Observation on the therapeutic efficacy of Tuina plus “three-bridge” exercise for non-specific low back pain
LI Jinhu (李金虎)
The First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Exercise Therapy; Low Back Pain; Pain Measurement; Visual Analog Scale; Randomized Controlled Trial
Non-specific low back pain (NSLBP) is a general term for a group of low back pain, the cause of which cannot be elucidated by objective clinical examinations, and no abnormalities can be detected in histopathological diagnosis[1]. The main symptoms are pain and functional disorder. The location of the pain is between the lower edge of the costal arch on one or both sides and the inferior gluteal striation, possibly including radiating pain down to the lower limbs[2]. It is the main reason for limited daily living skills among people under 45 years of age[3]. Some studies have shown that 58%-84% of people have suffered from this disease[4].The incidence rate is as high as 45% in some countries and regions[5], and the incidence of disability reaches up to 5%[6]. Due to its complex pathogenic factors[7]and diverse clinical manifestations, although there are many clinical treatments, the overall therapeutic effect is unstable and the condition is prone to be chronic and recurrent[8-9]. Domestic research showed that integrated Chinese and Western medicine treatment could achieve more significant effects[10-11]. This study aims to explore
Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage) plus “threebridge” exercise methods to relieve pain, improve function, and reduce the relapse rate in patients with NSLBP.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
According to the NSLBP diagnostic criteria developed by the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA)[12],the following conditions can be defined as NSLBP. Low back pain occurred under unrecognized or indefinite pathological changes (e.g., infection, tumor,osteoporosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and fracture). Pain and dysfunction were evident in patients. Clinical diagnoses belong to lumbar muscle strain, psoas fasciitis, acute lumbar sprain, sacroiliac arthritis, and so on.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Patients compliant with the diagnostic criteria of NSLBP; imaging examinations showing no noticeable abnormalities; aged between 25 and 50 years old;volunteered to participate in this study and signed the informed consent form.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those with lumbar tumors, tuberculosis, fractures,lumbar spondylolisthesis, ankylosing spondylitis,rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, etc.; women who were pregnant or planned to conceive; patients with heart, liver, or kidney problems or mental illness; those who cannot cooperate with treatment or evaluation.
1.4 Statistical methods
All data were processed by the SPSS version 21.0 statistical software. The measurement data with normal distribution and conforming to variance homogeneity were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s).The intra-group comparisons were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance, and the between-group comparisons were analyzed using the independent samplest-test. Enumeration data analysis was analyzed by the Chi-square test. The two-sided test levelαwas 0.05. The difference was considered statistically significant whenP<0.05.
1.5 General data
The study followed the ethical principles of medical research formulated in theWorld Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. The NSLBP patients admitted to our hospital between March 2017 and August 2019 and meeting the NSLBP diagnostic criteria developed by the APTA were selected in this study. A total of 80 patients were allocated to a control group or an observation group by the random number table method, with 40 cases in each group. There were no significant differences between the two groups in the general data(P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).

Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
The control group was given Tuina treatment. The patient was in a prone position, and a soft pillow was placed under the abdomen. The manipulations of onethumb Tui-Pushing (Figure 1), Gun-Rolling (Figure 2),and Rou-Kneading (Figure 3) were applied to the lower back and the courses of the Governor Vessel and Bladder Meridian on the lumbosacral area and buttocks.An-Pressed and Tanbo-Plucked Zhishi (BL52),Dachangshu (BL25), Huantiao (GB30), Weizhong (BL40),Ashi points, and their surrounding areas (Figure 4). The post-extension Ban-Pulling (Figure 5), Qu-Flexing(Figure 6), and Juan-Looping (Figure 7) manipulations were used to stretch out the fascia, muscles, and
ligaments of the back, the low back, and the buttocks to relax the sinews and muscles, and unblock meridians and collaterals. Each treatment was performed for 20 min, once a day for 5 consecutive days, at an interval of 2 d, for a total of 4 weeks.

Figure 1. One-thumb Tui-Pushing manipulation

Figure 2.Gun-Rolling manipulation

Figure 3. Rou-Kneading manipulation

Figure 4. Tanbo-Plucking manipulation

Figure 5. Post-extension Ban-Pulling manipulation

Figure 6. Qu-Flexing manipulation

Figure 7. Juan-Looping manipulation
2.2 Observation group
The observation group was given both Tuina and the“three-bridge” exercise. The Tuina manipulations were the same as those in the control group. The“three-bridge” exercise was carried out as follows.
Prone bridge (plank) exercise: The patient took a prone position, with the two elbows shoulder-width apart. The patient used the elbows to support the body off the bed. The upper limbs and torso should be kept at a 90° angle as possible with the feet put together.The neck relaxed and extended naturally, with eyes looking forward. The head, shoulders, hips, and lower limbs should remain on the same plane, with the abdomen tightened. The patient should breathe naturally, hold the position for 10-15 s, and then relax for 3-5 s. Repeated it 5 times as one set (Figure 8).
Side bridge (side plank) exercise: Side-lying position was taken. The upper forearm flexed against the bed’s surface to support the body, and the other one fully extended and relaxed by the side of the bed, with the feet naturally put together. The supporting forearm and foot pushed down to lift the body upward and hold for 10-15 s, with the head and back straight and extended.Then lowered the hip, relaxing for 3-5 s. Repeated the exercise 5 times and then alternated left and right as one set (Figure 9).
Back bridge exercise: The supine position was taken.Both arms extended flat by each side of the body, with the back closely against the bed surface. Both ankles should be dorsiflexed at about 90°. While inhaling,raised the hips so that the shoulders, back, and thighs were in a straight line. Held for 10-15 s and then relaxed for 3-5 s. Repeated the exercise 5 times as one set(Figure 10).
The above exercises were performed once a day,3 sets each time.

Figure 8. Prone bridge exercise

Figure 9. Side bridge exercise

Figure 10. Back bridge exercise
3 Observation of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 Evaluation methods
3.1.1 Visual analog scale (VAS)[13]
The VAS score ranges from 0 to 10 points. It was measured using a 10-centimeter ruler marked with “0”on one end and “10” on the other. Zero suggests painless, and 10 is the most severe pain. The patient indicated the corresponding number on the ruler according to the degree of pain. The higher the score,the more intensive the pain.
3.1.2 Oswestry disability index (ODI)[14]
The ODI is a questionnaire for patients to selfevaluate their dysfunctional status. It consists of ten questions, each with 6 options. Each option corresponds to 0-5 points. The highest total score is 50 points. The ODI final score = Actual score ÷ Highest score × 100%. The higher the ODI final score, the more severe the physical impairment.
3.1.3 Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score[15]
The scoring symptoms include pain in the low lumbar spine, leg pain, and gait, making a total of 9 points. The signs include straight leg raising tests, sensory disorders,and movement disorders, earning 6 points. The daily activity limitation consists of 14 points, including lying on the back and turning over, standing, and washing.The highest score is 29, while the lowest score is 0: a score of 10 points or less, a poor function; between 10 and 15 points, moderate; 16-24 points, good; 25-29 points, excellent. The lower the score, the more severe the dysfunction.
The above assessment methods were evaluated before treatment, after 4 weeks of treatment, and at 6-month follow-up.
3.2 Therapeutic efficacy criteria
The criteria for therapeutic efficacy referred to theCriteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine[16].
Cured: The pain disappeared, and the activity and work were normal.
Effective: The pain was relieved, activity improved,and there was no impact on life.
Invalid: No improvement in pain or activity.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy
After 4 weeks of treatment, the total effective rate was 92.5% in the observation group and 80.0% in the control group. The total effective rate in the observation group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05).At the 6-month follow-up, the total effective rate was 85.0% in the observation group versus 67.5% in the control group, and the total effective rate in the observation group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05). It is shown in Table 2.
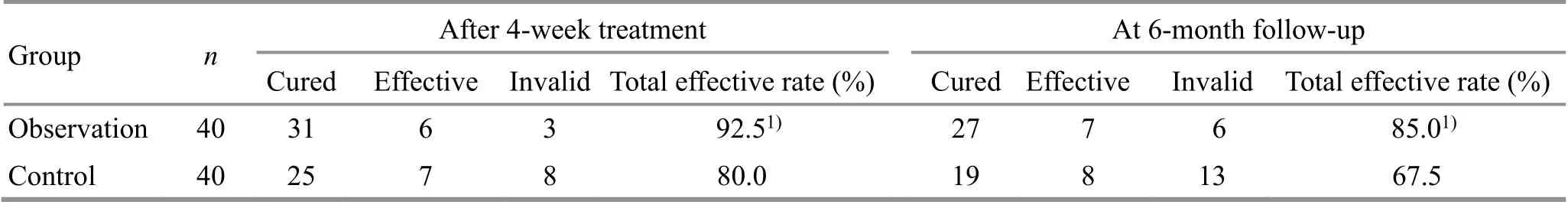
Table 2. Comparison of therapeutic efficacy after treatment and at follow-up between the two groups (case)
3.3.2 Comparison of the VAS, ODI, and JOA scores
Before treatment, there were no statistical differences in the VAS, ODI, or JOA scores between the two groups (P>0.05). After 4 weeks of treatment, the VAS and ODI scores in the two groups were decreased,the JOA scores were increased, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05); the VAS and ODI scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, while the JOA score was higher than that in the control group, and the inter-group differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). At the 6-month follow-up, the VAS and ODI scores in the two groups were lower than before treatment, the JOA scores were higher than before treatment, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05); the VAS and ODI scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, while the JOA score was higher than that in the control group, and the inter-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). See Table 3 to Table 5.
Table 3. Comparison of the visual analog scale (VAS) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)

Table 3. Comparison of the visual analog scale (VAS) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group at the same time point, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 4-week treatment At 6-month follow-up Observation 40 6.28±1.13 1.54±1.131)2) 1.81±0.961)2)Control 40 6.26±1.12 2.63±1.211) 2.96±1.231)t-value 0.58 4.88 5.87 P-value 0.64 0.00 0.00
Table 4. Comparison of the Oswestry disability index (ODI) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)

Table 4. Comparison of the Oswestry disability index (ODI) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group at the same time point, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 4-week treatment At 6-month follow-up Observation 40 30.75±3.32 10.64±2.131)2) 12.73±6.941)2)Control 40 31.45±3.24 14.86±2.731) 17.65±10.041)t-value 1.13 5.58 6.37 P-value 0.26 0.00 0.00
Table 5. Comparison of the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)

Table 5. Comparison of the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score between the two groups ( ±s, point)
Note: Compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the control group at the same time point, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 4-week treatment At 6-month follow-up Observation 40 9.41±3.25 26.32±3.341)2) 22.76±3.581)2)Control 40 9.69±3.17 20.62±3.971) 17.73±3.491)t-value 0.48 9.15 7.83 P-value 0.63 0.00 0.00
4 Discussion
NSLBP accounts for about 85% of adults with low back pain[17]. The symptoms, signs, and reactions of NSLBP are a complete manifestation of neurological,muscular, and skeletal disorders. There is a mutually causal relationship between pain and motion control dysfunction of the spinal stabilization system, which is the root cause of pain and dysfunction. Building spinal stability is the basis for avoiding soft tissue damage and eliminating pain[18]. Traditional passive rehabilitation treatments can only relieve patients’ pain on a short-term basis but cannot improve the symptoms of patients with low back pain in the long term, increase muscle strength in the waist, or effectively prevent relapse. Core stabilization exercises have become a new trend in rehabilitation therapy in China and abroad[19]. A study has shown that in NSLBP patients, the lumbar deep stable muscle group endurance declines, and the response delays[20]. Strengthening core stabilization exercises and restoring the functions of the spine’s passive, active, and neural control sub-systems are the key to curing NSLBP and preventing relapse. European NSLBP management guidelines recommended exercise therapy as the first treatment choice, and this study followed the same principle. The research of MCGILL S M[21]argues that only by keeping the spine stable can it generate the force and torque necessary to improve limb movements. The “three-bridge” exercise is a multi-joint, closed-chain exercise that does not apply any additional shearing force to the joints. This can train the overall coordination of the joints, promote the functional recovery of sensory receptors in the joints,enhance stimulation to the proprioceptive input in the low back, and improve the function of the patient’s low back, to maintain lumbar stability and prevent recurrence[22-23].
According to its location and clinical manifestations,NSLBP can be categorized under the scopes of “Yao Tong” and Bi-Impediment syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine[24]. It is related to exogenous wind,cold, and dampness, or liver and kidney deficiency,causing blockages in meridians, impaired Qi and blood circulation, and pain due to obstruction. Tuina is a conventional non-invasive method for treating NSLBP in traditional Chinese medicine. The advantages are that it can correct the structural disorders of the spine, open up localized capillaries, promote blood and lymph circulation, improve muscle nutrition, reduce muscle tension and spasms, and accelerate the absorption of painkillers, thus reducing the degree of pain in the affected area[25-26].
The results of this study show that Tuina can effectively reduce pain, correct spinal structural disorders, promote the functional recovery of the neuromusculoskeletal system, and create conditions for early core strength training in the treatment of NSLBP.At the 6-month follow-up, it was found that Tuina plus“three-bridge” exercise could restore the coordination and stability of the core muscle group, relieve pain and related symptoms, produce long-term positive effects,and effectively prevent a recurrence. Therefore, using the approach of combining Tuina and the “threebridge” exercise is a more effective way to treat patients with NLBP.
Conflict of Interest
This research has no conflict of interest with any medical institution or individual.
Acknowledgments
The research sincerely appreciates the support of the Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Geriatrics of the First Affiliated Hospital of China University of Science and Technology (Anhui Provincial Hospital).
Statement of Ethics
The research followed the ethical principles of medical research formulated in theWorld Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. In this research, Tuina and the“three-bridge” exercise were used to treat non-specific low back pain. The subjects included were all informed and voluntary participants, and the research methods,procedures, and treatment fully respected and protected the subjects’ health and power. Tuina and the “three-bridge”exercise are non-drug therapies without any side effects.The research does not adversely affect the environment or the health of the subjects. The therapeutic effect of the study justifies the study.
Received: 10 November 2020/Accepted: 29 June 2021
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年5期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年5期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Efficacy of mild moxibustion combined with surgery for meniscal injury and its effect on TGF-β1 and PDGF levels in the fluid of knee joint
- Clinical study on tube moxibustion plus point-toward-point needling method in treating refractory facial paralysis
- Effect of electroacupuncture at different time points on the recovery of gastrointestinal function after surgery for gastrointestinal malignant neoplasms
- Influence of buccal acupuncture on analgesic effect,immune indicators, and expression of Survivin and Livin proteins in patients with advanced-stage primary liver cancer
- Effect of acupuncture-like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on labor pain in nulliparous women: a randomized controlled trial
- Influence of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on lumbar functions and inflammatory factors in patients with lumbar disc herniation due to kidney deficiency and blood stasis
