Tanreqing injection auxiliary in the treatment of heart failure with pulmonary infection: A systematic review
YAN Long-mei, ZHANG Jing-chun, AI Yu-zhen, XING Ya-xuan, GAO An-ran, XU Qi-wu, OUYANG Jia-hui
1. Graduate School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
2. Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
Keywords:Tanreqing injection Heart failure Pulmonary infection Traditional Chinese medicine Meta-analysis
ABSTRACT Objective: To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Tanreqing injection in the treatment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection. Methods: The database of CNKI, SinoMed, VIP full text database, Wanfang database, Cochrance Library,Web of Science and PubMed were searched. The retrieval time was from the inception to August 2021. Clinical randomized controlled trial of Tanreqing injection in the treatment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection was collected, and two researchers independently screened the document data. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4.1 software. Results: A total of 10 documents were included, including 862 cases of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection, including 431 cases in the test group, and 431 cases in the control group. The Meta analysis showed that compared to the control group, the test group increased clinical efficiency [OR=4.56, 95% CI(2.79, 7.52), P<0.000 01], reduced the value of C-reactive protein [MD = -7.55, 95% CI (- 11.40, -3.69), P=0.000 1], reduced the time required to correct heart failure [OR=-4.04, 95% CI (-4.59, -3.49), P<0.000 01], reduced the number of days of the average hospitalization [MD = -4.78, 95%CI (-6.67, -2.89), P<0.000 01], and there were no statistically significant differences in the incidence of adverse reactions. Conclusion:Tanreqing injection, as an auxiliary treatment for heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection, has significantly effective effect on improving efficiency. Tanreqing injection has a certain advantage in reducing C-creative protein values, shortening the time of correcting heart failure, and reducing the number of days of the average hospitalization, and the adverse reactions are smaller. However, the overall quality of the included studies is low, and more high-quality randomized controlled trials are needed to increase the evidence-based basis.
1. Introduction
Heart failure is a group of complex clinical syndromes caused by abnormalities in the structure or function of the heart, leading to ventricular systolic or diastolic dysfunction[1].Heart failure is also the final stage of the development of various cardiovascular diseases. Its acute attack seriously threatens the life safety of patients. More than 23 million people are ill all over the world,which has become a major global public health problem[2].The most common complication of heart failure is pulmonary infection.Modern medicine believes that cardiac insufficiency leads to reduced cardiac output, which is often accompanied by pulmonary and systemic congestion. Pulmonary congestion is prone to pulmonary infection and aggravates the progression of heart failure.The two influence each other and cause a vicious circle. Decreased heart function in patients with heart failure can easily lead to pulmonary congestion, reduced lung compliance, swelling of the bronchial mucosa, and decreased tracheal ciliary epithelial function,which can provide favorable conditions for bacterial growth to cause infection. Pulmonary infection can cause pulmonary inflammatory reaction, lead to ventilation dysfunction[3], increase the heart volume load, lead to further aggravation of the disease, and threaten the lives of patients.
At present, for patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection,cardiotonic, diuretic, vasodilator and other treatments are used clinically, combined with antibacterial drugs to control infection,and have certain curative effects. However, if long-term application is easy to produce drug resistance. Once the disease breaks out, it is difficult to control the infection in a short time[4]. The auxiliary traditional Chinese medicine treatment is more conducive to the recovery of the disease. In recent years, the diagnosis and treatment model of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine has been gradually promoted. On the basis of conventional western medicine for the treatment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection [5-6], the unique advantages of Chinese medicine holistic view, syndrome differentiation and individualized treatment have been exerted. "Chinese Heart Failure Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines 2018 Edition"[7] and "Chinese Medicine Single Use/Combined Antibiotic Treatment of Community Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Practice Guidelines"[8]both mention the diagnosis and treatment characteristics of Chinese medicine, and the adjuvant treatment of traditional Chinese medicine can improve Symptoms and reduce mortality.
Tanreqing injection is the first traditional Chinese medicine injection approved by fingerprint detection in China[9], which has been highly valued by researchers at home and abroad. Relevant studies have confirmed that Tanreqing injection has a definite effect on patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection[10-19], but there is still a lack of more comprehensive conclusion support. Therefore, this study is based on the published literature to systematically evaluate the safety and effectiveness of Tanreqing injection for adjuvant treatment of heart failure with pulmonary infection, hoping to provide a reference for clinical practice and research.
2. Data and methods
2.1 Literature search
The databases CNKI, SinoMed, VIP, Wanfang Data, Cochrane Library, web of science and PubMed were searched by computer.The retrieval time was from the establishment of the database to August 15, 2021.Data retrieval uses the combination of free words and subject words, and makes specific adjustments according to different database characteristics. Chinese search terms include:Tanreqing, heart failure, Cardiac failure, Heart decompensation,Pneumonia, Lung inflammation, Pulmonary infection. English search terms include: tanreqing, Heart failure, Cardiac failure,Heart decompensation, Pneumonia, Lung inflammation, Pulmonary infection.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
2.2.1Research type
A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of Tanreqing injection combined with conventional western medicine in the treatment of heart failure complicated with lung infection.
2.2.2 Research object
Patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection have been clearly diagnosed, regardless of age, gender and course of disease.
2.2.3 Intervention measures
The experimental group was Tanreqing injection, single or combined with the control group; The control group was treated with routine treatment, and the routine treatment was diuresis, cardiac strengthening and vasodilation.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
Literature review or animal experiments; Unpublished literature;literature with incorrect or incomplete data; Re published literature;outcome indicators that do not meet the inclusion requirements.
2.4 Data screening and extraction
Two researchers independently screened the literature, first read the title and abstract to screen out the obviously irrelevant literature,read the full text of the literature that may meet the inclusion criteria,and finally determine whether the literature is included in strict accordance with the requirements of the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The quality of the literature is evaluated, data extracted and cross-checked. In case of disagreement, negotiate with a third party and communicate with the author if necessary. The data extraction content mainly includes: the first author of the included literature,the publication period, the sample size of the included study, age,gender, diagnostic criteria, intervention measures, treatment course,outcome indicators, bias risk evaluation, etc.
2.5 Literature quality evaluation
The quality of the included literature was evaluated by using the risk bias assessment tool recommended by Cochrane Collaboration Network, including selectivity bias, implementation bias,measurement bias, follow-up bias, reporting bias and other bias.Each item is assessed for risk deviation.
2.6 Statistical Processing
RevMan5.4.1 statistical software was used to conduct metaanalysis of the data. For the two-category count data, it is expressed in odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI),Heterogeneity test was used χ2Inspection (the inspection level is α= 0.1), and the statistical heterogeneity was evaluated by I2test: If P>0.1, I2<50%,it is considered that the heterogeneity of various studies is relatively small, and the fixed effect model is used for analysis; If P<0.1,I2≥50%, it is considered that the heterogeneity of various studies is relatively large, and the random effect model is used for analysis.If more than 10 studies were included, funnel plot was drawn to analyze potential publication bias.
3. Results
3.1 Literature search and results
Preliminarily searched 157 relevant literatures, excluded 51 duplicate documents, read the title and abstract of the preliminary screening of 106 literatures that met the standard, eliminated 92 irrelevant literatures, downloaded the full text for reading and excluded 1 unreported literatures and 3 articles In a non-randomized controlled study, 10 articles were finally screened out. The literature screening process and results are shown in Figure 1.
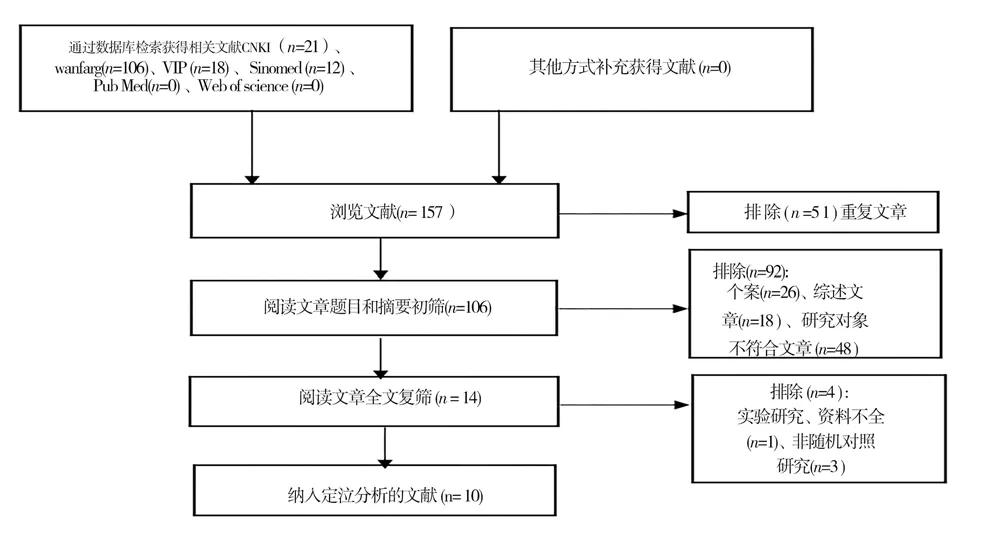
Fig 1 Document screening flowchart and results
3.2 Basic characteristics of literature
A total of 10 [10-19] articles were included in this study. There were 431 cases in the test group and 431 cases in the control group.In 10 [10-19] studies, the manufacturer of Tanreqing injection is Shanghai Kaibao Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd. 10 [6-15,10-19]studies were administered by intravenous drip. Three[10,13,14]studies included patients with cardiac function above grade 2, and the other seven[11,12,15-19]studies did not mention cardiac function.The dosage of Tanreqing Injection in 10[10-19] studies was 20 mL.Five[11,14,16,18,19]studies reported adverse reactions. Table 1 shows the basic information of the included study.
After that I asked somebody how to deal with the customer’s food in the restaurant in that case, because they went out to leave because of the fire, but hadn t finished their food. They told me that the customers who had bought food or drinks there could get a new one.
3.3 Basic evaluation of research literature deviation
The "RCT bias risk assessment" tool provided by Cochrane Collaboration Network was used to analyze the included literature.10 studies were included, all using the random grouping method.5[11,12,14,15,17]were the random number table method, and 5[10,13,17,18,19]did not mention the specific grouping method.Whether the allocation concealment method is used is not mentioned in all the test articles included in the study. The risk assessment of literature bias is shown in Figure 2, 3.
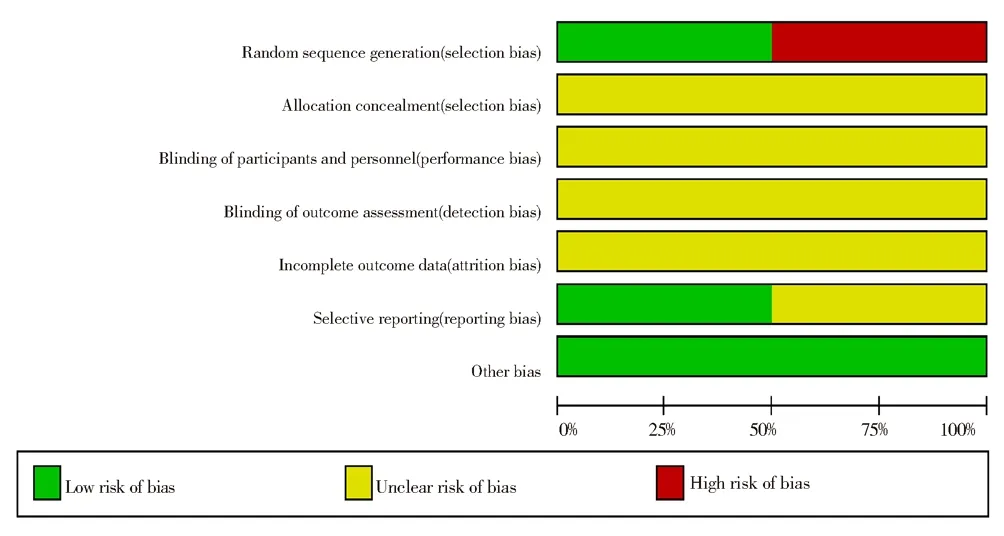
Fig 2 Bias risk diagram

Fig 3 Summary of risk of bias
3.4 Meta analysis
3.4.1 Efficient
There were 10 [10-19] studies that reported the total effective rate,involving 852 patients. The research data are homogeneous(P=1.00,I2=0%), so the fixed effect model is used. The results of metaanalysis showed that compared with conventional western medicine treatment, the difference was statistically significant[OR=4.56,95%CI(2.79, 7.52), P<0.000 01]. See Figure 4.

Tab 1 The basic characteristics of the included studies

Fig 4 Meta-analysis of clinical total effective rate
3.4.2 CRP
A total of 2[10,12] studies reported CRP, involving 188 patients.There is great heterogeneity among the research data (P=0.000 02,I2=93%), so the random effect model is used. The results of metaanalysis showed that compared with conventional western medicine treatment, the difference was statistically significant [MD = -7.55,95% CI (-11.40, -3.69), P = 0.000 1]. See Figure 5.
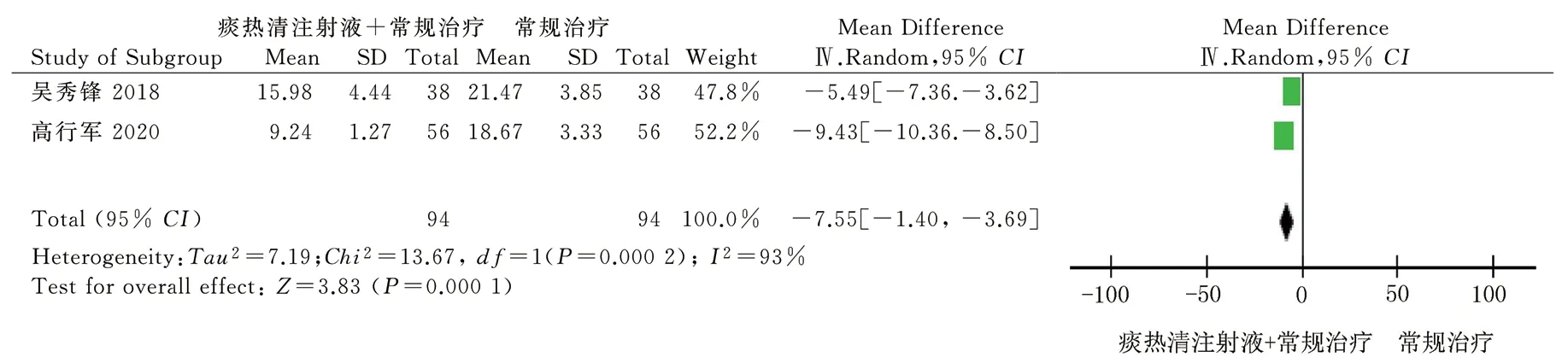
Fig 5 Forest plot of CRP levels between the two groups
3.4.3 Time to correct heart failure

Fig 6 Forest plot of the time levels of correcting heart failure between the two groups
3.4.4 Average length of stay
A total of 3 [13,16,18] studies reported the average length of hospital stay, involving 210 patients. There is great heterogeneity among the research data(P=0.02, I2=75%), so the random effect model is adopted. The results of meta-analysis showed that Tanreqing injection could reduce the average length of hospital stay compared with conventional western medicine treatment, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -4.78, 95% CI (- 6.67, - 2.89), P <0.000 01]. See Figure 7.

Fig 7 Forest plot of the average length of hospital stay between the two groups
3.5 Adverse reaction
Five[11.14.16.18.19]studies conducted safety evaluation, and two[18,19]studies showed that Tanreqing injection combined with conventional western medicine and conventional western medicine had no adverse drug reactions. In the other three[11.14.16] studies, the test group (Tanreqing injection combined with conventional western medicine treatment) or the control group (conventional western medicine treatment) had adverse drug reactions such as skin allergy,gastrointestinal reaction, nausea and vomiting, chest tightness and blood cell decline, and meta-analysis of adverse reactions: there was little heterogeneity among the study data(P=0.49,I2=0%), so the fixed effect model was used. The results of meta-analysis showed that there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the test group and the control group [OR = 0.67,95% CI (0.27,1.62), P = 0.37]. See Figure 8.
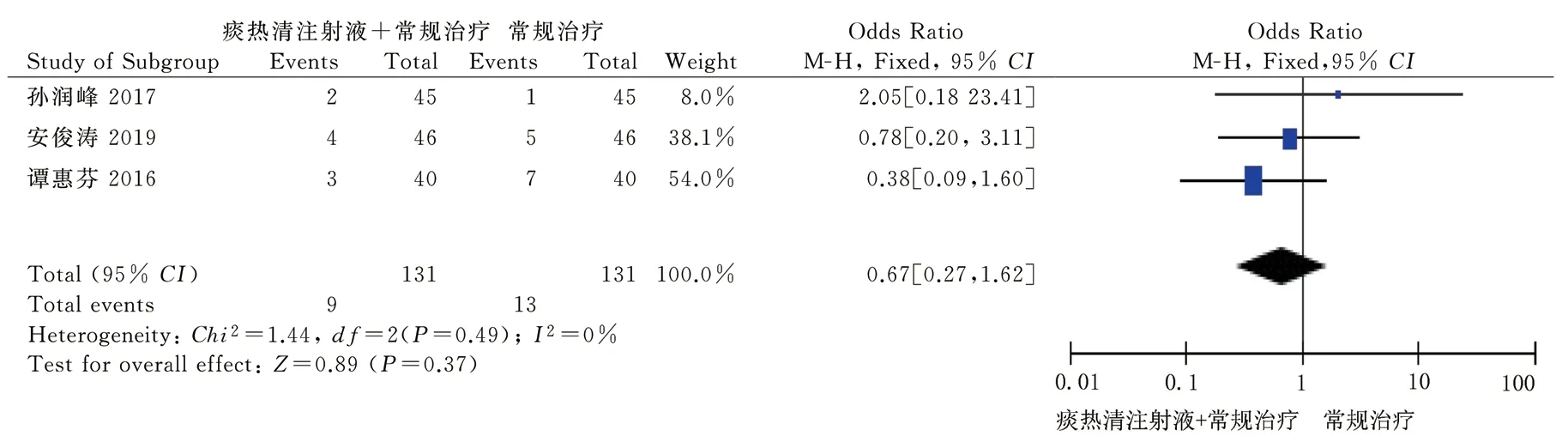
Fig 8 Forest plot of the levels of adverse reactions between the two groups
3.6 Publication bias analysis
The deviation risk assessment of the results of the total clinical efficiency showed that the funnel diagram was roughly symmetrical,suggesting that there may be no publication deviation. See Figure 9.
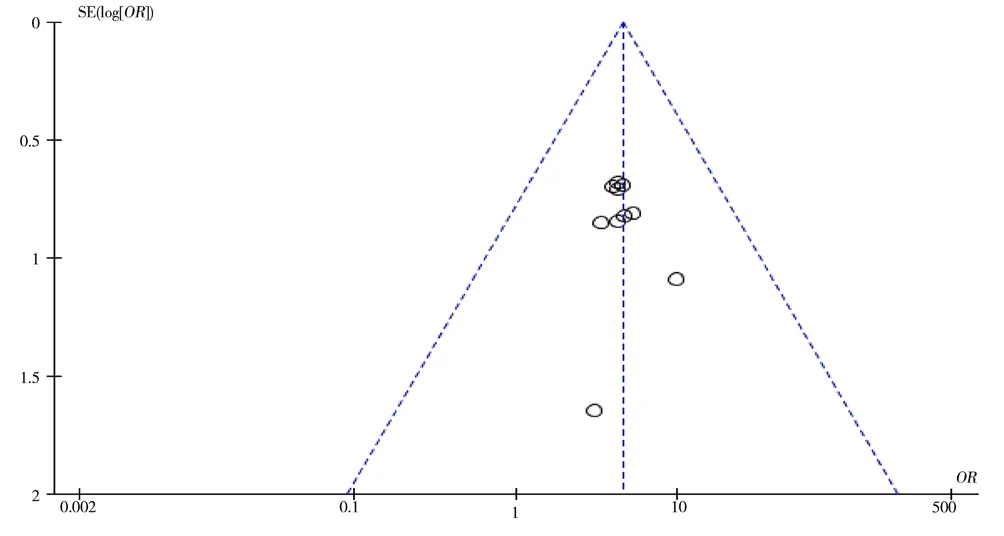
Fig 9 Funnel plot of publication bias of clinical total effective rate
4. Discussion
From the clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection, it belongs to the category of "lung distention", "asthma syndrome" and "suspending fluid retention" in traditional Chinese medicine. As early as in "Suwen Bilun" mentioned: "Patients with heart disease, the swelling will not disappear, the annoyance will cause the heart to bulge, and the breath will become wheeze." It is recorded that the heart disease is accompanied by symptoms such as edema and wheezing. The heart and lungs live together in the upper focal point, and are closely related in function and physiology. The heart governs blood, the lungs govern Qi, and the coordination of the heart and lungs can help blood circulation and breathing exercise. When the disease occurs, it also needs to be another. When the heart-qi is insufficient,the blood flow is not smooth and the blood stasis is blocked in the lungs, which makes the lung breathing function abnormal,chest tightness, dyspnea and other symptoms; If the lung-qi is insufficient, the qi machine will not run smoothly, which affects the function of the heart to govern the blood vessel, and the blood will run abnormally, and the manifestations of heart blood stasis appear. The basic pathogenesis is based on the deficiency of Yang in the heart and lungs, the exogenous evil invades the lungs as the target, the deficiency in the original and the actual insufficiency,and the mutual accumulation of phlegm, blood stasis, and drinking water .Therefore, the symptoms of emergency treatment should be based on clearing away heat and toxins, dispersing wind and evil,and resolving phlegm and spasm as the main treatment principles.Tanreqing injection is a second-class new national Chinese medicine[20]. Its prescriptions are scutellaria baicalensis, bear bile powder,goat horn, honeysuckle, and forsythia. Among them, the sovereign drug is Scutellaria baicalensis, which has the functions of clearing away heat and dampness, purging fire and detoxification, and clearing away lung heat, and has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects[21];The minister drug is bear bile powder and goat horn, which assist the sovereign drug to strengthen the effects of clearing away heat and detoxification, calming the liver and relieving convulsions, dispelling blood stasis and relieving pain; The assistant drug is honeysuckle sweet-cold and forsythia bitter-cold, which further enhance the efficacy of clearing away heat and detoxification, dispelling masses and reducing swelling.Modern pharmacological studies have confirmed that Tanreqing injection has the effects of anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral,antipyretic, and enhancing immune regulation[22]. Compared with oral administration, the injection method takes effect more quickly and can relieve the condition. Prevent the undesirable consequences of disease evolution.
A total of 10 randomized controlled studies were included in this study for meta-analysis, involving 862 patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection. The results show that Tanreqing injection assists in the treatment of patients with heart failure and pulmonary infection, and its total clinical effective rate is better than that of conventional western medicine, and it has obvious advantages in improving CRP value, shortening the time to correct heart failure, and reducing the average length of hospital stay. CRP is a non-specific marker of inflammation and tissue injury and an important indicator of treatment and prognosis[23].The length of hospital stay is a key outcome indicator in the quality control index system of "Chinese Heart Failure Medical Treatment"[24].The above results preliminarily confirmed that Tanreqing injection has a good clinical effect in adjuvant treatment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection. In terms of safety evaluation, two[18,19]studies reported that patients had no adverse reactions during medication.Three[11,14,16]studies reported that patients had adverse reactions such as skin allergy, gastrointestinal reaction, nausea and vomiting,chest tightness and blood cell decline during medication, which may be related to the patient's constitution or basic diseases. However,the difference between the test group and the control group was not statistically significant, reflecting the safety of Tanreqing injection in adjuvant treatment of heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection.
The limitation of this study is that some literatures do not mention the occurrence of adverse events or whether to conduct safety evaluation. The blind method and allocation concealment method were not mentioned in the included trials, which affected the authenticity of the analysis results. The included literatures are all Chinese, not English, and the overall quality is low, which may have a certain bias on the research results. Most trials only reported the clinical effective rate after treatment, and other observation indexes after treatment were different, so it was difficult to evaluate.Therefore, in future clinical studies, in addition to the effective rate,increasing clinical observation indexes such as Type B Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction(LVEF) can be more comprehensive and effective for the overall evaluation of the clinical efficacy of patients with heart failure complicated with pulmonary infection. Therefore, in the future, we should carry out multi-center, large-sample and high-quality randomized controlled trials as much as possible, hoping to provide more effective and authoritative evidence-based basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment, and further show the characteristic curative effect of traditional Chinese medicine.
Author's contribution
Yan Long-mei: determine the search words, responsible for literature retrieval, screening, data collection and processing and thesis writing; AI Yu-zhen: determine the search terms, and be responsible for literature retrieval, screening, data collection; Xing Ya-xuan: participated in data collection and analysis; Gao An-ran:check the data information; Xu Qi-wu: auxiliary picture drawing;Ouyang Jia-hui: responsible for the improvement and revision of the content of the article; Zhang Jing-chun: responsible for the topic selection and review of the article.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年22期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2022年22期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research advances in functional heartburn based on Rome Ⅳ criteria
- Research progress on modern pharmacological action of Radix bupleuri
- Mechanism of total flavonoids in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis based on network pharmacology
- Clinical characteristics of 72 cases with neuromyelitis optical associated optic neuritis
- Application of SOAT1 combined with multiple markers in the auxiliary diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Study on the relationship between psoriasis vulgaris and GC gene in Hainan Han nationality based on target gene capture sequencing
