Effect of pestle intervention in type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy on Keap1 / Nrf2 / ARE pathway and the relationship with oxidative stress
FangWang, Hui Yang, Shun-Qi Liao, Yao Wang, Han Wang, Xi-Mei Weng , Ya-Ling Huang
1. Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610032, China
2. Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610075, China
ABST RACT Objective: To investigate the effect of pestle needle treatment on Nrf2 pathway and the relationship with oxidative stress in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Methods: Patients with DPN who met the inclusion criteria were randomly divided into control and test groups with 30 patients in each group in a 1:1 allocation ratio. Both groups were given basic treatment,and the pestle group was treated with needle pestle therapy 5 times a week for a total of 4 weeks of intervention. Serum SOD and GSH PX levels were examined by colorimetry before and after intervention; Serum Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway related factors expression levels were measured by ELISA; Keap1 and Nrf2 mRNA expression was determined by RTPCR. Results: Compared with the control group, SOD and GSH-Px in the test group were significantly increased, Keap1 expression was decreased, Nrf2 expression was increased,Keap1 mRNA expression was significantly decreased, and Nrf2 mRNA expression was significantly increased. Conclusions: the pestle needle may enhance the body's antioxidant capacity by modulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway to enhance the production of its downstream antioxidant enzymes SOD and GSH Px, thereby protecting and repairing the damaged peripheral nerves in DPN patients.
Keywords:Diabetic peripheral neuropathy Pestle needle Oxidative stress Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway
1. Introduction
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy,DPN) refers to the symptoms and/or signs of peripheral nerve injury in patients with diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus, DM), excluding neuropathy caused by other reasons. Among them, at least 50% of DM patients develop DPN [1-2]. DPN mainly affects the symmetrical sensory function of the distal extremities, and is an important cause of lower extremity ulcers and non-traumatic amputation. Current studies have found that oxidative stress is the initiating factor of DPN. In the state of hyperglycemia, reactive oxygen species(ROS) and advanced glycosylation end products (AGEs) increase significantly, weakening the body’s antioxidant defense capabilities,damaging tissue cells, and destroying vascular endothelial function.Cause ischemic nerve damage [3]. Among them, Keap1/Nrf2/ARE is the key pathway of oxidative stress. Whether the signal pathway can be regulated to inhibit oxidative stress, thereby protecting and repairing DPN nerve damage has become a research hotspot. The National Intangible Cultural Heritage Li's Pestle Needle is a secret method passed down from the family by Professor Li Zhongyu,a famous and old Chinese doctor in Sichuan Province. The pestle acupuncture therapy uses special needles and techniques to stimulate the special acupoints and acupoints on the body surface to act on the meridians and viscera to guide the movement of the meridians and promote the circulation of qi and blood in the meridians. The team’s previous research found that the clubbing can improve the sensory nerve function and clinical symptoms of DPN patients, and the patient’s compliance is high [4-5], but its mechanism of action is still unclear. From the perspective of oxidative stress, this study revealed the mechanism of pestle acupuncture treatment of DPN. The results are now reported as follows.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 General information
From April 2021 to September 2021, 60 inpatients meeting the inclusion criteria were selected from the Department of Endocrinology, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, and randomized to the control group and the clubbing group according to a 1:1 distribution ratio. An independent person conducts random groupings and uses a computer to generate random numbers (1 to 60). It is stipulated that subjects with odd numbers shall be included in the clubbing group, and subjects with even numbers shall be included in the control group. Then, seal the random number in an opaque envelope, and let the patient extract the sealed number. There were 30 cases in the clubbing group, including 17 males and 13 females, aged 59-75 (66.72±5.47) years old,diabetes course 2-18 (9.79±4.45) years, DPN course 1-9 (4.98±3.56)years; control There were 30 cases in the group, 16 males and 14 females, aged 49-75 (63.87±6.46) years old, diabetes course 3-18(10.75±3.67) years, DPN course 2-9 (5.43±2.46) years. There was no statistically significant difference in general information between the two groups of patients (P>0.05). The research design complies with the ethical standards of human trials and was approved by the ethics committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The ethical approval number is 2021KL-107. All patients signed an informed consent form before the intervention.
2.2 Diagnostic criteria
All patients conformed to the diagnostic basis for type 2 diabetes and DPN in the Chinese Diabetes Prevention and Control Guide of the Chinese Medical Association Diabetes Branch (2020) [6].
2.3 Inclusion criteria
(1) The patient meets the above diagnostic criteria; (2) The age is 18-75 years; (3) The person who is conscious and cooperating with the examination and treatment; (4) The person who voluntarily participates in the study and signs the informed consent.
2.4 Exclusion criteria
(1) Complicated with serious diseases of important organs; (2)Acute complications of diabetes; (3) Skin damage at the acupoint and pestle site; (4) Pregnant or lactating women.
2.5 Case elimination and termination
(1) Those who fail to follow the research protocol for routine treatment and pestle intervention; (2) Those who are unwilling to continue participating; (3) Those who have worsened or complicated other serious diseases.
2.6 Treatment methods
2.6.1 Control group
In the control group, α-lipoic acid (specification: 12 mL: 300 mg)was used on the basis of conventional hypoglycemic and lipidlowering treatments, and the administration method was intravenous drip, once daily.
2.6.2 Pestle needle group
Use pestle needle treatment on the basis of the control group
2.6.2.1 Pestle Needle
Instruments for pestle acupuncture therapy: including Kuixing pen,vajra pestle, Qiyao Hunyuan pestle, and five-star three pestle. (see Figure 1)2.6.2.2 Point selection with pestle and needle

Figure1 Pestle and needle therapy appliances
According to "Chu Needle" [7], "Acupuncture and Moxibustion" [8]and related diabetes and acupuncture expert consultation results, it is determined that the main point of Chu Needle is the Zhiyang Bazhen(the distance between Zhiyang and Geguan Point is eight). Array),Mingmen Eight Arrays (the eight arrays arranged by the distance between Mingmen and Zhishi acupoint), Heche Mingqiang segment(total 7 lines, drawn by 0.5, 1.5, and 3 inches on the left and right sides of the center line) Line) and matched with Zusanli, Sanyinjiao,Taixi and Yongquan. (See Figure 2)2.6.2.3 Pestle needle operation technique
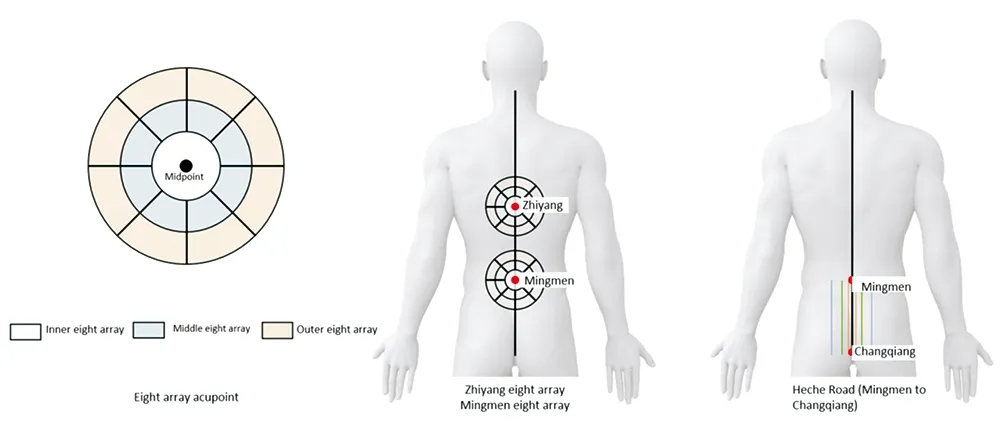
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of acupoints
The method of applying the pestle is in accordance with the operating specifications described in the "Puzzle Needle". According to the characteristics of acupuncture points, select the appropriate operation technique, and each operation technique takes 7 times as a cycle. (1) The patient lay prone on the bed and repeatedly tapped the Zhiyang Bazhen acupoint with the point of a five-star threepoint pestle, like a bird pecking. It takes about 3-5 minutes to press until the skin flushes. Use the needle handle of the Qiyao Hunyuan pestle to close the skin of the surgical acupoints, and perform the Tai Chi movement from the middle palace to the outer eight formations. Repeat the operation for about 3-5 minutes. (2) The operation technique of the eight acupoints of Mingmen is the same as 1. (3) Use the tip of the Qiyao Hunyuan pestle to travel on the 7 lines of the Mingqiang section of the Heche, and do the splitting technique of pushing left and right, and pushing up and down, for about 5 minutes. Then use the five-star three-point pestle to tap 7 lines repeatedly for about 2 minutes. (4) Take the supine position,hold the vajra pestle to reach Zusanli with the point of the pestle,move the pestle downward, and then slowly lift it up, but the tip of the needle cannot leave the skin, open and close. Approximately 2-3 minutes; then hold the Kuixing pen to do the tapping technique for approximately 2-3 min; finally hold the five-star three pestle needle handle for approximately 2-3 min. (5) Sanyinjiao, Taixi, and Yongquan Chu acupuncture are the same as Zusanli. The pestle acupuncture treatment is about 30 minutes each time once a day, 5 times a course of treatment, 2 days of rest during the treatment, a total of 4 courses of treatment.
2.7 Observation indicators
Detection of oxidative stress related indicators: colorimetric method to detect serum SOD, GSH-Px content; ELISA method to detect serum Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signal pathway related factors expression level; RT-PCR to detect Keap1, Nrf2mRNA expression. 5ml of blood was collected before and after treatment and sent to the central laboratory of our hospital for testing.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Use Spss22.0 statistical software to analyze the data.±s describes continuous variables, and absolute numbers and percentages describe categorical variables. Statistical analysis was performed by t test, and P<0.05 was statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1 Comparison of serum SOD and GSH-px levels before and after treatment in the two groups
Compared with before treatment, SOD content in the control group and clubbing group increased significantly after treatment (t=-2.467,P=0.043; t=-3.642, P=0.008), and serum GSH-px content also increased significantly (t =-4.163, P=0.004; t=-7.728, P<0.001);After treatment, compared with the control group, the content of SOD and GSH-px in the clubbing group were significantly increased(P<0.05). (See Table 1)
3.2 Comparison of serum Keap1 and Nrf2 factor levels before and after treatment in the two groups
Compared with before treatment, the content of Keap1 and Nrf2 in the control group did not change significantly after treatment(t=1.946, P=0.093; t=-2.072, P=0.077), and the expression of Keap1 in the pestle acupuncture group was significantly reduced (t=8.039,P <0.001), the content of Nrf2 was significantly increased (t=-7.874,P<0.001); after treatment, the content of Keap1 in the clubbing group was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the content of Nrf2 in the clubbing group was significantly higher than that of the control group (P< 0.05). After treatment, the content of Keap1 in the clubbing group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the content of Nrf2 was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). (See Table 2)
3.3 Comparison of serum Keap1 and Nrf2mRNA expression levels before and after treatment in the two groups
Compared with before treatment, the expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 mRNA in the control group did not change significantly after treatment (t=0.989, P=0.356; t=-0.674, P=0.0.50), and the expression of Keap1 mRNA in the pestle needle group was significantly reduced(t= -2.629, P=0.002), the expression of Nrf2mRNA was significantly increased (t=4.640, P=0.047); After treatment, the expression of Keap1mRNA in the clubbing group was significantly lower than that of the control group, and the expression of Nrf2mRNA was significantly higher than that of the control group (P <0.05). (See Table 3)
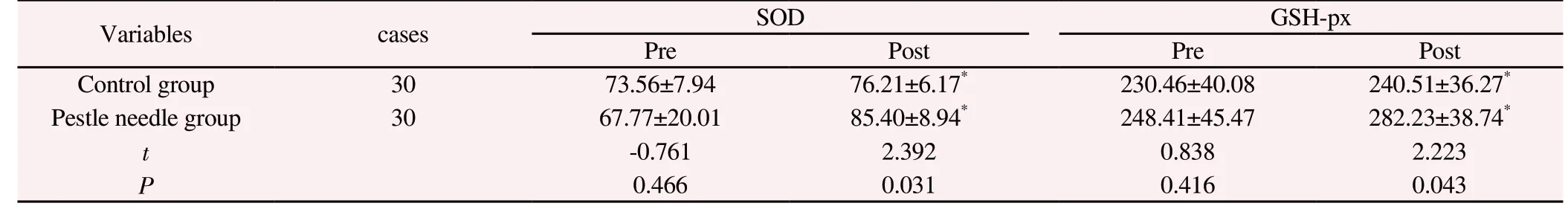
Table 1 SOD and GSH-px levels before and after treatment in the two groups
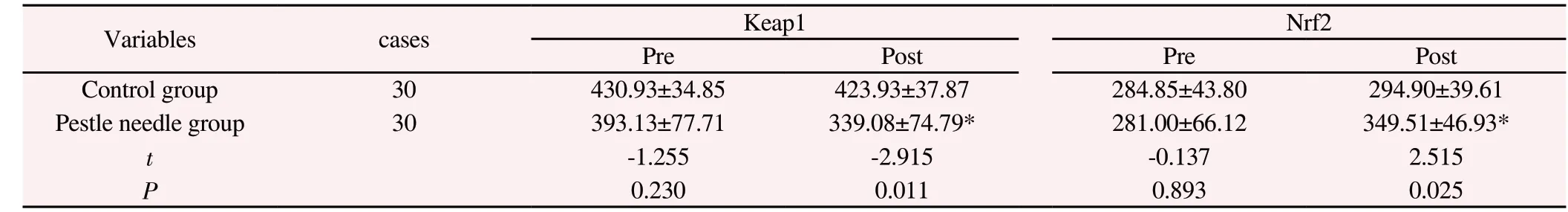
Table 2 Keap1and Nrf2 levels before and after treatment in the two group
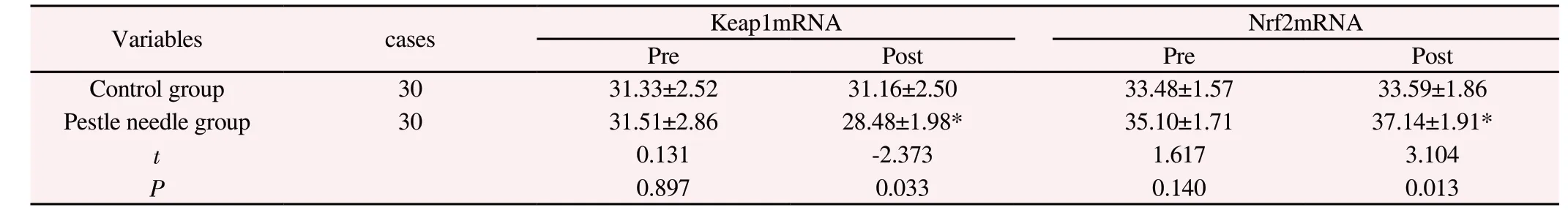
Table 3 Keap1mRNA and Nrf2mRNA levels before and after treatment in the two groups
4. Discussion
DPN is characterized by diffuse damage to peripheral nerve fibers, leading to numbness, pain, and loss of sensation. The unique external treatment of Chinese medicine has achieved good results in DPN treatment through a multi-target and holistic treatment plan[9-11]. The pestle acupuncture acts on the meridian qi and blood of the muscles on the body surface, so that the evil qi is removed without hurting the righteousness of the muscles and fascia. It is also long of acupuncture and massage. It is mainly used for DPN and other diseases with muscle arthralgia as the main symptom.This study selected Zhiyang Bazhen acupoints, Mingmen Bazhen,and Heche Mingqiang as the basic prescriptions, and applied special pestle methods (clicking, lifting, separating, opening and closing)to stimulate meridian qi, guide the movement of meridian qi, and promote The circulation of qi and blood in the meridian can achieve the functions of nourishing qi and blood, calming yin and yang,nourishing the spleen and kidney, and promoting blood circulation and dredging collaterals. The team’s previous research found that[12,13], clubbing therapy can reduce the superficial peroneal nerve of the feet and the front L4/L5/S1 section of the middle of the ankle. The rapid current sensory threshold and the vibration sensory threshold of the first toe abdomen and instep of the patient's feet, but the mechanism of action has not yet been elucidated.
Oxidative stress is caused by hyperglycemia and is considered to be the initiating factor of the pathogenesis of DPN [14-16].Hyperglycemia generates oxidative stress through the selfoxidation of glucose, which increases the production of ROS and reactive nitrogen substances. Oxidation substances exceed the antioxidant capacity, which reduces the body's antioxidant defense ability [17]. ROS damages nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and other macromolecules in nerve cells through oxidative stress, resulting in nerve cell damage [15]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px) and glutathione (GSH) are one of the main antioxidant enzymes that protect cells from ROS damage [18].Previous studies have shown that in peripheral blood cells and RSC96 cells treated with high glucose, the content of antioxidant enzymes (GSH, SOD, GSH-Px) decreases, while malondialdehyde(MDA) and ROS accumulate [17]. However, the results of this study indicate that the pestle needle can increase the content of antioxidant enzymes, thereby antagonizing oxidative stress. The results in Table 1 show that the pestle needle effectively increased the serum SOD and GSH-px levels in DPN patients. It indicates that the treatment of DPN with pestle needle may increase the content of antioxidants in the serum and maintain the balance of ROS in patients with DPN, so as to achieve the effect of anti-oxidative stress.
Nuclear factor-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and its gene targets are key components of the endogenous antioxidant system [19,20]. Under the normal physiological state of the body, Nrf2 is in a stable state combining with Keap1 in the cytoplasm. When cells are exposed to oxidants and poisons, Nrf2 is released from Keap1, transferred to the nucleus, and combined with antioxidant response elements (ARE) to induce gene transcription of downstream antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and GSH-px, thereby Protect cells from damage caused by ROS [21,22]. Studies have found that promoting the expression of Nrf2 has been shown to have a protective effect on DM and DPN induced by streptozotocin (STZ) [23]. The results of this study show that clubbing can increase the level of Nrf2 in the serum of patients with DPN. In addition, the needle club can block the high-level expression of Keap1 in the serum of DPN patients. From a genetic point of view, we have deeply studied the mRNA expression of Nrf2 and Keap1. Knurling significantly increased the expression of Nrf2 mRNA in the serum of patients with DPN, and decreased the expression of Keap1 mRNA, indicating that the knurling has a regulatory effect on the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE pathway.
In summary, the results of this study indicate that the protective effect of the club against oxidative damage in patients with DPN is related to the activation of the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE pathway. This study provides clinical experimental evidence. Animal experiments can be carried out in the next step to further explore the mechanism of action of pestle needle therapy on DPN from the molecular level and morphology.
Authors’ conflict of interest description
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author’s Contribution
Wang Fang and Yang Hui are responsible for project design and clinical trial guidance; Wang Fang and Liao Shunqi are responsible for article writing; Wang Han and Wang Yao are responsible for data collection and statistical analysis; Weng Ximei and Huang Yaling are responsible for patient treatment; Wang Fang is responsible for data review.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年6期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年6期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Systematic review of Shufeng Jiedu capsules for acute attack of chronic bronchitis
- Study on the mechanism of Shenling Baizhu Powder in the treatment of diarrhea-type irritable bowel syndrome based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Research on the possible molecular mechanism of Fructus cnidii to improve sleep based on network pharmacology
- Network pharmacological study and molecular docking verification of Capparis spinosa in the treatment of systemic sclerosis
- Experimental study on the effect of cryoablation on lung cancer mice based on MAPK/ERK signaling pathway
- Effects of Qishen Yiqi dripping pills-containing serum on KATP channel opening and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in hypoxic/reoxygenated H9C2 cardiocytes
