ZMYND10 downregulates cyclins B1 and D1 to arrest cell cycle by trimethylating lysine 9 on histone 3
Long-Ji Wu,Xiang-Ning Zhang*,Jian Wang,Xia Kong,Bi-Ying Zheng,Jing Huang,Hong-Bing Yu,Zhi-Wei He,*
1Department of Pathophysiology,School of Basic Medical Science,Guangdong Medical University,Dongguan,Guangdong,China.2Chinese-American Tumor Institute,Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Diagnostics,Guangdong,China.3Department of Clinical Microbiology,Institute of Laboratory Medicine,Guangdong Medical University,Dongguan,Guangdong,China.
Abstract The BLU gene coding for zinc finger,MYND-type containing 10(ZMYND10)protein is mapped on chromosomal region 3p21.It is frequently lost in some kinds of cancers due to hypermethylation on its promoter region and identified as a tumour suppressor gene.The underlying mechanisms for BLU-mediated tumor suppression remain unclear.BLU has been reported to disturb cell cycle progression.The present study aims at examining whether ZMYND10 prevents progression of the cell cycle by targeting to repressive histone marks and downregulating the level of cyclins.Proteins structurally similar with ZMYND10 have been shown to recognize DNA sequence upstream of coding portion of the gene encoding cell cycle regulators.Enzymes,notably demethylases modifying the lysine residues are over-expressed line oncoproteins,and targeted in anti-cancer therapy.BLU was re-expressed in H1299 and HepG2 cells.The level of cyclin D1,cyclin B1 and trimethylate lysine 9 on histone 3(H3K9me3)and the binding of BLU with SIN3A(a component of the co-repressor)were detected.Cell cycle profile was measured.The evolutionary relationship between ZMYND10 and other ZMYND proteins was analysed by phylogenetic tree construction.We found that BLU expression induced G1 arrest in H1299 cells,and induced G1/G2 arrest in HepG2 cells.Cell cycle arrest was correlated with reduced activities and levels of cyclins;cyclin D1 was downregulated in H1299 cells;Both cyclin B1 and D1 were downregulated in HepG2 cells;and that BLU was associated with SIN3A.In both cell lines,the expression of H3K9me3 was induced.BLU was clustered with histone methyltransferase SMYD3 and SMYD1 on the same clade of the deduced phylogenetic tree.The results thus suggested that ZMYND10 encoded by BLU inhibited cyclins activity to prevent cell cycle progression through interaction with repressors and histone repressive marks to block the expression of genes coding for cyclins.
Keywords:BLU/ZMYND10;tumor suppression;cell cycle arrest;cyclin;trimethylated lysine 9 on histone 3
Introduction
BLU is a tumor suppressor gene(TSG)that maps to the chromosome 3p21 region,which harbors multiple TSGs and is frequently lost in a variety of tumors.BLU is mainly inactivated by hypermethylation on the promoter region,in lung,breast,liver,and nasopharyngeal cancers,as well as in neuroblastoma[1-5].However,the mechanisms underlying the tumor suppression remain unclear.We previously showed that BLU expression engaged the JNK/mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK)pathway,blocked progression of the cell cycle with G1 arrest[6],and inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase(ERK)/MAPK by antagonizing signaling by the oncoprotein Ras[7].BLU has also been shown to induce G2 arrest in breast cancer-derived MCF-7 cells[8].
BLU encodes a protein with domain of zinc finger myeloid,Nervy and DEAF1-type containing 10(ZMYND10).Some members of ZMYND family are known tumor suppressors,such as CBFA2T1/ZMYND2,which is inactivated by fusion with the transcription factor-coding gene RUNX1 leading to a common karyotype in acute myelogenous leukemia(AML),involving chromosomal translocation t(8:21)(q22:q22)[9,10].Physiologically,CBFA2T2/ZMYND2 represses gene transcription through association with components of co-repressors such as SIN3A.The findings raise a possibility that BLU protein involves molecular interactions to modulate the expression level of cell cycle regulators.
Gene expression is activated or repressed by the modification of amino acid residues on extended peptide tails of histones.The marks like lysine 9 on histone 3(H3K9),and lysine 36 on histone 3(H3K36)are mono-,bi-,and tri-methylated by methyltransferases to regulate gene expression.In fact,the aberrant methylation of repressive mark H3K9 contributing to gene deregulation has been utilized as a therapeutic target for antitumor treatment[11].Demethylases which function to modify the histone marks are over-expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and other human cancers.Their inhibitors,therefore,have been demonstrated to be promising therapeutic agents in chemotherapy resistant clinical cases[12].A protein of ZMYND family,BS69/ZMYND11 has been known to regulate gene expression through its methylation on lysine residues on histone 3 and its mutants[13].Another protein of the ZMYND family,RACK7 /ZMYND8 interacts with the selective epigenetic marks dimethylated H3.1K36(H3K36me2)/acetylated H4K16(H4K16ac),and its expression inhibited the motility and migration of breast cancer cells[14,15].Both RACK7/ZMYND8 and BS69/ZMYND11 have been identified as a tumor suppressor.Based on the structural similarities of BLU and CBFA2T2,RACK7,and BS69,we speculated that BLU/ZMYND10 might exert tumour suppressive effects by binding co-repressor proteins and interacting with histone marks.
The transition from gap 1(G1)to synthetic(S)phase of cell cycle is controlled by complexes of cyclin D/CDK4/6,and entry to mitosis from G2 phase,by the complex of cyclin B/CDK1[16,17].Regulation of cell cycle is achieved by the association of sequence upstream of the coding portion of cell cycle regulator with repressors and activators of gene transcription,including histone marks or histone modifying enzymes,for example,methyl transferase of a repressive mark H3K9[18].
In the present study,we therefore assessed the cell cycle regulatory activity of BLU according to its capacity to reduce cyclin D1 and cyclin B1 levels.We also intend to examine whether the alteration of cell cycle profile and level of relevant cyclins are correlated with some histone marks.A repressive mark,trimethylated H3K9(H3K9me3)is to be tested in view of the findings that H3K9 methyltransferase associates with promoter of the cyclin D1 coding gene CCND1.
Phylogenetic tree describes the evolutionary relationship between structurally and functionally related proteins based on sequence alignment.It is constructed by inputting retrieved gene or protein sequences to analysis software.Among ZMYND proteins,RACK7/ZMYND8(PKCB1)and BS69/ZMYND11(ZMY11)share domain compositions and are both known to recognize genomic marks,while other proteins SMYD3/ZMYND1 and SMYD1/ZMYND22 have been reported to exert methyltransferase activity to modify histone and non-histone proteins.In fact,SMYD proteins are defined by a SET(Suppressor of variegation,Enhancer of Zeste,Trithorax)domain divided into two segments by an MYND domain,and a SET domain is followed by cysteine-rich post-SET domain[19].SMYD3 is often upregulated in cancer cells and plays an oncogenic role in different types of cancers,including colorectal,prostate and breast cancers[20,21].SMYD3 contributes to carcinogenesis through methylation of active marks,as H3K4 and histone 4 lysine-5(H4K5)methyltransferase[22,23].In addition,PDCD2/ZMYND7 has been known as a pro-apoptotic molecule and identified as a TSG[24].We intend to characterize the evolutionary relationship between these proteins so as to formulate a hypothesis on function of BLU/ZMYND10.
Methods
Cells,Adenoviral Construct,and Plasmids
BLU-negative non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC)H1299 cells,hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells,and control BLU-positive NSCLC A549 cells for immunoblotting were obtained from the Type Culture Collection of the Chinese Academy of Science(Shanghai,China).BLU-expression plasmid BLU pCD316 was constructed by inserting full-length cDNA(NM_015896.4)into the enhanced green fluorescent protein-tagged plasmid pCD316,as described previously[6].Recombinant BLUAd5 was prepared by co-transfection of the plasmid with adenoviral structural proteincoding genes into packaging 293 cells[25].The reporter -1745CD1LUC containing the full-length cyclin D1 coding gene promoter was provided by Professor Richard G.Pestell(Pennsylvania Cancer and Regenerative Medicine Centre,PA,USA)[26].The firefly luciferase reporter construct of the human cyclin B1 promoter,hB1,was donated by Professor Kurt Engeland(Universität Leipzig,Leipzig,Germany)and was constructed by inserting the B1 promoter sequence into KpnI/NcoI sites in the pGL3-Basic vector[27].The pGL3-based vector with constitutiveRenillaluciferase expression was purchased from Promega Corporation.
Antibodies and Reagents
Rabbit anti-human BLU/ZMYND10 polyclonal antibodies(cat.nos.ab111862 and FNab09650)were purchased from Abcam(Cambridge,UK)and Fine Biotech Co.,Ltd.(Wuhan,China),respectively.Anti-H3K9 monoclonal murine(HW029;Signalway Antibody LLC),anti-SIN3A(G-11 clone;Santa Cruz Biotechnology,Inc.,Santa Cruz,CA,USA)and anticyclin D1 polyclonal(clone DCS-6;Sigma-Aldrich,Shanghai,China)antibodies were also used.Murine monoclonal anti-human cyclin B1 antibody(clone PC 12-301,cat.No.05-373)was purchased from Millipore(Guangzhou,China),and anti-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH)was from Bioworld Technology Inc.(Bloomington,Indiana,USA).The transfection K4 kit was kindly provided by Dr.Roland Klosel(Biontex GmBH,Munich,Germany).
Infection with Adenoviral Recombinant BLUAd5
Adenoviral infection was optimized by titrating virus to identify the multiplicity of infection(MOI).Cells were then infected with BLUAd5 at 0,10,20,and 40 MOI,together with pCD316 Ad5 at 40 MOI,and the infected cells were collected.
Transfection
Monolayer cells were grown up to 80% confluence on the bottom of the flask.Mycoplasma contamination was screened by staining cells with DNA dye propidium iodide(PI;Sigma-Aldrich,Saint Louis,Missouri,USA).The cells were detached,pooled in fresh DMEM medium(Gibco Biotechnology,Grand Island,New York,USA)and seeded into 12- or 6-well culture plates.The cells were co-transfected with plasmids mixed with the reagent,according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Cell Viability Assays
Up to 103monolayer cells infected with BLUAd5 and pCD316Ad5 were seeded into wells of 96-well culture plates in triplicate.After incubation for 24 h,the medium was sucked off and the cells were washed and incubated with Cell Counting Kit-8 reagent(Dojindo,Kumamoto,Japan).Absorbance values were read using a BioTek ELISA reader(Gene Company Limited,Hong Kong,China).
Western Blotting
After transfection,cells were harvested using RIPA buffer and scratched from the bottom of the culture plates.The lysates were then boiled at 95°C for 5 min and total protein was separated via SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis(PAGE).The resultant proteins were electroblotted to nitrocellulose membranes.Non-specific binding was blocked with 5%defatted milk diluted in PBS at room temperature for 1 h or at 4°C overnight,followed by co-incubation with primary antibodies.The reaction was developed after conjugation with labelled secondary antibodies(Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc.,Waltham,Massachusetts,USA).
Immunoprecipitation
Transfected cells were lysed with RIPA buffer,the cell lysates were pelleted,the supernatant was collected,and immunoprecipitation was performed as described[28,29].The supernatant was mixed with reaction buffer(50 mM Tris(pH 7.5),5 mM EDTA,150 mM NaCl,1 mM dithiothreitol(DTT),0.01% NP40,2 µg/ml bovine serum albumin,0.02 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride(PMSF),and 1× protease inhibitor mixture)containing anti-BLU antibodies and Sepharose 4B beads(150 µl),and rotated at 4°C overnight.The pre-washed beads were mixed with the antibodies and washed with washing buffer(50 mM Tris(pH 7.5),5 mM EDTA,450 mM NaCl,1 mM DTT,0.01% NP40 and 0.02 mM PMSF).Bound proteins were visualized via Western blotting and probed with G-11 anti-SIN3A antibody at 4°C overnight.
Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
As described previously[6],BLU pCD316 or empty vectors were cotransfected to H1299 cells with reporter -1745CD1LUC and renilla luciferase vector;BLU pCD316 or empty vectors were co-transfected to HepG2 cells with reporters hB1 and -1745CD1LUC and renilla vector.After transfection for time interval the cells were harvested at different times after transfection,via lysis with 1× diluted passive lysis buffer(Promega Corporation,Madison,Wisconsin,USA).And the luciferase activity was then determined using a luminometer(Promega Corporation,Madison,Wisconsin,USA).The ratios of firefly andRenillaluciferase fluorescence were calculated to calibrate the difference in transfection efficiency.
Cell Cycle Analysis
Cells were cultured in medium supplemented with 0.5% FBS to synchronize the cell cycle,and then transfected with plasmid BLU pCD316 or empty vector,as described previously[6].They were harvested at 12,and 24 h after transfection,fixed with 80% ethanol at −20°C,and stained with PI diluted in assay buffer.Samples were then measured with a FACScan machine(Becton Dickinson,Franklin Lakes,New Jersey,USA).Three independent experiments were performed and the proportions of G1,S,and G2/M populations were determined.The data were analysed using Modfit LT-BD version ModFit LT 3.1(Verity Software House,Biotechnology,Topsham,ME,USA).
Bioinformatics Analysis
The protein sequences of BLU/ZMYND10(O75800 in UniProtKB)and several other proteins from the same family,including ZMYND1(SMYD3;Q9H7B4),programmed cell death protein 2(PDCD2;Q16342),RACK7/ZMYND8(PKCB1;Q9ULU4),ZMYND9(USP19;O94966),BS69/ZMYND11(ZMY11;Q15326),and ZMYND22(SMYD1;Q8NB12),were retrieved from www.uniprot.org.The sequences in FASTA format were pasted into the dialogue frame of Clustal Omega(www.ebi.ac.uk).Phylogenetic trees were constructed after sequence alignment.
Statistical Analysis
For quantitation experiments,mean values were calculated using data from at least three independent experiments and presented as mean ±standard deviation.Paired values were compared using Student’sttests.A value of p<0.05 was considered to indicate a significant difference.
Results
BLU downregulated cyclins governing transition to different cell cycle phases
BLU is inactivated in different tumors due to hypermethylation on its gene promoter.We have previously reported that in nasopharyngeal carcinoma(NPC)derived CNE-2 cells,re-expression of BLU arrested cell cycle at G1 phase by inhibition of cyclin D1[6].G2 arrest induced by BLU was also reported but its correlation with cyclin alteration was lacking[8].In the present study,BLU was re-expressed in NSCLC derived H1299 cells and hepatoblastoma derived HepG2 cells by DNA transfection and infection with recombinant BLU Ad5.In H1299 cells,expression of BLU was validated by the presence of green fluorescence which was tagged with the expressor of BLU viewed microscopically(Fig.1A)and band on immunoblot tested by probing with specific antibody(Fig.1B,top row).The expression of BLU contributed to a reduced level of cyclin D1 in this lung cancer line(Fig.1B,second row),but did not alter the level of cyclin B1.BLU also induced a repressive histone mark H3K9me3(Fig.1B,).BLU potently inhibited the viability of the target cell when expressed by the recombinant adenovirus 5(Fig.1C).And in complementary with the expression level of cyclin D1 tested by immunoblotting,reporter assay for cyclin D1 coding gene CCND1 suggested that the promoter of CCND1 was inhibited in BLU expressing H1299 cells(Fig.1D).
In HepG2 cells,re-expressed BLU was demonstrated by fluorescence microscopy(Fig.2A)and immunoblotting(Fig.2B,top row),it was also noted that proteins of cyclin D1 and cyclin B1 were downregulated(Fig.2B,second row;Fig.2C);similar with H1299 cells,H3K9me3 mark was induced in HepG2 cells(Fig.2B,third row).The binding of BLU with SIN3A(a component of co-repressor)was shown by immunoprecipitation(Fig.2D).Luciferase assay suggested that promoters of both CCND1 and cyclin B1 coding gene CCNB1 were inhibited as measured by reporter gene assay(Fig.2E,2F).
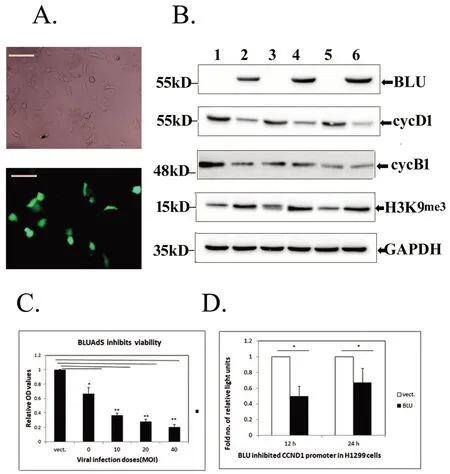
Figure 1.Re-expression of BLU downregulated cyclin D1 and induced H3K9me3 in H1299 cells.(A)The expression of BLU in H1299 cells after transfection was validated by the presence of green fluorescence tagged with the expressor(scale bar:5 μm).(B)The expression of BLU(top row)and regulated molecules cyclins D1(cycD1;second row),cyclin B1(cycB1,third row),and H3K9me3(fourth row)after its expression.GAPDH(bottom row)was loaded to calibrated protein amount.Samples 1 and 2 were untransfected H1299 and A549;3,4 and 5,6 were mock and BLU transfectant H1299 harvested at 12 h and 24 h.(C)BLU expressed by different dose of infected recombinant BLU Ad5 inhibited H1299 cell viability.Recombinant adenovirus 5 with vector(vect.)at 40 MOI served as control and the mean value of OD registered on CCK8 assay was set as 1 unit.* represented p<0.05,and ** as p<0.01 when comparing between vector control and BLU Ad5 infected at doses of 0,10,20,and 40 MOI.Data obtained from at least three independent tests,and the height of the columns represented mean±SD.(D)Luciferase assay.H1299 cells were co-transfected with BLU pCD316 or the empty vector(vect.)with firefly luciferase reporter with full length CCND1 promoter and renilla luciferase vector.The ratios of activity of two luciferase registered were calculated.The values for empty vector at 12 h and 24 h were set as 1 unit,and height of solid columns represented as fold number of reduction in BLU transfectants*represented p<0.05.Mean±SD was calculated using values obtained from at least three independent tests.
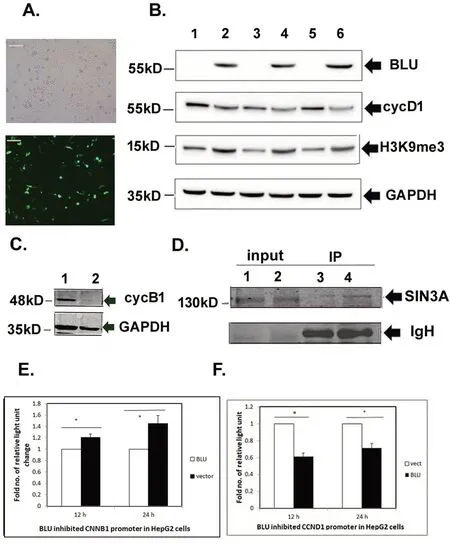
Figure 2.BLU re-expressed in HepG2 cells regulated cyclins B1 and D1,and was associated with repressor SIN3A.(A)Expression of BLU in HepG2 after transfection was validated by the presence green fluorescence tagged with the expressor pCD316(Scale bar=5μm).(B)Expression of BLU in HepG2 cells(top row),and the downregulated cyclin D1(cycD1),induced H3K9me3(third row).GAPDH was loaded as control for calibrating protein amount.The numbers 1,2 negative control H1299 and A549 cells;3,4 and 5,6 were mock and BLU transfectants after transfection after 12 h and 24 h respectively.(C)Cyclin B1,a G2 cyclin was downregulated by BLU.1,2 were mock and BLU transfectant H1299 cells.(D)Binding of BLU with transcription repressor SIN3A revealed by immunoprecipitation.The whole cell lysis input of the mock and BLU transfectants(1,2)and immunoprecipitate(IP;3,4)were assayed by immunoblotting,probing with specific anti-SIN3A antibody(Upper row);and the excessive immunoglobulin heavy chain(IgH)was present in the loaded IP sample(lower row).(E)HepG2 cells were co-transfected with BLU pCD 316 and the empty vector with firefly luciferase reporter hB1 with human CCNB1 promoter,and the internal control renilla luciferase vector.The ratios of firefly and renilla luciferase activity registered were calculated,and the values for BLU transfectants were set as 1 unit,the elevated fold numbers of the vector were represented as the height of the solid columns.*indicated p<0.05.Data obtained from at least three independent tests and presented as mean+/-SD.(F)HepG2 cells were co-transfected with pCD316,empty vector with firefly luciferase reporter with full length CCND1 promoter and renilla luciferase vector.The manipulation was identical with Fig.1D.
In summary,re-expressed BLU regulated the levels of G1 and G2 cyclins in a cell line or histologic origin dependent manner;it downregulated cyclin D1 in H1299 cells and both cyclins B1 and D1 in hepatoblastome line HepG2 cells.
BLU arrested cell cycle at different phases correlated with inhibition of cyclins.
When re-expressed with BLU,the two cell lines presented different patterns of arresting cell cycle.Similar with CNE-2 cells derived from NPC[6],G1 arrest was induced in H1299 cells at 12 h and 24 h after transfection with BLU(Fig.3A,3B).After expression of BLU,cells were accumulated at G0/G1 in comparison with the control,while the mock transfectants had stable level of cells of this phase,but more cells progressed to S phase(Fig.3C).Higher G1 population was seen in BLU expressing H1299 as registered in several independent tests(Fig.3D).
The hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells were re-expressed with BLU.At 12 h after transfection with BLU,cells population of G0/G1 was similar for BLU and mock transfectants,but the accumulation of G2/M cells indicated G2 arrest(Fig.4A);the downregulated cyclin B1 at the level of protein expression(Fig.2C)and activity of CCNB1 promoter(Fig.2E)in BLU expressing HepG2 cells explained G2 arrest in this line,as cyclin B1 functions to promote G2 to mitosis transition.At 24 h after transfection,G1 arrest was induced by BLU as evidenced by the accumulation of G0/G1 population(Fig.4B).The concurrent G1 and G2 arrest in a time course dependent manner induced by BLU was suggested by several independent tests(Fig.4D).
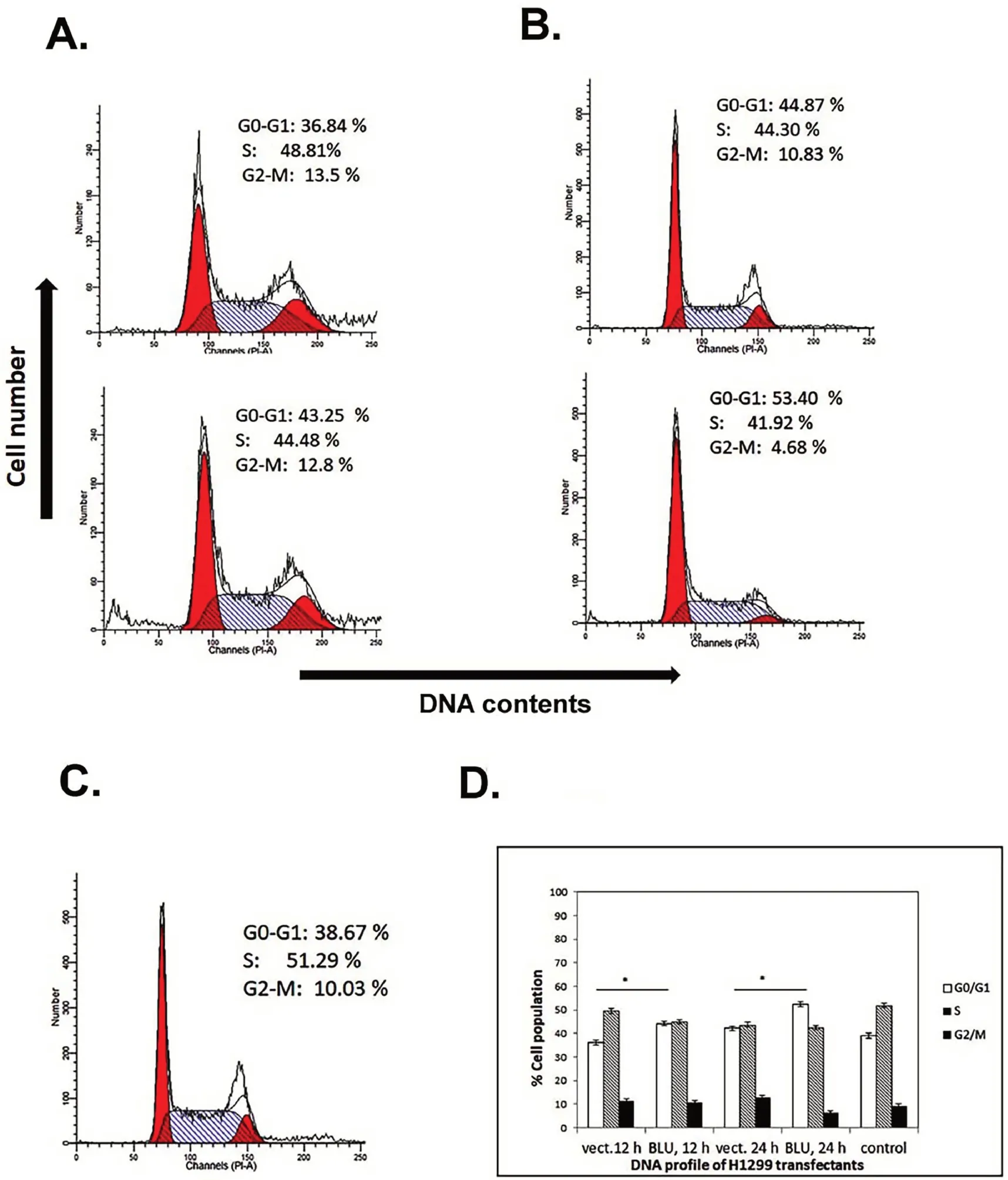
Figure 3.Cell cycle profile of BLU transfectant H1299 cells.(A)H1299 cells were transfected with empty vector(upper panel)and BLU pCD316(lower panel).In comparison with mock and untransfected(C),G1 arrest was induced in BLU transfectants as evidenced with accumulation of G0/G1 population.(B)Transfection after 24 h,BLU expressing cells showed G1 arrest as indicated by the consistently higher G0/G1 population.(D)Bar graph showed quantification of flow cytometric analysis.The values represented mean±SD calculated with data obtained from at least independent experiments.Statistical significance is shown using the Student t test analysis;*P<0.05.
The evolutionary similarity in structure suggested possible involvement of BLU in histone modification
The phylogenetic tree with the amino acid sequences of seven ZMYND domain containing proteins was constructed(Fig.5A).The result showed that a protein with deubiquitinase activity,USP19/ZMYND9 was located in a separate,distant branch.The rest of the six proteins fell into three distinct clades.Two proteins with bromo,PHD,PWWP,and MYND domains,RACK7/ZMYND8(PKCB1)and BS69/ZMYND11(ZMY11)were clustered together;they shared domain compositions and both function as genomic reader.Their closer relationship was suggested.BLU/ZMYND10 was clustered in a clade with SMYD3,SMYD1 and PDCD2.SMYD3 has been known as a methyltransferase of H3K4 with oncogenic potential[20-22],and SMYD1 is a H3K4 methyltransferase and functions to regulate mitochondrial energetics in mice[30].PDCD2/ZMYND 7 has a linear structure similar with BLU/ZMYND10;it is a pro-apoptotic molecule with DNA binding and regulation abilities according to www.uniprot.org.Its activity to modify histone and non-histone proteins remains to be dissected.
Discussion
BLU has been recognized as a TSG because of hypermethylation on its promoter,leading to reduced or silenced expression in human tumors[1-4].Its coding product,ZMYND10,was previously reported to downregulate cyclin D1 to prevent cell cycle transition from G1 to S phase[6,7].Ectopic expression of BLU additionally downregulated cFLIP and cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2(cIAP2)to potentiate death ligand TRAIL-induced apoptosis[25].
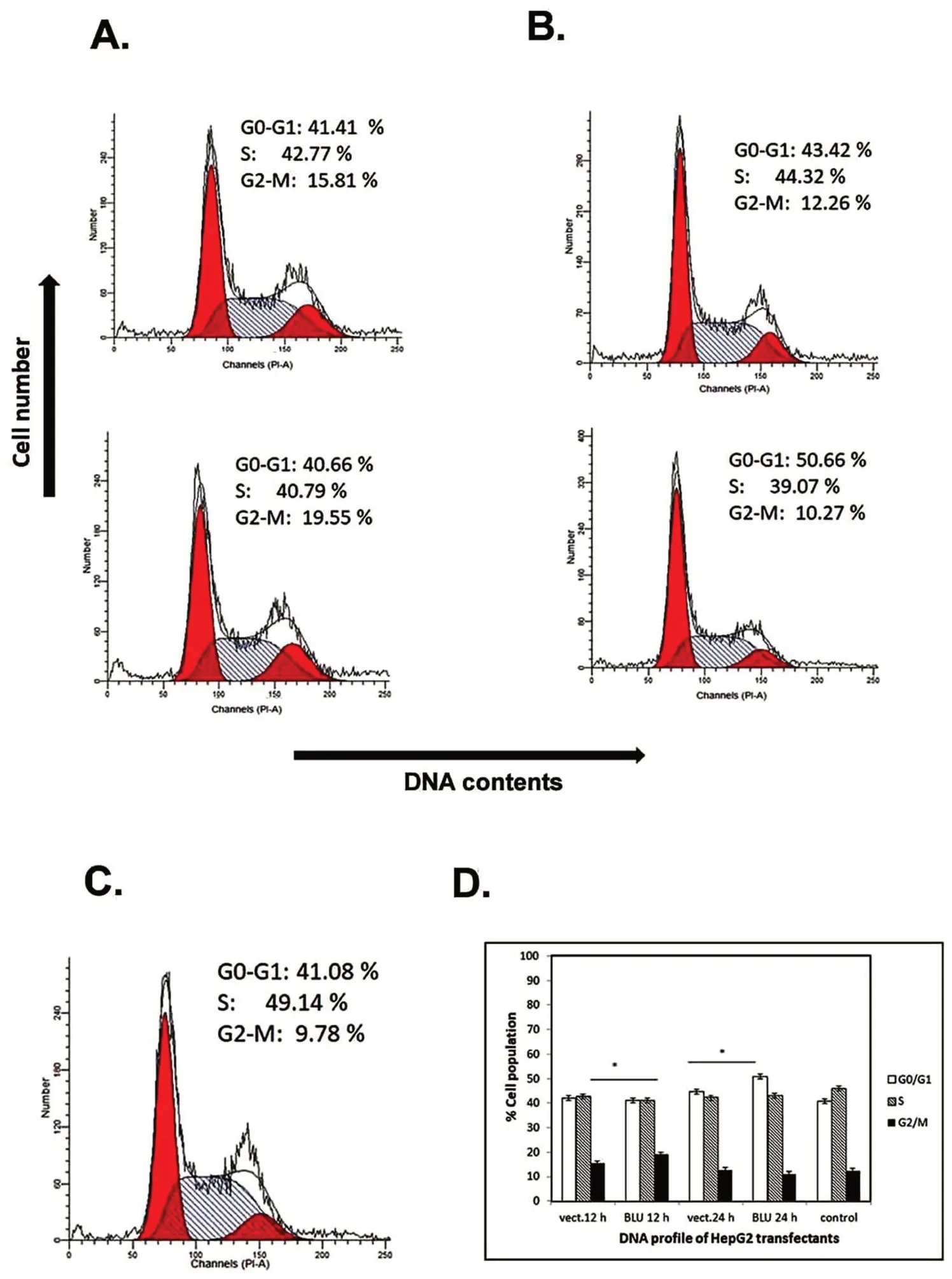
Figure 4.Cell cycle profile of BLU transfectant HepG2 cells.(A)HepG2 cells were transfected with empty vector(upper panel)and BLU pCD316(lower panel)for 12 h.G2 arrest was induced in BLU transfectants as the population of G2/M was accumulated in comparison with the mock and untransfected control(C).(B)G1 arrest was induced by BLU at 24 h after transfection,as indicated by the accumulation of G2/M population.(D)Bar graph showed quantification of flow cytometric analysis.The values represented mean ± SD calculated with data obtained from at least independent experiments.Statistical significance is shown using the Student t test analysis;*P<0.05.
Cell cycle progression is regulated by cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase(CDK)complexes formed at different phases of the cell cycle and is frequently targeted by tumour suppression.CDK acquires catalytic activity by binding to cyclins,which show oscillating expression levels during the cell cycle,attaining high levels during gap phases[16,17],.The expression has been reported to induce both G1 arrest[6]and G2 arrest[8].In the present study,BLU induced G1 arrest in NSCLC H1299 cells,and G1 and G2 arrest in hepatoblastoma HepG2 cells,in a time-dependent manner.These findings suggested that BLU targeted different cell cycle regulators in different cell types.
BLU induced G1 arrest at 12 h and 24 h after transfection in H1299 cells,as evidenced by accumulation of the G0/G1 cell population(Fig.3).In this cell line,the level of cyclin D1 was reduced by BLU,and the activity of the cyclin D1 coding gene CCND1 promoter was inhibited as revealed by luciferase assay(Fig.1D).The data suggested that BLU targeted to the sequence upstream of the coding portion of CCND1 coding for cyclin D1,through a mechanism(s)to be elucidated.As shown in cells of other origin[8],G2 arrest was induced in HepG2 cells 12 h after transfection with BLU,while G1 arrest occurred after further culture for 24 h(Fig.4).We demonstrated in this cell line that both cyclin D1 and cyclin B1were was downregulated by BLU.
In the present study the elevation of H3K9 me3 has been indicated in both cell lines tested,of different origins(Fig.1B and 2B);A relationship exists between chromatin structure,e.g.a certain degree of spatial organization,and gene expression(for review see 31).Modification of chromatin marks on extended peptide tails,notably lysine residues like H3K4 and H3K9 are essential for the activation or repression of genes[32].While methylated lysine 4 on histone 3(H3K4)is associated with transcriptionally active chromatin,trimethylated H3K9(H3K9me3)represses gene transcription.
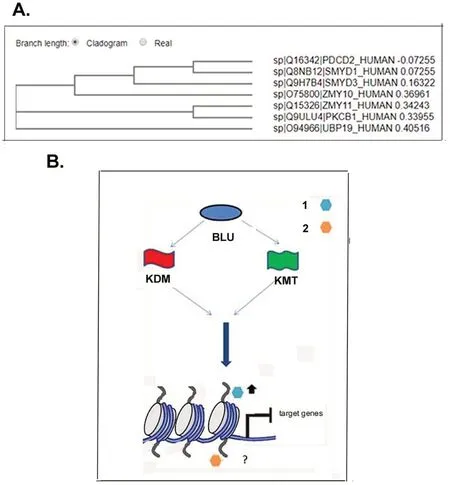
Figure 5.Phylogenetic tree and scheme of possible pattern of BLU mediated histone modification.(A)A phylogenetic tree was constructed after input of sequence of ZMYND proteins in FASTA format.UBP 19/ZMYND-9 with deubiquitinase activity was mapped on a distant clade;BS69/ZMYND-11(ZMY11)and RACK7/ZMYND8(PKCB1)have identical motif composition and both function as genomic reader;they were mapped on the same clade;BLU/ZMYND10(ZMY10)was located on the same clade with ZMYND1(SMYD3),ZMYND22(SMYD1)and ZMYND7(PDCD2).Among proteins with evolutionary similarities with BLU/ZMYND10,ZMYND7 is a pro-apoptotic factor,while both SMYD3 and SMYD1 possess catalytic activity of histone methyltransferase,suggesting a possible role of BLU in modifying histone modification.(B).Scheme of possible role of BLU in regulation of gene transcription through histone modification.When BLU/ZMYND10 is expressed,it interacts with enzymes catalyzing methylation,lysine methyltransferase(KMT,flag in green)or those catalyzing demethylation,lysine demethylase(KDM,flag in red),to induced trimethylation of repressive marks,as exemplified with H3K9(hexagon of light blue),or possibly,modify the activity of active marks(hexagon in orange).The marks in turn bind the target sequences upstream of coding portion of genes to prevent their expression.
It has been reported that the activity of cyclin D1 promoter is regulated by its crosstalk with histone mark on H2A.Z and involves interaction with modifying enzymes of H3K9 recruited to CCND1 promoter[33,34].The data prompted future efforts to validate the interactions between BLU/ZMYND10,promoter of cyclin D1 and H3K9me3 in cells in which BLU induced G1 arrest,to dissect the possible interaction between BLU,H3K9me3 and promoter of coding genes of cyclin D1
On re-expression in HepG2 cells,BLU was associated with the repressor of gene transcription SIN3A(Fig.2D).It had been previously known that CBFA2T2/ZMYND2 binds repressors nuclear co-repressor(NcoR)and SIN3A to repress transcription of genes,and the activity is disturbed when it is fused with RUNX1 protein on the chromosomal translocation during genesis of acute myeloid leukemia(AML)[9,10].It has been reported that the binding site for repressor peptides are highly conserved between CBFA2T2/ZMYND2(ETO),SMYD1,2,3,RACK7/ZMYND8,and BS69/ZMYND11[35,36].It remains to be tested the possible interactions between BLU,H3K9me3 and promoters of CCNB1 and CCND1,and whether BLU also represses gene transcription through association with co-repressors similarly with other ZMYND proteins.The interaction between BLU and SIN3A has been supported by the previous structural and functional study,and further validation is warranted.
The ZMYND family members RACK7/PKCB1/ZMYND8 and BS69/ZMYND11 have been shown to recognize genomic marks and to recruit marks like H3K36me3 to sequences upstream of the coding portion of target genes,to regulate gene expression[13-15].As for domains composition,the two proteins both contain domains bromo,PHD,PWWP,and MYND generally found in gene regulators(38-40;36;37,38).The present results showed that,while these two proteins mapped on the same clade,BLU was clustered with two methyltransferases,suggesting that BLU has an evolutionarily closer relationship with SMYD1 and SMYD3,both of which function as methyltransferase of histone marks(Fig.5A).SMYD3 has been known to catalyse methylation to an active mark H3K4.The present study suggested that BLU/ZMYND10 elevated H3K9me3 mark;it remains to be tested whether it alter the methylation modification of different histone marks including H3K36,H3K4 through interaction with demethylases and methyltransferases.The increased levels of a repressive H3K9me3 mark in BLU expressing cells(Fig.1B,2B)suggested that it may counteract or downregulate some enzymes,such as KDM4 family members to maintain repression of the upstream portion of the target genes.
Conclusion
In summary,the current study investigated the mechanism by which BLU/ZMYND10exerts its tumour suppressive activities.BLU may form a complex with a co-repressor SIN3A or bind and inhibit lysine demethylases(probably KDM4)with specific catalytic potential to demethylate modified H3K9.These activities may work independently or in synergy to repress the transcription of cell cycle regulators,thus preventing cell cycle progression,cell proliferation.
- Life Research的其它文章
- The impact of the COVID-19 outbreak on Australia’s public health and medical industry in 2020
- Coronary heart disease-related fatigue:risk factors,assessment and treatments
- The mechanism of DDR genes in tumor progression
- Microbiota-gut-brain axis and major depressive disorder:implications for fecal microbiota transplantation therapy
- The therapeutic potential of stem cell therapy for myocardial infraction
- Preoperative traction is a risk factor for osteonecrosis of femoral head in patients with stable femoral neck fractures