Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: Novel molecular insights and clinicopathologic updates
Reza Alaghehandan , Christopher G.Przyyin ,Virginie Verkarre , Rohit Mehra
a Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Royal Columbian Hospital, Vancouver, BC, Canada
b Robert J Tomsich Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute,Cleveland Clinic,Cleveland,OH,USA
c Department of Pathology,Georges Pompidou European Hospital,AP-HP,Paris University,INSERM UMR 970, PARCC, Paris, France
d Department of Pathology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
e Michigan Center for Translational Pathology, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
f Rogel Cancer Center, Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
KEYWORDS Renal cell carcinoma;Chromophobe;Immunohistochemistry;RNA in situ hybridization;Next-generation sequencing;Oncocytic tumors;Molecular
Abstract Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (ChRCC) is the third most common renal cell carcinoma(RCC)subtype,which predominantly occurs in sporadic setting.ChRCCs are considered to originate from the intercalated cell of distal tubules with two main morphological variants,classic and eosinophilic.Most ChRCCs carry a favorable clinical outcome.Histology alone is limited in predicting the behavior of ChRCCs that do not have overtly aggressive morphologic findings such as necrosis and sarcomatoid features.Along with positive CD117 expression,classic ChRCCs generally express diffuse and uniform CK7, while eosinophilic variant demonstrates more heterogeneous CK7 expression (rare or patchy).Multiple losses of chromosomes 1,2,6,10,13,17,and 21 are considered to be the genetic hallmarks of classic and eosinophilic ChRCCs,while chromosomal gains are known to be associated with sarcomatoid ChRCCs.TP53 and PTEN are the two most frequently mutated genes in ChRCCs.The major challenge in the differential diagnosis of ChRCCs includes considerations around the eosinophilic variant (of ChRCCs),where it may share overlapping features with oncocytoma or other recent emergent oncocytic tumors.Most eosinophilic ChRCCs share expression of the recently described biomarkers, LINC01187 and FOXI1, with classic ChRCCs, however, a subset of eosinophilic-likeChRCCs with lower biomarker expression have been demonstrated to harbor MTOR gene mutations.Overall, the morphologic features of ChRCCs and genetic profile with combinations of chromosomal losses and gains suggest this tumor entity to represent a distinct, yet heterogeneous group of renal neoplasms.
1.Introduction
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma(ChRCC)is the third most common renal cell carcinoma(RCC)subtype,accounting for 5%-7% of all RCCs.Although ChRCC was first reported and published in 1985 by Thoenes et al.[1],it appears that it was,in fact, first illustrated and described by Dr.Pierre Masson from Montreal,Quebec in 1955[2].In contrast to clear cell RCCs(CCRCCs)and papillary RCCs(PRCCs),ChRCCs originate from the intercalated cell of distal tubules [3].Two main morphological variants of ChRCCs, the classic and eosinophilic,have been described;ChRCCs may also be associated with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation, a kind of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition[4].
Over the last few decades, a large body of literature on ChRCCs, their morphologic variants, clinical behavior, molecular,and histogenetic studies has been published.In this perspective, we present most updated and pertinent information on clinicopathologic and translational aspects of ChRCCs, and their applicability and potential relevance in clinical practice.
2.Clinical spectrum of ChRCCs
Most ChRCCs occur sporadically,and predominantly earlier than CCRCCs at an average age of 59 years (range 17-88 years),with a slight male predominance[5-7].Three rare hereditary diseases that may predispose to the development of ChRCCs are the Birt-Hogg-Dube´ syndrome (BHD)with germline mutation of the folliculin gene (FLCN),mapped at 17p11.2[8-11],the tuberous sclerosis complex(TSC) with mutations involving either TSC1 (9q34) or TSC2(16p13) genes [8,12,13], and the Cowden syndrome associated with germline mutation of PTEN (10q23) gene [14].In such rare cancer susceptibility syndromes, genetic testing may be offered to patients and their families,when clinical and/or pathologic features are concerning(for example, multiple oncocytic renal tumors).
ChRCCs generally carry a favorable clinical outcome with a low tendency to progress or metastasize.Their prognosis is postulated to be better than CCRCCs, with a higher 5- to 10-year cancer-specific survival of 93%and 87%,respectively[7,15,16].Subsequent disease specific events including recurrence/metastasis/death have been reported in approximately 1.5% and 6.6% of cases, at 5 years and 10 years respectively [7,16,17].Patients with metastatic ChRCCs have a similar median overall survival compared to patients with CCRCCs, when treated with conventional targeted therapies [17].Unlike non-sarcomatoid ChRCCs,sarcomatoid ChRCCs are associated with poor prognosis and worse clinical outcome[18].Although given their rarity,the prognosis of rare subtypes of ChRCCs is currently unclear,we speculate their clinical behavior to be comparable to those of non-sarcomatoid ChRCCs.
3.Morphological correlates of ChRCCs
ChRCCs are characterized by neoplastic cells with prominent cell membranes and pale to eosinophilic cytoplasm,arranged in a solid-alveolar pattern.Characteristic features that facilitate the recognition of most ChRCCs include hyperchromatic and irregular wrinkled (raisinoid) nuclei,perinuclear clearing (halos), and binucleation (Fig.1A).Of note, electron microscopic analyses have revealed perinuclear halos and raisinoid nuclei to reflect cytoplasmic microvesicles and peripheral condensation of mitochondria, which may not be seen on cytologic imprints [19,20].
Two distinct morphological variants of ChRCCs are classic and eosinophilic.Classic ChRCCs exhibit mostly pale cells with raisinoid nuclei in an alveolar,solid to trabecular architectural growth pattern.Eosinophilic variant of ChRCCs was described in 1988 [21], following the initial description of classic ChRCCs.The most recent 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) renal tumor classification formally recognizes the eosinophilic variant of ChRCCs and acknowledges the challenges associated with making amorphologic distinction from benign oncocytoma but does not provide precise diagnostic criteria [4].The 2016 WHO classification only stipulates that eosinophilic ChRCCs should be “almost purely eosinophilic”.Eosinophilic ChRCCs typically demonstrate acinar architecture, abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm (almost purely eosinophilic),focal nuclear wrinkling, and subtle perinuclear clearing/halos(Fig.2A).It is important to recognize that eosinophilic ChRCCs can present diagnostic challenges in daily routine urology and pathology workup, and that not all tumors mimicking eosinophilic ChRCCs belong to the ChRCC family.
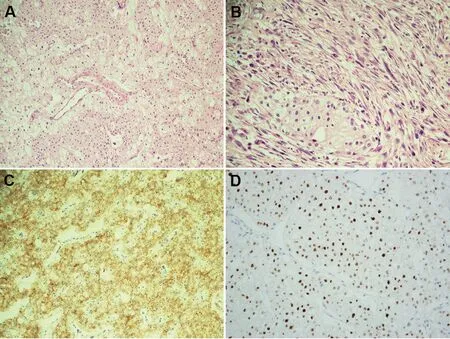
Figure 1 Classic and sarcomatoid ChRCCs.(A)Classic ChRCC H & E stain; (B) Sarcomatoid ChRCC H & E stain; (C) Membranous staining for CD117; (D) High-level nuclear LINC01187 expression.All images are at 200×.ChRCC,chromophobe renal cell carcinoma; H & E, hematoxylin and eosin.
Similar to other RCCs, ChRCCs may show sarco matoid features (Fig.1B) where the incidence of this epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary ChRCCs has been estimated at 2%-8%[7,16,18,22-24],which reaches a substantial 26% in metastatic disease [18].Furthermore, in recent years, multiple studies have shown ChRCCs to display morphologic heterogeneity including those with pigmented/adenomatoid, multi-cystic, neuroendocrine,and papillary features [25-31].
4.Immunohistochemical overview and novel biomarkers

Figure 2 Eosinophilic variant of ChRCC.(A) Eosinophilic variant of ChRCC H&E stain; (B) Predominantly membranous staining for CD117; (C) The nuclear staining for FOXI1 in eosinophilic variant of ChRCC; (D) High-level nuclear LINC01187 expression; (E) Another example of eosinophilic variant of ChRCC H & E stain; (F) With negative CD117 expression and MTOR gene mutation (data not shown).All images are at 200×.ChRCC, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma; H & E, hematoxylin and eosin.
ChRCCs, similar to oncocytomas, originate from the intercalated cells and hence exhibit positive CD117 immunohistochemical expression, known to be constitutionally expressed within some cells in the distal nephron.Along with positive CD117 expression (Figs.1C and 2B), classic ChRCCs generally express diffuse and uniform CK7, which may be of diagnostic utility for a practicing pathologist.In most cases, classic ChRCCs can be readily diagnosed on basis of a thorough histologic evaluation.However,in some instances such as limited samples (i.e., core biopsy), this may be challenging; confounding factors include other differential diagnoses and potential mimickers such as CCRCCs and miscellaneous tumors (such as adrenal neoplasms).Key histologic features such as nuclear atypia and prominent cell membranes along with pertinent immunohistochemical stains (i.e., positive expression for PAX8,CD117, and CK7) can assist in such settings.Other helpful markers, whose negative expression may support a ChRCC diagnosis where CCRCC is in the differential diagnosis,include vimentin and carbonic anhydrase-IX (CA-IX).
Distinguishing ChRCCs from other oncocytic neoplasms can be difficult, especially the eosinophilic variant, which can mimic other neoplasms.Eosinophilic variants of ChRCCs demonstrate rare or patchy CK7 expression,similar to oncocytoma [32,33].A morphologic assessment is often most helpful in distinguishing oncocytoma from classic and eosinophilic variants of ChRCCs, with immunohistochemical markers needed in occasional cases to support morphologic impression.Of note, Hale colloidal iron stain has historically been used in this differential diagnosis, with ChRCCs showing cytoplasmic positivity while oncocytoma is generally negative.The utility of this stain is limited due to potential technical process and interpretation challenges [34].
In terms of cell of origin,data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and others have demonstrated ChRCCs to exhibit a distal nephron-based mRNA expression signature(based on in silico data and immunohistochemistry);CCRCCs, on the other hand, displayed a proximal nephron based signature [35-37].TCGA also showed ChRCCs to express genes driven by the transcription factor FOXI1,which labels intercalated cells, a finding further validated by follow-up studies (Fig.2C) [38].Based on recently published data, ChRCCs are enriched for expression of intercalated cells markers such as FOXI1 protein and long noncoding RNA LINC01187 (Fig.2D) in both primary and metastatic sites, where these may serve as useful biomarkers especially in the metastatic setting (Fig.1D)[37,39].Sarcomatoid ChRCCs interestingly tend to lose expression of these novel markers in the high-grade spindle cell areas of such tumors,which otherwise tend to lose CK7 and in contrast acquire vimentin expression.Currently,there are no clinically available cancer- or lineage-specific biomarkers for oncocytoma, ChRCCs including the eosinophilic variant, or other related oncocytic tumors.The ongoing in-depth proteogenomic assessment of renal tumors by Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium(CPTAC) is likely to have a major impact on RCC protein biomarker identification [40].
5.Grading considerations
Most ChRCCs do not exhibit aggressive behavior,with only a small subset (approximately 5%) at risk of progression andmetastasis after surgery.Accurate prediction of the clinical behavior and trajectory of ChRCCs by histologic features has proven to be challenging.Historically, risk assessment of ChRCCs has not been successful with a number of studies attempting to address the value of histological grading for these tumors [6,16,41-43].The clinical significance of traditional grading systems applied to other RCC subtypes,such as Fuhrman nuclear grade and the WHO/International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) nucleolar system,could not be demonstrated for ChRCCs [44].In contrast to CCRCCs and PRCCs, the WHO/ISUP grading system is not applicable to ChRCCs [44,45].
Evaluation of a large ChRCC cohort previously demonstrated pT stage, tumor necrosis, and sarcomatoid change to be independently predictive of aggressive behavior on multivariable analysis [23].The largest single-institution morphology based study showed significant association of clinical outcome with tumor size, small-vessel invasion,sarcomatoid features, and microscopic necrosis [7].Since the prominent nuclear atypia and relative infrequency of conspicuous nucleoli inherent to ChRCCs pose challenges to applying conventional nuclear grading, a three-tiered grading system [46] has been proposed, correlating geographic nuclear crowding and anaplasia in predicting clinical outcome for patients with ChRCCs.A subsequent study, however, found that this grading system did not provide additional prognostic information once tumor stage and sarcomatoid features were included [43].Similarly,Ohashi et al.[6] were not able to validate the proposed three-tiered chromophobe grading system or the fourtiered WHO/ISUP grading system for outcome determination in ChRCC.They instead proposed a two-tiered grading system,based on sarcomatoid features and necrosis,which was successful at the multivariate level.In another large study, a modified tumor grading scheme using mitotic index, cytologic eosinophilia, and architecture was not significantly associated with outcome [7].
Overall,histology alone seems to be limited in predicting the behavior of ChRCCs that do not have overtly aggressive morphologic findings (e.g., necrosis and sarcomatoid features).Accordingly, supplementation with data from ancillary studies assessing other biomarkers, as they are discovered, may be necessary to accurately predict behavior in the majority of ChRCCs that do not otherwise have overtly adverse histologic findings.
Hopefully, discovery of novel molecular aberrations and genomic pathway derangements associated with aggressive ChRCCs can act as a surrogate to morphology for determination of clinical outcome of this disease.
6.Molecular underpinnings of ChRCCs
Recent comprehensive molecular characterizations, with identification of genetic aberrations and chromosomal abnormalities,have considerably improved our understanding of ChRCC, however, to date, predictive biomarkers remain to be identified [5,17].
Multiple losses of chromosomes 1,2,6,10,13,17,and 21 have historically been considered the genetic hallmark of ChRCC (both classic and eosinophilic variants).Earlier strategiesusingclassiccytogenetictechniquesestablished classic ChRCC to be associated with multiple losses of chromosomes 1,2,3,6,7,9,10,12,13,17,18,and 21[47-53].The TCGA analysis of ChRCC further confirmed the characteristic pattern of chromosomal losses of 1,2,6,10,13,and 17 in 86%of tumors(mainly classic type),with documented additional losses of chromosomes 3, 5, 8, 9, 11 and 18, and 21q in 12%-58% of tumors [54].In the last two decades, multiple studies have also demonstrated multiple chromosomal gains in ChRCCs [25,53,55-61].Although this has generally been deemed an uncommon phenomenon in ChRCCs,studies with larger cohorts showed a more variable genetic profile of ChRCCs with multiple chromosomal losses as well as multiple gains[25,53,55-61].Most frequently detected chromosomal gains are 4,7,15,19,and 20(mainly in classic and sarcomatoidtypes)[25,53,55-61].It isnoteworthy that,unlike classic ChRCCs, diploid chromosomal pattern is more commonly found in the eosinophilic variant[62].
It should be noted that although both oncocytomas and ChRCCs arise from the distal nephron,they do not represent a continuum of progression from benign to malignant disease.Even eosinophilic ChRCCs, which share some morphologic features with oncocytoma,have different chromosomal numerical aberrations (CNAs) and gene expression landscape than oncocytomas [36].On the other hand, sarcomatoid ChRCCs carry multiple chromosomal gains including 1,2,6,10 and 17, which are often different than CNAs seen in the epithelial component; these tumors appear to have lower frequency of chromosomal losses [53,55-58,63].Studies of other rare variants, such as ChRCCs with pigmented microcystic adenomatoid/multi-cystic growth[26-28,64],ChRCCs with neuroendocrine features[25,29,30,65,66],and ChRCCs with papillary architecture [31], also show variable CNAs including multiple losses (more common) and gains (less common).A survey of CNAs in metastatic ChRCC suggests distant metastases to demonstrate the same genetic patterns, usually chromosomal losses, as found in the primary tumors [55].Of note, no correlation between CNAs and the proposed three-tiered grading system for ChRCCs has so far been established [46,58].Distribution of chromosomal losses and gains in classic, eosinophilic, and sarcomatoid ChRCCs are presented in Fig.3[53].
A diverse molecular phenotype of ChRCCs has been highlighted by recent genetic studies encompassing eosinophilic variant,sarcomatoid,and metastatic ChRCCs.These studies provide valuable insight into characterization and sub-classification of ChRCCs, or evolutionary patterns associated with these malignancies.Classic ChRCCs displayfewer hypermethylation events and harbor a lower number of somatic variants (low mutational burden) compared to both CCRCCs and PRCCs [36,67,68].TP53 and PTEN are the two genes most frequently found to be mutated in respectively 32%-64% and 9%-45% of classic ChRCCs, independent of the presence of sarcomatoid features[18,36,68].TERT promoter mutations/rearrangements have also been detected in 6%-12%of cases and associated with TERT upregulation, without any distinct impact on clinical outcome [36,69].The TCGA analyses of ChRCCs labeled TP53 and PTEN as the most frequently mutated genes in ChRCCs [54,70].Loss of CDKN2A gene or its expression, by either deletion of 9p21.3 or hypermethylation, was the second most common alteration[54,70].Ricketts et al.[68]examined metabolic analysis of RCC histologic subtypes and found that metabolically divergent ChRCCs to be associated with high stage and lack the chromosomal copy number losses typically associated with ChRCCs; hence were associated with much poorer survival.
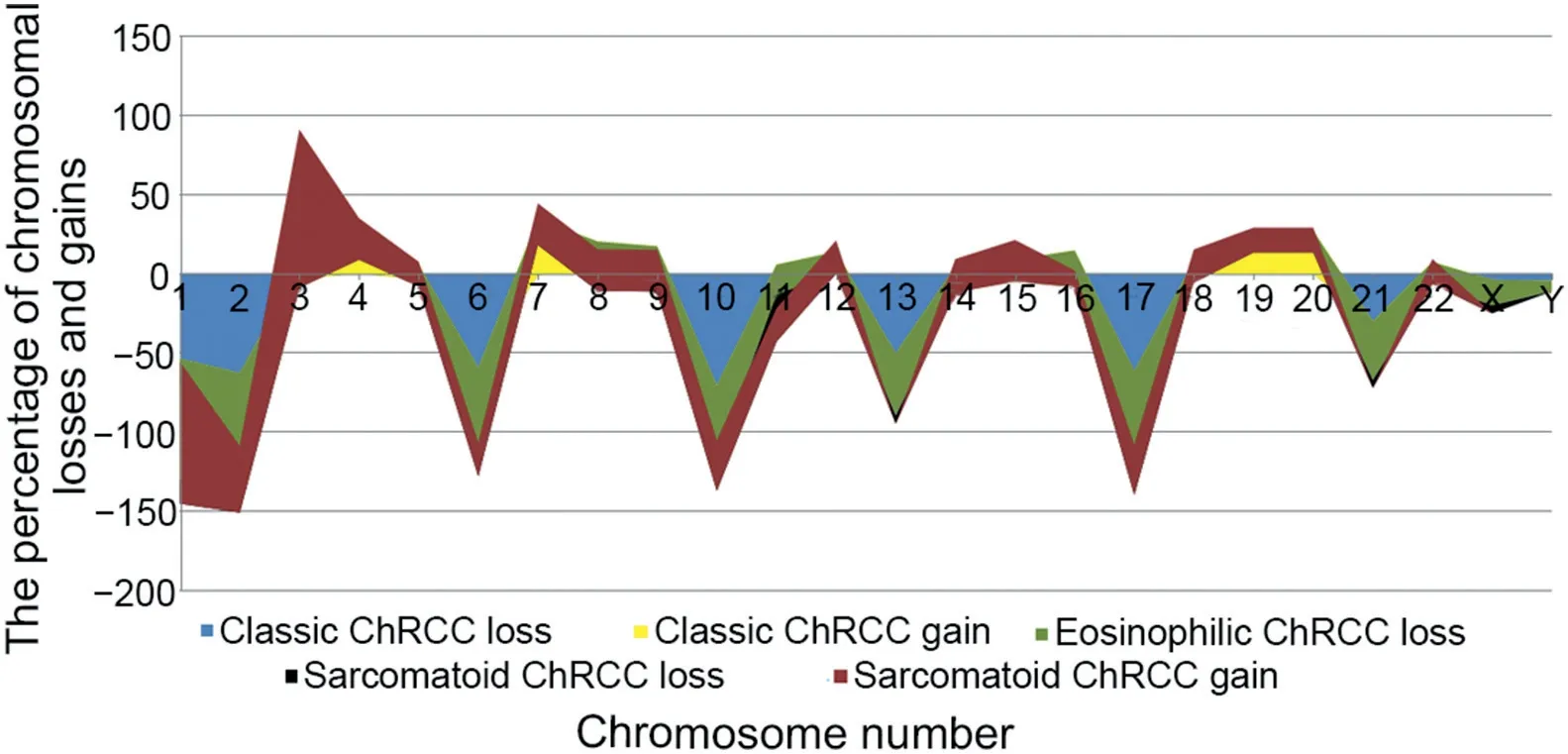
Figure 3 Distribution of chromosomal losses and gains in classic, eosinophilic and sarcomatoid ChRCC.ChRCC, chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.
Mutations identified in other genes have been identified in less than 5%of ChRCCs(mostly eosinophilic)including MTOR,TSC1,TSC2,NRAS,and others[67].In contrast to CCRCCs and PRCCs, no significant mutations have been identified in the three chromatin remodeling genes PBRM1, BAP1 and SETD2[68].Mutations in mitochondrial DNA within ChRCCs have enabledestablishmentofa link withalterationsof respiration and oxidative phosphorylation pathways [36].Additionally,pathway analysis demonstrated rare alterations in PI3K-AKTmTOR pathway genes,including PTEN,TSC1,TSC2 and MTOR,in ChRCC,which would potentially result in appropriate targets for mTOR inhibitors[54,70,71].Durinck et al.[67]identified TP53, PTEN, FAAH2, PDHB, PDXDC1 and ZNF765 to be significantly mutated in ChRCC, with frequent TP53 mutations being exclusively associated with classic ChRCCs.Most recently,Roldan-Romero et al.[72]found within the eosinophilic variant of ChRCCs an overrepresentation of mTOR pathway(MTOR,TSC1,and TSC2)mutations as well as aberrations in the mitochondrial genes encoding the complex I of the electron respiratory chain.
Interestingly, recent studies have allowed a greater insight into the genomic features of metastatic ChRCCs supporting TP53 mutations, PTEN mutations, CDKN2A alterations and imbalanced chromosome duplication(defined as duplication of ≥three chromosomes)as high-risk features associated with poor survival [68,73].DNA hypermethylation has also been associated with high-stage disease, TP53 mutation and poor survival in ChRCCs [68].Identification of such molecular genotypes provides hope for an integration of such tools into existing models of clinical care.
Overall, ChRCCs show variable morphology and genetic profile with combinations of chromosomal losses and gains,suggesting that they represent a heterogeneous group of neoplasms, both from a morphologic and a molecular perspective (Table 1).
7.ChRCCs and contemporary/emerging renal oncocytic neoplasms
The major challenge in the differential diagnosis of ChRCCs would be associated with its eosinophilic variant,especially in distinction from oncocytomas, and particularly in limited samples (i.e., core biopsy), where such a distinction may carry clinical implications.Oncocytomas typically show a relatively nested growth pattern where the neoplastic cells have uniform round nuclei, lack perinuclear halos, and a shared immunohistochemical phenotype with eosinophilic ChRCCs(CD117+,CK7-or only scattered positive cells).Liu et al.[62] recently examined a scoring system where histological patterns (organoid/nested, tubulocystic and solid/confluent), the quality of stroma (fibromyxoid and edematous),nuclear wrinkling,perinuclear halos,well-defined cell borders with clear cytoplasm,and CK7 immunohistochemical expression,were features found to be significantly discriminatory between oncocytoma and eosinophilic ChRCCs.
Other “eosinophilic” renal neoplasms that need to be considered in the differential diagnosis include WHO recognized renal entities such as succinate dehydrogenase(SDH)-deficient RCC, as well as provisional/emerging ones including eosinophilic solid and cystic RCC (ESC-RCC),low-grade oncocytic renal tumor (LOT), anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement-associated RCC (ALK-RCC),and eosinophilic vacuolated tumor (EVT) (Table 2).

Table 1 Molecular aberrations and mutation summary for ChRCC including a comparison with CCRCC and PRCC.

Table 2 Clinical, histologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular summary of ChRCC, eosinophilic variant, and overlapping entities.
7.1.SDH-deficient RCCs
These are rare renal neoplasms which occur in setting of germline mutation of one of the subunits of SDH gene(mostly SDHB and SDHA).Histologically, they exhibit solid,nested or tubular growth pattern, mimicking neuroendocrine tumors.Characteristic findings of this entity include neoplastic cells with flocculent cytoplasmic vacuoles with a pale eosinophilic or bubbly appearance and low-grade nuclei [74].In contrast to ChRCCs, CD117 and CK7 are usually negative [75].Loss of SDHB immunohistochemical staining is diagnostic [74] and should lead to genetic consultation, if germline setting is not previously established or known.
7.2.ESC-RCCs
Most ESC-RCCs are small, solitary with low stage that are predominantly found in females, and generally exhibit indolent behavior [76].Approximately 10% of these neoplasms occur in TSC patients.ESC-RCCs show solid and cystic growth pattern, with often scattered histiocytes and lymphocytes.The neoplastic cells are voluminous and eosinophilic with cytoplasmic coarse granularity (stippling)[76].Unlike conventional renal tumors, most ESC-RCCs(about 85%) are positive for CK20 (at least focal), while negative for CD117 and may rarely/focally express CK7[76].
7.3.LOTs
LOTs are typically single, small, low-stage tumors demonstrating an overlapping morphology with oncocytoma and eosinophilic ChRCCs [77,78].LOTs show solid growth pattern with sharply delineated edematous areas containing single cells and irregular cell cords.The eosinophilic cells show “low-grade”, round to oval nuclei,often with delicate perinuclear clearing.Immunohistochemically, these tumors consistently show CD117-/CK7 diffuse+ profile [78].Importantly, these tumors tend to share morphologic, immunophenotypic and molecular overlap with the eosinophilic-like variant of ChRCCs harboring MTOR mutations [37,79].Rare cases have been recently described in TSC setting [80,81].
7.4.ALK-RCCs
ALK-RCCs are solitary tumors with slight male predilection,and a significant potential for metastasis (up to 30%)[82,83].By definition,ALK-RCCs are associated with an ALK rearrangement at the genomic level.ALK-RCCs may show variable and admixed growth patterns (e.g., solid, tubular or tubulo-cystic, papillary, cribriform, trabecular, and signet-ring individual cell growth), often in a mucinous background [77].The neoplastic cells have eosinophilic cytoplasm and may show variable morphologies, including rhabdoid, vacuolated, pleomorphic, and giant cell [77].Diffuse cytoplasmic and membranous ALK protein expression by immunohistochemistry is diagnostic and can aid in screening suspicious cases, particularly in tumors difficult to classify (where immunohistochemistry for conventional markers is nonspecific or negative).
7.5.EVTs
EVTs present a unique morphology, relatively consistent immunophenotypic profile and distinct molecular/genetic features [75,77,84,85].These tumors demonstrate a solid to nested growth pattern.The neoplastic cells exhibit eosinophilic cytoplasm, with large intracytoplasmic vacuoles, prominent cell membranes, and round to oval nuclei,with enlarged nucleoli.Normal renal tubules and thickwalled vessels are frequently found at the periphery.The neoplastic cells are typically immunoreactive for cathepsin-K,CD117,and CD10.CK7 is variably positive,and negative stains include vimentin,CK20,HMB45, and Melan-A.EVTs have been shown to harbor TSC2 or MTOR somatic mutations [85,86].
7.6.Other “difficult to classify” oncocytic tumors
It is worth noting that the surgical pathology community,at large, still considers oncocytic neoplasms and their clinicopathologic spectrum as one of the most challenging areas in routine clinical practice.The diagnosis of tumors with overlapping morphologic features spanning a spectrum of entities like oncocytoma, ChRCC, and others, mentioned above, not surprisingly, presents a frequent clinical management dilemma.The Genitourinary Pathology Society(GUPS) has recently proposed the term “oncocytic renal neoplasm of low malignant potential,not further classified”for such “borderline” cases, which should be reserved for solitary,sporadic tumors with overlapping features[75].We believe this entity encompasses the currently so called“low-grade oncocytic renal cell carcinoma, type unclassified”tumor subtype.This approach recognizes the fact that this “clinical management” category likely includes a heterogeneous group of renal neoplasms that most likely have a significantly low risk for developing metastasis.Of importance, the term “hybrid oncocytic tumor” should be reserved for hereditary cases (i.e., BHD syndrome), as per the GUPS recommendations [75].
8.A practical diagnostic approach to ChRCCs
Most ChRCCs can be accurately diagnosed on the basis of a thorough histologic evaluation.However, the diagnosis of ChRCCs at times remains a challenge,particularly in limited samples, and when confounded by the presence of morphologic features overlapping with oncocytoma.The role of immunohistochemistry in ChRCCs (with its limitations)is evolving and may aid in challenging cases.It should be noted that a subset of TSC/MTOR-aberration associated RCCs have been demonstrated to harbor features morphologically similar to eosinophilic ChRCC, where, interestingly, these tumors may be negative for CD117 expression(Figs.2E and 2F) [13,79].Most eosinophilic ChRCCs share expression of the recently described biomarkers,LINC01187 and FOXI1, with classic ChRCCs, however, a subset of eosinophilic-like ChRCCs with lower biomarker expressionwere demonstrated to harbor MTOR gene mutations(Figs.2E and 2F) [37].
Presence of a renal tumor in general warrants dedicated cross sectional imaging for further characterization to facilitate treatment planning.It should be noted that oncocytoma cannot reliably be distinguished from RCC,but techniques such as diffusion-weighted (DW) MRI show promising results [87].Renal mass biopsy demonstrates a reliable ability to determine the presence of malignancy and characterize histology in small renal masses [88].The current clinical guideline panels suggest offering renal mass biopsy as an adjunctive option in the evaluation of patients with localized RCCs [88].Unfortunately, an accurate diagnosis of oncocytic renal tumors may be challenging upon renal mass biopsy; a limited sampling of tumor at the time of renal biopsy may or may not be representative of the entire lesion[89].This is most pronounced in distinguishing eosinophilic ChRCCs from oncocytoma, given the fact that this differential often carries significant clinical and management implications.As such, the field of urologic pathology is still relatively unclear as to whether it is preferable to issue an outright diagnosis of oncocytoma(when features are typical in the biopsy sample) or to use more general terminology, such as “low-grade oncocytic neoplasm” with a comment that the features are compatible with oncocytoma [90].At times, this distinction is impossible upon renal biopsy and a general terminology of“low-grade oncocytic neoplasm” is advisable, with comment that the differential diagnosis includes entities like renal oncocytoma and eosinophilic ChRCCs.
In perplexing cases,genomic profiling may be helpful in guiding towards the correct renal tumor categorization.In a comprehensive genomic study of non-clear cell RCCs,Durinck et al.[67] identified ADAP1, SDCBP2, HOOK2,BAIAP3,and SPINT1 as the top five genes with high level of expression in ChRCCs, while ITGB3, MINOS1-NBL1, and ASB1 were found to be upregulated in oncocytomas.Furthermore, a set of five genes including ASB1, GLYAT,PDZK1IP1, PLCG2, and SDCBP2 was reported to be sufficient to separate ChRCC, oncocytoma, and PRCC [67].These findings shed light on developing of companion diagnostic panels for renal neoplasms with oncocytic features.It is worth noting that such findings would require further validation studies before they are considered for application in clinical practice.
Concerning the utility of CNAs, it should be noted that classic ChRCCs show frequent loss of chromosomes 1, 2, 6,8, 10, 13, 17 and 21, while the eosinophilic variant of ChRCCs appears to be almost completely diploid [53].Oncocytomas, on the other hand, showed very few copy number alterations, with chromosome 1 deletion being the most frequent [53,67].We believe that in distinguishing ChRCC from its mimickers such as oncocytoma, careful histologic examination along with immunohistochemistry(as needed) may serve as a baseline approach.
Finally, other ancillary methods such as novel and emerging markers (i.e., FOXI1 and LINC01187) and molecular testing may be helpful, while a concise discussion of pertinent clinicopathologic features with clinicians is paramount in ambiguous and unresolved cases.
9.Management implications for ChRCCs and related oncocytic neoplasms
The clinical management of ChRCCs is relatively well established, while in some areas it continues to evolve.Similar to CCRCCs, the general approach for the treatment of localized and resectable ChRCCs is surgery, with no role for adjuvant therapy after definitive surgery for clinical Stages I-III [91].For advanced or metastatic ChRCCs, systemic therapies with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors (i.e., sunitinib) or mTOR inhibitors (i.e., everolimus) are currently preferred firstline options [91].Enrollment to clinical trials, immunotherapy, and cytoreductive nephrectomy could also be considered, whenever feasible, as well as molecular characterization of metastatic ChRCCs, to improve systemic therapy strategy.
There are currently limited clinical data available on the recently described and emerging oncocytic renal neoplasms which fall within the differential diagnosis of ChRCC, such as EVTs and LOTs, as well as borderline oncocytic tumors.From a practical standpoint,we believe that it would be appropriate, for the time being, to clinically manage such tumors similar to those with low malignant potential for recurrence/metastasis, such as eosinophilic ChRCCs.
10.Conclusion
ChRCCs represent a heterogeneous group of neoplasms demonstrating unique morphologic and genetic profiles.Most ChRCCs carry a favorable clinical outcome, with the exception of those with sarcomatoid features.Conventional WHO/ISUP grading system does not apply to ChRCCs as histology alone is limited in predicting the behavior of these tumors in the absence of known adverse factors such as necrosis and sarcomatoid features.To distinguish ChRCCs from its mimickers,careful histologic examination along with a small set of immunohistochemical stains including CD117/CK7/CA-IX is likely to serve as an optimum baseline approach.In perplexing cases, genomic profiling may be helpful.
Author contributions
Study concept and design: Reza Alaghehbandan, Rohit Mehra.
Data acquisition: Reza Alaghehbandan, Christopher G.Przybycin.
Data analysis: Reza Alaghehbandan, Christopher G.Przybycin, Virginie Verkarre.
Drafting of manuscript:Reza Alaghehbandan,Rohit Mehra.Critical revision of the manuscript: Reza Alaghehbandan,Rohit Mehra.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this manuscript were previously members of the Genitourinary Pathology Society (GUPS) working group for editing the chromophobe RCC section in the consensus GUPS update on renal neoplasia articles[75,92].We would like to acknowledge and thank the GUPS executives, particularly, Dr.Kiril Trpkov (GUPS past-president)and Dr.Ondrej Hes, for leading the joint GUPS initiatives and forming various working groups including ours on chromophobe RCC.The statements and views expressed in this review article reflect the opinions of all co-authors only.
 Asian Journal of Urology2022年1期
Asian Journal of Urology2022年1期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- The role of preoperative dutasteride in reducing bleeding during transurethral resection of the prostate: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Efficacy and safety of desmopressin on frequency and urgency in female patients with overactive bladder and nocturia,current clinical features and outcomes: A systematic review
- The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on elective urological procedures in Australia
- Efficacy of a combination of dutasteride,tadalafil,and solifenacin in the treatment of previously unsuccessful patients
- Associations between IL-1RN variable number of tandem repeat, IL-1β(-511)and IL-1β (+3954) gene polymorphisms and urolithiasis in Uighur children of China
- Ultrasound heterogeneity as an indicator of testicular salvage in testicular torsion: A single center experience
