Identification of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-related microRNAs based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis
Yan-Ning Wei, Qi-Sheng Su
1School of public health, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China.2Department of Clinical Laboratory, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China.
Abstract
Aim of this study was to identify potential microRNAs associated with the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.GSE36682 was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO), and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was constructed.The microRNA co-expression module was extracted from the network by WGCNA R software package.Hub microRNAs of module were Screened.miRNet was used to construct microNA-mRNA network and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)analysis was performed with the target genes in the network.917 microRNAs were included and five co-expression modules were identified.Blue and turquoise modules were associated with metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.KEGG results showed that blue and tturquoise modules were involved in six pathways: Pathways in cancer, p53 signaling pathway,Glioma, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Prostate cancer and Neurotrophin signaling pathway.TP53 occupies an important position in the network.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma; microRNA; WGCNA; metastasis; TP53
Introduction
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common malignant tumors that occurs at the top and lateral wall of nasopharyngeal cavity.It occurs mostly in southern China, especially in Guangdong Province, so it is called "Canton tumor".The formation,invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a multifactorial process, which is closely related to genetic factors, viral infection (mainly Epstein-Barr virus, EBV) and environmental factors[1].
In recent years, the effect of epigenetic modification on tumorigenesis and development has been paid more and more attention.As an important part of epigenetic modification, the regulation of non-coding RNA is widely involved in post-transcriptional regulation, and has been reported in cancer for many times.microRNAs (miRNA) are small (20-24 nucleotides)non-coding RNAs that are widely distributed in nature and regulate protein expression at transcriptional or post-transcriptional levels by incompletely complementary pairing with the 3'UTR region of multiple target genes usually [2].While miRNA-target interactions increased protein levels have also been reported [3].MiRNAs can form a complex network of regulatory systems to regulate a variety of RNA, and there is a certain degree of cell specificity.MiRNAs can regulate a wide range of biological processes, such as cell cycle, stress response, cell differentiation, cell apoptosis, cell migration and invasion.
Current studies have shown that microRNAs play an important role in the occurrence and development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[4-6].It is necessary to Screen microRNAs that play a key role in nasopharyngeal carcinoma for understand the mechanism of the occurrence and development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) is a systems biological method of mining module information from chip or sequencing data [7].In this method, modules are defined as a group of genes with similar expression patterns and are associated with phenotypic traits.In our knowledge, there have been no reports of WGCNA of miRNA expression data for nasopharyngeal carcinoma.In this study, we used WGCNA to construct a co-expression network of microRNAs and identify the microRNAs module related to its clinical phenotype, and identify hub microRNAs for further basic or clinical research of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Material and Methods
microRNA microarray of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
The nasopharyngeal carcinoma’s microRNA (miRNA) expression data of GSE36682 was obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).GSE36682 (platform: GPL 15311, Human miRNA 1K) includes 62 nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues (with complete clinical information) and 6 normal nasopharyngeal mucosa tissues (without clinical information), 62 samples of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissue were included into the study (Table 1).

Table 1 Information of nasopharyngeal carcinoma samples in GSE36682
Co-expression Module Analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
WGCNA was used to study the co-expression module of miRNAs associated with clinical traits of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Scale independence and average connectivity analysis of modules with different power values are performed to determine the soft threshold of module analysis.The power values are set to 1 to 30, and then the values of scale independence and average connectivity are generated based on these power values.The minimum module size is 30.
Modular Feature Analysis Based on clinical trait of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Through GEO database, we obtained the gender, age, maximum diameter of lymph node, survival time and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients in GSE36682.The module-trait relationship was calculated according to the correlation between modules and traits; the module significantly related to individual traits was determined (P< 0.05); then the microRNAs in important modules were output, and hub microRNAs in important modules were screened according to gene significance values (GS) and module membership values (MM) for further analysis.
Construction of miRNA-mRNA network based on miRNet
miRNet (https://www.mirnet.ca/) is a tool suite designed for comprehensive analysis and functional interpretation of miRNAs by Xia Lab [8].In this study, miRNet was used to construct miRNAsmRNA regulatory network.The hub microRNAs in clinical phenotyperelated modules are introduced into miRNet.The target genes of miRNAs are predicted based on miRanda algorithm [9].The miRNA-mRNA regulatory network is constructed and the genes in the network are enriched and analyzed by KEGG pathway options.
Results
Analysis of Co-expression Module
917 microRNAs and 62 samples were included to WGCNA.In order to ensure scale-free network, this study chooses a soft threshold of beta= 3 (scale-free R2= 0.884).The minimum module size is 30, and the combined cutting height is 0.25.Finally, five modules were identified(Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 2).
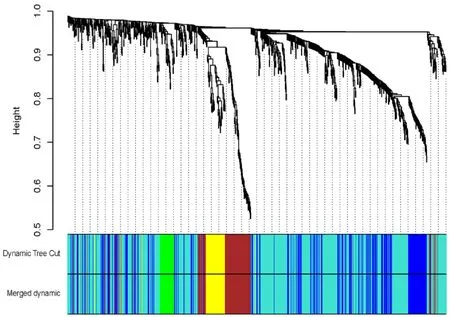
Figure 1 miRNA modules identified by Weighted gene co-expression network analysis

Figure 2 Network heatmap plot of all miRNA in GSE36682

Table 2 miRNA module of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Modular-trait relationship analysis based on clinical trait
Through module-trait relationship analysis, blue (included 220 miRNAs) and turquoise (included 505 miRNAs) modules were identified to be highly correlated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis (Figure 3), and there was a great similarity between the two modules (Figure 4).According to the critical criteria (|MM| > 0.8 and |GS| > 0.2), 31 hub miRNAs in blue and 16 in turquoise modules were identified (Table 3, Table 4).

Figure 3 Module-trait relationships A.Relationships of consensus module eignegenes and different trait of nasopharyngeal carcinoma; B.blue module-trait relationships; C.turquoise module-trait relationships.
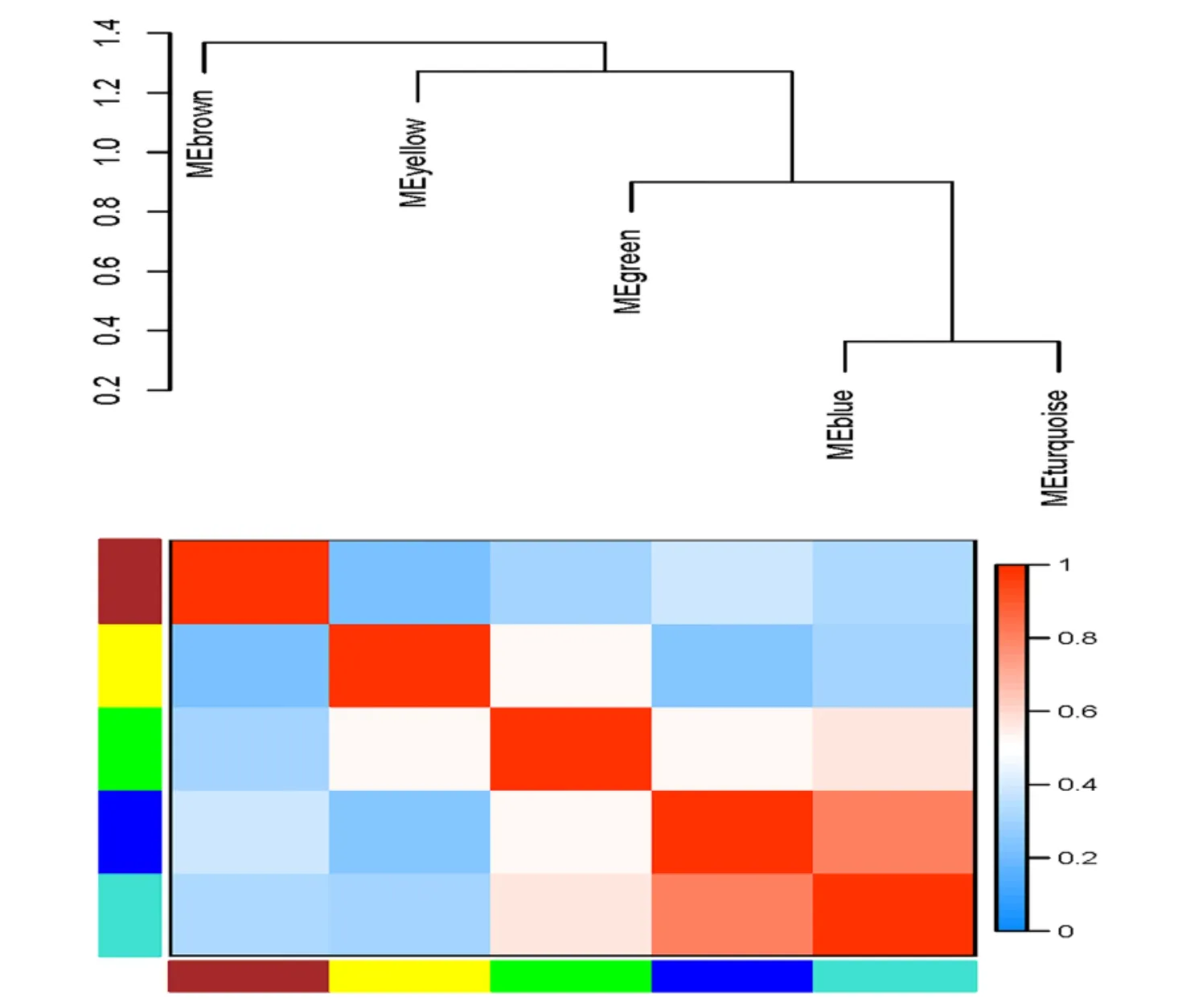
Figure 4 Module-based eigengenes clustering tree

Table 3 Hub microRNAs in blue module (|MM| > 0.8, |GS| > 0.2)

Table 4 Hub microRNAs in turquoise module (|MM| > 0.8, |GS| > 0.2)
Construction of miRNA-mRNA regulatory network by miRNet
Hub miRNAs of blue and turquoise modules were imported into miRNet to construct miRNA-mRNA regulatory network.In blue module network, 3742 target genes were predicted.The top five target genes of Degree were NUFIP2, NACC1, CDKN1A, NFIC and TP53.In Turquoise module network, 2073 target genes were predicted.The top five target genes of Degree were SLC7A5, CDC5L, GATAD2A, TP53 and AURKA.Through KEGG analysis, Pathways in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, Glioma, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Prostate cancer and Neurotrophin signaling pathway were found to be CO-enriched in target genes of blue (Table 5) and Turquoise modules(Table 6) (P< 0.05).
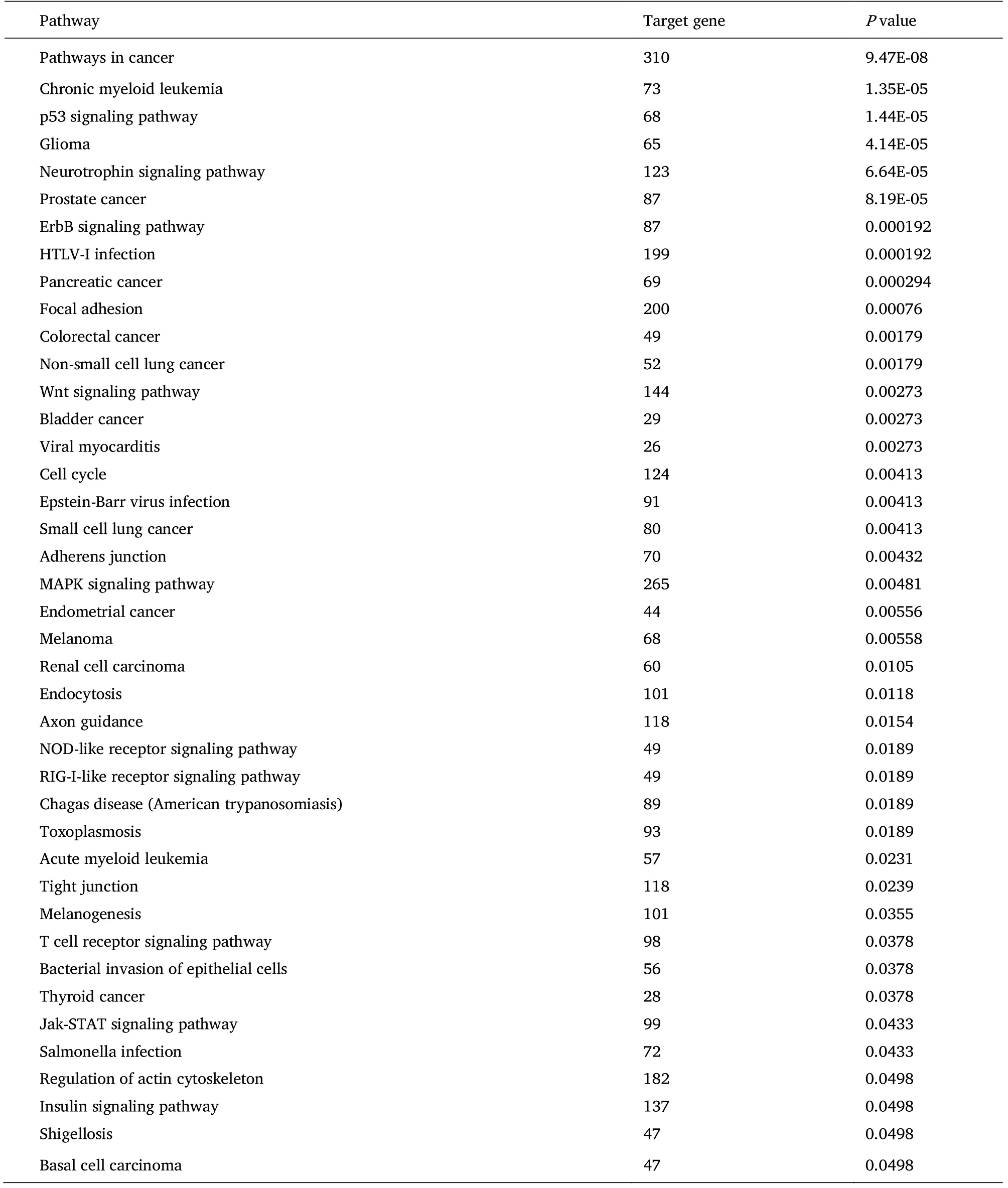
Table 5 KEGG pathway of target gene enriched in the miRNA of the blue module

Table 6 KEGG pathway of target gene enriched in the miRNA of the turquoise module
Discussion
In this study, the target genes and pathways of the obtained blue module and turquoise module microRNAs were analyzed.The target genes of Blue module and turquoise module were enriched in Pathways in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, Glioma, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Prostate cancer, Neurotrophin signaling pathway, which are highly related to the occurrence and development of tumors.It is suggested that blue and turquoise modules may participate in these pathways and thus participate in the metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.In addition, the target genes of blue module are also enriched in ErbB signaling pathway, Pancreatic cancer, Wnt signaling pathway and other cancer-related pathways.
TP53 is a potential target gene of multiple microRNAs in the two modules, and the target genes of blue module and turquoise module are enriched in p53 signaling pathway.TP53, as a classical tumor suppressor gene, is related to the occurrence and development of various tumors.The anti-cancer effect of wild TP53 is mainly to prevent G1/G0 phase, so that cell division cannot enter the DNA synthesis phase (S phase), thus inhibiting cell proliferation.When the p53 gene is mutated for various reasons, its molecular configuration changes and loses the role of cell growth monitoring and cell cycle regulation, leading to the occurrence of gastric cancer [10], liver cancer [11, 12], cervical cancer [13] and other tumors, and participate in the proliferation and metastasis of tumors [14].The high expression of mutant TP53 has been reported to be positively correlated with the adverse prognosis of tumors [11].
The mechanism of TP53 development in nasopharyngeal carcinoma has also been confirmed.The incidence of EBV infections which is considered as an important factor in the occurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma is significantly correlated with TP53 [15].TP53 also was reported to be associated with T stage of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[16].Modular-trait relationship analysis shows that Blue module and turquoise module miRNAs are related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis.We speculate that this may be related to the regulation of TP53 and p53 signaling pathway molecules by miRNAs in the module.Hub microRNAs in the two modules, many of which have been proved to play an important role in cancer.miR-1254 accelerates the growth of breast cancer cells by activating AKT signal transduction pathway,and inhibits apoptosis by targeting RASSF9 to inhibit p53 expression[17].miR-638 directly targets HOXA9 to inhibit its expression,leading to cell proliferation, colony formation and cell cycle progression, and enhance the level of basic cell apoptosis [18].Bioinformatics analysis showed that miR-1914 may be associated with the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma and may be involved in the pathogenesis of gastric signet ring cell carcinoma [19, 20], but its role in cancer needs further experimental verification.
In our knowledge, there are some microRNAs of blue and turquoise modules which have not been reported in tumor, such as miRNA-1273 and miRNA-1250.They have similar expression patterns with the microRNAs already studied in the module, which may regulate the same or similar biological processes and play an important role in the process of tumor metastasis.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is characterized with high latency, rapid development and prone to distant metastasis.Recurrence and distant metastasis of NPC are important reasons for poor prognosis of NPC patients.The purpose of this study is to identify the microRNAs associated with clinical characteristics of nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC) by WGCNA, and to successfully discover that blue and Turquoise modules are associated with metastasis of NPC.Some of these microRNAs have not been reported in tumors, which deserve further exploration.There are some limitations in this study: due to the limited clinical information available, more traits could not be included.Some of our result may be need experimental verification.We will conduct further research when conditions permit.
 Precision Medicine Research2022年1期
Precision Medicine Research2022年1期
- Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Advances in Mig6 gene in tumor research
- Clinical research progress of first-line immunotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
- Predictive value of initial procalcitonin level in perioperative period of critically ill cancer patients
- Recognition of prognostic biomarker and its association with immune infiltrates in breast cancer associated with inflammation
