Cloning and Functional Analysis of Calcineurin Subunits A and B in Development and Fecundity of Nilapavata lugens (Stål)
Cloning and Functional Analysis of Calcineurin Subunits A and B in Development and Fecundity of(Stål)
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA

Fig. S1. Primary sequence and domain structure of CNA (A) and amino acid sequence alignment ofNlCNA proteins (B).
The catalytic region of CAN was marked with black; CNB (calcineurin B) marked with red; CaM (calmodulin) marked with yellow; Ai (autoinhibitory) marked with green. ClustalX (2.1) program was used for multiple sequence alignment. Secondary-structure elements were marked with arrows (β strands) and filled orange rectangles (helices).

Fig. S2. Amino acid sequence alignment of CNB proteins from 11 insects.
ClustalX (2.1) program was used for multiple sequence alignment. Secondary-structure elements were marked with arrows (β strands) and filled with orange rectangles (helices); EF-hand domain was marked with red; Different amnio acids fromwere marked with black.

Fig. S3. Amino acid sequence alignment of CNBH proteins from 11 insects.
ClustalX (2.1) program was used for multiple sequence alignment. Secondary-structure elements were marked with arrows (β strands) and filled with orange rectangles (helices); EF-hand domain was marked with red; Different amnio acids fromwere marked with black.
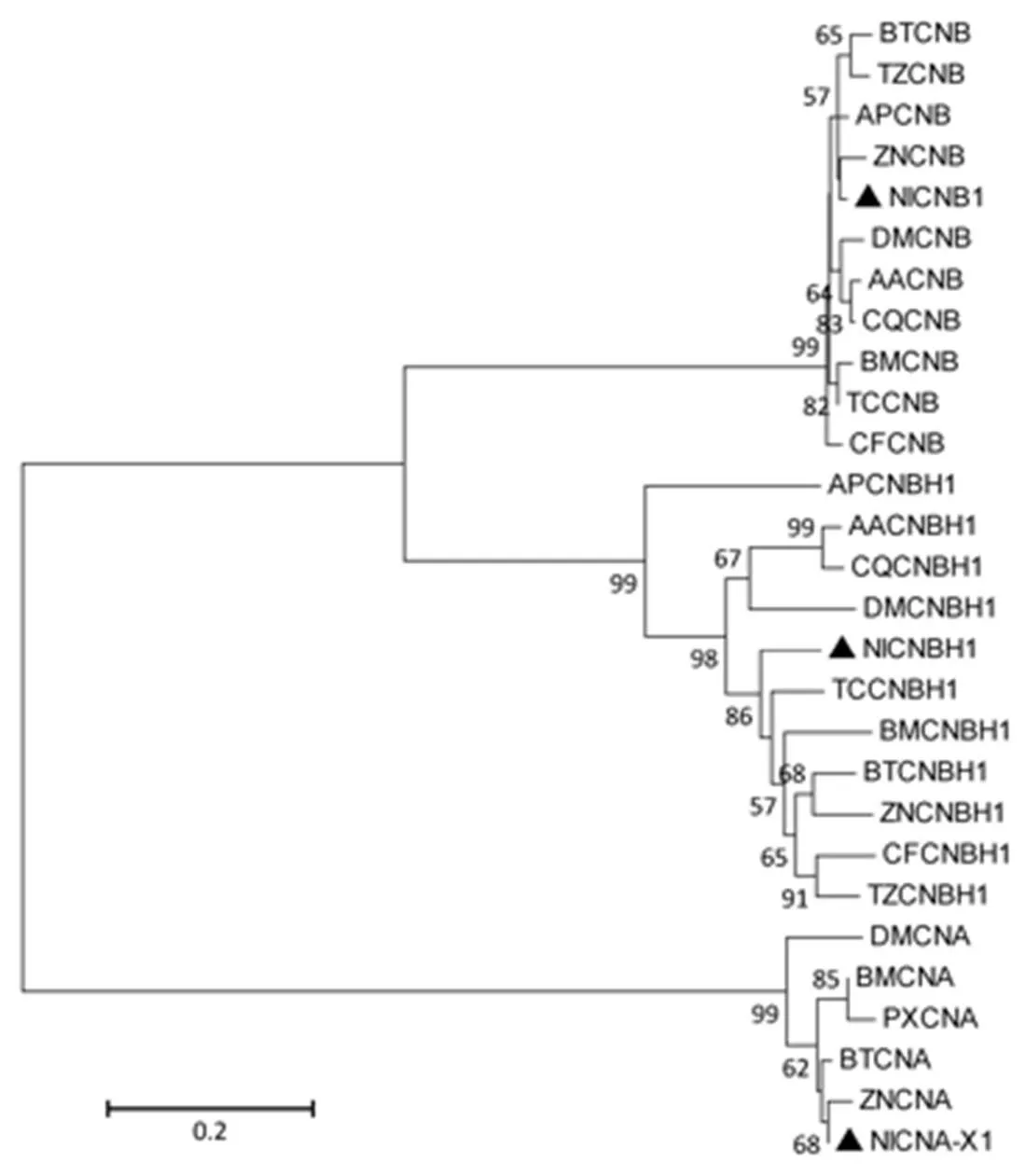
Fig. S4. Unrooted phylogenetic tree of NlCNA-X1, NlCNB1 and NlCNBH1 fromand representative insect species.
An unrooted phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbour- joining method, together with 1 000 bootstrap replicates based on the protein sequence alignments. NlCNA-X1, NlCNB1 and NlCNBH1 are marked with filled triangle.
See Table S2 for details of GeneDB accession number.
Table S1. Primers used in this study.

PrimerPrimer sequence(5′-3′)Length (bp) For full-length cDNA amplification NlCNB1F: TGCCAAAGAAAATCAGCTGTGTA720 R: TCGACACCAAAAGATGGCAA NlCNBH1F: CAGTTCCTTGTTGCATTTCTTTGT1003 R: TACTCTGTTCAGGAGTAATTTTTGG NlCNAF: AGTTGGAAGTGCGACGTTTG1680‒1758 R: TTCCGATGCGCCAGTGAAAA For qRT- PCR qNlCNB1F: TTCGACGAGGACGGAAACGG200 R: TGGGTGTCTTTCAAATTGTTGCC qNlCNBH1F: CGATCGAGTCAACTTCAGGCA184 R: AACCATCATATGGAGAACAGCCA qNlCNAF: TTCAACTGTTCGCCTCACCCA148 R: CATCGCCGTCTGACATGAGTT For dsRNA synthesis dsNlCNB1F: TGCCAAAGAAAATCAGCTGTGTA720 R: TCGACACCAAAAGATGGCAA dsNlCNBH1F: AGTTCCTTGTTGCATTTCTTTGT653 R: TTTGTGCTACAACCAAAAGGCT dsNlCNA1F: AACTGTTCGAGGTGGGAGGA607 R: AACGATGGAAACCCCGTTGT dsNlCNA2F: CAGCAGTTCCTCTGCGTACA809 R: GCGAACGACGTGATCTTGTG
Table S2. Sequence information used in phylogenetic analysis.

Sequence IDAccession No.Length (aa) Organism NlCNA536Nilaparata lugens NlCNB1100 NlCNBH1191 AACNBXP_001660865.1170Aedes aegypti AACNBH1XP_001652782.1189 APCNBNP_001155538.1170Acyrthosiphon pisum APCNBH1NP_001280255.1191 BMCNANP_001037025.1495Bombyx mori BMCNBNP_001037026.1170 BMCNBH1NP_001040173.1189 BTCNAXP_018912022.1522Bemisia tabaci BTCNBXP_018901633.1170 BTCNBH1XP_018915145.1189 CFCNBXP_014219748.1170Copidosoma floridanum CFCNBH1XP_014212409.1189 CQCNBXP_001864848.1170Culex quinquefasciatus CQCNBH1XP_001846776.1189 DMCNAAAB29893.1560Drosophila melanogaster DMCNBNP_001246192.1170 DMCNBH1NP_001262295.1189 PXCNANP_001296069.1495Plutella xylostella TCCNBXP_975270.1170Tribolium castaneum TCCNBH1XP_971411.1190 TZCNBXP_018317657.1170Trachymyrmex zeteki] TZCNBH1KYQ59586.1189 ZNCNAXP_021914061.1543Zootermopsis nevadensis ZNCNBXP_021913093.1 170 ZNCNBH1XP_021918337.1189
- Rice Science的其它文章
- Functions of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium in Energy Status and Their Influences on Rice Growth and Development
- Epoxiconazole Improved Photosynthesis, Yield Formation, Grain Quality and 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis of Fragrant Rice
- Comparisons of Metabolic Profiles for Carbohydrates, Amino Acids, Lipids, Fragrance and Flavones During Grain Development in india Rice Cultivars
- Cloning and Functional Analysis of Calcineurin Subunits A and B in Development and Fecundity of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)
- Improving Rice Blast Resistance by Mining Broad-Spectrum Resistance Genes at Pik Locus
- Genetic Improvement of Rice for Bacterial Blight Resistance: Present Status and Future Prospects

