Network pharmacological study and molecular docking verification of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of systemic sclerosis
Jia Guo, Hua Bian, Yu Shan, Jing-Jing Zhao, Xiao-Wen Zhang, Shuang Chen, Bo Bian
1. Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450008, China
2. Zhang Zhongjing College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanyang Institute of Technology, Zhang Zhongjing, Key Laboratory of Recipe and Immunomodulation, Henan Province, Nanyang 473004, China
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of systemic sclerosis ((SSC)) based on network pharmacology. Methods: GEO, Genecards,Pharmgkb, TTD and Drugbank databases were used to obtain SSC targets, related literatures and Swisstargetprediction databases were used to obtain the main components of Citrus and their corresponding targets, and intersection was used to obtain prediction targets. Log in to the String database to analyze the protein interaction of the prediction target(PPI), further used Cytoscape to obtain the core gene by network topology analysis, and the core gene was docked with the main components of Capparis spinosa. The prediction targets were analyzed by gene ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG)pathway analysis using R software. Results: A total of 15 active components and their targets were obtained, 3171 SSC targets were obtained, and 66 predicted targets were obtained by intersection. Ten PPI core genes such as VEGFA, TNF, AKT1, PTGS2 and MMP9 were obtained by topological analysis. GO analysis involved many biological processes such as reactive oxygen species metabolic process、protein kinase B signaling、regulation of inflammatory response、phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling and so on. KEGG pathway analysis showed PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer, Focal adhesion, Rap1 signaling pathway and other signaling pathways. Conclusion: The molecular mechanism of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of SSC is predicted by the method of network pharmacology,which provides theoretical basis and data support for the basic research of Citrus officinalis in the treatment of SSC.
Keywords:Capparis spinosa Systemic sclerosis Network pharmacology Molecular docking✉Corresponding author: BIAN Hua, Professor, Ph.D..E-mail: biancrown@163.com.
1. Introduction
Systemic sclerosis (Systemic Sclerosis, SSC) is an immunemediated disease, which is a major clinical challenge for doctors and patients. Its pathogenesis is the complex interaction of vascular lesions, immune system activation and extensive tissue fibrosis [1].Although there is evidence that its survival rate has improved, the mortality rate is still high, higher than any other rheumatic disease[2, 3]. At present, immunosuppressants and hormones are commonly used to control the disease. With regard to immunosuppressants,a variety of treatments for SSC have been explored, including cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, methotrexate, and recently targeted therapy with monoclonal antibodies [4]. However,although they have shown possible improvements in skin and lung involvement and have been used in a series of studies, there is no conclusive evidence that they can effectively alter the natural history of scleroderma [5, 6].
Capparis spinosa is a common medicine used in the treatment of rheumatism in Uygur nationality, including root bark, leaves and fruits, with the functions of dispelling wind, dispelling cold and dehumidification [7]. In recent years, a number of basic studies have shown that Capparis spinosa can affect the disease progression of SSC by regulating multiple pathways and cytokines in SSC mouse model [8-11]. This study uses the method of network pharmacology and the existing database to boldly predict the possible targets and pathways of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of SSC, so as to provide theoretical basis and data support for related clinical research in the future.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Collection of SSC targets
Log into the GEO database to obtain the GSE76807 chip, P<0.05,|logFC|>0.5 as the filter condition, use R software to draw a volcano map and screen the differential genes. Log in to GeneCards,PharmGkb, TTD, and DrugBank to search for SSC related targets using "scleroderma" as the keyword.
2.2 Target prediction of Capparis spinosa for SSC treatment
Consult the related literature [7, 12, 13] to obtain the chemical components of Capparis spinosa, enter the PubChem database to obtain the 2D structure, and import the SwissTargetPrediction database to obtain the Capparis spinosa target. Delete duplicate data after aggregation. Take the intersection of the Capparis spinosa target and the SSC target, and draw the Venn diagram to obtain the effective target. Use Cytoscape 3.8.0 to draw Capparis spinosacomponent-target network diagram.
2.3 PPI network construction and topology analysis to obtain core genes
Log in to the String database, import effective targets, select human species, set a minimum score of 0.4, obtain the PPI network map and save the CSV file. Open Cytoscape 3.8.0 and import the CSV file, and use the built-in CytoNCA plug-in for topology analysis.The filter conditions are betweenness centrality (BC), closeness centrality, degree centrality (DC), Eigenvector centrality (EC), local average connectivity-based method (LAC), information centrality(information centrality) and network centrality (network centrality)are greater than the median each time Value, and finally get the core gene.
2.4 Molecular docking verification
Log the obtained core gene into the PDB database to download its structure, remove water molecules and small molecule ligands,and use AutoDock Vina software for molecular docking with their corresponding compounds. Select the combination result with the lowest binding energy, and use Pymol software for visual drawing.
2.5 GO and KEGG analysis
Use ClusterProfiler in R software to perform gene ontology (Gene Ontology, GO) biological process (BP), molecular function (MF),cellular component (CC), and Kyoto genes Analyze the pathway with Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), correct the P value by FDR (False Discovery Rate), set the threshold qvalue<0.05, and use R software for drawing.
3. Results
3.1 SSC related targets
The GSE76807 chip was filtered to create a volcano map (Figure 1), and 1431 differential genes were obtained. 1796, 74, 8 and 1 SSC-related targets were obtained from GeneCards, PharmGkb,TTD and DrugBank databases respectively. Repetitive genes were removed, and a total of 3171 SSC-related targets were obtained.

Figure 1 Gene difference volcano map of GSE76807 chip
3.2 Target prediction of Capparis spinosa for SSC treatment
After removing the components and duplicate genes without effective targets, the effective components of Capparis spinosa(Wogonin, Isorhamnetin, Kaempferol, Quercetin), flavonoids,Isoginkgetin, Ginkgetin, Prunetin, Isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside,Quercetin 3-O-glucoside-7-O-rhamnoside, Quercetin 3- There are 15 O-glucoside, kaempferol-3-glucoside, Rutin), alkaloids (Cadabicine,Niacinamide and Stachydrine), corresponding to 178 targets. Take the intersection of the SSC target and the caper target to obtain 66 predicted targets, and draw them in Cytoscape 3.8.0 software (Figure 2), where the size of the nodes in the graph is positively related to the number of edges in the network.
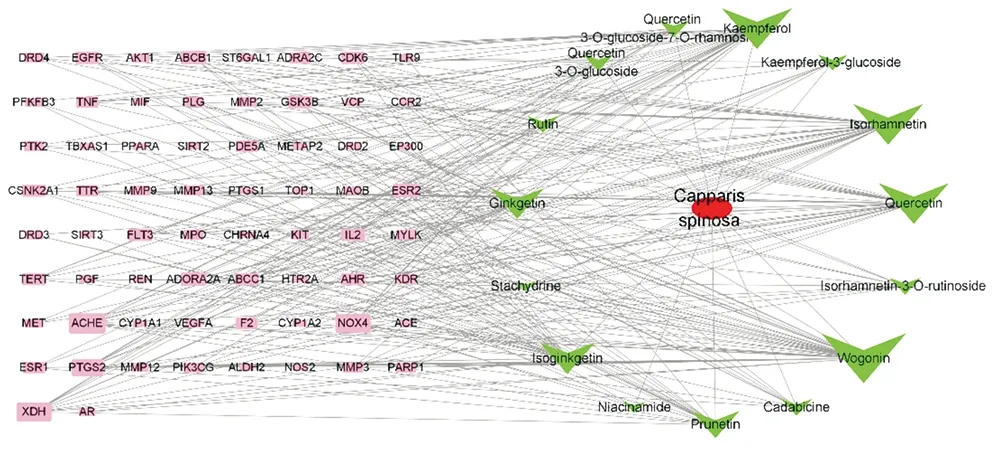
Figure 2 Capparis spinosa-active ingredients-target network diagram
3.3 PPI network construction and topology analysis to obtain core genes
Log in to the String database, enter the predicted target, select human as the species, and the filter score is 0.4, and draw the PPI network diagram (Figure 3). Save the TSV file and import it into Cytoscape 3.8.0 software for topological analysis (Figure 4), and finally get the core genes VEGFA, TNF, AKT1, PTGS2, MMP9,MMP2, ACE, IL2, EGFR and ESR1.
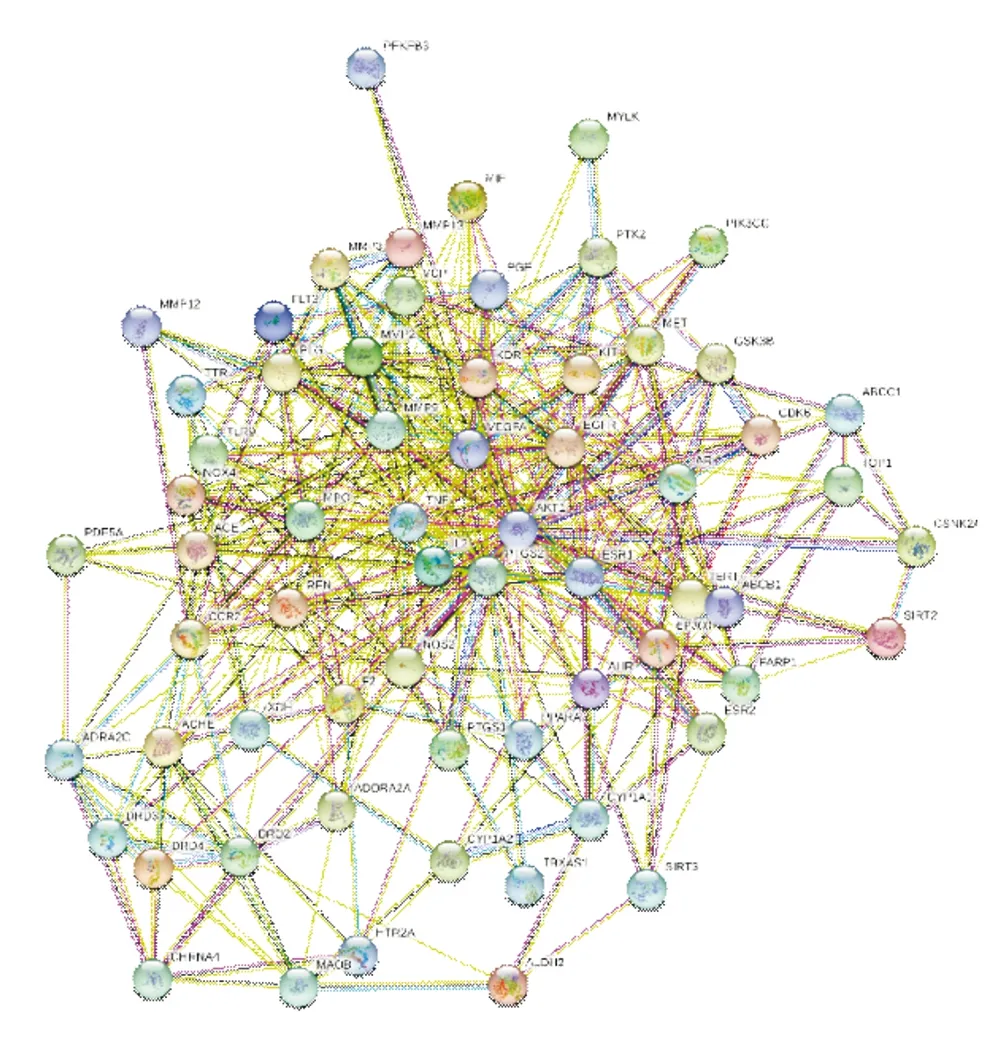
Figure 3 PPI network diagram
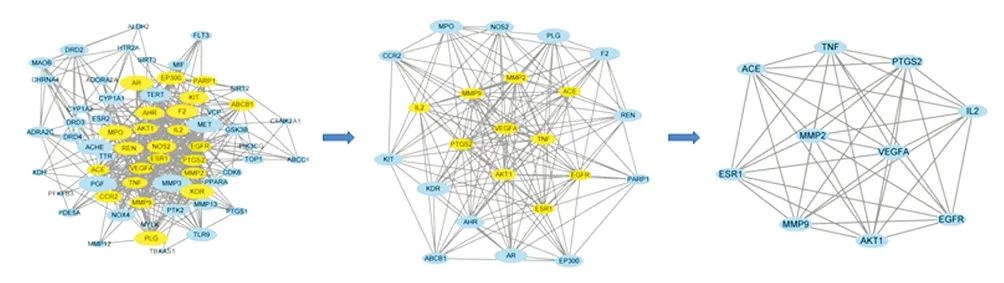
Figure 4 Cytoscape topology analysis
3.4 Molecular docking verification
Select the top VEGFA, TNF, AKT1, PTGS2, MMP9 target proteins of the core genes and the top 6 compounds (wogonin, isorhamnetin,kaempferol, quercetin, isoginkgetin, ginkgetin) Flavin) for molecular docking, select the lowest binding energy combination (Table 1) and use Pymol software for drawing (Figure 5). The lower the minimum binding energy, the higher the binding activity between the target protein and the active ingredient, indicating that the binding capacity between the two is better. The results show that the target protein has a strong binding ability with the main active ingredients of Capparis spinosa.
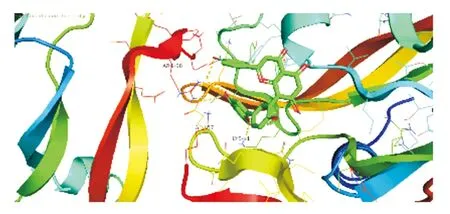
Figure 5E VEGFA- Isoginkgetin
3.5 Analysis of GO and KEGG pathways
GO analysis (Figure 6) shows that the BP processes involved include reactive oxygen species metabolic process, protein kinase B signaling, regulation of inflammatory response, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling, cellular response to drug.The CC process involves dopaminergic synapse, integral component of synaptic membrane, intrinsic component of synaptic membrane,and glutamatergic synapse, integral component of postsynaptic membrane, etc. MF process involves heme binding, tetrapyrrole binding, catecholamine binding, nuclear receptor activity, ligandactivated transcription factor activity, transcription coactivator binding, G protein-coupled amine receptor activity, transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity, metallopeptidase activity,etc. KEGG pathway analysis (Figure 7) shows that PI3K-Aktsignaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer, Human papillomavirus infection, and focal adhesion are involved, Rap1 signaling pathway,MAPK signaling pathway, MicroRNAs in cancer and other pathways.

Table 1 Results of molecular docking between core targets and active ingredients
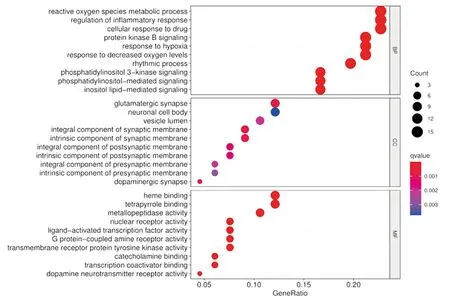
Figure 6 GO enrichment analysis

Figure 7 KEGG enrichment analysis
4. Discussion
Modern pharmacological studies have found that Capparis spinosa contains a wide range of biologically active compounds, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, steroids, terpenes and tocopherols [14], and their isolation and identification are mainly concentrated in the fruit.This study found that the main chemical components of Capparis spinosa for the treatment of SSC are wogonin, isorhamnetin,kaempferol, quercetin and so on. The protective effect of wogonin on liver fibrosis. Wogonin significantly reduced CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice and liver fibrosis of hepatic stellate cells activated by TGF-β1 [15]. Wogonin can more effectively inhibit the up-regulation of type I collagen and α-smooth muscle actin expression induced by TGF-β1, and can reduce Smad3 phosphorylation, thereby playing an anti-fibrotic effect in renal tubular epithelial cells [16]. Ismomusin inhibits the Smad3 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways mediated by TGF-β1, thereby reducing the formation of extracellular matrix(ECM) and autophagy, and has a protective effect on liver fibrosis[17]. Kaempferol injection can significantly reduce the number of SMA+ myofibroblasts, CD3+ T cells and CD68+ macrophages in damaged skin [18]. In addition, kaempferol can significantly reduce the mRNA levels of oxidative stress-related factors HO-1 and NOX2,and the mRNA levels of inflammatory and pro-fibrotic cytokines IL-6, TGF and TNF in hardened skin. Kaempferol can inhibit the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in SSc fibroblasts induced by oxidation, and reduce the apoptosis of SSC fibroblasts induced by oxidation [18]. Quercetin can inhibit the polarization of F4/80+/CD11b+/CD206+ M2 macrophages, and by antagonizing TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling, reducing the excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix and interstitial fibrosis, to improve renal fibrosis [19].
SSC endothelial dysfunction is its most important feature, which involves large blood vessels and microvessels. The progressive disorder of microcirculation leads to chronic tissue hypoxia and stimulates the release of angiogenic growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Compared with healthy people,SSC patients have higher serum VEGF levels [20]. Basic studies have shown that the total alkaloids of Capparis spinosa have a certain regulatory effect on the abnormal expression of VEGF and ET-1 in SSc [21]. IL-22 can make fibroblasts respond to TNF, and promote the phenotype of pro-inflammatory fibroblasts by promoting TNFinduced activation of keratinocytes. These results confirm a new role of keratinocyte-fibroblast interaction in skin fibrosis [22]. PTGS2 is also known as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and its role in endothelial function includes vascular reactivity and angiogenesis [23]. Studies have shown that in patients with elevated COX-2, in addition to elevated levels of TNF-α, the incidence of toe ulcers and arthritis is also high [24]. The main pathological feature of SSC is skin and internal organ fibrosis, which is caused by normal tissue structure changes and extracellular matrix (ECM) protein deposition. ECM components are degraded by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) [25].Domestic studies have shown that capparis total alkaloids can reduce the synthesis of Col-IV and improve SSc tissue fibrosis by regulating the imbalance of MMP-9/TIMP-1.
Pathway analysis showed that the treatment of SSC with Capparis spinosa may involve multiple pathways. Studies have shown that PI3K-Akt signaling pathway has the closest correlation and temporal pattern to skin fibrosis score. COMP, THBS1, THBS4, FN1 and TNC are the leading genes of PI3K-Akt pathway in skin fiber formation [26]. Tests have shown that BBEZ235 blocking PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway has a better inhibitory effect on dermal fibrosis, which suggests that vertical inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway may have therapeutic potential for SSC [27]. Viral infection is considered to be a common factor in the occurrence of SSC [28]. Although the role of HPV has not been evaluated so far, a screening of human papillomavirus infection in SSC women showed that multiple HPV infections in the SSC group.The frequency is twice that of the control group [29]. Proteoglycan can affect cell signal transduction, movement, adhesion, growth and apoptosis through various interactions between its core protein and glycosaminoglycans and extracellular matrix proteins, growth factors and chemokines [30]. Cell changes and enzyme activities in the process of tumorigenesis can change the composition and structure of proteoglycan, thereby changing its function, which may be related to the pathogenesis of SSC. Regarding the focal adhesion pathway, a study showed that the enhanced adhesion signal is closely related to the fibrotic phenotype of SSC fibroblasts. Blocking the adhesion signal or the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS)may be beneficial to control the observation in SSC Fibrosis [31].The Rap1 signaling pathway is related to many aspects of vascular development and endothelial cell biology [32], which is closely related to the degeneration of SSC skin endothelial cells. The three major categories of mammalian MAPK family include ERKs, c-jun amino-terminal or stress-activated protein kinases (JNK/SAPKs)and p38 kinase [33]. The p38MAPK signaling pathway is in the human α2(I) collagen mediated by TGF-βGenes play an important role in the regulation of normal skin fibroblasts and the structural up-regulation of type I collagen and fibronectin in SSC fibroblasts[34]. Professor Bagnato, G. believes that miRNAs are biologically more complex than just endogenous regulators of mRNA stability,and may also provide inflammatory signals like cytokines, further extending the role of miRNAs to participate in the pathogenesis of fibrotic diseases Direct regulator of the immune process [35].
In summary, the treatment of SSC with Capparis spinosa may be through various compounds such as wogonin, isorhamnetin,kaempferol, quercetin, etc., acting on VEGFA, IL-22, TNF, PTGS2,MMP2, MMP9, etc. Protein targets and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, proteoglycans and cancer, focal adhesions, Rap1 signaling pathways, MAPK signaling pathways, and microRNAs in cancer are effective. This study provides theoretical basis and data support for the follow-up study of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of SSC.However, due to objective reasons such as limited access to the database, there may be errors. The research team will continue to follow up this research in the future.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年6期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年6期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Systematic review of Shufeng Jiedu capsules for acute attack of chronic bronchitis
- Study on the mechanism of Shenling Baizhu Powder in the treatment of diarrhea-type irritable bowel syndrome based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Research on the possible molecular mechanism of Fructus cnidii to improve sleep based on network pharmacology
- Effect of pestle intervention in type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy on Keap1 / Nrf2 / ARE pathway and the relationship with oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the effect of cryoablation on lung cancer mice based on MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
- Effects of Qishen Yiqi dripping pills-containing serum on KATP channel opening and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hypoxic/reoxygenated H9C2 cardiocytes
