Effectiveness of Shengmai Injection on angina pectoris based on realworld propensity score method
Zong-Liang Yu, Chun-Quan Sun, Fu-Mei Liu, Long-Tao Liu, Yan-Ming Xie✉, Shu Chen
1. Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine,China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences,Beijing 100700, China
2. Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
3. School of Statistics, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
Keywords:Shengmai injection Angina pectoris Propensity score Real world
ABSTRACT Objective: Shengmai injection is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of angina pectoris. However, there is still a lack of high-quality clinical research evidence for the treatment effect of Shengmai injection for angina pectoris. Real-world studies based on large samples can provide Shengmai injection. Researches on the treatment of angina pectoris with Shengmai injection provide important evidence. Methods: This article is based on the information collected by the hospital information system (HIS) database of 22 tertiary A general hospitals for all patients who used Shengmai injection and those who did not use Shengmai injection. The propensity scoring method was used to evaluate the possible existence of the research data. The confounding factors are controlled. Through the general Logistic regression analysis method, the propensity score weighted Logistic regression analysis method and the propensity score weighted Logistic regression analysis method with covariates, the therapeutic effect of Shengmai injection on angina pectoris was explored. Results: Three kinds of logistic regression analysis showed that there were statistical differences in the treatment effect of Shengmai injection on angina pectoris in the group without Shengmai injection.Propensity score weighted logistic regression analysis with covariates balanced the effect of multiple confounding factors. Using real-world data to construct a retrospective cohort study confirmed the clinical effectiveness of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris,and at the same time confirmed the wide application of Shengmai injection in angina pectoris complicated with multiple organ failure. Conclusion: Shengmai injection is effective in the treatment of angina pectoris. The weighted method of propensity score removes confounding factors, which improves the reliability of real-world research results.
1. Introduction
Shengmai injection is made from the three traditional Chinese medicines of schisandrae, Ophiopogon japonicus, and red ginseng.The main chemical components include schisandrae alcohol A,saponins of Ophiopogon japonicus, and ginsenosides [1-3]. It comes from the traditional Chinese medicine compound Shengmai San. Studies have shown that Shengmai preparations have the effects of nourishing yin and qi [4]. It is widely used in cardiogenic shock, heart failure, and other cardiovascular diseases and tumor chemotherapy [5-7]. Clinical studies have found that the combined use of Shengmai injection based on conventional treatment can significantly improve the total effective rate of treatment of patients with angina pectoris, and can reduce the release of serum inflammatory factors and improve the state of hemorheology [8-9].
However, the current research on the effectiveness of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris still has problems such as insufficient sample size and lack of high-quality randomized controlled studies. Real-world studies based on a large amount of clinical research data can effectively verify the results of randomized controlled trials. Therefore, this study adopts the propensity scoring method to balance the confounding factors through three logistic regression analyses, and explores the true efficacy of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris based on real-world data.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Data sources and standardization
The research data is based on the HIS database covering 22 large tertiary hospitals across the country constructed by the Institute of Basic Research in Clinical Medicine, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences. The study extracts the information of hospitalized patients who are discharged from the hospital and diagnosed with angina pectoris from the entire population of Shengmai injection users. It includes 5 parts: basic patient information, diagnosis of traditional Chinese medicine, diagnosis of western medicine,medical order records, and physical and chemical indicators. The standardization of extracted data mainly includes the elimination of duplicate data, invalid records, the standardization of diagnostic names and medical order names, and the standardization of medication names. Western medicine diagnosis refers to the ICD-10 code, Western medicine uniformly adopts chemical names, and Chinese patent medicines only retain the original names.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
This study extracts data from the entire population of Shengmai injection users from the database and focuses on patients whose main diagnosis is angina pectoris and the treatment outcome is cured, improved, ineffective, dead, and others. The study excluded patients with unclear diagnostic criteria for angina pectoris and a lack of treatment outcomes.
2.3 Case matching and grouping
A non-randomized controlled matching method was used to match patients with angina pectoris who used and did not use Shengmai injection according to the principle of the same gender, age ± 5 years, and similar admission conditions. After matching, there were 2214 cases in the angina pectoris group (group A) who used Shengmai injection, and 2214 cases in the angina pectoris group(group B) who did not use Shengmai injection.
2.4 Definition of confounding factors
Using the expert interview method, combined with the actual situation of HIS data, the confounding factors are defined, including gender, age, fee, admission condition, combined disease, number of days of serious illness, combined medication.
2.5 Outcome indicators
The treatment results of angina pectoris were used as the outcome evaluation index of this study. The "cured" and "improved" were recoded as the treatment effective group, and the "other", "invalid"and "death" were coded as the treatment ineffective group. The treatment outcome after the recording was used as the outcome variable between the two groups.
2.6 Statistical methods
The statistical software adopts SAS 9.0 software and R 2.15 software. Descriptive analysis of the baseline data of the two groups of patients with angina pectoris after matching was performed by t-test, and the outcome variables were performed by chisquare test. Three methods were used: general logistic regression analysis without considering any confounding factors, weighted logistic regression analysis of propensity scores that balance most confounding factors, and weighted logistic regression analysis of propensity scores with covariates. By constructing a post-event randomized control environment, the bias caused by the uneven distribution of confounding factors in the observational data is eliminated, so that the observational data can achieve the effect of randomized data [10-11]. This method uses an adaptive algorithm to estimate the nonlinear relationship between the processing variable of interest and a large number of covariates. This method has greater advantages when there are many covariates in the model, and the linear, nonlinear, or interactive effects between the covariates and the processing variables cannot be determined. The flow diagram is shown in Figure 1.
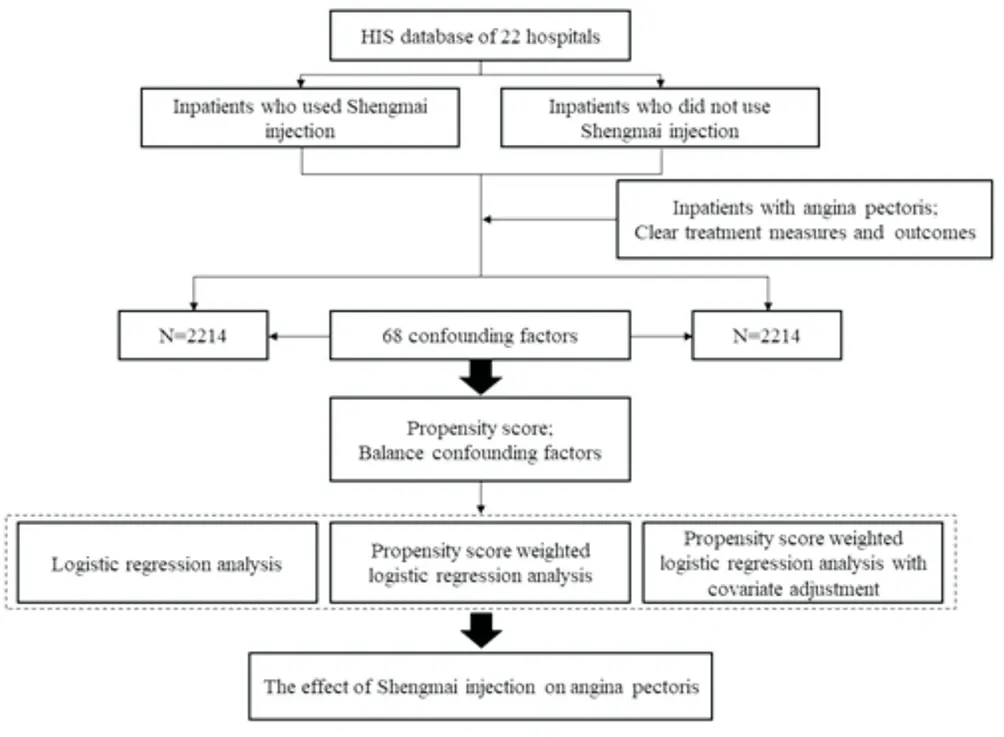
Figure 1 Flow diagram of research data analysis.
3. Results
3.1 Chi-square test
Regardless of the influence of confounding factors, the chi-square test is used to evaluate whether there is a difference in the efficacy of Shengmai injection and unused Shengmai injection on angina pectoris (Table 1). The results showed that the effective rate of treatment in the Shengmai injection group was 79.1%. The effective rate of the control group was 54.7%, P<0.001, indicating that under the influence of unbalanced confounding factors, it can be considered that there is a very significant difference between Shengmai injection and no use of Shengmai injection on angina pectoris.
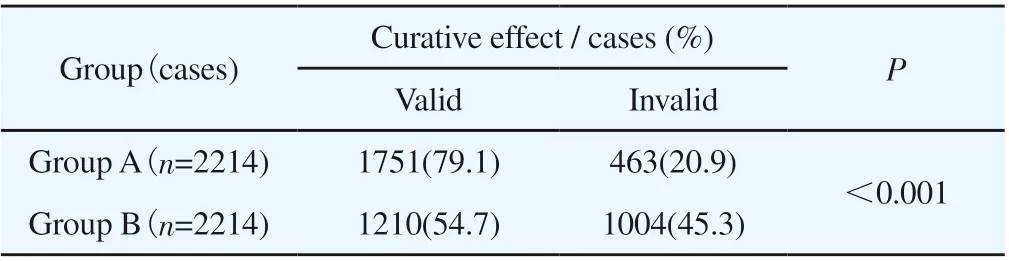
Table 1 The treatment results of the two groups.
3.2 The results of the propensity score
Clinically, the treatment of angina pectoris is affected by many factors, and these factors may become confounding factors in the study. Between the Shengmai injection treatment group and the control group, the distribution of confounding factors may be unbalanced, so the propensity score method is used to balance the confounding factors shared by the two groups. The higher the value of the relative influence degree, the greater the contribution of the confounding factor to the random allocation of groups. The top 10 factors with the largest influencing factors in the two groups are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2. It can be seen from the graph that the condition of the two groups has the largest impact, followed by the number of days of severe illness, department, and heart failure.
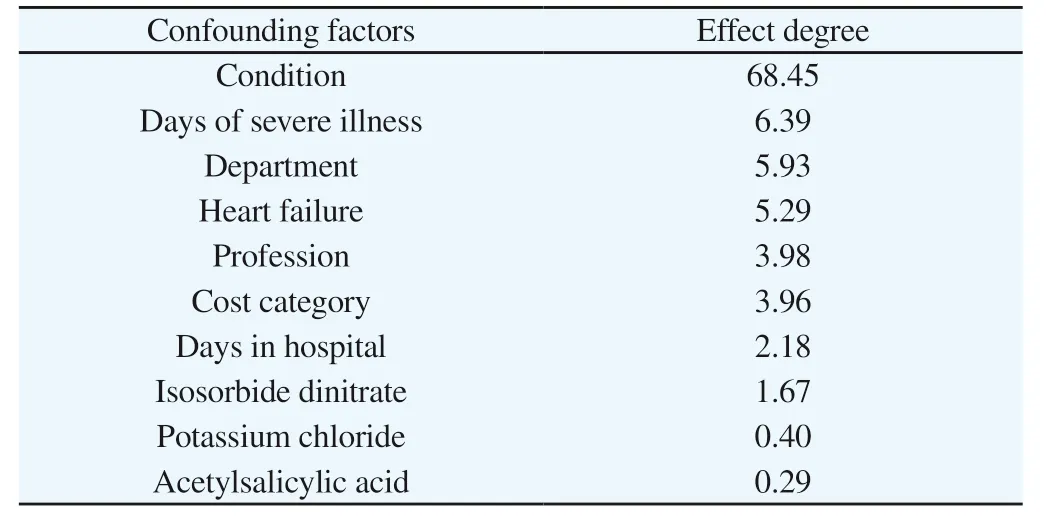
Table 2 The effect degree of confounding factors on treatment distribution (Top 10).
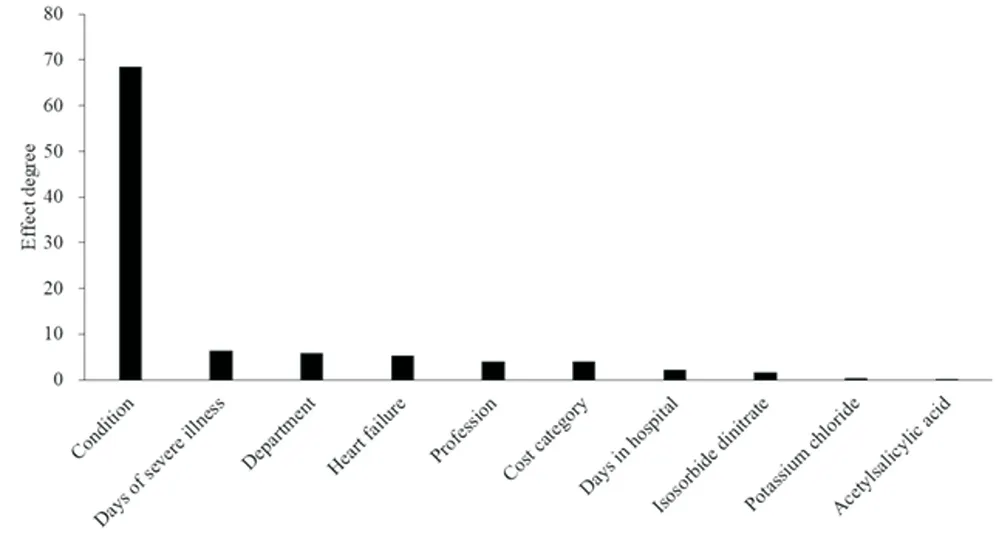
Figure 2 The effect degree of confounding factors on treatment distribution(Top 10).
K-S is used to evaluate the balance effect of each confounding factor before and after the propensity score weighting, as shown in Table 3. Before weighting, many confounding factors were significantly different between the two groups, P<0.05; after weighting, most confounding factors were not significantly different between the two groups. It can be considered that after weighting,the distribution differences of the two groups of confounding factors are well balanced. Figure 3 shows the changes in the effect size of the propensity score before and after weighting. After weighting,the effect has been greatly reduced (shown by the blue line), and the effect size of some variables has increased (shown by the red line), and the red solid dots Represents that the difference is statistically significant. Figure 4 shows the comparison between the distribution status of confounding factors before and after weighting and the uniform distribution value. The solid dots represent the confounding factors before weighting. Most of the P values are close to 0, indicating that the differences between groups are statistically significant. The open points represent the confounding factors before weighting, and most of the P values are scattered along with the cumulative distribution of uniform variables. It can be considered that after weighting, the difference in the distribution of confounding factors between the two groups of patients has been significantly improved.

Figure 3 Variation in effect size between covariate groups before and after propensity score weighting
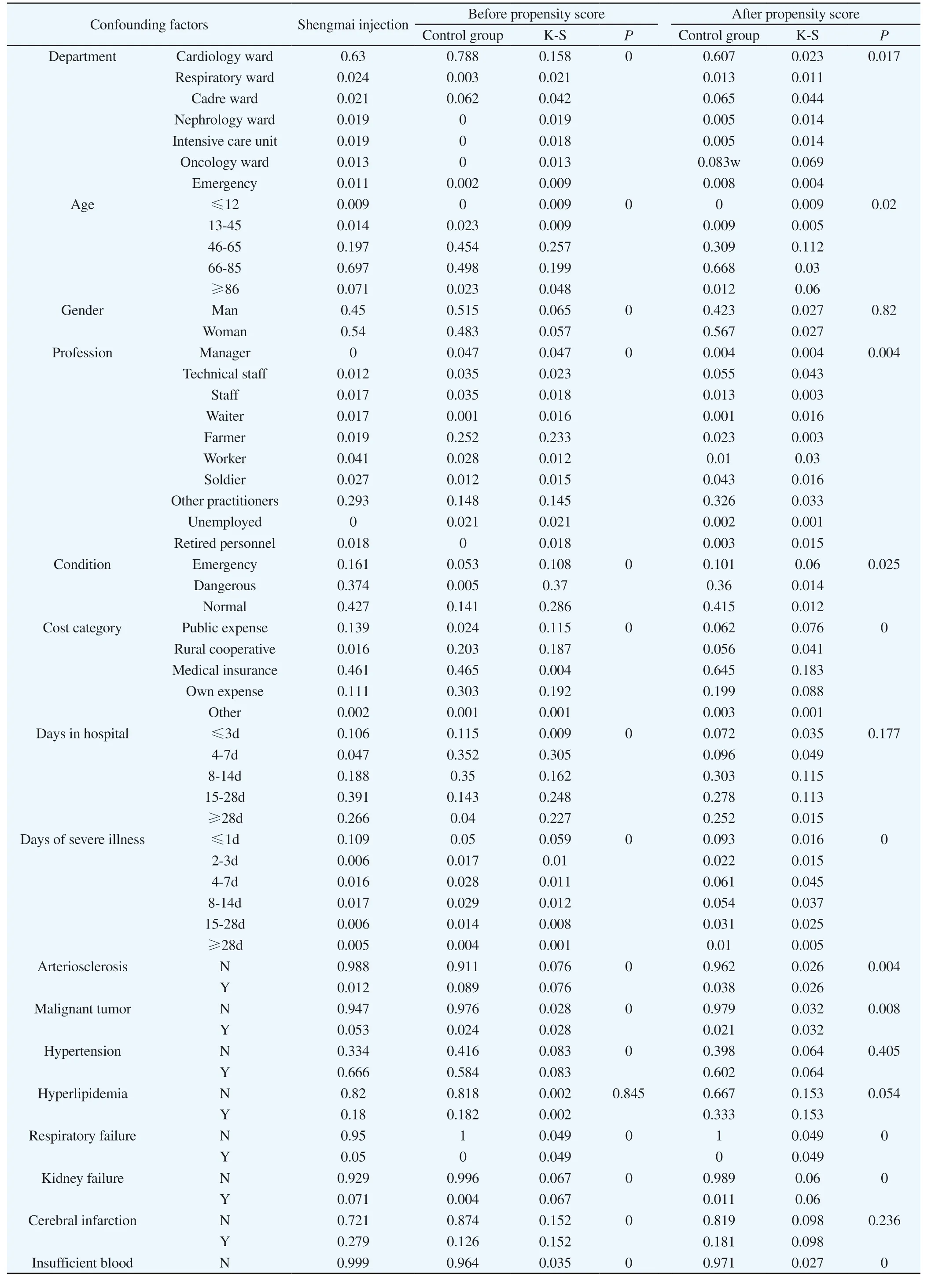
Table 3 Covariate balance before and after propensity score weighting.

?

Figure 4 K-S test for covariate balance of the two groups before and after weighting of propensity score
3.3 Logistic regression analysis
Three logistic regression analysis methods were used to compare the efficacy differences between the two groups of patients with angina pectoris (Table 4). The results showed that logistic regression,propensity score weighted logistic regression without covariates, and propensity score weighted logistic regression with covariates had regression coefficients greater than 0, and all P values were less than 0.05. Among them, the logistic regression and the weighted logistic regression with covariate propensity score P value were all less than 0.001, and the difference was significant. The use of Shengmai injection to treat angina pectoris has a significant effect.

Table4 Effect of three methods on angina pectoris.
4. Discussion
4.1 Analysis of the effectiveness of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris based on the real world
In order to understand the therapeutic effect of combined use of Shengmai injection on angina pectoris in clinical practical applications, this study analyzed HIS data from 22 large-scale tertiary hospitals across the country. After strict control of age,gender, and hospitalization, a 1:1 match was performed to obtain 2214 patients in each of the two groups. Without considering confounding factors such as demographic variables and disease status, comorbid diseases, medications, etc., a simple chi-square test was performed to obtain statistical differences between the two groups. However, due to the uneven distribution of confounding factors between the groups, the results obtained cannot truly reflect the difference between the therapeutic effect of the Shengmai injection group and the control group, and the direction of exaggerating or reducing the therapeutic effect is unpredictable.In this study, three logistic regression analysis methods were used to explore the therapeutic effect of Shengmai injection. The logistic regression method does not consider the influence of any confounding factors on the analysis, and its accuracy is poor. Its risk is similar to the chi-square test, that is, the assumed ideal situation does not match the clinical reality, and the analysis results cannot effectively represent the clinical reality [12-13]. The weighted logistic regression method of propensity score without covariates balances most of the confounding factors and has certain accuracy. However,the analysis of the results showed that confounding factors such as heart failure, respiratory failure, and chronic renal insufficiency were not fully balanced after being weighted by propensity scores. Using the weighted logistic regression method of propensity score with covariates, the unbalanced confounding factors are included in the analysis, and the influence of the known confounding factors on the research results is considered, and the conclusions drawn are more reliable and closer to the actual clinical efficacy [14].
Clinical studies have shown that Shengmai injection can effectively improve the total effective rate and hemodynamic indexes of patients with angina pectoris [15-16]. However, there is still a lack of largesample multi-center randomized controlled trials in the treatment of angina pectoris by Shengmai injection, and the quality of evidence is insufficient. "Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Stable Angina Pectoris of Coronary Heart Disease" [17] listed Shengmai injection as the B-level evidence of Qi and Yin Deficiency Syndrome,the strength is a conditional recommendation, which reflects the effectiveness of Shengmai injection in angina pectoris. However,the "Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Stable Coronary Heart Disease" [18] compiled by the Cardiovascular Branch of the Chinese Medical Association still contain few recommendations for proprietary Chinese medicines and no recommendation for Shengmai Injection. The reason is related to the low quality of the evidence for the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine injections[19-20]. This study adopts the real-world method to form a largesample retrospective cohort study through strict matching [21-22].At the same time, the propensity scoring method combined with the Logistic regression analysis of covariate processing is used to construct a post hoc randomized control environment. This method eliminates the bias caused by the uneven distribution of confounding factors in the observational data. Combining the characteristics of large samples in the real world, a large-scale cohort study is constructed to avoid bias caused by insufficient sample size, and the quality level is high. The role of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris of coronary heart disease is confirmed.The clinical effect and safety of Shengmai injection are expected to impact the stable coronary heart disease diagnosis and treatment guidelines after further prospective studies are confirmed.
Through the review of the research data, it can be noted that in the process of balancing confounding factors with propensity scores, the confounding factors such as arrhythmia, heart failure,and respiratory failure have not been fully balanced. The reason may be related to the interrelation of confounding factors and the existence of the Shengmai injection itself. In terms of comorbid diseases, it embodies the characteristics of multi-target system therapy of Shengmai injection. Clinical studies and systematic reviews have confirmed that Shengmai injection has a good effect in treating bradyarrhythmias. It can significantly increase the patient's 24-hour average heart rate, improve coronary blood supply,and fundamentally reduce the patient's clinical symptoms [23-25].Another systematic review believes that the addition of Shengmai injection based on conventional treatment can effectively improve the clinical symptoms of patients with chronic heart failure, increase the left ventricular ejection fraction and the total clinical effective rate [26]. The mechanism is related to correcting the secretion of angiotensin and brain natriuretic peptide content and improving myocardial remodeling [27]. At the same time, studies have pointed out that Shengmai injection can significantly improve the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide in patients with acute heart failure non-invasive positive pressure ventilation, and prevent the occurrence of respiratory failure and acid-base balance disorders [28].Shengmai injection can also play a good role in renal protection in the treatment of patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and renal insufficiency, and improve renal function indicators such as serum creatinine, urea nitrogen, and serum cystatin [29-30]. In addition,studies have shown that Shengmai injection can improve the immune function of cancer patients [31], and can also play an important role in the treatment of lung cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, and other malignant tumors, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy side effects[32-34]. It can be seen that Shengmai injection may play an important role in cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, respiratory system disease, and malignant tumors, especially in multi-organ failure, the combined use of Shengmai injection has been widely used in clinical practice. In terms of combination medications, the main confounding factors that have not been balanced are mainly clinical medications for hypertension and heart failure cardiovascular, which are highly overlapped with comorbid diseases, which also confirms the above conclusions. It is worth noting that in the process of propensity score balancing, diabetes as a confounding factor has been fully balanced,while injection insulin and its analogs as core drugs for diabetes have not been fully balanced. It may be related to the cardiovascular damage caused by long-term poor blood sugar control in patients with severe diabetes using insulin [35-36].
4.2 Study on the mechanism of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris
Shengmai injection is extracted from the classical famous prescription Shengmai Sanhua. In recent years, the research on the classical famous prescription has received extensive attention from researchers. In recent years, studies have confirmed that the use of Shengmai prescriptions to treat angina pectoris has a significant clinical effect [37-39].
The formation and development of atherosclerosis is the pathological basis of angina pectoris. Modern studies have shown that ginsenoside Rg3 can regulate peroxisome proliferators to activate receptor signaling pathways, reduce serum inflammatory factor levels, inhibit macrophage infiltration in the aortic intima,and play a protective role in vascular endothelial [40]. Research on the rat model of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease believes that ginsenoside Rg1 can increase the body's antioxidant enzyme activity and improve the pathological damage of the coronary arteries in rats[41]. Ginsenoside Rb1 can promote the secretion of interleukin-4/interleukin-13, induce polarization of M2 macrophages, and increase the stability of atherosclerotic plaques [42]. A similar study suggests that ginsenoside Rb1 activates macrophage autophagy by regulating the adenylate-activated protein kinase pathway to regulate atherosclerotic plaque lipid metabolism and plaque stabilization [43].In recent years, research on the treatment of atherosclerosis with extracts of Ophiopogon and Schisandra has attracted the attention of researchers. Ren et al. found that Schisandra C can significantly reduce the expression levels of serum tumor necrosis factor-α,interleukin-6, and other inflammatory factors in ApoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet [44]. The study of Schisandra chinensis believes that the alcohol extract of Schisandra chinensis can promote the metabolism of blood lipids in rats, regulate the level of oxidative stress in the body and maintain the function of endothelial cells, and play an anti-atherosclerotic effect [45]. Another network pharmacology joint experimental study confirmed that the molecular mechanism of Ophiopogon japonicus and Schisandra chinensis combined to prevent atherosclerosis may be related to the inhibition of endothelial damage induced by oxidative stress. It can be seen that various active ingredients of ginseng Chinese medicine, Ophiopogon japonicus,and Schisandra extract can play a good vascular protective effect,delay the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, and reduce the occurrence of angina pectoris.
Shengmai injection has a definite clinical effect in the treatment of angina pectoris. It is widely used in patients with angina pectoris due to deficiency of both qi and yin. It has been confirmed in clinical and experimental studies. Its mechanism is related to lipid regulation,anti-inflammatory, inhibiting oxidative stress, and protecting vascular endothelium. At the same time, for patients with angina pectoris combined with multiple system diseases, Shengmai injection can also exert a good effect [46-47].
4.3 Limitations of the study
The data in this study are retrospective and non-random observational data. The existence of a large number of confounding factors is one of the main obstacles to the current study. The propensity score weighting method used in this study can estimate the nonlinear relationship between the variable of interest and a large number of covariates, and then make the results of the analysis more realistic. However, many factors are influencing the process of Shengmai injection in the treatment of angina pectoris.Although 68 known variables are included in this study, there may still be unobserved confounding. This will undoubtedly reduce the credibility of the results of this study. The impact of Shengmai injection on angina pectoris still needs to be further confirmed by a large-sample prospective study.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年12期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年12期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress of Cassytha filiformis L
- Research on anti-pancreatic cancer mechanism of Codonopsis codonopsis based on network pharmacology
- Risk factors for infection with multidrug-resistant organisms in diabetic foot ulcer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Correlation between NF-κB/TNF-αpathway and atrial fibrillation
- Construction and validation of prognostic model of hepatocellular carcinoma based on epigenetic factors
- Preparation and characterization of hemihydrate calcium sulfate-calcium hydroxide composite bone repair materials
