Accuracy of shoulder joint injections with ultrasound guidance:Confirmed by magnetic resonance arthrography
INTRODUCTION
Intra-articular glenohumeral joint injections are essential procedures for treating various shoulder disorders at clinical settings,such as frozen shoulder,osteoarthritis,and rheumatoid arthritis[1].These injections are distinguished from subacromial injections commonly used for treating subacromial bursitis,rotator cuff tears,and impingement syndrome.Accurate intra-articular injections of drugs can provide good clinical outcomes and enhance patients’ satisfaction with treatment.Furthermore,accurate intra-articular injections of lidocaine,commonly referred to as the lidocaine test,help develop accurate clinical diagnoses.Conversely,injections at erroneous locations may cause damage to nerves,vessels,muscles,or ligaments around the shoulder,and inaccurate injections of lidocaine may mislead the clinical assessment.
Various shoulder injection techniques have been used by orthopedic surgeons or radiologists in their efforts to perform arthrograms.These injection techniques include:(1)blind injections with structures that can be palpated from the body surface,such as the acromion and coracoid process;and(2)imageguided injections with fluoroscopic or ultrasonic guidance,using the anterior,posterior,or supraclavicular approach[2-5].
The words of Proverbs 11 came to mind: “A good man [person] is guided…and directed by honesty…Be sure you know a person well before you vouch9 for his [or her] credit
Conversely,magnetic resonance arthrography(MRA)is a valuable tool used for detecting rotator cuff tears or anterior shoulder instabilities associated with anterior labrum and capsular pathologies.Some studies have reported that MRA is superior to magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)and computed tomography arthrography(CTA)in detecting lesions associated with anterior shoulder instabilities[6,7].Precise imaging of these shoulder abnormalities can help plan operative procedures.
A fluoroscopy-guided shoulder injection has been extensively used in conjunction with MRA.This technique was first reported by Baertin 1933[8],while other studies have reported that the accuracy of fluoroscopy-guided shoulder injections is in the range of 62%-100%[9-11].However,fluoroscopyguided injections expose both the examiners and patients to radiation.When MRA is considered helpful for diagnosis,outsourcing the MRA examinations to special institutions is common.However,in Japan,only a few institutions offer MRA examinations because of the lack of dedicated radiologists who can conduct arthrograms.Accordingly,orthopedic surgeons themselves are often needed to perform intraarticular injections before MRI examinations.In these cases,fluoroscopy and MRI reservations are required that is cost-demanding and time-consuming.Therefore,at our institution,we typically perform ultrasonography-guided shoulder injections in conjunction with MRA.The ultrasonographic examinations can be performed before MRI.These procedures are not as time-consuming as the injections performed with fluoroscopy.Recently,ultrasonography has become a widely used diagnostic tool in the field of orthopedics because of its availability,safety,and high diagnostic potential.Particularly,the shoulder joint is one of the bodily areas for which ultrasonography is most useful.Ultrasonography can detect tendons,fluid around the biceps or subacromial bursa,and the contours of the glenohumeral joint clearly that it enables early detection of rotator cuff or intra-articular pathologies,such as tears and fractures[12].Moreover,ultrasound-guided injections have been gaining attention due to their accessibilities and safety withoutradiation exposure and direct observation of the needle[13].Although some reports have described the convenience of ultrasound-guided injections,no reports have evaluated its accuracy.
20.Marquis of Carabas: A marquis is a nobleman in various countries such as France, England, and Germany, usually ranking above a count or earl and below a duke. Visit this offsite link to see a table of Hereditary Western European Titles of Nobility.
40. She killed, cooked, and ate him: The witch is a cannibal. Cannibalism105 is one of the most reviled106 crimes in the world. It is considered the quintessential expression of savagery107 and evil. Charges of cannibalism have long been used as justifiable108 reasons for enslaving or destroying a population or person.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
After everyone had gone, my mother told me, You want to be the same as American girls on the outside. She handed me an early gift. It was a miniskirt in beige tweed. But inside you must always be Chinese. You must be proud you are different. Your only shame is to have shame.
Injection technique
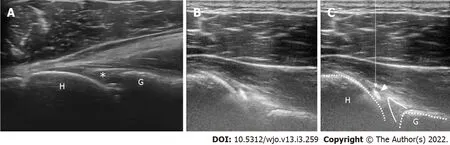
All injections were performed by an experienced surgeon(M.T.).The procedures were performed with the patients in the upright sitting position with their shoulders at the neutral rotation position.Ultrasound examinations were performed using a portable equipment(HI VISION Avius,HITACHI,Japan).The linear ultrasonic probe was operated within a variable frequency range(,6–14 Hz)and was held horizontally and placed over the posterior aspect of the shoulder(Figure 2),allowing the detection of the glenohumeral joint space(Figure 3A).A 23-gage cathelin needle was inserted using an out-of-plane technique toward the gap between the humeral head and glenoid rim,and 12 mL lidocaine(1%)was administered.In the out-of-plane technique,observing the needle tip at all times during injection is difficult;however,the movement of the needle tip can be detected through the movement of soft tissues.Furthermore,as long as the needle does not deviate from the center of the ultrasound probe,the needle tip theoretically reaches the target in the glenohumeral joint.When the needle tip reaches the joint,the drug can be smoothly injected,and simultaneously,the flow of the fluid can be confirmed in the joint on the ultrasound image(Figure 3B and C).
MRI scans were obtained within 60 min after the injections.
RESULTS
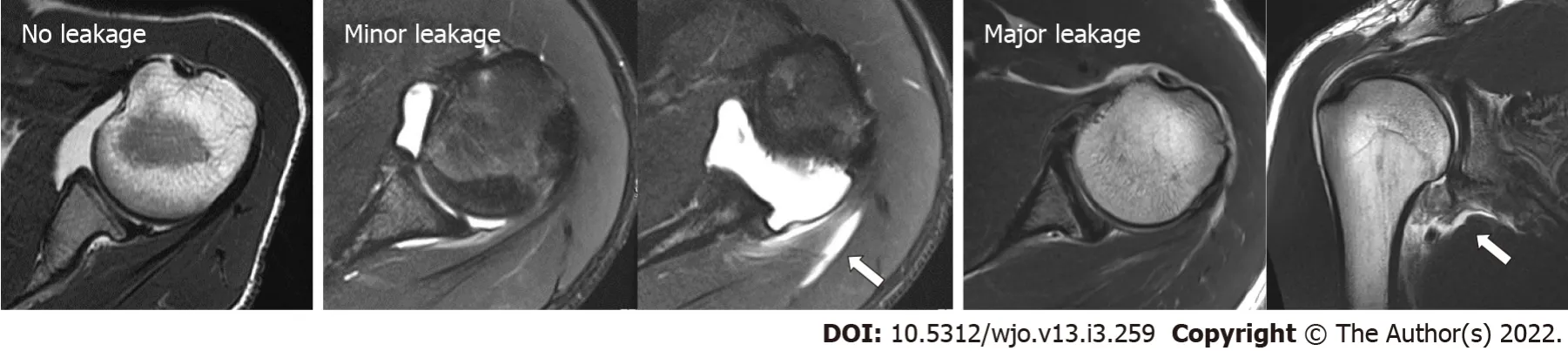
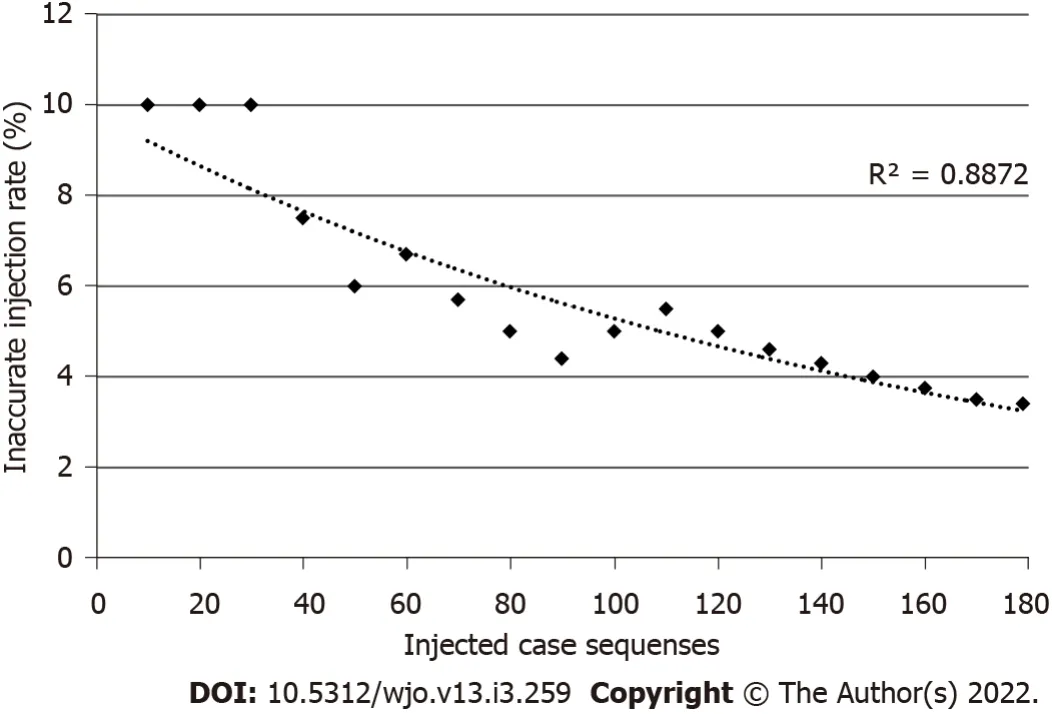
No patient complained of poor physical conditions after the injections.Additionally,no neurological disturbances were observed.From the 179 injections,163(91.0%)were completely administered in the glenohumeral joint and were classified as “no leakage.” Furthermore,intra-articular injection with some leakage out of the rotator cuffs was detected in 10 shoulders(5.6%),and these were classified as “minor leakage”(Table 1).We could detect anterior labrum and capsular pathologies in 96.6%(173/179 shoulders)of the tested cases.Six shoulders were classified as “major leakage.” In these cases,the leakages were mostly observed around the axillary area.No significant differences in the accuracy were observed between the right and left shoulders.Regarding the inter-rater reliability,the kappa coefficient was 0.925,indicating consistency in the evaluations by both examiners.Regression analysis of the inaccurate injection rate showed that the curve was logarithmic with a downward trend(R= 0.887;<0.001)(Figure 4).Three(50%)of the six inaccurate injections that were classified into “major leakage”were observed in the first 30 injections.This indicated that the accurate injection showed a leaning effect.

DISCUSSION
An intra-articular shoulder injection is an important technique for diagnosing and treating various shoulder disorders.However,it is reported:(1)that these injections are more difficult to perform than other joint injection types;and(2)that theaccuracy of injection into the glenohumeral joint is poor when performed without image guidance.
Some studies have reported about the accuracy and techniques of shoulder injection.Cunnington[2]have compared the accuracy of ultrasound-guided injections conducted by research fellows with that of blind(clinical examination-guided)injections conducted by rheumatology consultants for the shoulders,elbows,knees,and ankles and found that ultrasound-guided injections were significantly more accurate than blind injections.Moreover,they have reported that the accuracy of blind injections to the glenohumeral joint was only 40%(8/20 shoulders),which tended to be more difficult than other joint injections.Tobola[14]have reported on the technique and accuracy of blind injections using theanterior,posterior,and supraclavicular approaches implemented by different providers.As indicated,the anterior approach was the most accurate(22/34 shoulders,64.7%)in shoulder cases,regardless of the experience of the clinicians who performed them.Patel[4]have evaluated the accuracy of the ultrasound-guided posterior approach on fresh cadaver shoulders and reported that the accuracy was 92.5%(37/40 shoulders)and showed no significant differences owing to the clinical experiences of the injectors.Most injection accuracy reports have been associated with the use of fluoroscopic images(acquired after the injection procedures)to confirm the intra-articular contrast.Sethi[15]performed injections using the blind approach with an accuracy of 26.8% with fluoroscopic confirmation.In this study,we evaluated the accuracy of intra-articular shoulder injections using the ultrasound-guided posterior approach in conjunction with MRA images acquired from 179 shoulders(150 patients)for the preoperative diagnosis of anterior shoulder instabilities.
Intra-articular glenohumeral joint injections are essential procedures in a clinical setting of shoulder surgery.In general,a fluoroscopy-guided shoulder injection has been extensively used.
They lived together in peace and harmony, although they were very different in character, the man being good-natured and honest, and the wife being greedy and quarrelsome when anyone came her way that she could possibly quarrel with
In current clinical settings,a fluoroscopy-guided injection technique is still extensively used when CTA or MRA is available.Dépelteau[9]have reported the accuracy of fluoroscopy-guided injections.In these,59/65 shoulders(90.8%)were successfully injected on the first attempt,four shoulders(6.2%)on the second attempt,and one(1.5%)shoulder on the third attempt.A fluoroscopyguided technique allows multiple punctures until accurate injection is achieved given that judging whether the contrast material has been injected into the joint during the injection is possible.Conversely,in an ultrasound-guided technique,only indirect information,such as the patient’s pain or injector’s sensation(,injection pressure),can determine whether the injection is accurate or not.Another disadvantage of an ultrasound-guided injection technique is that detecting the glenohumeral joint space in obese patients it could be difficult because of deep attenuation of ultrasound,unlike the fluoroscopy-guided injection.In such cases,passive movement of the upper arm during ultrasound examination could make detecting the joint space easier.Eventually,we could perform intra-articular injections into the glenohumeral joint with the same or higher accuracy than that reported previously in fluoroscopy-guided injections.
Ultrasound-guided injections have some benefits.They allow more accurate intra-articular injections based on the visualization of the needle’s position.Additionally,the portability of the ultrasound equipment could allow the execution of the injections quickly in the examination room;thus,reserving a fluoroscopy room is not needed,and there is no risk of radiation exposure for both doctors and patients.Additionally,the ultrasound-guided injection technique is a simple procedure and is considered superior to fluoroscopy-guided injection techniques in terms of time and cost-effectiveness[16].
In this study,we performed injections using the ultrasound-guided out-of-plane technique;however,observing the needle path continually from the insertion point was more difficult than that using the inplane technique.Therefore,fulfilling the aim of this injection is necessary,that is,the clear detection and visualization of the gap between the glenoid rim and humeral head achieved by holding the probe in a stable manner at the target position.Conversely,unlike the in-plane technique,in the out-of-plane technique,the injector does not need to change the hand sides that hold the ultrasound probe or the syringe,depending on the side the patient’s shoulder.Correspondingly,we can always perform injections using the same procedure.In a blind injection technique,an anterior approach was reported to be the most accurate.In previous reports,fluoroscopy-guided injections had been performed using the anterior approach.This is because landmarks around the shoulder palpated from the anterior body surface,such as the acromion and coracoid process,can provide helpful indications for the injection.However,in an ultrasound-guided injection technique,a posterior approach may allow easier detection of the joint space,given that there are no structures on the posterior shoulder.
The study strengths are the patient size and the technique used to accurately evaluate the accuracy of intra-articular shoulder injections.This study represents the largest patient size among all available reports that targeted the accuracy of injection techniques.In previous reports,fluoroscopy images were used to evaluate the condition of the joint and the accuracy of the injection;however,MRA images could allow us to clearly evaluate intra-articular contrast and leakage outside the joint because identifying the location of the contrast material in a three-dimensional view is possible.
They belonged to her daughter; and surely no one who had such adaughter could be silly. The mother was like a fountain ofquestions; and the daughter, who listened but never spoke8, mighthave passed for the beautiful maid of the fountain. How charming shewas! She was a study for the sculptor to contemplate9, but not toconverse with; for she did not speak, or, at least, very seldom. Has the pope a great family? inquired the lady.
This study has some limitations.First,this study evaluated the accuracy of ultrasound-guided injections performed by a single shoulder surgeon.Whether inexperienced physicians,surgeons who do not specialize in shoulder surgeries,or trainee surgeons who specialize in shoulder surgeries could equally achieve accurate injection outcomes is unclear.Additional studies,including the participation of injectors with different experiences and comparisons with other image-guided techniques or approaches are needed.Second,this study has no control group with blind injections.MRA is an essential test for patients with anterior shoulder instability to detect capsular and labral pathologies.A control group could not be established because of the potential disadvantage to the patients if ultrasound guidance is not used.
Kuratani K performed the research,contributed to the analysis and wrote the paper;Tanaka M designed and performed the research and supervised the report;Hanai H supervised the statistical analysis;Hayashida K designed the research and supervised the report.
CONCLUSION
Ultrasound-guided intra-articular glenohumeral injections using the posterior approach were an accurate procedure.Of the 179 shoulders,163(91.0%)were accurately injected,and 173/179 injections were conducted intra-articularly and provided useful MRA images to detect abnormalities in the glenohumeral joint.We encourage using ultrasonic guidance during shoulder injections because it is a simple and cost effective procedure with acceptable accuracy.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
There have been various reports of the accuracy of shoulder injections.However,no reports have neither evaluated injections into the shoulders of living patients nor assessed these using MRA images.In this study,intra-articular shoulder injections that can provide helpful information on labrum and capsular pathologies were performed on 173/179 shoulders(96.6%).The accuracy was equally good or better than those reported in previous cadaveric studies[4].
Research motivation
At our institution,we typically perform ultrasound-guided shoulder injections for magnetic resonance arthrography(MRA).The accuracy of ultrasound guided shoulder injection has not been reported.
Research objectives
To evaluate the accuracy of ultrasound-guided shoulder injections with MRA images.
Research methods
We reviewed the shoulder MRA images of patients with anterior shoulder instability and classified the intra-articular condition in three groups and calculated the injection accuracy.Research results
Patients were not required to give informed consent to this study because the analysis used clinical data that were obtained after each patient agreed to treatment by written consent.
Research conclusions
The ultrasound-guided shoulder injection was shown to be a very accurate procedure.
Research perspectives
Further,it is necessary to evaluate whether this technique is effective even for inexperienced examiners.
She made a bread-soup as well as she possibly could, and when it was done, she fetched her gold ring from her little room, and laid it in the tureen in which the soup was to be served up
FOOTNOTES
Third,the subjects of this study were patients with anterior shoulder instabilities in a relatively young age.We have not assessed the accuracy of intra-articular injections for other shoulder disorders,such as osteoarthritis,rheumatoid arthritis,and frozen shoulders.An ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection could be more difficult for older patients owing to capsular contractures or the presence of osteophytes.
This research has been approved by the IRB of the corresponding author’s affiliated institution.
This study was designed to evaluate the accuracy of ultrasound-guided glenohumeral joint injections using a posterior approach confirmed using MRA.
We retrospectively reviewed the MRA images of patients with recurrent anterior shoulder instability.This study has been approved by the Internal Review Board of the corresponding author’s affiliated institution.We excluded patients with rotator cuff tears and posterior shoulder instabilities and those who underwent surgeries.In total,179 shoulders of 150 patients(including 103 right and 76 Left shoulders;160 males and 19 females;average age of 20.5 years;age range,14–63 years)were included in this study.Injections were performed with ultrasound guidance using the posterior approach,followed by MRI examinations(Magnetom Spectra 3T;Siemens Japan,Tokyo,Japan).Two shoulder surgeons,except for the injector,evaluated the transverse relaxation(T2)-weighted images of axial planes and classified the intra-articular condition of the injected contrast into three groups based on one of the three following scenarios.“No leakage” indicates injection into the glenohumeral joint without evidence of leakage.“Minor leakage” indicates intra-articular injections with some leakage outside the posterior rotator cuffs.“Major leakage” indicates inaccurate injection with severe/mass leakage without any contrast into the glenohumeral joint.Diagnosing joint pathologies in the last case was impossible(Figure 1).The chi-square test was used to compare the injection accuracy of the right and left shoulders.The inter-rater reliability between two assessors was evaluated by calculating Cohen’s kappa coefficient.Moreover,the learning curve was assessed by determining the inaccuracy rate relative to the total cases.We defined inaccurate injection rate as the total number of “major leakage” divided by the total number of cases that was recorded every 10 cases and examined the correlation between the inaccurate injection rate and number of cases.This was analyzed using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient.All statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences(version 26;IBM,NY,United States),and P values of less than 0.05 were used to denote statistical significance.
From the total of 179 injections,163(91.0%)were completely administered in the glenohumeral joint.In addition,intra-articular injection with some leakage was detected in 10 shoulders(5.6%).
We have no financial relationships to disclose.
Men have a strong, firm tread, so that if they happen to walk over peas not one will stir, but girls trip, and slip, and slide, so that the peas roll all about
No additional data are available.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See:http://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Japan
Kosuke Kuratani 0000-0002-2874-9254;Makoto Tanaka 0000-0001-6461-1642;Hiroto Hanai 0000-0001-5549-005X;Kenji Hayashida 0000-0003-2166-2735.
Lo, and behold10! the spindle leapt from her hand and rushed out of the room, and when she had sufficiently11 recovered from her surprise to look after it she saw it dancing merrily through the fields, dragging a long golden thread after it, and soon it was lost to sight
Zhang H
For that very reason, just before bedtime, Mother tip-toed quietly to Kelly’s room to lay out the little blue nightgown and turn down the bed. But she stopped in the doorway37, surprised. Someone had already been there. The nightgown was laid neatly across the bed and a small red race car rested next to it on the pillow.
A
Zhang H
 World Journal of Orthopedics2022年3期
World Journal of Orthopedics2022年3期
- World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Impact of enhanced recovery pathways on safety and efficacy of hip and knee arthroplasty:A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Surgical treatment of femoral deformities in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia and McCune-Albright syndrome:A literature review
- Plate vs reverse shoulder arthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures:The psychological health influence the choice of device?
- Diagnostic role of Xpert-MTB RIF assay in osteoarticular tuberculosis:A retrospective study
- Comparative study of intertrochanteric fracture fixation using proximal femoral nail with and without distal interlocking screws
- Ilizarov bone transport combined with the Masquelet technique for bone defects of various etiologies(preliminary results)
