性对合同分解决策的影响。
常用的考虑不确定性的决策模型包括随机优化(stochastic optimization, SO)模型和鲁棒优化(robust optimization, RO)模型。SO假定不确定性因素服从确定的概率分布,而RO采用不确定集合描述不确定参数的波动范围[13-14]。文献[15]从管理者角度出发,以电网购电成本最小化为目标,提出了年度合同电量向月度分解的SO模型,其中假设现货价格服从正态分布。文献[1]从系统运营商的角度,采用SO方法,对不同类型机组进行区别化的合同分解。文献[2]考虑日前现货价格的不确定性,构建了梯级水电站日合同分解RO模型。
近年来,分布鲁棒优化(distributionally robust optimization, DRO)[16-19]逐渐得到关注。DRO寻求不确定参数服从模糊集中最恶劣概率分布下的决策结果,可改善决策的经济性和保守性。一般地,根据构建的模糊集不同,DRO可以分为基于矩信息的DRO[20-22]和基于距离的DRO[23-28]。其中,文献[27-28]给出基于Wasserstein距离构建模糊集的方法,该方法考虑真实分布与经验分布之间的差异程度,可充分利用历史数据,灵活控制优化方案的保守性,并且转化后的模型易于求解,适用性较强。
综上,针对发电商中长期合同电量分解问题,现有相关研究存在以下不足:(1) 现有研究大多从管理者或电网公司角度出发,研究电网公司购电费用最小、社会福利最大等目标最优的合同分解方法。然而,随着我国电力市场的发展,发电商递交带时标的合同电力曲线将成为趋势,这需要各发电商自主确定合同电量分解曲线。(2) 现有的考虑现货价格不确定性的合同分解模型中,虽然SO模型在给定的样本数据下有着优异的表现,但是面对样本外的数据,则鲁棒性较差。RO模型只是优化最恶劣场景下的决策方案,然而最差的场景往往很难发生,因此会使优化结果过于保守。
考虑到发电商合同分解决策时通常可根据有限的历史样本数据得到现货价格的经验分布,而DRO方法可基于经验分布较好地平衡决策的经济性和鲁棒性,适合于不确定性较为严重的决策环境。因此,本文采用DRO方法研究现货市场价格严重不确定环境下发电商中长期合同的自主分解问题。首先,以Wasserstein距离作为分布函数距离测度,构建了现货价格分布不确定性的模糊集。其次,建立了发电商合同分解的DRO模型,其中,以发电商利润最大化为目标,考虑发电商运行约束和合同分解约束,并采用对偶理论等将模型转化为可高效求解的二次规划问题。最后通过算例分析验证了本文模型的有效性。
1 基于DRO的发电商合同分解优化模型
1.1 模型假设
1) 假设某一发电商的中长期合同已分解到日,需要解决日合同电量在一天24 h各时段的分解问题。
2) 在各时段,发电商合同电力之外的出力可参与日前现货市场竞争,并按日前现货价格结算。在参与日前现货市场竞争前,发电商需要确定合同电量分解曲线。
3) 发电商无法得到各时段日前现货价格精确的概率分布,但存在一些历史样本数据,并可通过历史数据构造现货价格的经验分布。
4) 采用DRO方法来考虑日前现货价格概率分布的不确定性,将不确定性建模为模糊集,其中模糊集采用Wasserstein距离来构建。
1.2 模糊集的构建

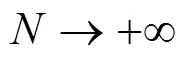
3) DRO模型必须能够转化为现有求解器可求解的确定性优化问题。
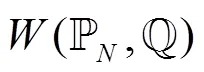
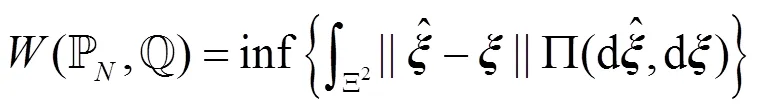
基于Wasserstein距离定义的模糊集为


图1 以为半径的Wasserstein球
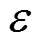
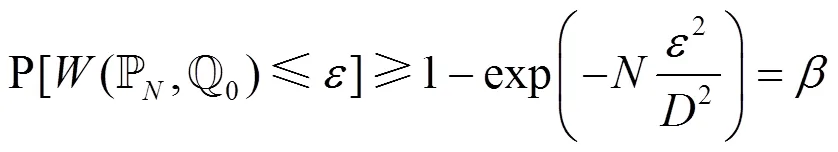
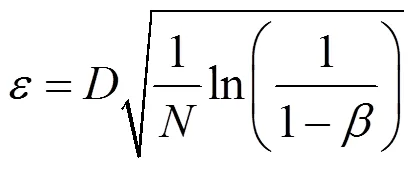

1.3 发电商合同分解优化模型
虽然发电商中长期合同的收益已经提前锁定,但是仍可通过调整合同分解策略,使其在现货市场的收益最大化。本文以发电商的收益最大为目标,确定发电商各时段的合同分解电量和总发电出力,决策目标如式(7)所示。
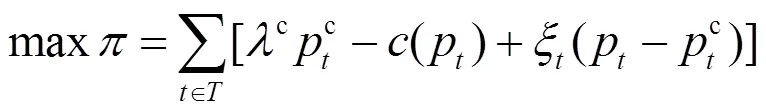
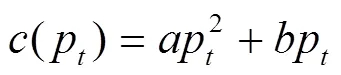
考虑的约束条件如下:
1) 发电商出力约束

2) 发电爬坡速率约束
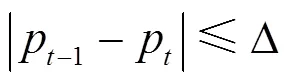
3) 日电量分解约束
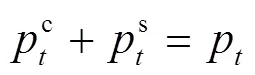
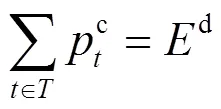

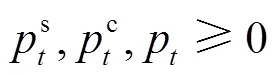
DRO寻求不确定参数服从最恶劣概率分布时的决策结果。在DRO模型中,发电商所面对的最恶劣的分布是模糊集中使其在现货市场收益最少时的分布。
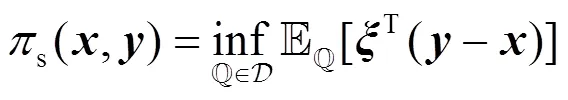
综上,基于式(7)—式(14),在目标函数前添加负号,可构建如式(16)紧凑形式的DRO模型。
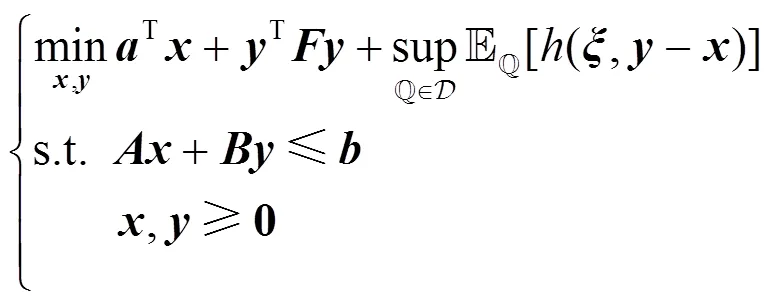
2 模型求解
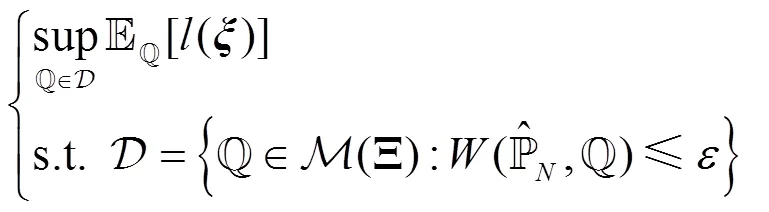
首先,根据条件概率分布的概念,将Wasserstein距离改写为

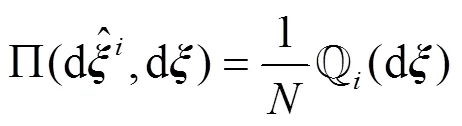
其次,改写式(17)中的目标函数为
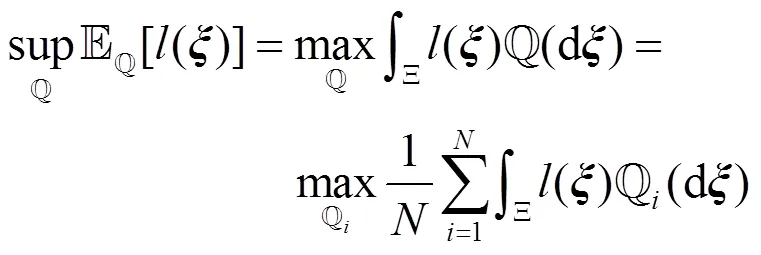
式(20)中,第2个等号的推导基于全概率公式:

因此,问题(17)可以改写为
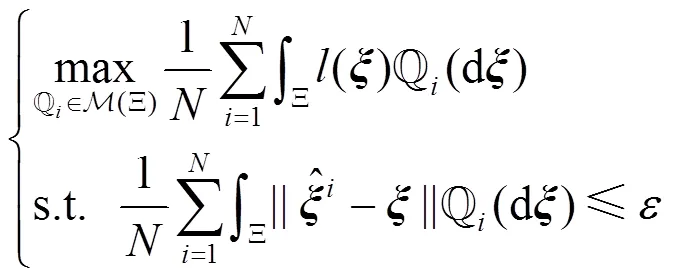
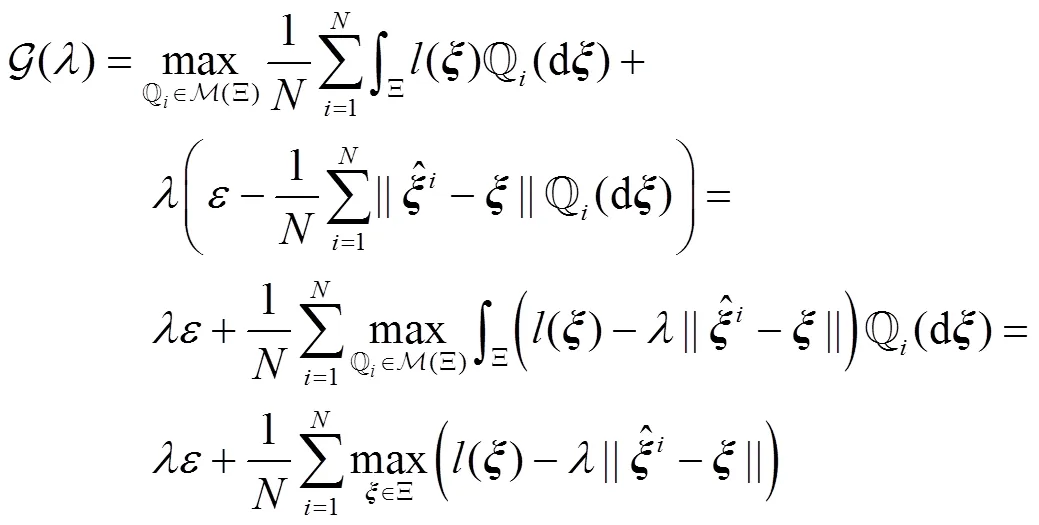

根据对偶范数的定义,问题(24)中第一组约束条件可等价为
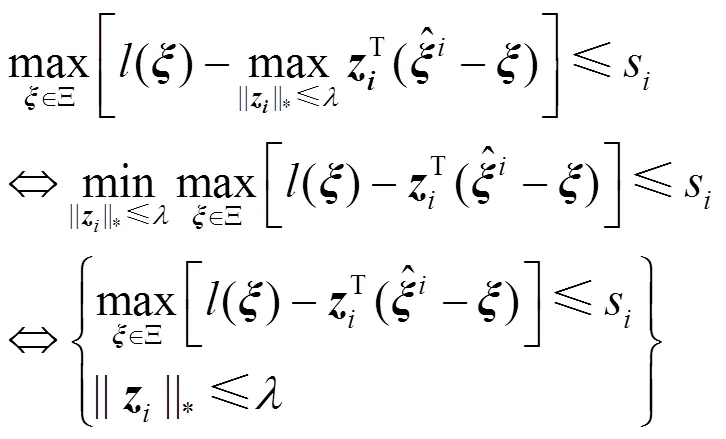
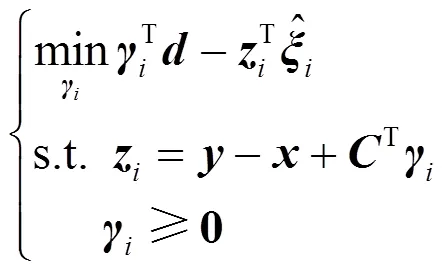
将上述结果代入问题(24)中可得
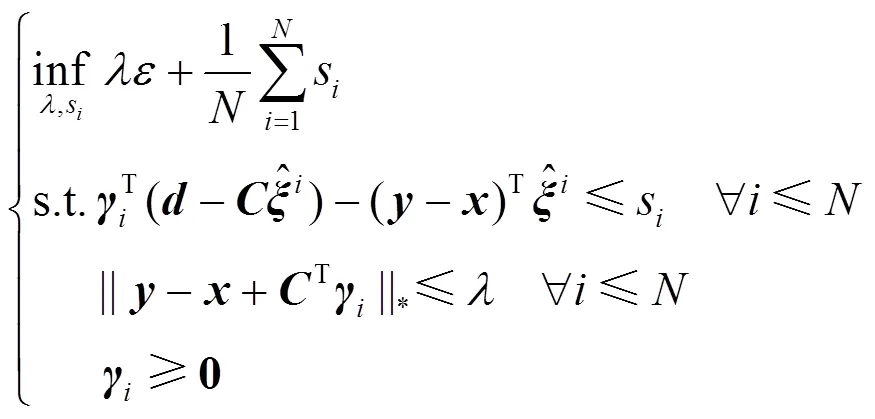
因此,基于DRO的发电商日合同电量分解模型可等价为如下可求解的问题:
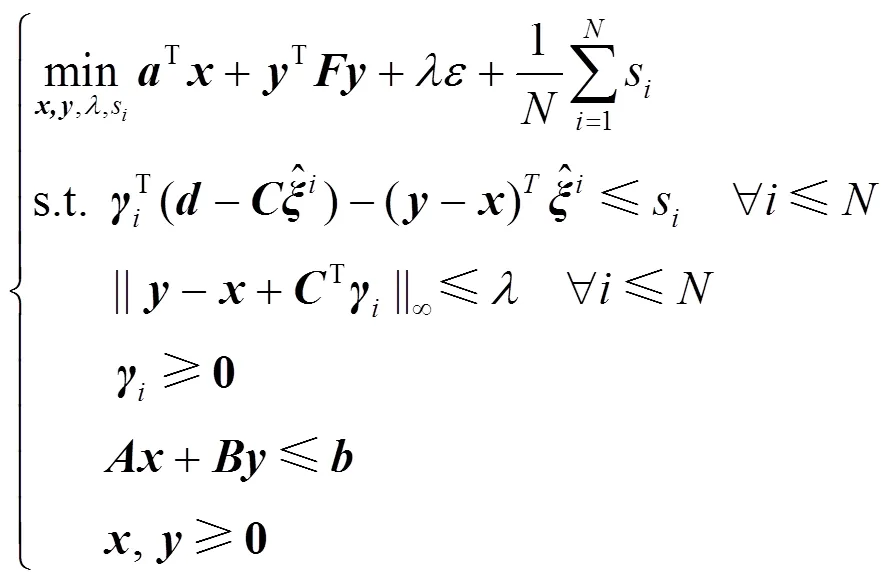
无穷范数约束可以转化为线性约束,因此该模型为可高效求解的二次规划问题。本文采用GAMS软件中的CONOPT求解器进行求解。
3 算例分析
3.1 场景生成

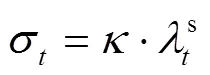
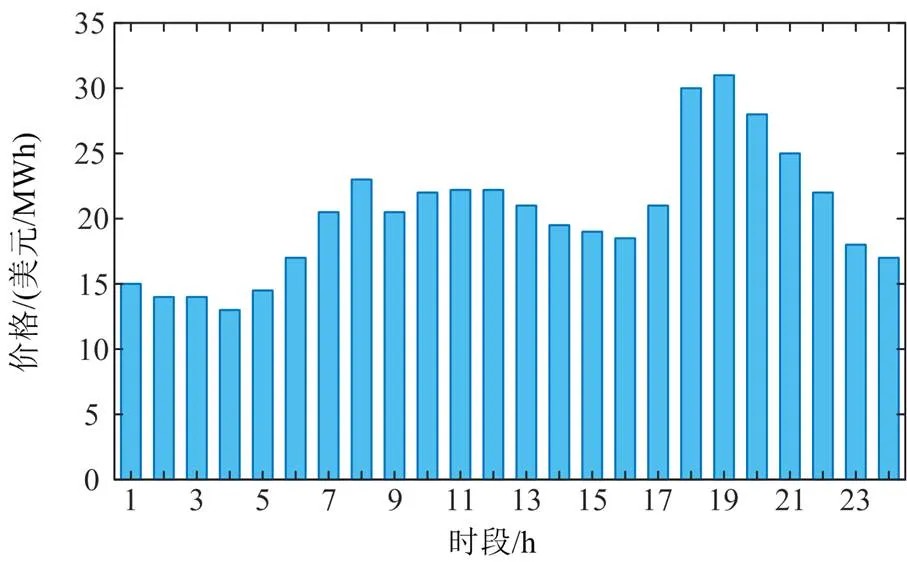
图2 预测的现货市场平均电价
3.2 参数设置
3.3 仿真结果分析
为验证本文DRO模型的优越性,将DRO决策结果与SO和RO进行对比。其中SO模型中优化目标为发电商在现货市场收益的期望值,即
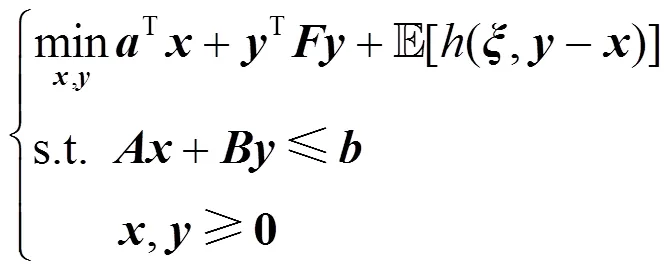
本文通过样本均值近似方法(sample average approximation, SAA)来计算期望值:

本文中RO模型寻求发电商在面对最恶劣场景时的决策,即
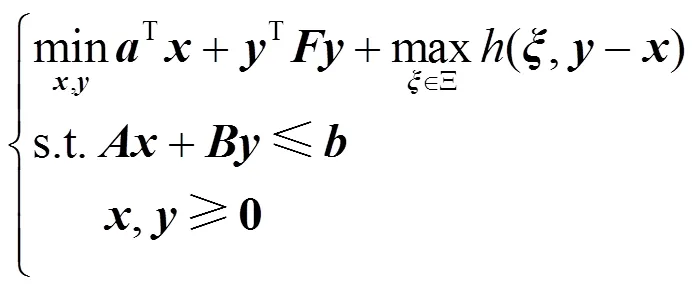
3.3.1Wasserstein半径对结果的影响
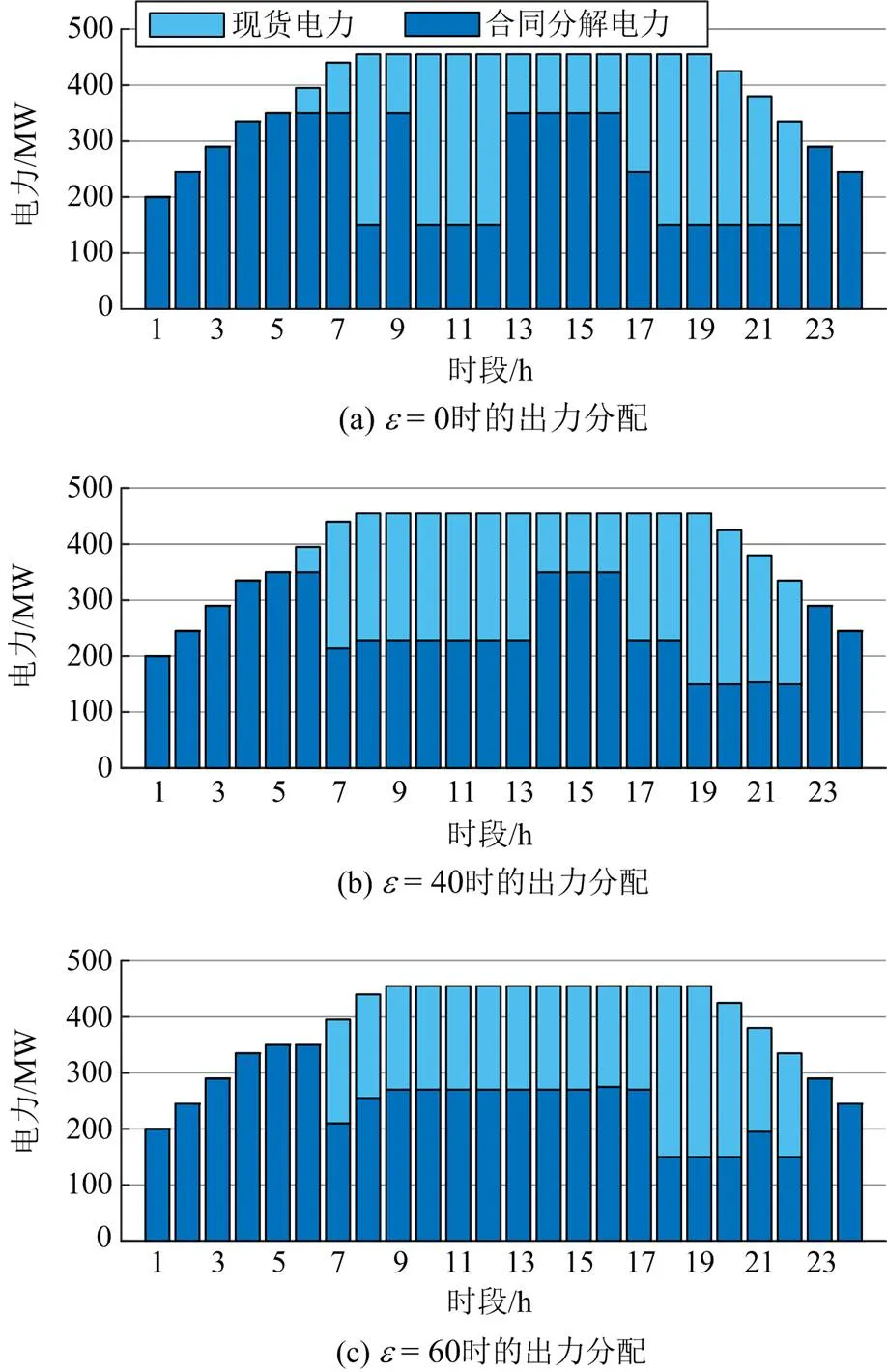
图3给出了SO、RO和不同Wasserstein半径下DRO决策的发电商预期收益,图4给出了不同Wasserstein半径下的发电商合同电力和现货电力的分配策略。由图3可以看出,为追求较大的预期收益,风险喜好的发电商会选择较小的Wasserstein半径,其决策结果会更加接近SO;而风险厌恶的发电商为了决策更具有鲁棒性,会偏向于选择较大的Wasserstein半径,其决策结果接近于RO。

图3 不同决策模型下的发电商预期收益
3.3.2鲁棒性分析

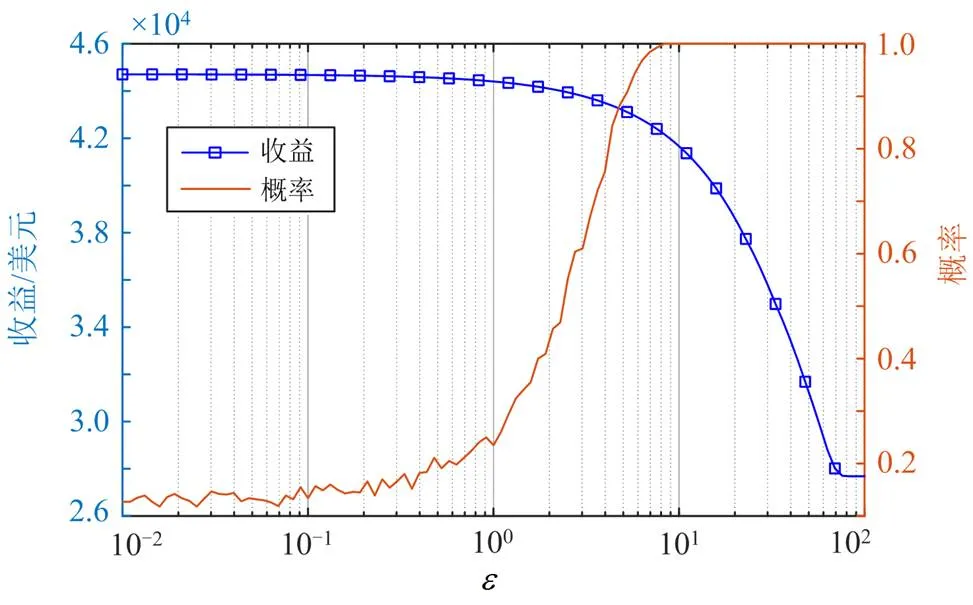
图5 预期收益与概率η随Wasserstein半径的变化曲线
3.3.3样本容量对发电商预期收益的影响
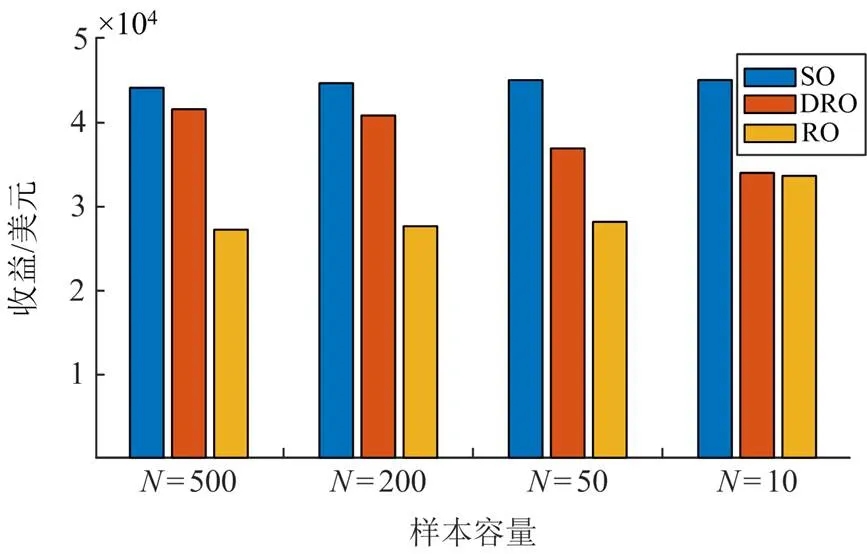
图6 不同样本容量下SO、DRO和RO的预期收益对比
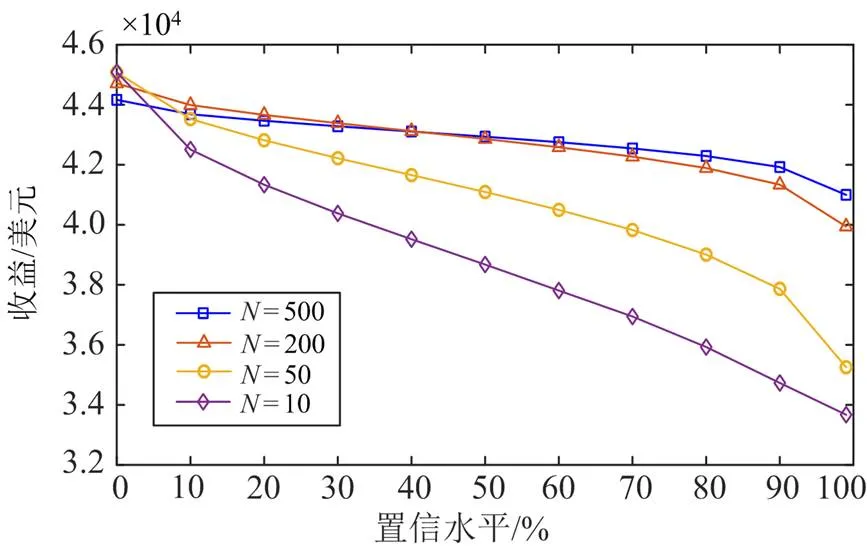
图7 不同样本容量下预期收益随置信度的变化曲线
3.3.4发电商合同量对收益的影响
定义发电商合同占比为其日合同电量与日最大发电量之比。图8对比了不同Wasserstein半径下发电商合同占比对其预期收益的影响。可以看出,给定Wasserstein半径,当合同占比较低时,发电商抵御现货价格不利波动的能力不足;合同占比过高则会限制发电商的现货市场收益空间。因此,存在一个最优的合同占比使得发电商的预期收益最大。此外,随着Wasserstein半径的增大,即现货价格不确定性越严重,发电商最优的合同占比也就越高。

图8 不同Wasserstein半径下预期收益随合同占比的变化
4 结论
本文从发电商的角度出发,对中长期合同电量分解方法展开研究。考虑现货电价的严重不确定性,提出了一种基于DRO的发电商中长期合同电量分解模型。所提模型可转化为二次规划问题,能够以较高的效率求解。最后通过算例仿真验证了所提模型的有效性,得出以下主要结论:1) 与SO和RO方法相比,基于DRO的合同分解模型在处理现货价格不确定性时,能有效兼顾发电商合同分解决策的经济性和鲁棒性。2) 具有不同风险偏好的发电商可以根据预期收益或置信度来调整Wasserstein半径的大小,以应对不同程度的现货价格不确定性,确保合同分解决策的鲁棒性。3) 发电商有关现货价格的历史样本信息越多,则相同置信水平下合同分解决策的预期收益越高,鲁棒性也越好。
本文为不确定环境下发电商中长期合同的自主分解提供了新方法,但仅考虑发电商的日合同电量分解问题,且假设发电商为日前现货市场的价格接受者。下一步需要研究发电商的周/月合同电量自主分解问题,并研究发电商作为价格影响者参与现货市场竞争时的合同分解策略等问题。
[1] HUANG Y, WANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Energy decomposition of long and middle term contract in multi-energy system[C] // 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies-Asia (ISGT Asia), May 21-24, 2019, Chengdu, China: 3735-3740.
[2] 于旭光, 李刚, 李亚鹏, 等. 耦合日合同分解及日前市场竞价的梯级水电站短期鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(10): 4016-4025.
YU Xuguang, LI Gang, LI Yapeng, et al. Short-term robust optimization scheduling of cascade hydropower stations coupled with daily contract decomposition and day-ahead market bidding[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(10): 4016-4025.
[3] 邹鹏, 陈启鑫, 夏清, 等. 国外电力现货市场建设的逻辑分析及对中国的启示与建议[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2014, 38(13): 18-27.
ZOU Peng, CHEN Qixin, XIA Qing, et al. Logical analysis of electricity spot market design in foreign countries and enlightenment and policy suggestions for China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2014, 38(13): 18-27.
[4] 刘军, 龚建荣, 孙瑜, 等. 考虑风电不确定性的中长期合同电量分解[J]. 电力科学与技术学报, 2021, 36(3): 84-91.
LIU Jun, GONG Jianrong, SUN Yu, et al. Mid-long term contract energy decomposition considering wind power uncertainty[J]. Journal of Electric Power Science And Technology, 2021, 36(3): 84-91.
[5] 于旭光, 李亚鹏, 贾泽斌, 等. 考虑现货市场竞价空间的梯级水电站中长期合同电量分解模型[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(6): 62-71.
YU Xuguang, LI Yapeng, JIA Zebin, et al. Medium-and long-term contract energy decomposition model for cascade hydropower station considering spot market bidding space[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(6): 62-71.
[6] 黎灿兵, 胡亚杰, 赵弘俊, 等. 合约电量分解通用模型与算法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2007, 31(11): 26-30.
LI Canbing, HU Yajie, ZHAO Hongjun, et al. General model and algorithm for contract energy decomposition[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2007, 31(11): 26-30.
[7] 王冠群, 刘锋, 梅生伟, 等. 合同电量优化分解模型及算法[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2012, 16(7): 58-64.
WANG Guanqun, LIU Feng, MEI Shengwei, et al. Optimization model and algorithm for contract energy decomposition[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2012, 16(7): 58-64.
[8] 陈建华, 杨莉, 张宁, 等. 基于发电商申报的差价合同电量分解[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2009, 33(3): 30-34, 63.
CHEN Jianhua, YANG Li, ZHANG Ning, et al. Decomposition of contract for difference based on generation companies' declaration[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2009, 33(3): 30-34, 63.
[9] 程雄, 唐应玲, 申建建, 等. 电力市场环境下大规模水电站群月度交易电量分解与校核方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(8): 2514-2525.
CHENG Xiong, TANG Yingling, SHEN Jianjian, et al. Decomposition and checking method for large-scale hydropower plants monthly trading energy in electricity market[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(8): 2514-2525.
[10] 王雁凌, 张粒子, 舒隽, 等. 合同交易量和竞价交易量在日计划中的经济分配[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2002, 26(9): 45-48.
WANG Yanling, ZHANG Lizi, SHU Juan, et al. Coordination of the dispatching relationship between the contract volume and competitive bidding volume in daily generation scheduling[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2002, 26(9): 45-48.
[11] XU C, PANG K, WEN F, et al. Decomposition model of contract for difference considering market power mitigation[C] // 2020 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2020 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC / I&CPS Europe), June 9-12, 2020, Madrid, Spain: 1-5.
[12] 苗树敏, 罗彬, 申建建, 等. 考虑市场过渡和中长期合约电量分解的水火电短期多目标发电调度[J]. 电网技术, 2018, 42(7): 2221-2231.
MIAO Shumin, LUO Bin, SHEN Jianjian, et al. Short-term multi-objective hydro-thermal generation dispatch considering electricity market transition and mid- and long-term contract decomposition[J]. Power SystemTechnology, 2018, 42(7): 2221-2231.
[13] BOUBAKIR A, TOUIL S A, LABIOD S, et al. A robust model-free controller for a three-phase grid-connected photovoltaic system based on ultra-local model[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2021, 6(4): 538-550.
[14] 臧海祥, 马铭欣, 周亦洲, 等. 电力市场环境下风电-光热-生物质混合电站鲁棒优化调度模型[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50(5): 1-11.
ZANG Haixiang, MA Mingxin, ZHOU Yizhou, et al. Robust optimal scheduling model for a ‘wind power- concentrating solar power-biomass’ hybrid power plant in the electricity market[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50(5): 1-11.
[15] 张少迪. 基于CSS的年度合约电量分解方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 34(11): 135-141.
ZHANG Shaodi. Annual contract power decomposition method based on CSS[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34(11): 135-141.
[16] 贺帅佳, 阮贺彬, 高红均, 等. 分布鲁棒优化方法在电力系统中的理论分析与应用综述[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(14): 179-191.
HE Shuaijia, RUAN Hebin, GAO Hongjun, et al. Overview on theory analysis and application of distributionally robust optimization method in power system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(14): 179-191.
[17] 于腾凯, 董靓媛, 杜晓东, 等. 考虑机会约束的配电网光伏并网容量分布鲁棒优化方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(10): 43-50.
YU Tengkai, DONG Liangyuan, DU Xiaodong, et al. Distributionally robust optimization method of PV grid-connected capacity in a distribution network considering chance constraints[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(10): 43-50.
[18] 陈泽雄, 张新民, 王雪锋, 等. 分布式光伏电站接入配电网的分布鲁棒优化配置方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(13): 30-42.
CHEN Zexiong, ZHANG Xinmin, WANG Xuefeng, et al. A distributionally robust optimal allocation method for distributed photovoltaic generation stations integrated into a distribution network[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(13): 30-42.
[19] 尉耀稳, 李跃龙, 陈思超, 等. 多类型源储协调互动的配电网分布鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电力工程技术, 2021, 40(5): 192-199.
YU Yaowen, LI Yuelong, CHEN Sichao, et al. Distributionally robust optimal dispatch of distribution network considering multiple source-storage coordinated interaction[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2021, 40(5): 192-199.
[20] HAN X, HUG G. A distributionally robust bidding strategy for a wind-storage aggregator[J]. Electric Power Systems Research, 2020, 189.
[21] XIONG P, JIRUTITIJAROEN P, SINGH C. A distributionally robust optimization model for unit commitment considering uncertain wind power generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 32(1): 39-49.
[22] HE C, ZHANG X, LIU T, et al. Distributionally robust scheduling of integrated gas-electricity systems with demand response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34(5): 3791-3803.
[23] 孙旭, 邱晓燕, 张志荣, 等. 基于数据驱动的交直流配电网分布鲁棒优化调度[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(12): 4768-4777.
SUN Xu, QIU Xiaoyan, ZHANG Zhirong, et al. Distributed robust optimal dispatching of AC/DC distribution network based on data driven mode[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(12): 4768-4777.
[24] CHEN Y, GUO Q, SUN H, et al. A distributionally robust optimization model for unit commitment based on Kullback-Leibler divergence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33(5): 5147-5160.
[25] 高晓松, 李更丰, 肖遥, 等. 基于分布鲁棒优化的电-气-热综合能源系统日前经济调度[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(6): 2245-2254.
GAO Xiaosong, LI Gengfeng, XIAO Yao, et al. Day ahead economical dispatch of electricity-gas-heat integrated energy system based on distributionally robust optimization[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(6): 2245-2254
[26] 周计晨, 吕胤杰, 杨诚之, 等. 考虑风电出力不确定性的分布鲁棒主备协同优化调度[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(20): 66-73.
ZHOU Jichen, LÜ Yinjie, YANG Chengzhi, et al. Distributionally robust co-optimization of energy and reserve dispatch considering uncertain wind power output[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(20): 66-73.
[27] POOLLA B K, HOTA A R, BOLOGNANI S, et al. Wasserstein distributionally robust look-ahead economic dispatch[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 36(3): 2010-2022.
[28] ZHU R, WEI H, BAI X. Wasserstein metric based distributionally robust approximate framework for unit commitment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2019, 34(4): 2991-3001.
[29] ZHOU A, YANG M, WANG M, et al. A linear programming approximation of distributionally robust chance-constrained dispatch with Wasserstein distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35(5): 3366-3377.
[30] GAO R, KLEYWEGT A J. Distributionally robust stochastic optimization with Wasserstein distance[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1604. 02199, 2016.
[31] ESFAHANI P M, KUHN D. Data-driven distributionally robust optimization using the Wasserstein metric: Performance guarantees and tractable reformulations[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2018, 171(1): 115-166.
[32] DUAN C, FANG W, JIANG L, et al. Distributionally robust chance-constrained approximate AC-OPF with Wasserstein metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33(5): 4924-4936.
[33] ZHOU Y, WEI Z, SHAHIDEHPOUR M, et al. Distributionally robust resilient operation of integrated energy systems using moment and Wasserstein metric for contingencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021, 36(4): 3574-3584.
[34] ZUGNO M, MORALES J M, PINSON P, et al. A bilevel model for electricity retailers’ participation in a demand response market environment[J]. Energy Economics, 2013, 36: 182-197.
[35] 赵琛, 张少华. 基于信息间隙决策理论的发电商电量分配策略[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(4): 751-754.
ZHAO Chen, ZHANG Shaohua. Generation asset allocation strategies based on IGDT[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(4): 751-754.
A distributionally robust optimization model for power generators' medium and long-term contracted energy decomposition
ZHANG Shaohua, LIU Shuai, WANG Xian, WU Biao
(School of Mechatronic Engineering and Automation, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China)
Given the requirement of time linkage between the medium and long-term contract and spot market trading, power generators’ long-term contracted electricity must be decomposed to a short time scale. To help a generator’s self-decomposition of medium and long-term contracted energy, a novel decomposition model based on distributionally robust optimization is proposed, taking into consideration the serious uncertainty of spot market prices. First, the ambiguity set for the distribution uncertainty of spot market prices is constructed using a Wasserstein metric as the distance measurement between distribution functions. Second, a distributionally robust optimization model for a generator’s contract decomposition is presented, in which the objective is to maximize the generator’s profit in the spot market, and the generator’s operational and contract decomposition constraints are considered. In addition, a dual theory is employed to transform the model into a quadratic programming problem which can be solved efficiently. Finally, case studies are presented and comparisons with the traditional stochastic and robust optimization models are also conducted. It is shown that the proposed model can effectively balance the economics and robustness of the generator’s contract decomposition in the presence of serious uncertainty in spot market prices.
power generator’s contract decomposition; spot market prices uncertainty; distributionally robust optimization; dual theory
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220379
国家自然科学基金项目资助(61773252)
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61773252).
2022-03-31;
2022-08-25
张少华(1966—),男,博士,教授,研究方向为电力市场风险管理、需求响应和博弈分析等;E-mail: eeshzhan@ 126.com
刘 帅(1997—),男,硕士,研究方向为电力系统优化调度与风险管理;E-mail: shuailiuuu@163.com
王 晛(1970—),女,博士,副教授,研究方向为电力市场均衡分析。E-mail: xianwang@shu.edu.cn
(编辑 魏小丽)

