Development of Solid Rocket Motor for Manned Launch Vehicle Escape System
LI Dongchun,SHI Hongbin,WEI Kunlong
Xi’an Aerospace Solid Propulsion Technology Institute,Xi’an 710025
Abstract: The solid rocket motors for the escape system of China’s LM-2F manned launch vehicle are described,the key technologies and technical innovations utilized are summarized.The technical features and development of foreign manned launch abort systems are also presented.The development trends of the solid rocket motor for future Chinese manned launch vehicle escape systems are proposed,which can provide a reference for the future development of manned launch vehicle escape systems.
Key words: solid rocket motor,manned launch vehicle escape system,key technologies,development trends
1 INTRODUCTION
Manned spaceflight is a large-scale project with extremely high risk,and the escape system can ensure the safety of astronauts effectively in case of a launch rocket malfunction.At 16:40 on October 11,2018,the Soyuz MS-10 rocket carrying two astronauts was launched at the Baikonur launch site,in accordance with the established work plan of the International Space Station.The rocket malfunctioned 118 s after the launch,the escape system was triggered and brought the astronauts down to safety,which demonstrates once again an escape system can guarantee astronauts’ lives effectively.
The mission of the escape system is to take the capsule with astronauts away from the dangerous area and provide necessary conditions for the separation of the capsule from the escape spacecraft when life-threatening accidents occur before the jettisoning of fairing of the launch vehicle.A solid rocket motor is generally adopted as the propulsion for the escape system.The requirements call for a complex structure,special shape,short operating time,large thrust and high reliability.
The escape system development of the LM-2F manned launch vehicle was started in 1992,and the first zero altitude escape flight was completed in 1998,which demonstrated the capability of the escape system.In the subsequently 14 flights of the Shenzhou spaceships,the escape system fulfilled its mission successfully.With the development of new generation manned launch vehicles and spaceships,higher requirements are required to meet the novelty,reliability and safety of the solid rocket motor used for the escape system.The technical features,key technologies and future trends at home and abroad are summarized and discussed in this paper.
2 OVERALL SCHEME OF ESCAPE SYSTEM
The escape system of the LM-2F manned launch vehicle consists of an escape tower,a top fairing,grid fins and their release devices,an up supporting mechanism,a bottom supporting mechanism and a fire extinguishing apparatus.The escape system uses solid propulsion motors,a total of five types of twelve motors are used,including an abort motor,a jettison motor,four attitude control motors,four high-altitude abort motors,plus two high-altitude jettison motors.Four attitude control motors are assembled on the cover body to form a control motor assembly,the abort motor,jettison motor and control motors are installed on the fairing.Except for the high-altitude jettison motors,the other four types of motors were specially developed for the LM-2F manned launch vehicle escape system.

Figure1 Launch escape system on LM-2F manned launch vehicle
The LM-2F manned launch escape system has a lifeguard role from takeoff to fairing separation.Its mission can be divided into two stages according to the escape system operating mode,the first stage is from pre-takeoff to a flight altitude of 39 km,the second stage is from 39 km to fairing separation (about 110 km).In the second stage,the high-altitude abort motors and high-altitude jettison motors take on the role of the lifeguard mission.In normal flight,the escape tower (consists of an abort motor,a jettison motor and a control motor assembly,a balance weight segment and an end skirt) is separated from the launch vehicle by jettison motor and control motors at altitude of 39 km.
3 SOLID ROCKET MOTORS OF LM-2F MANNED LAUNCH VEHICLE ESCAPE SYSTEM
3.1 Abort Motor
The abort motor is located at the bottom of the escape tower and consists of a front combustion chamber,a back combustion chamber,nozzles, igniter device and a remote trigger device.The four fixed nozzles are prepositioned and uniformly distributed around the circumference of the cylinder of the front combustion chamber,and the four nozzles’ axes are 30 degrees from the motor axis and intersect at a point.The tail skirt connection ring is fitted on the cylinder near the aft-dome,the shell section beneath the ring is spherical for vector control.The combustion chamber case is made of high strength steel and charged with the star-hole grain with a high burning rate and low aluminum powder from wall casting.A high-energy pyrotechnic compound BPN tablet is adopted as the powder of the basket igniter.The remote trigger device is connected to the ignition device through two partition igniters,and safety mechanism while dual trigger elements are utilized.
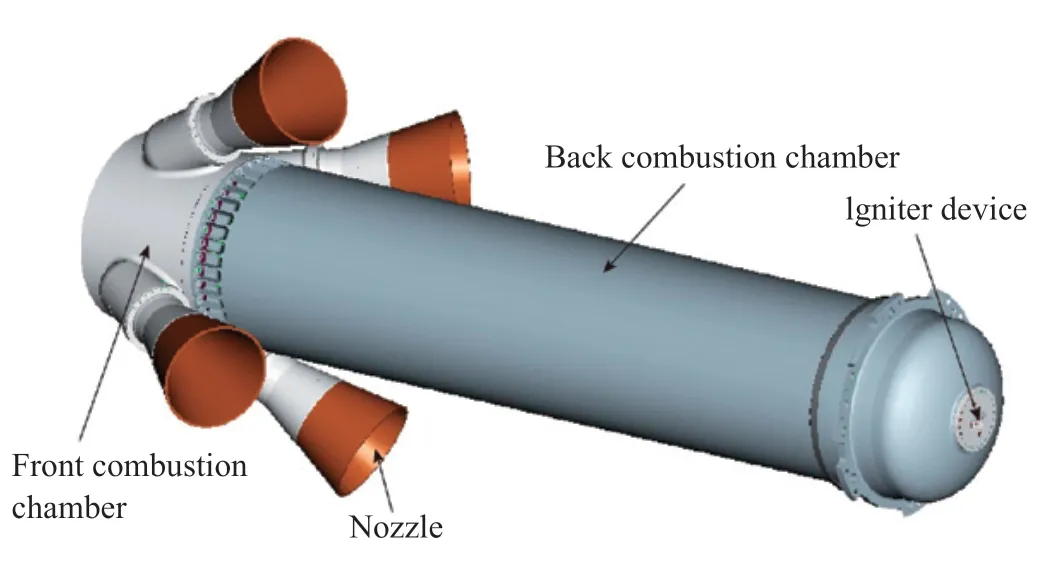
Figure 2 Abort motor
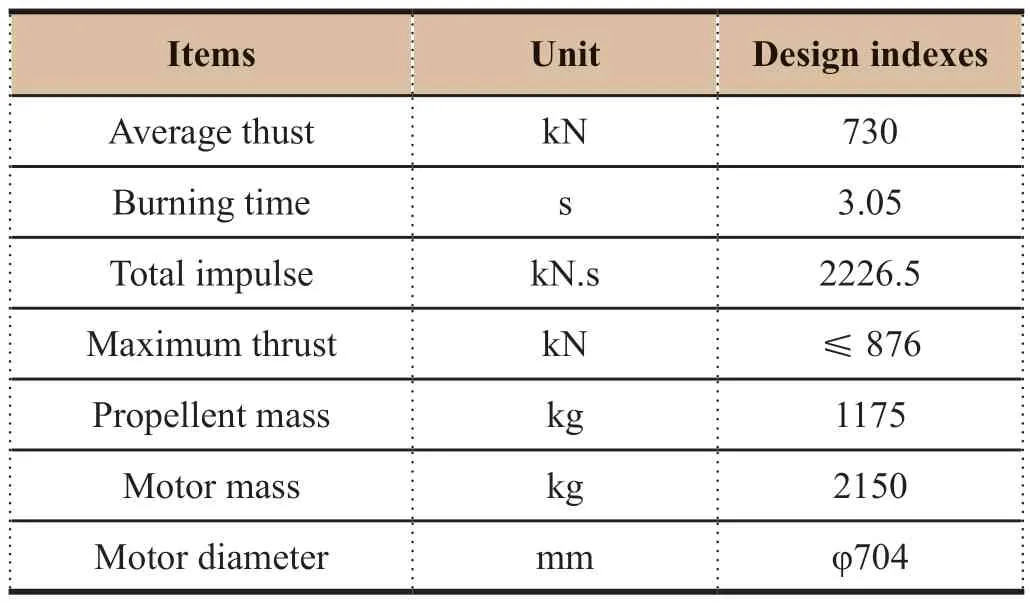
Table 1 Properties of abort motor of LM-2F manned launch vehicle escape system
3.2 Jettison Motor
The jettison motor is fixed in the middle of the escape tower.It consists of a front combustion chamber,a back combustion chamber,nozzles and igniter device.The eight fixed nozzles are prepositioned and uniformly distributed around the circumference of the cylinder at the back chamber,while the eight nozzles’ axes are 30 degrees from the motor axis and intersect at a point.The combustion chamber case is made of high strength steel and charged with the wheel shaped grain with high burning rate and low aluminum powder from wall casting.A high-energy pyrotechnic BPN tablet and two parallel ignition pipes are adopted for the basket igniter.

Figure 3 Jettison motor

Table 2 Properties of Jettison motor of LM-2F manned launch vehicle escape system
3.3 Attitude Control Motor
The attitude control motors are installed on the top of escape tower and four control motors are arranged in the same cover body.A variable thrust baffle device is installed at the nozzle outlets of two control motors to realize two working conditions with different thrust.The attitude control motor is composed of a front combustion chamber,eight nozzles and an igniter device,while the nozzle axis is 90 degrees from the motor axis.All the above components are connected together using a screw joint structure.The combustion chamber case is made of high strength steel,the grain is made of high burning rate propellant,and a high-energy pyrotechnic BPN tablet and two parallel ignition pipes are adopted for the basket igniter.
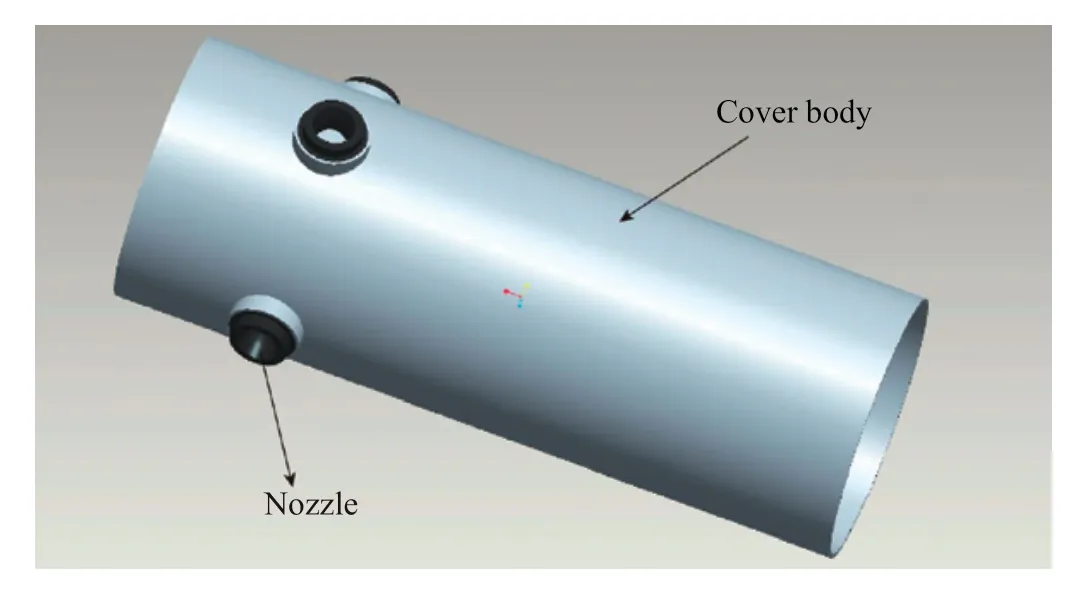
Figure 4 Attitude control motor

Table 3 Properties of attitude control motors of LM-2F manned launch vehicle escape system
3.4 High-altitude Abort Motor
Configured outside of the fairing,the high-altitude abort motor consists of a remote trigger device,an igniter device,a combustion chamber,a nozzle and associated components.The nozzle axis is 20 degrees from the motor axis.Two welded supports on the combustion chamber case are used to fit on the rocket body and transfer thrust.The combustion chamber case is made of high strength steel,charged with the star-hole grain with high burning rate and low aluminum powder from wall casting.A high-energy pyrotechnic compound BPN tablet is adopted as the powder of the basket igniter.The remote trigger device is connected to the igniter device through two partition igniters,and safety mechanism and dual trigger elements are utilized.

Figure 5 High-altitude abort motor
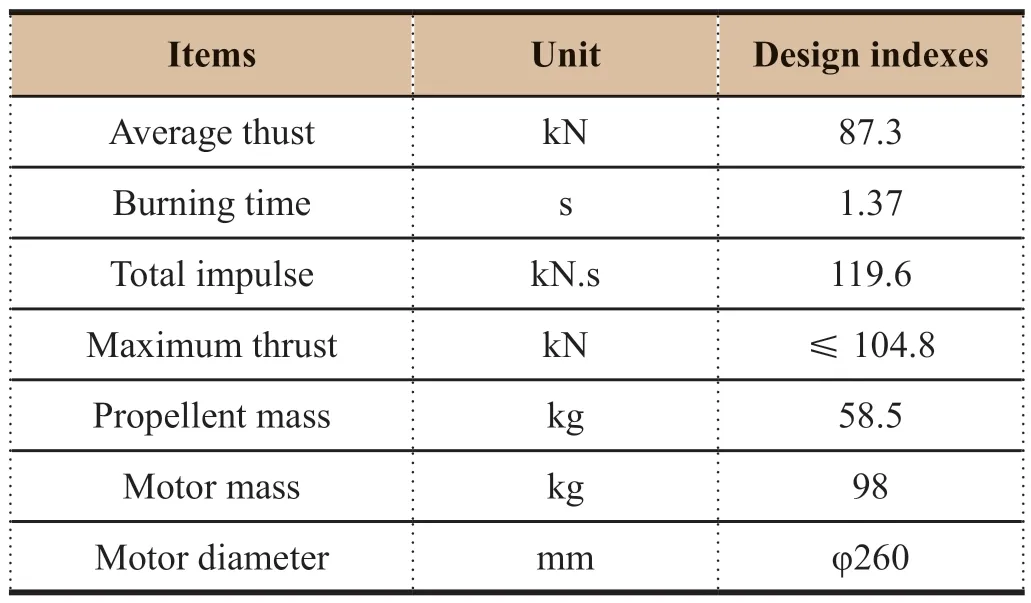
Table 4 Properties of high-altitude abort motor of LM-2F manned launch escape system
4 OPERATING MODES OF THE ESCAPE SYSTEM OF LM-2F MANNED LAUNCH VEHICLE
There are three operating modes of the escape system:escape tower mode;normal flight mode;and mode without escape tower.The escape mode with escape tower is utilized for the rocket flight from -30 min to 120 s,the escape mode without tower is applied for flight from 120 s to fairing separation.
From the time the launch tower is deployed to 20 s after the rocket takes off,then 0.45 s after the abort motor ignites,the attitude control motor installed in the third quadrant starts to work with 100% standard thrust.Four high-altitude abort motors ignite simultaneously when the abort motor has operated for 3.8 s,the jettison motor starts to operate when it receives the signal for separation of orbital and return units,0.32 s later,the attitude control motor installed in the fourth quadrant starts to operate with 70% standard thrust.
From 20 s point after takeoff to the separation of the escape tower,0.45 s after the abort motor ignites,the attitude control motor installed in the third quadrant starts to operate with 70%standard thrust.The jettison motor operates when it receives the separation signal of orbital and return units,and 0.32 s later,the attitude control motor installed in the first quadrant starts to work.
From the separation of the escape tower and the rocket to the jettisoning of the fairing,two high-altitude abort motors in the first quadrant start to operate,and then 0.1 s later,two high-altitude abort motors in the third quadrant initiate operation.
When the rocket reaches 39 km,the escape tower is separated from the rocket,and the jettison motor and attitude control motors with 70% standard thrust in the third and fourth quadrants begin to ignite to guarantee a successful separation.
5 KEY TECHNOLOGIES OF SOLID MOTORS OF LM-2F MANNED LAUNCH VEHICLE ESCAPE SYSTEM
Through 30 years of research and development,the escape motors of the LM-2F manned launch vehicle have successfully supported 13 manned spaceship launches,and multiple key technologies have been introduced,making the reliability of the escape motors an order of 0.9994 -0.9999.
5.1 High Burning Rate of Propellant
The escape motors require a propellant burning rate of up to 36 mm/s (20°C,10 MPa),which is the highest burning rate propellant adopted for solid rocket motors in the past,and there is no more mature formula.In order to reduce the erosion and ablation of the insulating layer under high temperature and high speed Al2O3 condensed phase particles,the aluminum powder content in propellant is reduced.The basic burning rate is ensured through fixing the burning rate catalyst content in the propellant formula,and burning rate deviation is controlled by adjusting the coarse and fine oxidant gradation.
5.2 Thermal Structure of Prepositioned Nozzle with Large Angle
Both the abort motor and jettison motor adopt prepositioned nozzles,and the large flow gas from the combustion chamber to nozzle outlet turns 150 degrees,causing the combustion inner wall to be severely eroded and ablated.This is the most difficult and risky technology in the escape motor development,and there was no mature experience to refer to at home or abroad.Three actions were taken to insure the thermal protection reliability.Firstly,reducing the aluminum powder content as much as possible on the basis of ensuring energy and combustion stability.Secondly,reducing the combustion gas flow velocity near the front chamber head and curved spout through the combustion inner profile design.Thirdly,using good scouring resistance insulation material.
5.3 Assembled Combustion Chamber
In order to optimize the design,reduce the manufacturing difficulties,and facilitate the insulating layer pasting process,the abort motor adopts a combined combustion chamber comprising front and back chambers,which are connected with a flange with reinforced fins.The flange is designed with a special shape to meet the aerodynamic configuration.
5.4 Propellant Casting with Core-mould
The grain of the escape motor was designed to be a thinwall structure to achieve large thrust over a short time,and there are four and eight curved spouts in the back combustion chamber of the abort motor and jettison motor respectively.It is hard to control the propellant mass using conventional casting process,and the propellant entering the curved spouts is increased,which brings difficulties in grain reshaping and cleaning.Therefore,the weighting pouring method and core-mould process were adopted to guarantee the charged propellant mass.
5.5 Motor Vertical Ground Firing and High-precision Testing
Both the abort motor and jettison motor have multiple prepositioned nozzles,and the combustion gas and flame will destroy the test equipment.The large-thrust and high-precision vertical firing test stand and the instantaneous data process software were developed,to address the special-shaped motor firing and thrust data process for multiple nozzles,to ensure accurate performance data for vehicle flight.
Although the escape system has been developed successfully and performed several China’s manned spaceflights in the past,there are still some differences and deviations compared with foreign abort systems,especially in the thrust control and attitude regulation.
6 ORION’S LAUNCH ABORT SYSTEM[3-8]
Orion’s launch abort system (LAS) consists of six components — from top to bottom:a nose segment,an attitude control motor,a forward interstage,a jettison motor,an abort motor and a fairing assembly.Overall,the escape tower stands about 13.3 m tall with a loaded mass of over 6 metric tons.
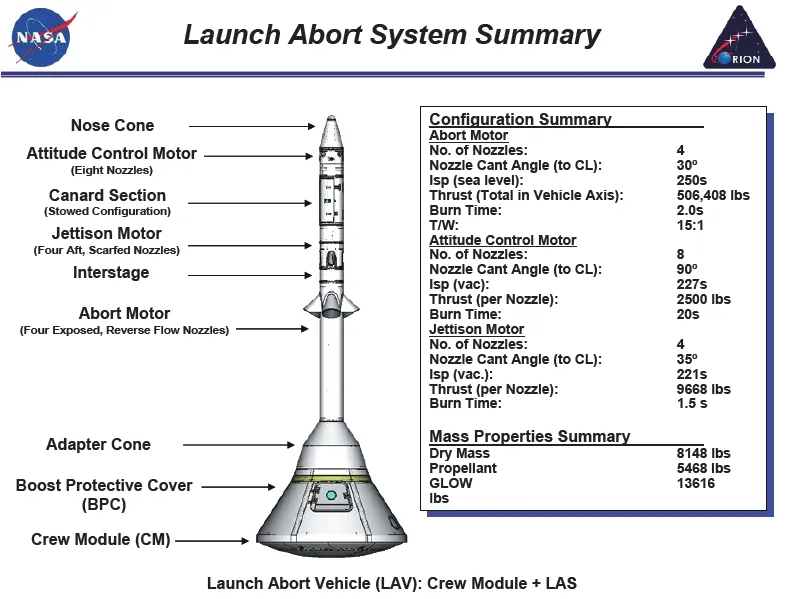
Figure 6 Orion’s launch abort system
6.1 Orion’s Abort Motor of LAS
The lower segment of the LAS comprises an abort motor(AM) that is manufactured by ATK (Alliant Techsystems).The AM consists of a carbon-fiber composite case that holds the solid propellant consumed by the motor.On top of the case is a convergent manifold that contains four nozzles employing a turn-flow design which means that the exhaust flow of expanding gas is directed through a turn to generate thrust in the desired direction.The four nozzles (spaced 90 degrees apart) are canted 25 degrees from the motor central line,creating a total turn of 155 degrees.
The titanium manifold is designed to stabilize the exhaust flow,balance the thrust across the four nozzles and maximize overall engine performance.AM uses a solid propellant with a high burn rate achieved by using a mixture containing high surface area grains allowing the motor to achieve the required abort performance.The motor is ignited by a high-performance pyrogen igniter that is capable of starting the solid rocket motor with extremely low latency to achieve spacecraft motion within a few milliseconds after the abort command is issued.
The 3,464 kg abort motor delivers 1,760 kN of thrust along the vehicle axis to pull the spacecraft away from the failing launch vehicle.The motor achieves a sea level impulse of 245 s.AM consumes most of its propellant during the first three seconds of operation with thrust residuals beginning to tail off after about 7 s.In abort scenarios,crews endure over 10 G when being pulled away from the launch vehicle.
6.2 Orion’s Launch Abort System Jettison Motor
Residing above the abort motor is the jettison motor (JM),weighing 410 kg.It is responsible for pulling the separated LAS away from the crew module in both nominal flight and abort scenarios.The JM was developed by Aerojet Rocketdyne and consists of a shroud assembly,a nozzle assembly and a gas generator assembly.
The clamshell shroud assembly includes structural ribs for reinforcement and provides the interface to the abort motor in the aft and the interstage adapter in the forward direction.All structural components are made with 6Al-4V titanium alloy.The interstage is provided by Orbital Sciences.
The nozzle assembly contains four nozzles all made with 17-4 stainless steel,canted 35 degrees from the centerline of the launch escape tower.Three nozzles have large throat while one has a smaller throat to create a thrust offset that places the LAS on a trajectory leaving the flight path of the launch vehicle.

Figure 7 Orion’s launch abort system abort motor
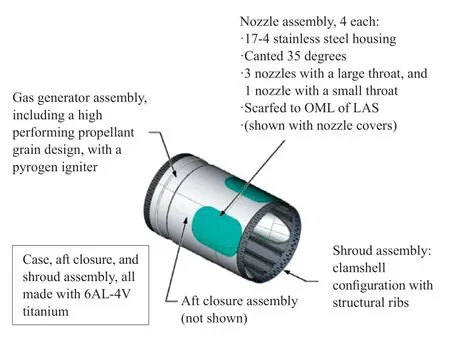
Figure 8 Orion’s launch abort system jettison motor
The gas generator is located above the nozzle assembly since the JM does not employ turn-flow technology.High-performance propellants are initiated by a pyrogen igniter to create high pressure gas feeding the nozzles.
The JM delivers a total thrust of 178 kN (147 kN axial) at an impulse of 221 s over the course of 1.7 s of burn time.
6.3 Orion’s Launch Abort System Attitude Control Motor
Stacked atop the JM and interstage is the 760 kg attitude control motor (ACM) that is used to stabilize the stack during the launch abort and provides the re-orientation maneuver to put the crew module into the correct attitude for separation and parachute deployment.ACM is a product of ATK.
The ACM consists of a D6AC steel case and closure with aluminum skirts to provide stability to the gas generator that burns solid propellant to deliver high-pressure gas to the nozzles.A total of eight nozzles are installed on the motor with a radial spacing of 45 degrees to be able to provide directional thrust components to control pitch and yaw during the abort sequence.Thrust on each nozzle is regulated individually by pintle valves in each of the thrusters as commanded by the ACM controller.
During the first 7 s of operation (coinciding with the firing of the abort motor) the ACM can deliver up to 58 kN of thrust that can be distributed and balanced between one and all ACM nozzles.From +7 s to +27 s,the ACM will operate at a thrust level around 22.3 kN.
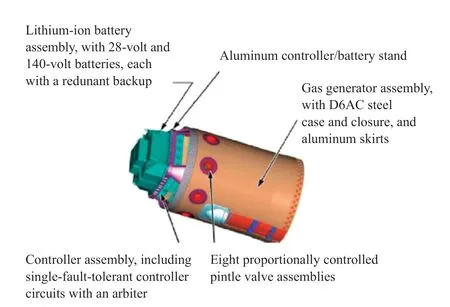
Figure 9 Orion’s launch abort system attitude control motor
The ACM assembly includes a battery stack comprised of 28 V and 140 V batteries,each with a redundant backup to feed the ACM controller and actuate the pintle valves to the commanded thrust settings.The ACM controller uses a single-fault tolerant architecture and receives inputs from the guidance platform of the command module to compute the required thrust setting to achieve the planned attitude.
The ACM working principle includes two phases of operation — the boost phase during which the abort motor is fired which is followed by a directional control phase during separation from the launch vehicle.After burnout of the AM,the ACM is commanded to initiate a pitch maneuver to deliver Orion to a heat-shield forward attitude in preparation for LAS jettison and parachute deployment.
6.4 Abort Modes
A number of abort modes have been developed for Orion providing abort capability from pre-launch to orbital insertion.
In a pad abort and low-altitude (<7.5 km) scenario,Orion would fire its LAS in case the launch vehicle suffering a major failure prior to launch or during ignition when crew emergency egress is not an option.The LAS abort motor and ACM would ignite simultaneously and a separation ring would actuate the separation of the command module from the Orion service module to allow only the crew module to be pulled away by the LAS.After 7 s,AM thrust tails off and 3 s later,ACM initiates the pitch-over that takes about 6 s to complete during which the vehicle reaches its apogee altitude of nearly 2 km.
The JM fires after 21 s to separate the crew module.The forward bay cover is jettisoned after 22 s followed by the deployment of the drogue chutes just over 30 s after the abort is initiated.The pilot mortar fires a little over 50 s after the abort to slow the vehicle down to its touchdown speed for a splashdown nominally in the Atlantic Ocean just off the coast of Florida in an established landing zone.
In the event of a mid-altitude abort from 7.5 -45.5 km in altitude,the LAS is commanded to fire and the ACM and AM are ignited with the separation ring releasing the crew module to be pulled free of the failing launch vehicle.After operation of the AM,Orion is taken through its pitch-over by the ACM and enters a short free falling segment,still retaining the LAS.The LAS is released at the appropriate altitude for parachute deployment.
A high-altitude abort up to 100 km in altitude is also accomplished by firing the LAS to pull the vehicle away from the launcher and includes the pitch-over to point Orion to a good direction for re-entry into the atmosphere.After ACM burnout,the JM fires and LAS is separated while Orion continues on its own using its Hydrazine attitude control system to maintain a nominal orientation throughout entry,through to the drogue deployment altitude.
After LAS and fairing jettison,Orion will still have a launch abort capability.In case of a serious issue with the launch vehicle,all engines would be shut down by emergency command and the Orion service module stack would separate by firing its own main propulsion system.This will either leave the spacecraft on a path towards re-entry or in a lower than planned orbit depending on the timing of the abort.
Orion will also have an abort once around (AOA) feature in which it will perform a retrofire during its first orbit for a landing in the Pacific Ocean in the event of major systems problems aboard the spacecraft or an off-nominal orbital insertion.With SLS,there will be a limited abort to orbit (ATO) capability which involves a restart of the second stage to correct an erroneous orbit or deliver the stack from a sub-orbital to an orbital trajectory.
7 DEVELOPMENT TRENDS OF SOLID ROCKET MOTORS FOR MANNED LAUNCH ESCAPE SYSTEM
There are several development trends seen from the foreign advanced escape systems of manned launch vehicles perspective:
First,innovation based on inheritance is the main approach for future escape motors.Based on the mature design and manufacturing,the performance and reliability of escape motors can gradually improve through advancing the design and utilizing new material and technologies.
Second,higher requirements are put upon the escape system with the rapid development of new launch vehicles and manned spaceships.High reliability,high safety and high controllability are the natural development trend for escape motors,and omnidirectional thrust control is an effective way to achieve high reliability,high safety and high controllability.
Third,digital modeling and system integration simulation are of great significance to ensure good product design,fault analysis and simulation testing.Digital model integration and application,improve the product entire life-cycle management,along with whole-process digital manufacturing and simulation verification.
Fourth,motor vertical ground firing tests,mechanical-thermal environment testing and multi-component force measurements are important means to obtain the precise performance parameters and environmental adaptability of escape motors.The motor performance can be fully examined using advanced test equipment and testing methods.
8 CONCLUSION
In this paper,the technical scheme and key technologies of solid rocket motors of China’s LM-2F manned launch vehicle escape system are summarized.The key technologies such as high burning rate of propellant,thermal structure design,assembly combustion chamber,propellant casting and vertical ground firing test are overcome,and the escape system has successfully conducted 14 manned spaceship flights,making a high operating reliability.Meanwhile,compared with American Orion’s LAS,the following aspects such as new materials and technologies,omnidirectional thrust control,the digital modeling and system integration and advanced testing methods need to be developed in the future to further improve the performance and reliability.
- Aerospace China的其它文章
- Shenzhou 12 Under Development
- The Development of Memory Alloy Satellite-Rocket Separation Device for Commercial Small Satellites
- The Development Status and Main Application Progress of China’s Ocean Satellites
- A Brief Introduction to China Manned Space Program Missions
- The Propulsion System of Shenzhou 13 Manned Spaceship
- High Reliability LM-2F Launch Vehicle for Space Station Mission

