含磷超支化阻燃剂改性环氧树脂研究进展
杨青松, 李金伦, 黄彩娟
含磷超支化阻燃剂改性环氧树脂研究进展
杨青松, 李金伦, 黄彩娟*
(贵州大学 材料与冶金学院,贵州 贵阳 550025)
综述了近年来含磷超支化阻燃剂改性环氧树脂(EP)的研究进展,主要包括含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂、超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂、超支化含磷/氮阻燃剂和超支化含磷/氮/硅阻燃剂等其他类型超支化阻燃剂,介绍了不同类型的阻燃剂对EP的阻燃性能和机械性能的影响,并总结对比了添加不同阻燃剂后EP复合材料的阻燃性能、机械性能、玻璃化转变温度(Tg)等性能,最后指明了超支化阻燃剂当前面临的主要挑战并展望了未来的发展趋势。
环氧树脂;超支化;含磷阻燃剂;阻燃性能;机械性能
环氧树脂(EP)作为重要的热固性塑料之一,具有机械强度高、附着力优异、耐化学性和电绝缘性好等特点,在建筑、汽车、电子和航空航天领域得到了广泛的应用[1-4]。但EP固有的易燃性、发烟量大等问题极大的限制了其在某些特定领域的应用[5-7]。因此,对EP进行阻燃改性具有重要意义。
添加卤素阻燃剂是提高EP阻燃性能的传统方法,特别是溴化阻燃剂对EP阻燃性能的提高尤为突出,但此类阻燃剂存在有毒烟雾的释放和溴的环境危害等不利因素[8-9]。目前,已经开发了很多无卤阻燃剂,如无机阻燃剂(氧化铝[10-11]、二氧化硅[12-13]、石墨烯[14-15]等)、磷系阻燃剂(多磷酸铵[16-17]、红磷[18]、有机磷[19]等)、氮系阻燃剂[20-22]等。在所有无卤阻燃剂中,因含磷阻燃剂具有高效、低烟、低毒、具有多种阻燃机理等特点使其成为最有前景的一类阻燃剂,并且已广泛应用在包括EP在内的多种聚合物材料中[23-25]。
随着聚合物技术的发展,含磷超支化阻燃剂可以通过一锅法简易合成而被应用于阻燃领域。此外,超支化阻燃剂具有的低浸出、低特性粘度、与其他基体材料混溶性好、大量的反应性端基等优点使其可提供比单分子阻燃剂更高效、更优异的阻燃性能,有的超支化阻燃剂还能提高EP复合材料的强度、玻璃化转变温度(Tg)等性能[26-27]。含磷超支化阻燃剂同时具有含磷阻燃剂和超支化聚合物的优点,具有广阔的应用前景。
因此,本文将阐述含磷超支化阻燃剂改性环氧树脂的研究进展和现状,侧重讨论阻燃剂对环氧树脂的阻燃性和机械性能的影响,并展望了超支化阻燃剂未来的发展趋势。
1 含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂
由于9,10-二氢-9-氧杂-10-磷杂菲-10-氧化物(DOPO)及其衍生物含有特殊的磷杂菲基团,具有高阻燃效率、良好的高热稳定性和抗氧化性,被广泛应用于EP阻燃改性中[28-29]。利用DOPO中的活性PH基团合成的DOPO衍生物可用于制备各种含磷杂菲基团的超支化阻燃剂。
Tang等[30]利用10-(2,5-二羟基苯基)-10-氢-9-氧杂-10-磷杂菲-10-氧化物与硼酸反应合成了一种超支化阻燃剂ODOPB-Borate,结构如图1所示。将ODOPB-Borate用于EP中能同时提高材料的阻燃性、Tg和冲击强度。由于磷杂菲和硼酸盐基团在凝聚相和气相中的协同作用,添加6.0%(wt)的ODOPB-Borate后,改性EP的极限氧指数测试(LOI)值达到31.6%,水平垂直燃烧测试(UL-94)达到V-0等级。在50 kW/m2的外部热通量下,峰值放热率(PHRR)和总放热量(THR)分别降低约 24.0%和13.7%。 此外,与纯EP相比,改性EP的 Tg从194.2℃增加到 196.4℃,冲击强度从9.72 kJ/m2增加到 21.92 kJ/m2,提高约55.7%。
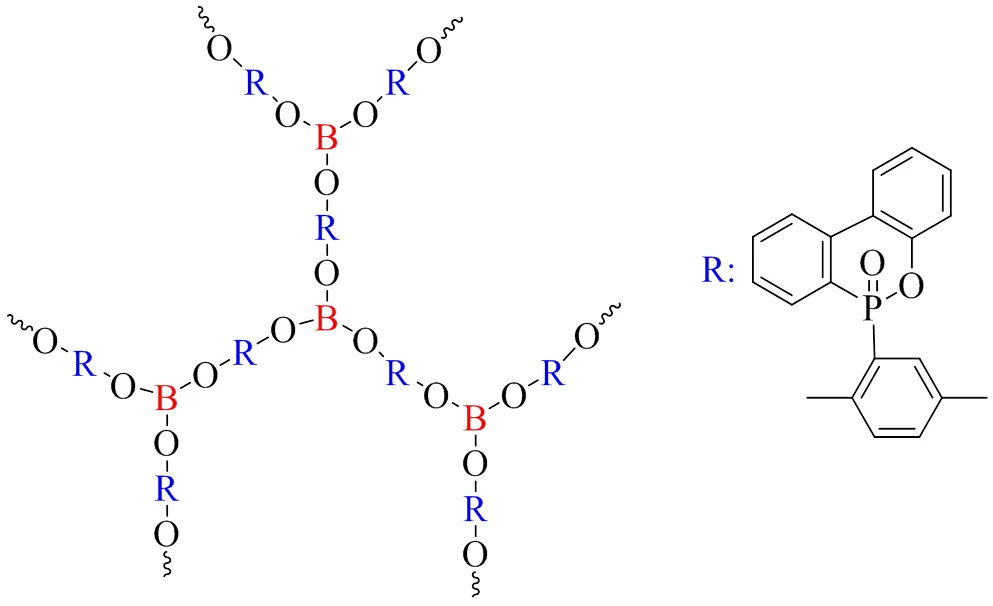
图1 ODOPB-Borate的结构示意图[30]
Zhang等[31]以衣康酸酐(ITA)、DOPO和二异丙醇胺(DIPA)为原料合成了一种超支化阻燃剂(ITA-HBP),结构如图2所示。由于ITA-HBP在气相和凝聚相的阻燃作用,加入3.82%(wt)ITA-HBP[0.26%(wt)的磷含量]的EP 的LOI值增加到36.3%,UL-94达到V-0等级。并且在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,当ITA-HBP添加量为7.35%(wt)[0.48%(wt)的磷含量]时,与纯EP相比,PHRR和总烟雾释放量(TSR)均降低,且拉伸强度、弯曲强度和冲击强度分别提高了37.8%、55.6%和133.2%。
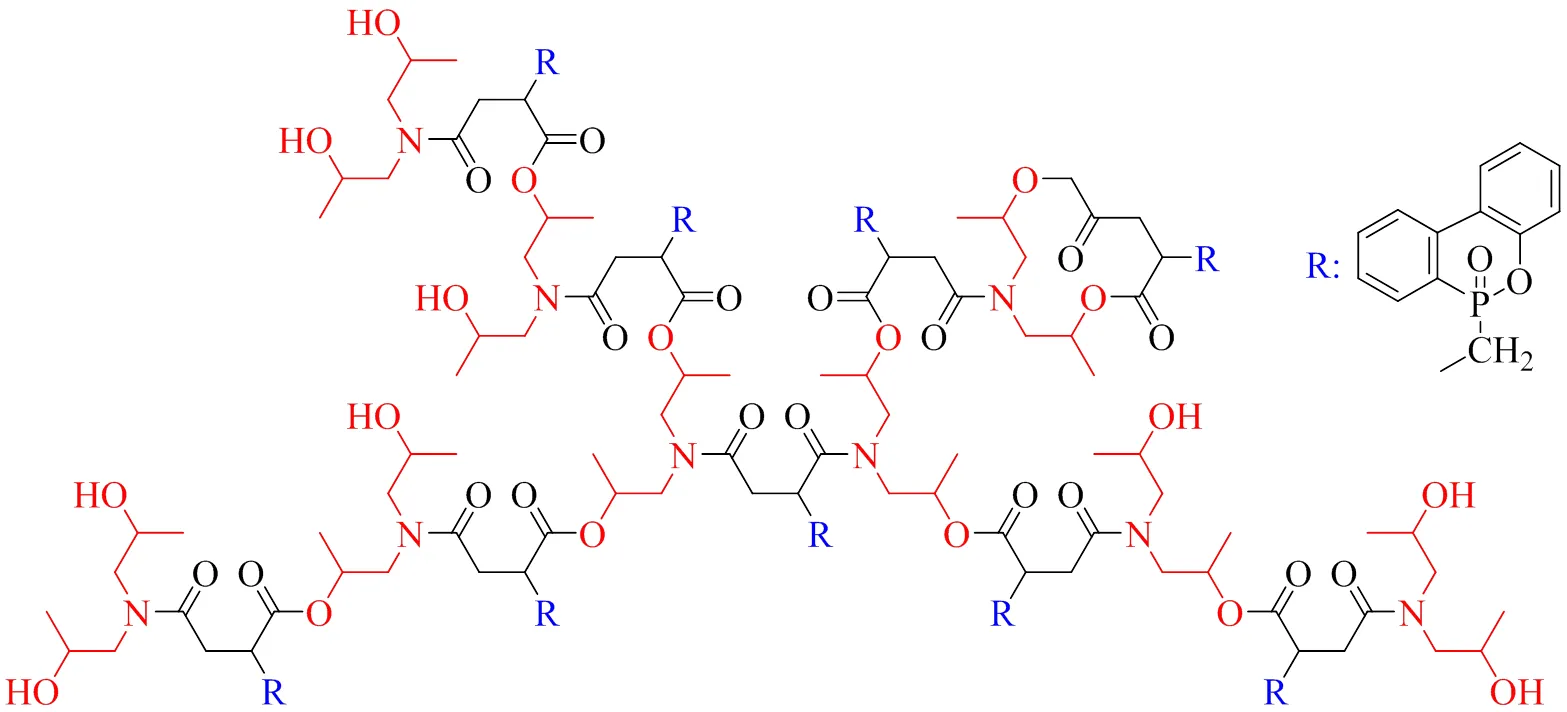
图2 ITA-HBP的结构示意图[31]
Luo等[32]合成了含DOPO的超支化聚酰胺低聚物阻燃剂(HPD)。结果表明,当HPD添加量仅为7.5%(wt)时,EP7.5的LOI值为29.6%,UL-94达到V-0等级。另外,EP7.5的Tg值为176.2℃,高于纯EP(168.2℃)。由于HPD会导致自由基的淬灭和不可燃气体的稀释作用,并且其分解产生的磷酸衍生物会形成含磷保护性炭层而显著提高EP的阻燃性。如图3所示,在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,引燃时间(TTI)时间延长,PHRR,HRR平均值(av-HRR),THR,烟雾释放速率(SPR)和总烟雾释放量(TSP)均降低。

图3 EP-0和EP-7.5的放热速率HRR曲线(A);THR曲线(B);SPR曲线(C)和TSP曲线(D)[32]
Chen等[33]合成了一种含有P/N/Si/B元素和具有刚性、柔性结构的超支化阻燃剂(PTDOB)。结果表明,PTDOB能同时增强EP的阻燃性和机械性能。当添加7.5%(wt)的PTDOB时,EP7.5的LOI值为34.1%,UL-94达到V-0等级。在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,PHRR和THR值为550.3 kW/m2和121.1 MJ/m2,比纯EP低约47.1%和22.3%。并且,EP7.5的Tg值从159.4℃提高到162.9℃。同时,机械性能也得到提高,EP7.5的冲击强度和弯曲强度分别为43.2±5.3 kJ/m2和105.3±7.8 MPa,与纯EP相比,分别增加了55.4%和37.5%。
Battig等[34]利用10-(2,5-二羟基苯基)-10-氢-9-氧杂-10-磷杂菲-10-氧化物(DOPO-HQ)、三(4-羟基苯基)氧化膦(THPPO)和1,4-对苯二甲酰氯(TPC)合成了一种新型芳香族含磷超支化阻燃剂(PDTT)。结果表明,当添加10%(wt)[0.6%(wt)的磷含量]的PDTT后,由于阻燃剂含量较低,UL-94没有等级。但改性后的EP的放热速率(HRR)、总放热量(THE)、PHRR、有效燃烧热(EHC)分别降低了20%、26%、31%、21%。其Tg值为162℃,与纯EP(154℃)相比有所提高。表明PDTT在低负载下具有优异的性能和增韧效果,是一种极有前景的阻燃剂。
Teng等[35]通过含DOPO的生物基三酚(PDG)、1,4-二溴丁烷和环氧氯丙烷之间的反应合成了一种环氧基封端的超支化阻燃剂(EHBFR),合成路线见图4A。结果表明,磷含量仅为1.04%的EP30,LOI值为33.0%,UL-94达到V-0等级,微型燃烧量热仪(MCC)测试结果,如图4B、4C所示,PHRR和THR分别比纯EP降低了43.5%、44.2%。如图4D所示,由于含刚性DOPO结构与高交联密度的协同作用,EP10的Tg升高到194℃。并且,由于超支化结构中的大量分子内腔,EP30的冲击强度比纯EP增加了135%(25℃)、114%(-196℃),EP的缺口冲击强度见图4E。该课题组还从DOPO、香草醛和愈创木酚合成6-(双(4-羟基-3-甲氧基苯基)甲基)二苯并[c,e]氧膦6-氧化物(BDB)[36],然后将BDB与1,3,5-异氰脲酸三缩水甘油酯(TGIC)反应合成了一种新型超支化阻燃剂(HBFR)[37]。在添加HBFR后,改性EP具有优异的阻燃性能,复合材料的韧性、强度和Tg均得到提高。

Peng等[38]合成了含有DOPO和双邻苯二甲腈基团的单分子含N/P阻燃剂(PBD)。由于在加热时双邻苯二甲腈基团会生成三嗪环或酞菁而自交联,通过简单的热处理即可将单分子阻燃剂PBD转变为超支化阻燃剂。用于改性EP后,当PBD添加量为0.5%(wt)[磷含量仅为0.03%(wt)]时,PBD-0.5的LOI值为32.1%,UL-94达到V-0等级。当PBD含量为20%(wt)时,PBD-20的LOI值高达49.5%,且PHRR、THR值与EP相比降低了71.6%、48.8%。而Tg则在PDB添加量为10%(wt)时达到最大值,为210℃。
对于以上文献中报道的含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂改性EP的阻燃性能、机械性能、玻璃化转变温度(Tg)等性能总结见表1。含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂在气相和凝聚相的综合作用实现了EP复合材料优异的阻燃性。比如添加超支化阻燃剂ITA-HBP[31]改性EP时,在气相中,由ITA-HBP分解形成的磷自由基发生猝灭作用,可以淬灭活性自由基,而抑制燃烧。在凝聚相中,含磷碎片的脱水生成芳香碳层,形成的炭层可以有效地减缓热传递,并将氧气与EP基体隔离,抑制了材料的进一步燃烧。在TA-HBP添加量仅为3.82%(wt)时,改性EP的LOI值就高达36.4%,UL-94达到V-0等级。由于含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂中的磷杂菲刚性基团、超支化结构、大量反应端基,使得改性后EP复合材料的交联密度提高,机械性能、Tg也得到提高。利用超支化阻燃剂EHBFR[35]改性EP时,EP10的Tg升高到194℃,EP30的冲击强度比纯EP增加了135%(25℃)、114%(-196℃)。此外,由于PBD[38]在EP网络内部发生交联,形成半互穿网络,使阻燃剂与EP基体接触得更近,PBD添加10%(wt)时,改性EP的LOI值高达46.8%。

表1 总结比较不同含磷杂菲基团超支化阻燃剂改性EP的性能

(续表1)

图5 表格1和表格3中R1-R16的结构
2 超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂
在合成超支化聚合物时,有两种常用方法:AB(≥2)或A+B(,≥2)[39-40]。在 AB方法中,使用具有 AB(≥2)结构的单体,当 A 和 B 基团选择性地相互反应时,则会生成一种没有交联的支化聚合物[41]。在 A+B方法中,使用两种单体进行缩聚反应[A和 B(,≥2)],最常用的方法是 A2+B3方法,即通过A的两个相同官能团和B的三个相同官能团之间的缩聚反应制备超支化聚合物[42-43]。利用具有AB(≥2)结构的含磷单体或三氯氧磷(POCl3)及其衍生物,通过AB(≥2)或A+B(,≥2)逐步增长缩聚等方法即可获得不同的超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂。
董杰等[44]以苯膦酰二氯(BPOD)为A2单体,三羟甲基丙烷(TMP)为B3单体,合成了一种超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂。将其用于EP的改性,分别添加10%(wt)、15%(wt)阻燃剂后,LOI值达到最大值,为33%。并且,改性EP的拉伸强度、弯曲强度、冲击强度均得到提高,添加10%(wt)阻燃剂后,拉伸强度提高了27%,为51.52 MPa。添加15%(wt)阻燃剂后,冲击强度提高了306%,为33.83 kJ/m2,弯曲强度也达到最大值141.62 MPa。但是,由于较大尺寸阻燃剂的加入,降低了环氧树脂分子间作用力,导致改性EP的Tg略有下降,添加15%(wt)阻燃剂后,Tg降至140.60℃。
Zhang等[45]利用三(2-羟乙基)异氰酸酯(A3单体)和POCl3(B3单体)的缩聚反应合成了一种新型超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂(HPPE),并合成了不同分子量和羟基端基数的阻燃剂HPPE-1/2/3。结果表明,当添加12%(wt)的HPPE-2时,改性后EP的LOI值达到最大值,为30.25%,比纯EP提高了21.2%,冲击强度达到16.2 kJ/m2。此外,添加8%(wt)的HPPE-2后,改性EP的拉伸强度和弯曲强度达到最大值,分别为91.5 MPa和79.9 MPa。
Chen等[46]利用双酚-A(BA)和三氯氧磷合成了一种反应型超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂(HPE),HPE的合成路线见图6。将HPE和BA混合作为EP的固化剂使用。结果表明,当掺入 33%(wt)的HPE时,改性EP的LOI值增加到27.5%。在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,随着HPE含量的增加,HRR、THR、EHC降低,而残炭量和消烟面积(SEA)增加。并且,只用HPE固化的EP的Tg(135.3℃)比双酚A固化的EP的Tg(128.7℃)高。

图6 HPE的合成路线[46]

图7 hbPPE的结构示意图[48]
Huang等[47]先是利用POCl3和丙烯酸羟乙酯(HEA)反应合成三(丙烯酰氧基乙基)磷酸酯(TAEP),TAEP与哌嗪通过迈克尔加成反应合成了HPPA大分子,然后通过“硫醇-烯”点击反应将SH-mSiO2纳米颗粒与HPPA共价官能化,合成了一种含有多种阻燃元素的混合材料(HPPA-SH-mSiO2)。在35 kW/m2的热通量下,与纯EP相比,EP/HPPA-SH-mSiO2改性EP的PHRR和THR分别降低了28.7%和16.0%。并且EP/HPPA-SH-mSiO2的加入提高了EP基体的高温稳定性。
Schartel等[48-53]合成了一系列不同种类的含磷超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂,并将其用于阻燃改性EP。例如,他们合成了一种结构新颖的超支化无卤聚(磷酸酯)(hbPPE)[48],结构如图7所示。将其作为阻燃剂改性EP,并与商业化的阻燃剂双酚 A 双(磷酸二苯酯)(BDP)进行比较。结果表明,由于hbPPE在提高残炭量方面效果更好,在添加量相同的情况下,hbPPE改性的EP比BDP改性的EP表现出更低的THE和更高的LOI值。添加10%(wt)BDP的EP的THE和LOI值分别为83 MJ/m2和22.6%,UL-94没有评级。而含有10%(wt)hbPPE的EP的THE和LOI值仅为62 MJ/m2和23.6%,UL-94达到HB等级。
该课题组还研究了基于磷的不同类型阻燃剂对化学性质不同的EP的影响[51]。对于不同的超支化阻燃剂,发现它们与 EP 基体之间分解温度的重叠在提高阻燃性中起重要作用。当FR与基体的这种重叠达到最大时,化学相互作用最大,导致残炭量更高,PHRR和THE降低,而产生更好的阻燃性。此外,对一系列含硫和无硫超支化聚磷酸盐添加剂的阻燃性进行了比较[53]。硫的引入提高了阻燃剂的热稳定性和凝聚相的活性,同时硫自由基的交联促进了残留物的产率。
对于以上文献中报道的超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂改性EP的阻燃性能、机械性能、玻璃化转变温度(Tg)等性能总结见表2。由BPOD和TMP合成的超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂[44]改性EP后具有最优的阻燃性能,该阻燃剂与EP基体的相容性好,从而提高了EP复合材料的韧性和强度。此外,由于超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂在凝聚相和气相的阻燃作用,添加10%(wt)的超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂后,LOI值即达到33%。

表2 总结比较不同超支化聚磷酸酯阻燃剂改性EP的性能
3 其他类型的超支化阻燃剂
Tan等[54]利用超支化聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)通过阳离子交换反应改性聚磷酸胺(APP),得到了一种高效的用于EP的阻燃固化剂PEI-APP。经改性后的APP提升了APP与EP的相容性。PEI-APP提升了APP与EP的相容性,同时改善了EP的阻燃和抑烟性能。当添加15%(wt)的PEI-APP-3时,改性EP的LOI值为29.5%,UL-94达到V-0等级。在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,与PEI/EP相比,PEI-APP 15/EP的PHRR和THR分别下降了73.8%和76.1%。另外,PEI-APP固化后抑烟效果增强,总烟雾产生量(TSP)下降了70.5%。
Ma等[55]合成了一种新型超支化聚(氨基甲基氧化膦-胺)共固化剂(HPAPOA),合成路线见图8。计算出HPAPOA的胺当量为190.8 g/mol,将其用作共固化剂改性EP。结果表明,添加3.0%(wt)的HPAPOA时,EP3.0的LOI值为30.7%,UL-94达到V-0等级。在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,除了EP1的PHRR外,随着HPAPOA含量的增加,PHRR、THR、CO生成速率峰值(p-COPR)、CO总生成量(TCOP)、产烟率峰值(p-SPR)和TSP均降低。Tg则随着HPAPOA含量的增加逐渐增加,EP3.5的Tg值(164.0℃)比纯EP高7.4℃。与纯EP相比,EP2.0的拉伸和弯曲性能得到提高,具有较优的机械性能。

图8 THP和HPAPOA的合成路线[55]
该课题组还利用4,4ʼ-二苯基甲烷二异氰酸酯(MDI)和三羟甲基氧化膦(THPO)合成了一种新型超支化(氨基甲酸乙酯-氧化磷)(HPUPO)[56]。HPUPO在EP的凝聚相形成的保护性炭层提高了阻燃性。添加4%(wt)的HPUPO时,EP4的LOI值达到30.5%,UL-94达到V-0等级。改性EP的拉伸模量、强度、断裂伸长率、冲击强度和储能模量因 HPUPO 的刚性骨架和氢键相互作用而提高。
Hu等[57]利用甲基膦酸二甲酯(DMMP)和三(2-羟乙基)异氰脲酸酯(THEIC)的酯交换反应合成了一种透明的新型超支化含磷/氮阻燃剂(HPNFR),合成路线见图9。当HPNFR的含量为4%(wt)时,EP4.0的LOI值为34.5%,UL-94达到V-0等级。在35 kW/m2的外部热通量下,EP4.0的PHRR和 THR值分别为734.9 kW/m2、55.2 MJ/m2,与纯EP相比,分别降低了16.77%和13.88%。并且,HPNFR的低负载对EP的透明度几乎没有影响。

图9 HPNFR的合成路线[57]
Zhang等[58]合成了一种非芳香族含Si、P、N超支化聚硅氧烷阻燃剂(HBPSi)。当添加8%(wt)的HBPSi时,EP-8的LOI值达到26.8%,比EP-0提高了31.4%。UL-94达到V-0等级。此外,由于HBPSi的支化结构和Si-O链段,当添加4%(wt)的HBPSi时,EP-4的弯曲强度和冲击强度达到最大值,为140.02 MPa和23.63 kJ/m2,比相同条件制备的纯EP分别提高了22.0%和72.9%。同时,由于HBPSi 中含有伯胺和叔胺基团,还能降低EP的固化温度,效率与市售固化剂相当。
彭凡畅等[59]利用羧基化碳纳米管(CNT-COOH)作为载体,以POCl3和N,N-二氨基二苯甲烷(DDM)为反应单体,制备了3 种不同厚度的超支化聚磷酰胺包覆碳纳米管(CNT/HBPPA-1.5/3/6)阻燃剂。当添加2%(wt)的CNT/HBPPA-3后,改性EP的LOI值达到最大值,为28.2%,UL-94达到V-1等级。并且,添加2%(wt)的EP/CNT/HBPPA-3复合材料的拉伸强度和冲击强度达到最大值,分别为53. 287 MPa 和11. 19 kJ/m2,比纯EP提升了51%和18.9%。
以上文献中报道的超支化含磷/氮阻燃剂和超支化含磷/氮/硅阻燃剂等其他类型超支化阻燃剂改性EP的阻燃性能、机械性能、玻璃化转变温度(Tg)等性能总结见表3。超支化含磷/氮阻燃剂HPNFR[57]赋予了EP复合材料在低添加量下具有优异的阻燃性能,致密连续炭层的阻隔作用、热解气体的吹出作用和自由基的淬灭作用是EP复合材料阻燃性能提高的原因。而超支化聚硅氧烷阻燃剂HBPSi[58]因为具有独特的支化结构和灵活的Si-O链段,添加在EP中后,均匀分散在EP基体中,与树脂基体结合紧密,能增加EP的交联密度,在EP分子内腔形成自由体积,导致EP复合材料具有优异的机械性能,当添加4%(wt)的HBPSi时,EP-4的弯曲强度和冲击强度比相同条件制备的纯EP分别提高了22.0%和72.9%。

表3 不同超支化含磷/氮阻燃剂、超支化含磷/氮/硅阻燃剂等其他类型超支化阻燃剂改性EP的性能

(续表3)
4 总结与展望
含磷超支化阻燃剂改性的EP能极大改善复合材料的阻燃性,并且有的含磷超支化阻燃剂能显著提高EP的机械性能、Tg等其他性能。随着阻燃剂向着高效、低毒、低烟、绿色环保、多功能的方向发展,含磷超支化阻燃剂因其简单的合成步骤、低毒高效和对力学性能的积极影响而具有广阔的应用前景。尽管近年来超支化含磷阻燃剂取得了重大进展,但仍有一些挑战尚未解决。首先是缺乏阻燃效率的优化,目前的工作还主要集中在含磷超支化阻燃剂的不同阻燃基团和不同添加量上。若要实现工业应用,仍需要进一步提高阻燃性和抑烟性。其次是可持续性发展问题,合成超支化阻燃剂的原料大多来自石油基资源,随着石油基资源的使用,必将会引起可持续性问题。最后是EP复合材料的多功能改性,比如EP通常由于高交联密度而具有很大的脆性,而限制了其在航空航天等特定领域的应用。因此,未来开发高效含磷超支化阻燃剂将会从以下几个方面发展:1)研究开发具有磷元素与其他阻燃元素(氮、硅、硼等)协同作用的超支化阻燃剂。2)利用生物基原料合成环境友好、可持续的含磷超支化阻燃剂。3)开发除阻燃性外同时具有更多功能的超支化阻燃剂。
[1] Maychahal C , Verschuren C A , Tanaka G Y. Epoxy resins: Chemistry and technology[M]. New York: Dekker, 1973.
[2] Kumar S, Krishnan S, Samal S K,. Toughening of petroleum based (DGEBA) epoxy resins with various renewable resources based flexible chains for high performance applications: A review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(8): 2711-2726.
[3] Wang X, Guo W W, Song L,. Intrinsically flame retardant bio-based epoxy thermosets: A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 179: 107487.1-107487.13
[4] Jin F L, Li X, Park S J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 29: 1-11.
[5] Liu Q, Zhao Y, Gao S,. Recent advances in the flame retardancy role of graphene and its derivatives in epoxy resin materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 149: 106539.1-106539.11
[6] Luo H, Rao W, Zhao P,. An efficient organic/inorganic phosphorus-nitrogen-silicon flame retardant towards low-flammability epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2020, 178: 109195.1-109195.9
[7] Fang F, Ran S, Fang Z,. Improved flame resistance and thermo-mechanical properties of epoxy resin nanocomposites from functionalized graphene oxide via self-assembly in water[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 165: 406-416.
[8] Waaijers S L, Kong D, Hendriks H S,. Persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity of halogen-free flame retardants[M]. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. New York, NY; Springer New York, 2013: 1-71.
[9] Luda M P, Balabanovich A I, Zanetti M. Pyrolysis of fire retardant anhydride-cured epoxy resins[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2010, 88(1): 39-52.
[10] Guan F-L, Gui C-X, Zhang H-B,. Enhanced thermal conductivity and satisfactory flame retardancy of epoxy/alumina composites by combination with graphene nanoplatelets and magnesium hydroxide[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 98: 134-140.
[11] Wang J, Qian L, Xu B,. Synthesis and characterization of aluminum poly-hexamethylenephosphinate and its flame-retardant application in epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2015, 122: 8-17.
[12] Kawahara T, Yuuki A, Hashimoto K,. Immobilization of flame-retardant onto silica nanoparticle surface and properties of epoxy resin filled with the flame-retardant-immobilized silica (2)[J]. Reactive & Functional Polymers, 2013, 73(3): 613-618.
[13] Jiang S D, Tang G, Chen J M,. Biobased polyelectrolyte multilayer-coated hollow mesoporous silica as a green flame retardant for epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 342: 689-697.
[14] Zhang J, Li Z, Zhang L,. Bimetallic metal-organic frameworks and graphene oxide nano-hybrids for enhanced fire retardant epoxy composites: A novel carbonization mechanism[J]. Carbon, 2019, 153: 407-416.
[15] Qu L J, Sui Y L, Zhang C L,. POSS-functionalized graphene oxide hybrids with improved dispersive and smoke-suppressive properties for epoxy flame-retardant application[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2020, 122: 109383.1-109383.12
[16] Rajaei M, Wang D Y, Bhattacharyya D. Combined effects of ammonium polyphosphate and talc on the fire and mechanical properties of epoxy/glass fabric composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2017, 113: 381-390.
[17] Xu X W, Wang S, Ma S Q,. Vanillin-derived phosphorus-containing compounds and ammonium polyphosphate as green fire-resistant systems for epoxy resins with balanced properties[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2019, 30(2): 264-278.
[18] Cheng C, Lu Y L, Ma W N,. Preparation and characterization of polydopamine/melamine microencapsulated red phosphorus and its flame retardance in epoxy resin[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(33): 20391-20402.
[19] Wang G Y, Nie Z B. Synthesis of a novel phosphorus-containing epoxy curing agent and the thermal, mechanical and flame-retardant properties of the cured products[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 130: 143-154.
[20] Yang S, Wang J, Huo S Q,. Synthesis of a phosphorus/nitrogen-containing compound based on maleimide and cyclotriphosphazene and its flame-retardant mechanism on epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 126: 9-16.
[21] Wang P, Chen L, Xiao H,. Nitrogen/sulfur-containing DOPO based oligomer for highly efficient flame-retardant epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2020, 171: 109023.1-109023.10.
[22] You G Y, Cheng Z Q, Peng H,. The synthesis and characterization of a novel phosphorus-nitrogen containing flame retardant and its application in epoxy resins[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(22): 41079.1-41079.8.
[23] Fang F, Song P, Ran S,. A facile way to prepare phosphorus-nitrogen-functionalized graphene oxide for enhancing the flame retardancy of epoxy resin[J]. Composites Communications, 2018, 10: 97-102.
[24] Sag J, Goedderz D, Kukla P,. Phosphorus-containing flame retardants from biobased chemicals and their application in polyesters and epoxy resins[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(20): 3746.1-3746.31.
[25] Seidi F, Movahedifar E, Naderi G,. Flame retardant polypropylenes: A review[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(8): 1701.1-1701.49.
[26] Zhang J, Chen S, Qin B,. Preparation of hyperbranched polymeric ionic liquids for epoxy resin with simultaneous improvement of strength and toughness[J]. Polymer, 2019, 164: 154-162.
[27] Wang Y, Chen S, Chen X,. Controllability of epoxy equivalent weight and performance of hyperbranched epoxy resins[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 160: 615-625.
[28] Mu X, Wang D, Pan Y,. A facile approach to prepare phosphorus and nitrogen containing macromolecular covalent organic nanosheets for enhancing flame retardancy and mechanical property of epoxy resin[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 164: 390-399.
[29] Qiu Y, Qian L, Feng H,. Toughening effect and flame-retardant behaviors of phosphaphenanthrene/phenylsiloxane bigroup macromolecules in epoxy thermoset[J]. Macromolecules, 2018, 51(23): 9992-10002.
[30] Tang S, Qian L, Qiu Y,. High-performance flame retardant epoxy resin based on a bi-group molecule containing phosphaphenanthrene and borate groups[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2018, 153: 210-219.
[31] Zhang J, Mi X, Chen S,. A bio-based hyperbranched flame retardant for epoxy resins[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122719.1-122719.14.
[32] Luo Q, Sun Y, Yu B,. Synthesis of a hyperbranched polyamide oligomer containing DOPO for simultaneously enhancing the flame retardance and glass transition temperature of epoxy resin[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2020, 32(2): 525-537.
[33] Chen M, Lin X, Liu C,. An effective strategy to enhance the flame retardancy and mechanical properties of epoxy resin by using hyperbranched flame retardant[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(9): 5956-5974.
[34] Battig A, Müller P, Bertin A,. Hyperbranched rigid aromatic phosphorus-containing flame retardants for epoxy resins[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2021, 306(4): 2000731.1-2000731.12.
[35] Teng N, Dai J, Wang S,. Hyperbranched flame retardant to simultaneously improve the fire-safety, toughness and glass transition temperature of epoxy resin[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 157: 110638.1-110638.14.
[36] Liu J, Dai J, Wang S,. Facile synthesis of bio-based reactive flame retardant from vanillin and guaiacol for epoxy resin[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 190: 107926.1-107926.13.
[37] Teng N, Dai J, Wang S,. Hyperbranched flame retardant for epoxy resin modification: Simultaneously improved flame retardancy, toughness and strength as well as glass transition temperature[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 428: 131226.1-131226.11.
[38] Peng X, Liu Q, Wang D,. A hyperbranched structure formed by in-situ crosslinking of additive flame retardant endows epoxy resins with great flame retardancy improvement[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 224: 109162.1-109162.15.
[39] Gao C, Yan D. Hyperbranched polymers: From synthesis to applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2004, 29(3): 183-275.
[40] Bhat S I, Ahmadi Y, Ahmad S. Recent advances in structural modifications of hyperbranched polymers and their applications[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(32): 10754-10785.
[41] Shi Y, Graff R W, Cao X,. Chain-growth click polymerization of AB2monomers for the formation of hyperbranched polymers with low polydispersities in a one-pot process[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(26): 7631-7635.
[42] Barua S, Chattopadhyay P, Karak N. s-Triazine-based biocompatible hyperbranched epoxy adhesive with antibacterial attributes for sutureless surgical sealing[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2015, 3(28): 5877-5885.
[43] Zhou D, Pierucci L, Gao Y,. Thermo- and pH-Responsive, Coacervate-Forming Hyperbranched Poly(β-amino ester)s for Selective Cell Binding [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(7): 5793-5802.
[44] 董杰, 陈晓婷, 李艳青, 等. 超支化聚膦酸酯改性环氧树脂的研究[J]. 天津科技大学学报, 2010, 25(6): 30-32, 38.
[45] Zhang D, Wu H, Li T,. Preparation of high-performance flame-retardant hybrid material by hyperbranched polyphosphate ester[J]. Polymer Composites, 2011, 32(1): 36-43.
[46] Chen X, Jiao C, Li S,. Flame retardant epoxy resins from bisphenol-A epoxy cured with hyperbranched polyphosphate ester[J]. Journal of Polymer Research, 2011, 18(6): 2229-2237.
[47] Huang Z, Wang D, Zhu Y,. The influence of mesoporous silica modified with phosphorus and nitrogen-containing hyperbranched molecules on thermal stability, combustion behavior, and toxic volatiles of epoxy resin[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2018, 29(1): 372-383.
[48] Täuber K, Marsico F, Wurm F R,. Hyperbranched poly(phosphoester)s as flame retardants for technical and high performance polymers[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2014, 5(24): 7042-7053.
[49] Battig A, Markwart J C, Wurm F R,l. Hyperbranched phosphorus flame retardants: Multifunctional additives for epoxy resins[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2019, 10(31): 4346-4358.
[50] Markwart J C, Battig A, Kuckhoff T,. First phosphorus AB2monomer for flame-retardant hyperbranched polyphosphoesters: AB2vs. A2+ B3[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2019, 10(43): 5920-5930.
[51] Battig A, Markwart J C, Wurm F R,. Matrix matters: Hyperbranched flame retardants in aliphatic and aromatic epoxy resins[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2019, 170: 108986.1-108986.14.
[52] Markwart J C, Battig A, Velencoso M M,. Aromatic vs. aliphatic hyperbranched polyphosphoesters as flame retardants in epoxy resins[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(21): 3901.1-3901.15.
[53] Battig A, Markwart J C, Wurm F R,. Sulfurʼs role in the flame retardancy of thio-ether-linked hyperbranched polyphosphoesters in epoxy resins[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2020, 122: 109390.1-109390.12.
[54] Tan Y, Shao Z-B, Yu L-X,. Polyethyleneimine modified ammonium polyphosphate toward polyamine-hardener for epoxy resin: Thermal stability, flame retardance and smoke suppression[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 131: 62-70.
[55] Ma C, Qiu S, Yu B,. Economical and environment-friendly synthesis of a novel hyperbranched poly(aminomethylphosphine oxide-amine) as co-curing agent for simultaneous improvement of fire safety, glass transition temperature and toughness of epoxy resins[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 322: 618-631.
[56] Ma C, Qiu S, Wang J,. Facile synthesis of a novel hyperbranched poly(urethane-phosphine oxide) as an effective modifier for epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2018, 154: 157-169.
[57] Hu X, Yang H, Jiang Y,. Facile synthesis of a novel transparent hyperbranched phosphorous/nitrogen-containing flame retardant and its application in reducing the fire hazard of epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: 120793.1-120793.11.
[58] Zhang Y, Yan H, Feng G,. Non-aromatic Si, P, N-containing hyperbranched flame retardant on reducing fire hazards of epoxy resin with desirable mechanical properties and lower curing temperature[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 222: 109043.1-109043.12.
[59] 彭凡畅, 陈小随, 张爱清, 等. 超支化聚磷酰胺包覆碳纳米管的可控制备及阻燃应用[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(9): 55-63.
Progress of Phosphorus-containing Hyperbranched Flame Retardant Modified Epoxy Resin
YANG Qing-song, LI Jin-lun, HUANG Cai-juan*
(College of Materials and Mertallurgy, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China)
The research progress of phosphorous-containing hyperbranched flame retardant modified epoxy resin (EP) in recent years is reviewed,mainly including phosphorus-containing phenanthrene group hyperbranched flame retardant, hyperbranched polyphosphate flame retardant, and hyperbranched phosphorus-containing flame retardant /Nitrogen flame retardants and hyperbranched phosphorus/nitrogen/silicon flame retardants and other types of hyperbranched flame retardants. The effects of different types of flame retardants on the flame retardant and mechanical properties of EP are introduced, and the flame retardant properties, mechanical properties, glass transition temperature (Tg) and other properties of EP composites after adding different flame retardants are summarized and compared. Finally, it points out the main challenges currently faced by the phosphorus-containing hyperbranched flame retardants and looks forward to the future development trend.
epoxy resin; hyperbranched; phosphorus-containing flame retardant; flame retardant property; mechanical property
2021-11-26
贵州大学大学生创新创业训练计划项目(项目编号:S202010657056)。
杨青松(1994~),男,硕士研究生;主要从事生物基阻燃材料合成与性质研究。1347283416@qq.com
黄彩娟(1974~),女,硕士,副教授;主要从事绿色催化和生物基高分子材料合成的研究。Cjhuang98@163.com
TQ323.5
A
1009-220X(2022)03-0007-14
10.16560/j.cnki.gzhx.20220307

