The Propulsion System of Shenzhou 13 Manned Spaceship
GU Shuaihua,LU Fei
Shanghai Institute of Space Propulsion,Shanghai 201112
Abstract: Based on the requirements of manned spaceships,this paper introduces the characteristics of the propulsion system from the perspectives of design scheme,basic composition,safety and reliability measures,and also introduces the ground test verification and on-orbit flight characteristics of the Shenzhou 13 propulsion system.According to the flight results,it was seen that the performance of the Shenzhou 13 propulsion system fully met the engineering requirements for the manned space mission.
Key words: manned spaceflight,Shenzhou 13 spaceship,propulsion system
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the beginning of the manned space program,approved by the Chinese government in 1992,one of the most critical parts of the Shenzhou spaceship which is the only manned space shuttle in China,the propulsion system,has completed 13 space missions successfully.Between October 16,2021 and April 16,2022,the propulsion system and other parts functioned normally,enabling the Shenzhou 13 manned spaceship to finish the half-year flight as planned,and returning the 3 astronauts back to the Earth safe and sound.
2 REQUIREMENTS OF THE SHENZHOU 13 SPACESHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
As the power source of a manned spaceship,the propulsion system was designed considering many factors,especially the reliability and redundancy,because a fatal fault should never be allowed to be occur,as it would endanger the normal function of the spaceship and the safety of the astronauts.As the same requirements as the Shenzhou 12 manned spaceship,the main functions of Shenzhou 13 spaceship were as follows:
1) Providing the necessary power for the normal flight of the spaceship after it separates from the rocket,such as for orbital maneuvers,attitude control,rendezvous and docking,return braking and reentry control;
2) Providing the reentry power for the return module in an emergency such as during the initial launch phase,as well as for providing power for attitude adjustment,braking and landing control,and reentry of the spaceship if the rocket or spaceship has a catastrophic failure after rocket fairing separation;
3) Providing quick-start power for emergency departure of the spaceship when it is docked with the space station.
3 DESIGN OF THE PROPULSION SYSTEM
As with the design of the Shenzhou 12 spaceship,the Shenzhou 13 spaceship had a propulsion module and a return module,which was propelled respectively by a bi-propellant unified system with constant pressure,which could provide power for attitude or orbit control,and a monopropellant system with constant pressure which could provide power for attitude or reentry control.
3.1 Propulsion Module Subsystem
The propulsion module subsystem was composed of a gas management system for pressurization,propellant storage and transportation,plus many sized thrusters.There were 6 titanium alloy cylinders of 20 L volume with a 23 MPa working pressure,4 metal diaphragm tanks of 223 L volume,capable of storing 1000 kg N2O4/MMH bi-propellant,4 orbit-control thrusters of 2450 N,12 large attitude-control thrusters of 156 N,16 small attitude-control thrusters of 28 N,and 8 translational engines of 117 N,along with thermal control on pipes and valves,with several control units,of which all of these functioned properly in a unified system.
The 4 metal diaphragm tanks and propellant were shared by the attitude and orbit control thrusters,where the pressurization gas path,liquid path,and thrusters were symmetrically designed,such that they could be interconnected or isolated through a explosively actuated valve or latch valve.The crosstype layout for the propellant supply was proposed taking into consideration the redundancy of the propellant supply,maintaining the equal expulsion and the centroid stability of the tank.In addition,it also eliminated the possible impact of valve flow resistance in the transverse pipes on thrustor performance.
The 40 thrusters were also symmetrically designed,where the attitude and orbit control pipes were of a unified design but independently managed via a self-latch valve,so if a fault occurred,it could be quickly switched to the other group with no affect on the rest of the system.
3.2 Return Module Subsystem
The return module subsystem was composed of a gas management system for pressurization,propellant storage and transportation,several sized thrusters and a pressured gas emission and propellant venting system.The pipe design was like the Chinese character “jing”,which enables the cross supply of the two propellant paths providing mutual backup,and fully system redundancy.The upstream solenoid valves for gas emission and propellant venting can be closed after the emission and venting,which can prevent residual propellant outflow which can impact astronaut safety during landing.
4 CHARACTERISTICS OF PROPULSION SYSTEM DESIGN
The principle of adopting a redundant design,with rigorous assessment and derating were applied for the propulsion system of Shenzhou 13 manned spaceship,thus negating common defects such as pipe blocking,sticking, leakage so improving the reliability and safety of the system.
The principles to counter blocking were as follows:
1) The diameter of the flow channel in the system should not be less than 0.2 mm;
2) The cleanliness of the assembly workshop and components were strictly controlled to be better than gradeone hundred thousand standard;
3) The particle size of the internal cleaning fluid or gas,propellant and gas filling in the system was in accordance with 50 grade US military standard;
4) Filters were designed on the upstream side of the pressure reducer and main control valve,as well as on the downstream side of the tank.
The principles for leakage mitigation were as follows:
1) A welded connection or double sealing structure were better than a releasable connection;
2) Independent double-spool valves were better than single-spool valves for the electromagnetic valve of thrusters which would be opened and closed frequently;
3) Leakage measurement and vibration tests were conducted in turn to verify the functions and performance before delivering for assembly into the spaceship.
The principles for sticking mitigation were as follows:
1) Filters should be adopted on the upstream side of moving components;
2) The contact area between the moving components should be as small as possible;
3) A guiding structure should be applied,moreover,the material should have a smooth surface but with a certain hardness and wear resistance;
4) Strictly applied a process of removing metal burrs.
Other measures included:
1) An automatic temperature control design was adopted to ensure pipeline safety and reliability for on-orbit start of the thrusters;
2) Mutual backup paths which can be switched through manual control by astronauts or by remote control from the control center on the Earth;
3) Adoption of automatic fault detection and real-time automatic switching functions in launch phase realized through software imbedded in electrical units of subsystems to ensure fault isolation and safety of the system;
4) There were three kinds of devices on the downstream of the tank,such as a rupture diaphragm,a latch valve and a solenoid valve,which could prevent the leakage of propellant to ensure a safe environment for those working on or near the system.
5 TEST VALIDATION
In order to qualify the design of the propulsion system,coordination of procedures,and parameter harmonization of the whole system,the propulsion module subsystem,whole vehicle and the return module subsystem test firings were arranged separately,thus the flow-resistance characteristics of the pipes,the performance of the whole system and the performance of the key parts after the mechanical test could be obtained.
Another whole system hot firing test to verify reliability was arranged by simulation as a confidence check to ensure as close as possible the orbit-flight procedures for the spaceship,and to evaluate all the normal and emergency conditions,to provide a reference set of parameters for on-orbit comparison purposes.
Every component of the propulsion system was tested from the production batch instead of sampling test to verify its function and performance,only when this was finished and passed,they were assembled together.Once the assemly was finished,electrical performance tests,leakage measurement and mechanical tests were conducted to verify their function and performance,they were then delivered for assembly into the spaceship.
The propulsion system testing was an integral part of the final spaceship test phase and only then was the final ready to launch testing,such as electrical performance test,leakage measurement and mechanical test and thermal characteristic test in vacuum chamber were conducted.
6 FLIGHT MISSION OF SHENZHOU 13 SPACESHIP
The Shenzhou 13 spaceship was successfully launched on October 16,2021,and then after the rapid rendezvous and docking,it was docked to the China Space Station.
6.1 From Launch to Rendezvous
When the rocket was ready for launch,it was time to prepare for the propulsion system ensuring complete vacuum discharge,gas pressurization and attitude control pipe-filling.When vacuum discharge was completed,the pressure of the propulsion system was 0 MPa to ensure that there was no air in the propellant,which would have a hazard effect on the thrusters.When gas pressurization was complete,the pressure of the tanks was maintained between 1.656 — 1.666 MPa(see Figure 2),which was verified during the whole system engine vehicle test.When the attitude control pipe-filling was finished,the fault detection self-test during rocket-launching phase was enabled to ensure that any fault could be dealt with immediately to preserve the safety of the whole spaceship.

Figure 1 Shenzhou 13 spaceship is preparing for launch
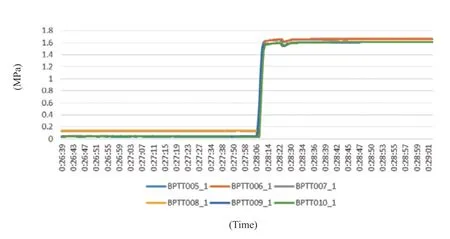
Figure 2 The pressurization process
After the separation of the rocket,the orbit-control pipe-filling completed,it allows an escape under emergency conditions and reentry back to Earth at any time.In addition,a thruster test was conducted by the Guidance Navigation and Control (GNC)system to ensure their operational status.
The fast rendezvous docking mode lasts 6.5 h.Here changing of orbit occurs 6 times during the long-distance navigation process,in which two orbit-control thrusters were used 3 times and attitude-control thrusters 3 times.The system pressure was between 1.61—1.62 MPa during the process,which is consistent with the data verified during the whole system engine vehicle test.In the homing phase,the orbit was adjusted 4 times using only the attitude control thrusters.The system pressure was in the range of 1.62-1.65 MPa,and the system operated normally.
6.2 Docking with the Space Station
After successfully completing the rapid rendezvous and docking with the space station,the propulsion system was put into docking mode.The high pressure self-latch valves were closed,the pressure relief valves were not working,and the system was in a safe mode.
During the docking period,two on-orbit inspection tests were conducted on November 18,2021 and April 6,2022 respectively.The power supply and valve action functioned well in the propulsion module and in the return module subsystem,which indicated that the whole propulsion system was in good condition.
6.3 Return to Earth
On April 16,2022,the spaceship separated from the China Space Station and returned to the Earth.After the orbit-control thruste worked for about 173 s,the spaceship completed the return brake,which was the most important phase during the return plan.During the whole process,the orbit-control thrusters performed well and all the temperatures and pressures were all in their corresponding range.
In preparation for this phase the return module subsystem prepared to work.Heaters for the pipes and valves began to operate with a constant power of 74 W,until the temperatures at the top of the thrusters reached the range 67.5-71.7°C (see Figure 3),which was optimum for the monopropellant thrusters of the return module.

Figure 3 Temperatures of the top of the thrusters after heating
Then after completing the vacuum discharge,gas pressurization and pipe-filling,the pressure of the return module subsystem was in the range of 1.58—1.60 MPa,which was consistent with the value during the whole system engine vehicle test on the ground.
After the separation of the return cabin from the propulsion module and the orbit module,the 8,150 N thrusters were applied to adjust the attitude according to the attitude of the return module.Each engine worked normally,and the pressure and temperature were within their normal ranges.
Considering the safety of the spaceship and astronauts,the return module subsystem carried out residual propellant venting and pressurized gas emission during the landing phase.
After the liquid explosively actuated valve of the propulsion system of the return module was opened,the pressure of the main cylinder decreased to less than 4 MPa after 19 s,and the pressure of the auxiliary cylinder decreased to less than 4 MPa after 20 s,and finally decreased to 0.1 Mpa equal to atmospheric pressure,which indicated that the subsystem was in a safe state,and the emission results were normal.The variation of the system pressure during the whole emission process is shown in Figure 4.
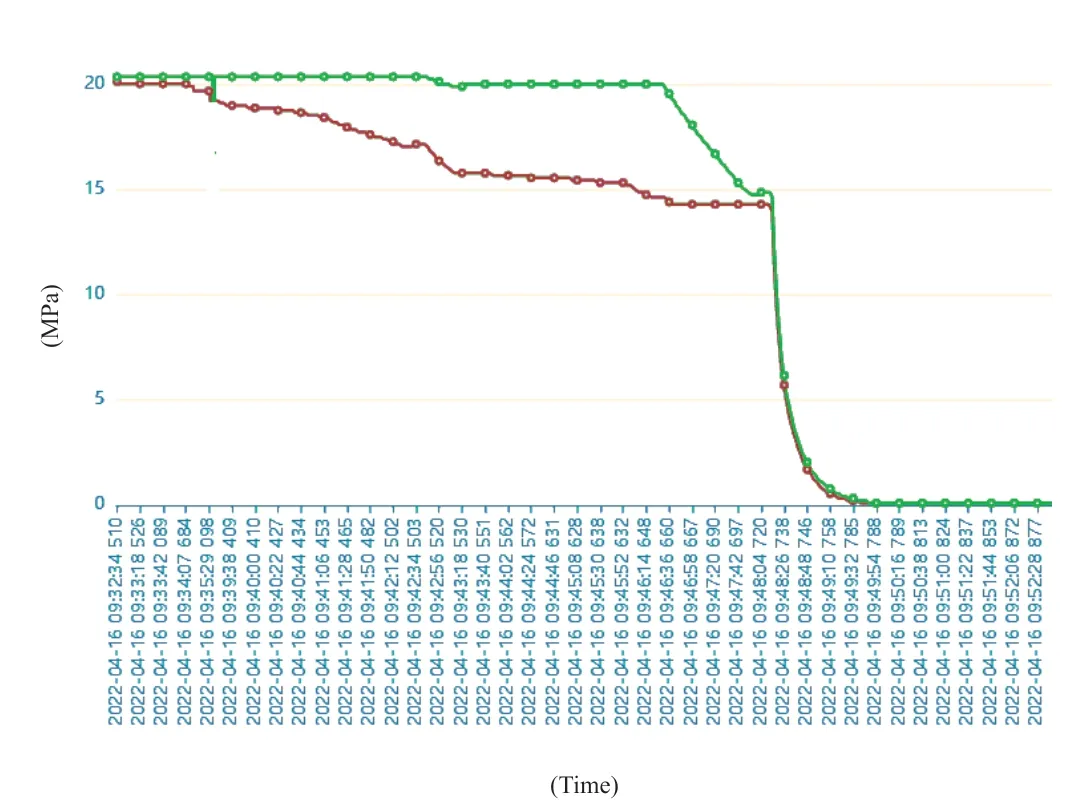
Figure 4 Variation of the system pressure during the whole emission process
6.4 Propellant-consumption Imbalance
There was a residual propellant-consumption imbalance in the propulsion module subsystem of the Shenzhou 13 mission,which was accumulated during the flight.The deviation of two oxidant tanks was about 13 kg and about 19 kg of two fuel tanks after the return braking,but this was still better than that experienced by the Shenzhou 10,11 and 12 spaceships.
The main reason for the imbalance of propellant consumption was due to the use of metal diaphragm tanks,which have a characteristic imbalance in the process of diaphragm extrusion and folding,resulting in a pressure difference between the gas-liquid cavities of each diaphragm.The propellant was consumed faster with smaller pressure difference than others,and the cumulative effect caused the imbalance of propellant consumption.In addition,the other influencing factor was the deviation of the flow resistance of the pipeline downstream from the tank.The unbalanced consumption was the inherent characteristic of the parallel system and did not affect the normal operation of the subsystem.

Table 1 Imbalance of propellant consumption of Shenzhou 10—13 and the whole system engine vehicle
7 CONCLUSION
The Shenzhou 13 manned spaceship has finished its halfyear plan in space,which was the longest mission to date,successfully providing the necessary power for orbital maneuvers,attitude control,rendezvous and docking,return braking and reentry control with excellent performance.This fulfilled the manned space engineering requirements,and laid a solid foundation for the construction of the China Space Station,demonstrating a safe transportation solution for astronauts during longterm operation.
- Aerospace China的其它文章
- Shenzhou 12 Under Development
- The Development of Memory Alloy Satellite-Rocket Separation Device for Commercial Small Satellites
- The Development Status and Main Application Progress of China’s Ocean Satellites
- A Brief Introduction to China Manned Space Program Missions
- Development of Solid Rocket Motor for Manned Launch Vehicle Escape System
- High Reliability LM-2F Launch Vehicle for Space Station Mission

