Corneal epithelial defects following vitreoretinal surgery:incidence and outcomes from the DlSCOVER study
INTRODUCTION
Corneal epithelial defects (CED) following vitreoretinal surgery may result spontaneously or from intraoperative debridement due to the lack of corneal clarity that impairs fundus visibility during the operation. CED may increase discomfort postoperatively, impair visualization of the posterior segment, increase frequency/number of postoperative visits, and potentially result in corneal scarring. Although most post-surgical CEDs heal quickly without sequelae, these patients require close follow-up and treatments. There have been limited studies on the preoperative and intraoperative risk factors of postoperative CEDs or intraoperative debridement to avoid late period complications.
Various risk factors have been associated with postoperative CEDs, including: diabetes mellitus (DM), par plana vitrectomy(PPV) combined with lensectomy, tamponade usage, prolonged surgical duration, and postoperative ocular hypertension(HTN). In addition to its association with spontaneous postoperative CEDs, prolonged surgical duration has been linked to the need for intraoperative corneal debridement.DM, HTN, tamponade usage are factors associated with delayed closure. Epithelial defects with delayed healing are at risk for corneal scarring, neovascularization, infectious keratitis, corneal melting, and perforation.The main goal of this study to investigate the incidence and risk factors associated with intraoperative debridement and postoperative CEDs following PPV. This study is unique given its large sample size and long-term follow-up (,1y). Previous studies evaluated the postoperative cases by excluding subjects who underwent intraoperative epithelial debridement. In this study, we evaluated subjects with either intraoperative debridement or postoperative CEDs in terms of late-stage corneal complications.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Delayed epithelial healing occurred in 25 eyes (26.6%) in the postoperative CED group (mean 6.8wk) and in 11 eyes(18.0%) of the intraoperative debridement group (mean 6.3wk). When the risk factors for delayed healing were analyzed in 155 subjects with all epithelial defect subjects,tamponade usage was found to be statistically significant and postoperative hypotony trended towards significance (=0.02 and=0.05, respectively). DM, duration of surgery, and ocular hypertension were not found to be predictive risk factors for delayed epithelial healing.Corneal scarring developed in 16 (10.3%) of 155 subjects with epithelial defects and 1.8% overall. In eyes that developed corneal scarring, epithelial defect resolution time was a mean of 5±8wk, while eyes that did not develop corneal scarring had defect resolution in 2±2wk. There was a statistically significant relationship between corneal scar development and defect closure time (=0.00006, odd ratio=0.729/wk), as well as prior glaucoma surgery (=0.042, odd ratio=11.1; Table 4).
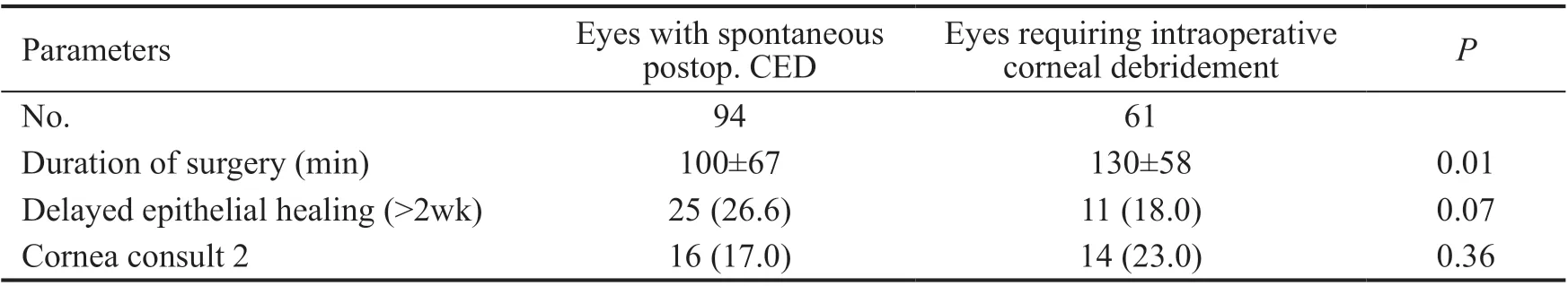
ParametersCED with scarringCED without scarringOdd ratioand may overestimate time to closure since these eyes were not typically followed daily. Comparative assessment between the intraoperative debridement group and postoperative CED’s group was performed in regard to surgical time, delayed epithelial healing, requirement cornea specialist consult (Table 3).Cornea specialist consultation was requested in 16 (17.0%)subjects in the postoperative CED group and in 14 (23.0%)subjects in intraoperative debridement group. No occurrences of infectious ulceration, corneal melting or perforation were observed in either group. Postoperative herpes simplex virus(HSV) epithelial keratitis developed in one subject with a history of preoperative HSV keratitis. This subject had epithelial keratitis resistant to topical and systemic antiviral therapy resulted in the development of corneal scar.
All the subjects underwent small gauge PPV for various diagnoses by surgeons at the Cole Eye Institute, Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, USA. In select cases, phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation were performed simultaneously.Corneal debridement was performed when corneal epithelial edema significantly decreased fundus visualization quality or pre-existing corneal pathology (, irregular epithelium)prevented required posterior pole visualization. In some subjects who underwent corneal debridement, a bandage contact lens was placed intraoperatively, according to the surgeon’s preference and/or an occlusive pressure patch was applied at the conclusion of surgery. Combined surgery,duration of surgery, gauge of surgery, and tamponade type were all recorded.
All data was analyzed with SPSS version 18. Continuous variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation for demographic data. The Mann-Whitneytest and Student’s-test were used to compare nonparametric and parametric values, respectively, between the two groups.The Chi-squared test with Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical data analyses. The percentage of patients with CED at the different time points were represented using a Kaplan-Meier curve. Regression analysis was used to identify predictive risk factors of CED and for primary and secondary outcomes. Statistical significance was defined as avalue<0.05.
除了记录沿破裂带的宽度和断错外,委员会的地质学家还发现断层带内有走向与断层带平行的小规模的线性山脊和山谷。特别是Gilbert掌握了这些地形特征的意义,评论道:“很容易理解这些山脊和山谷的起始以及维持是由于断层作用”(Ⅰ卷,33页)。他进一步指出:“在这一破裂带内与此地震相关的地表变化趋向于增加陆地形成山脊和山谷的分化”,由此建立了最近地震沿断层重复发生的证据。这些观察资料拓展了他根据博纳维尔湖海岸线的反复垂直断错得出沿犹他州沃萨奇断层带复发地震的结论(Gilbert,1884),并为构造地貌学的现代领域提供了基础(Prentice,1999)。
The primary outcome was the presence of postoperative CED on postoperative day one and the incidence of required intraoperative debridement. Secondary outcomes included:total time to resolution of epithelial defect, frequency of delayed epithelial healing (>2wk), frequency of patients requiring consultation with a cornea specialist, presence of new (, postoperative) corneal scarring at one year. Based on slit‐lamp biomicroscopy examination, corneal opacification or corneal irregularities that caused by marked treatment resistant corneal edema at the end of 1y was defined as corneal scar.Assessment of the visual significance of the corneal scar was unable to be assessed given the retrospective nature of the review and complexities of the underlying retinal disease.
As part of the prospective data collection within the DISCOVER study, CED presence, intraocular pressure (IOP)and visual acuity (VA) were collected on postoperative day 1. Subjects who underwent intraoperative debridement were defined as the intraoperative debridement group. Subjects who presented with a spontaneous epithelial defect on postoperative day one (, without intraoperative corneal debridement) were defined as the postoperative CED group. Eyes with ⅠOP >21 mm Hg or <7 mm Hg within 1wk postoperatively were defined having ocular hypertension or ocular hypotension, respectively. Eyes requiring greater than 2wk to achieve corneal epithelial closure were defined as having delayed epithelial healing. All CED subjects received an ophthalmic ointment in addition to their postoperative topical treatments (topical antibiotic and steroid).The clinical charts of all patients for both the intraoperative debridement and postoperative CED groups were reviewed retrospectively. In addition, control eyes were matched 2:1 by age/gender from those eyes not requiring without postoperative CED within the DISCOVER study for comparative assessment. Subjects with a follow-up period of less than 6mo were excluded from the study. Preoperative demographic features, systemic and ophthalmic clinical histories, ocular co‐morbidities, previous surgical or non‐surgical treatments, VA,IOP, anterior and posterior segment slit lamp biomicroscopic findings were recorded.
RESULTS
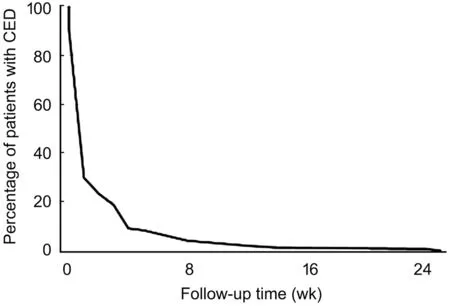
This study included 856 eyes undergoing vitrectomy surgery.Intraoperative corneal debridement was required in 61 (7.1%)subjects and spontaneous postoperative CED developed in 94(11.0%) subjects. Of the 574 subjects without postoperative CED, 188 were selected as control group with matching the age (±3y) and gender in a 2:1 ratio. The demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects are indicated in Table 1.In the postoperative CED group, the length of the surgery time(<0.01), ocular hypotension (<0.01), and DM (=0.04) were found as associated risk factors (Table 2). The mean surgical times in the intraoperative debridement and postoperative CED group were 130±58 and 100±67min, respectively; while in the control group it was 88±38min (=0.003). Operationlength was significantly greater in the intraoperative CED group compared to the postoperative CED group (=0.01).There was no statistically significant association with gauge of surgery (=0.98), combined phacoemulsification surgery(=0.13), tamponade usage (=0.37), prior glaucoma surgery(=0.50) and other corneal features (laser-assistedkeratomileusis, dystrophy, trauma, transplant;=0.90).The median time of documentation of resolution epithelial defects in the postoperative CED group and the intraoperative debridement group was 1wk (range: 1-24wk; Figure 1). It is important to note that the 1wk visit was usually the first returning postoperative visit after the postoperative day 1 visit

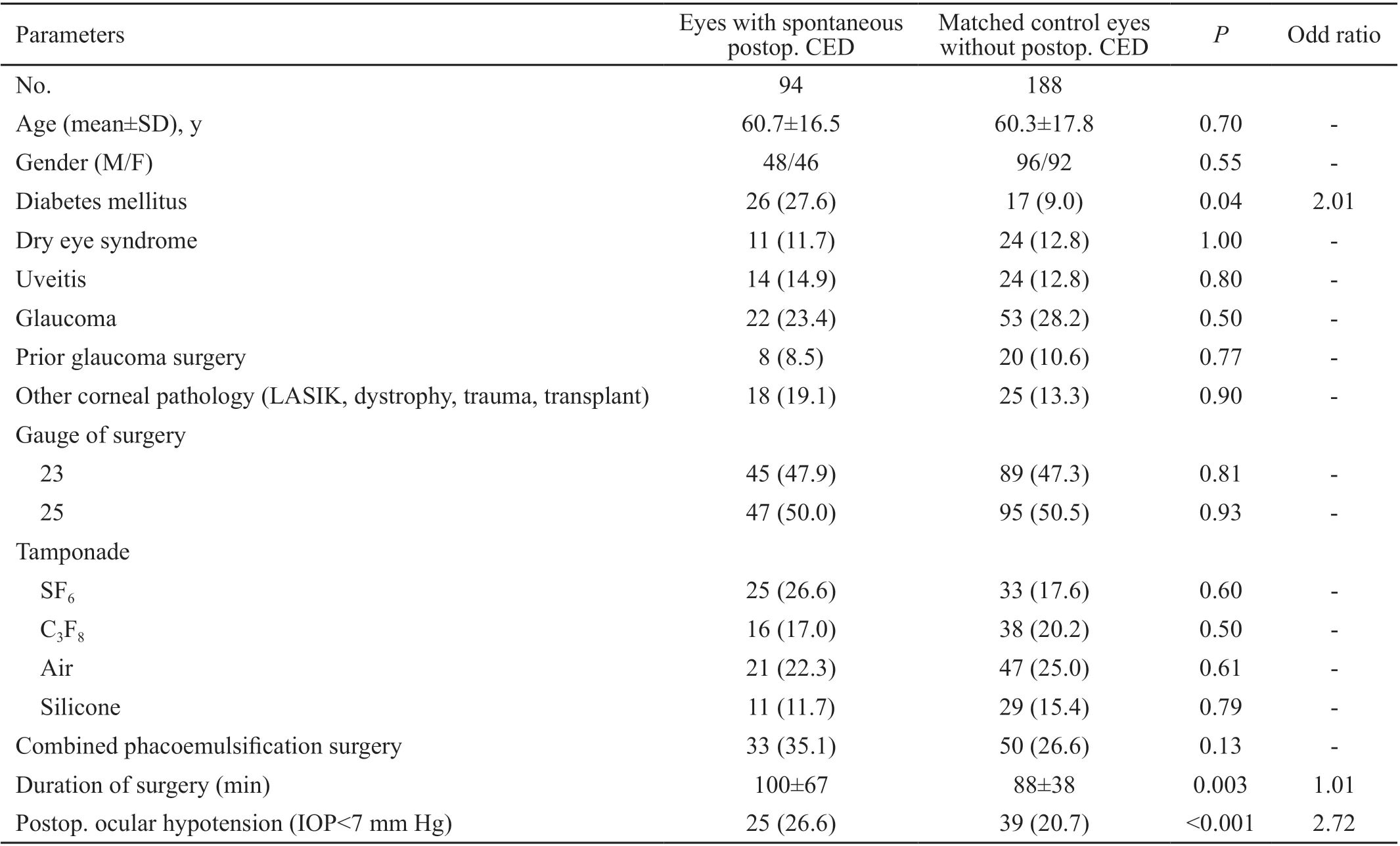
The primary inclusion criterion of this study is all subjects in the DISCOVER study database who underwent vitreoretinal surgery. The DISCOVER (Determination of Feasibility of Intraoperative Spectral Domain Microscope Combined/Integrated OCT Visualization during En Face Retinal and Ophthalmic Surgery) study is a prospective, ophthalmic surgery study evaluating the role of intraoperative OCT in ophthalmic surgery. The methods of the DISCOVER study have been previously described.

The Institutional Review Board approved the study adhered ethical principles of the Helsinki Declaration and written informed consent was given by all subjects.
We demonstrated that, like other studies in the literature, the presence of DM is associated in the formation of postoperative CEDs. DM causes structural changes and functional impairment in corneal epithelium, stroma and endothelium.There are studies showing that DM contributes to delays in healing of corneal epithelial defect. Interestingly, we did not find a relationship between DM and delayed epithelial healing and corneal scar at the end of the first year. However,this may be related to a high prevalence of DM in less complex cases and the pathology complexity (a possible surrogate for tamponade requirement) may be a more a significant factor.While the tamponade usage was not associated with the incidence of postoperative CED, we found that the use of tamponade among all epithelial defects was associated delayed epithelial healing. Previous studies have demonstrated that tamponade use is associated in CED development and delayed corneal recovery. Both gas tamponade and silicone tamponade have been linked to endothelial cell loss and CED. In the literature, there is no consensus on the impact of specific tamponade type. We did not find a statistically significant difference in the sub‐analysis of tamponade type in cases with delayed epithelial healing.
DISCUSSION
Corneal complications may be encountered by surgeons following vitreoretinal surgery. The incidence of post vitrectomy CEDs ranges from 6.1% to 28.1% in the literature. In our study,postoperative epithelial defects developed in 94 of 795 (11.8%)subjects who underwent vitrectomy. Prolonged duration of surgery, HTN and hypotension, and DM were found to be risk factors for postoperative CED formation. In previous studies,prolonged duration of surgery is associated with increased postoperative CED formation and intraoperative debridement rate. In our study, while the duration of surgery was significantly higher in both groups compared to the group without CEDs, the operation length in the intraoperative debridement group (130±58min) was significantly higher than the postoperative CED group (100±67min) likely contributing in these cases to the need for intraoperative intervention due to loss of visualization. Chendid not identify surgery duration as a factor for persistent corneal epithelial defect formation in their study. While Hiraokacreated a risk scale predictive of postoperative CEDs that included surgical time, intraoperative lensectomy, tamponade.
Published reports have identified the intraoperative debridement rates during vitrectomy to be between 8% and 24%.In our study, the intraoperative debridement rate was 7.1%.The operation time in the intraoperative debridement group was longer than the postoperative CED group. This result is consistent with the study in which Viratastated that the duration of surgery was higher in subjects undergoing intraoperative debridement. Interestingly, extended exposure to microscope light may result in long-term dysfunction in the corneal epithelium and corneal film layer. Finally,the potential high complexity of these cases and overall disease burden in these eyes may be a major factor for poorer prognosis, including long-term hypotony, severe ocular ischemia, and long-term tamponade requirements.
Intraocular pressure changes are common issues following vitrectomy. In studies conducted in the literature on the formation of post vitrectomy CED, ocular hypertension has been predominantly evaluated with minimal attention to hypotony. Chiangfound that ocular hypertension was not associated with post vitrectomy CED’s, while Chenfound it to be a contributing factor. In our study, we demonstrated that postoperative ocular hypotension was found to be associated with the development of post vitrectomy CEDs. Ocular hypotony can disrupt intraocular fluid dynamics,causing endothelial dysfunction and consequently corneal epithelial complications.
1.4.1 防疫设施 场区周围应设有3m以上的防疫隔离墙,管理区、生产区及每栋羊舍的入口处应设有消毒通道。场区内应分设净道和污道。在场区空旷地带种植无毒无害的绿色植物。羊场应配备药浴池。药浴池应建成长方形,以1只种羊能通过而不能转身为宜,药浴池出口端应设滴流台。
对比疑似乳腺病变患者2种检查准确性情况(见表2),乳腺MR动态增强扫描联合扩散加权成像检查结果灵敏度90.63%、特异度80.00%、准确性88.10%均高于乳腺MR动态增强单一检查(56.25%、30.00%、50.00%),两者差异明显(P<0.05)。
There are important limitations in this study that should be recognized. Defect diagnosis and closure times can only be determined based on the frequency of clinical visits. The study may not be adequately powered to detect true differences in the risk factors for postoperative CED compared to intraoperative debridement. A binary distinction for DM may not provide maximum differentiation for defining risk, such as HbA1c or duration of DM. Variable thresholds for epithelial debridement by different surgeons creates unique challenges for standardized risk assessment. Ⅰt is also difficult to estimate the clinical significance of corneal scarring given the underlying retinal disease and retrospective nature of the chart review. The retrospective assessment limits characterization by objective parameters such as depth, degree of opacity, or topographic irregularity
3.1 NEC的发病机制 研究表明,肠道发生炎症时,LPS激活大鼠核转录因子-B(nuclear factor-kap
This study demonstrated that longer duration of surgery is the most strongly associated factor with development of spontaneous CED and intraoperative corneal debridement.Further research is needed to better identify the critical factors involved in reducing risk of corneal scar formation and delayed healing. Using the results from this study, a potential future prospective trial could be considered in high-risk individuals for earlier more aggressive corneal intervention,including topical therapeutics, corneal specialist consultation and possible use of other healing-promoting modalities (,amniotic membrane, bandage contact lens).
后方法教学理论反对对于不同的教学环境和教学对象都采取完全相同的教学方法。学生的英语水平参差不齐,在教学过程中要结合学生的具体情况设计课程,采取不同的方式进行教学。会展英语教学是知识(语言知识和专业知识)和技能(交际技能和专业技能)相结合的教学,但根据学生的具体情况要有所调整:有的侧重于语言理解,有的侧重于课堂实践活动。
伴随社会经济和科技的全面发展,人们在生产或生活中对于能源的需求逐渐增多,作为重要能源的矿产资源,其需求量也随之逐渐增加,随着开采数量的增多,部分矿产资源开采难度也越来越大为。所以如何进一步利用现代遥感技术来实现科技化地质找矿工作已经成为集中关注的问题。基于此,笔者针对“对现代遥感技术在地质找矿中的应用研究”的讨论具有现实意义。
清初传记散文中遗民形象书写的道德范式—以清初遗民徐枋传记为例……………………………………杨旭辉(158)
Supported by National Institutes of Health/National Eye Institute, Bethesda, Maryland, USA (K23-EY022947-01A1).
None;None;None;None;served a speaker for Zeiss and Dompe;a consultant for Bausch and Lomb, Novartis, Carl Zeiss Meditec; a researcher for Allergan and Bausch and Lomb; and has a patent licensed to Leica;None;a consultant for Alcon,Allergan, Leica, Santen, Thrombogenics, Genentech, Novartis,Aerpio, Allegro, Regeneron, Roche, Stealth, Adverum and Zeiss; has intellectual property licensed to Leica; and receives research support from Alcon, Adverum, Genentech,Regeneron, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Novartis, Aerpio, and Thrombogenics.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年1期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2022年1期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- lnstructions for Authors
- Comment on: Trends in research related to high myopia from 2010 to 2019: a bibliometric and knowledge mapping analysis
- Progress of clinical therapies for dry age-related macular degeneration
- Observation seasonal variation of intraocular pressure in young healthy volunteers
- Effectiveness of oral probiotics supplementation in the treatment of adult small chalazion
- Characterization and validation of a chronic retinal neovascularization rabbit model by evaluating the efficacy of anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory drugs
