Assessment of anterior chamber angle changes after phacoemulsification with swept-source OCT
Qian Zheng, Man Hu, Zhang-Liang Li, Ping-Jun Chang, Yun-E Zhao
1Eye Hospital and School of Ophthalmology and Optometry,Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang Province, China
2National Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases,Wenzhou 325027, Zhejiang Province, China
Abstract
● KEYWORDS: anterior chamber parameters;phacoemulsification; shallow anterior chamber; anterior segment swept-source optical coherence tomography
INTRODUCTION
In 2016, a multicenter randomized controlled trial by Azuara-Blancoet al[1]found that the eyes after clearlens extraction had higher mean health status score and lower intraocular pressure (IOP) than eyes after laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI), with a difference of 0.052 and 1.18 mm Hg,respectively. Clear-lens extraction was more effective and cost-effective than LPI and should be an option for first-line treatment for primary angle-closure glaucoma (PACG). Current researches showed that cataract surgery with intraocular lens(IOL) implantation can deepen the anterior chamber and increase the width of the anterior chamber angles[2-7]. The effect of cataract surgery on IOP in glaucoma patients has been reported in many studies of different subtypes of glaucoma.Husainet al[8]reported that the 2-year IOP control failure in the LPI group (7/18, 38.9%) was significantly higher than that in the phacoemulsification/IOL group (2/19, 10.5%). Lamet al[9]found that prevalence of IOP rise for the LPI group (46.7%)was significantly higher than that in the phacoemulsification group for the follow-up at 18mo. The mean IOP in the LPI group (15.0±3.4 mm Hg) was always higher than that in the phacoemulsification group (12.6±1.9 mm Hg)[8-9]. In normaltension glaucoma cases, cataract surgery may have increased anterior chamber angle parameters and lowered IOP[10]. Lens extraction may be an alternative option for a subset of primary angle closure (PAC) patients[8-9,11].
Although the anterior chamber did deepen and the anterior chamber angle widen and IOP reduction after cataract surgery[12], whether the anterior chamber angle opening and anterior chamber depth (ACD), anterior chamber volume(ACV) in patients of shallow anterior chamber with narrow angle can reach the normal level after lens extraction remains to be studied.
The risk of angle closure is high among the Chinese individuals.The 10-year cumulative incidence of any forms of PAC was 20.5% in an urban Chinese population aged 50y and older.Small ocular dimensions with hyperopia at baseline may develop into angle closure[13]. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the effects of cataract surgery on anterior segment structure and angle parameters in Chinese subjects with anterior segment swept-source optical coherence tomography (AS-SS-OCT) technique. By comparing the anterior chamber angle parameters of shallow anterior chamber narrow angle with normal anterior chamber wide angle before and 3mo after operation, to investigate the ACD and anglerelated parameters changes after phacoemulsification. We hope to obtain more strong evidence from AS-SS-OCT to confirm whether there are any other factors affecting the anterior chamber angle structure other than lens.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Ethical Approval In this prospective study, consecutive cases who were prepared for phacoemulsification and IOL implantation at a tertiary referral center in Southeast China from September 2013 to May 2014. The research was carried out in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and with the approval of the institutional ethics committee. Each patient gave informed consent prior to the examination. Trial registration: Clinical Trials.gov ID:NCT03779542.
Subjects A comprehensive ophthalmic examination was performed for each patient, including visual acuity, manifest refraction, slit-lamp evaluation, noncontact tonometry (TX-F;Cannon, Tokyo, Japan), gonioscopy, fundus examination, and AS-SS-OCT scanning. Shallow anterior chamber was defined as: ACD≤2.68 mm (without corneal thickness) measured by the AS-SS-OCT[14]and angle ≤Shaffer 2 in four quadrants under gonioscope[15].
Inclusion criteria were age-related cataract patients with normal IOP who were scheduled for elective phacoemulsification and IOL implantation, including patients of shallow anterior chamber with narrow angle and wide anterior chamber with wide angle. In the patients who received surgery in both eyes,only the data of the right eyes were analyzed. Images with good quality from preoperative and 3-month postoperatively examinations were analyzed.
Exclusion criteria included diagnosed PAC with evidence of previous acute episode, established anterior adhesion of peripheral iris, established PACG with the optic nerve damage and visual field defects of glaucoma, other ocular comorbidity except of cataract (e.g., uveitis, primary open angle glaucoma, normal tension glaucoma, history of ocular surgery or injury), pterygium influencing AS-SS-OCT scanning,complications occurred during and after surgery (e.g., zonular dialysis, posterior capsule rupture, IOL decentration and tilting, dislocation, post-operative elevated IOP, prolonged postoperative inflammation).
Patients were divided into two groups according to the ACD and gonioscopy findings: normal anterior chamber with wide angle group (NAC group) and shallow anterior chamber with narrow angle group (SAC group), including patients with close angle but normal IOP.
Anterior Chamber Measurement AS-SS-OCT (SS-1000 CASIA; Tomey Co. Ltd., Nagoya, Japan) examination was executed preoperatively and 3mo postoperatively. For each patient each time, 3 consecutive examinations were done by a same skilled professional inspector without pupil dilation under the same lighting condition (300 lx).
For the purpose of avoiding lid artifact, the patient’s lower eyelid was pulled down that the inferior limbus was exposed,in the course of his or her upper eyelid was raised to expose the upper limbus during examination[16]. Two researchers confirmed that the images with the best exposure were analyzed.
ACD, ACV and angle opening distance at 750 μm (AOD750),anterior recess area at 750 μm (ARA750), trabecular iris space area at 750 μm (TISA750), trabecular iris angle at 750 μm(TIA750), iris volume (IV) and lens vault (LV) were measured and compared between the two groups.
AOD750 was determined as the perpendicular distance detected from the trabecular meshwork at 750 μm anterior to the scleral spur to the anterior iris surface[17]. ARA750 was the area of the boundary within the iris anterior surface,the corneal posterior surface and a line perpendicular to the corneal posterior surface from a point 750 μm anterior to the scleral spur to the iris surface[18]. TISA750 was an area located anteriorly by the AOD750, superiorly by the inner wall of corneoscleral, inferiorly by the anterior surface of iris, and posteriorly by a line from the scleral spur perpendicular to the plane of the inner wall of sclera to the opposing iris[16]. TIA750 was defined as an angle determined with the apex of the iris recess and the arms of the angle traversing through a point on the trabecular meshwork 750 μm from the scleral spur and the point on the iris perpendicularly opposite[19]. LV was the perpendicular distance from the anterior pole of the lens to the center of the line connecting the two iridocorneal angles. IV and ACV were computed and calculated automatically, with the device’s software determined the iris and cornea’s anterior and posterior border lines in the single B-scans[16](Figures 1 and 2).
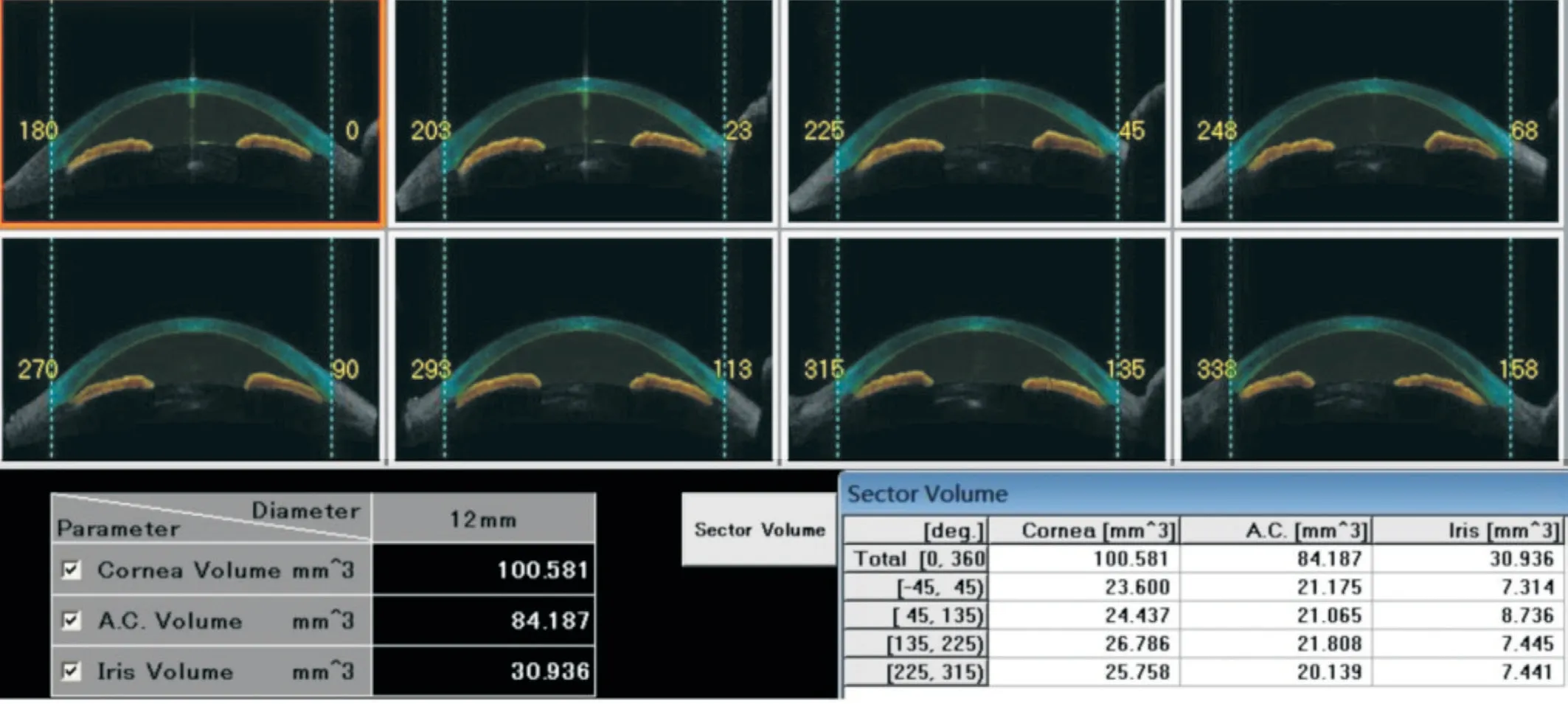
Figure 1 The images of angle meridians The cornea, iris and anterior chamber volume of total (360-degree) and four quadrants were calculated.
Statistical Analysis SPSS version 21.0 was applied in statistical analysis (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois, USA).Variables distributions were tested by Kolmgorov-Smirnov test. Parameters of non-normal distributions recommended non-parametric statistical analysis. Variables were showed as mean±standard deviation or median (range of quartiles). Oneway ANOVA or Mann-WhitneyUtest was used to test the difference of groups. PASS software (Version 11.0, NCSS,LLC, USA) was used to calculate the sample size, which was confirmed to be thirty samples (α=0.05; power=0.90). APvalue less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Basal Demographic and Clinical Characteristics Sixty eyes from sixty patients were included in the study. Table 1 showed the demographic characteristics. There were no significant differences of age, axial length (AL), corneal curvature, cornea diameter, IOP, and IV between groups of SAC and NAC(P>0.05). However, ACD, LV of SAC group was significantly larger than NAC group (2.25±0.28vs2.88±0.42 mm,P=0.001;0.91±0.24vs0.50±0.29 mm,P=0.000).
Preoperative Anterior Segment Comparison All the anterior segment parameters, including AOD750, ARA750,TISA750, TIA750, and ACV, ACD showed significant differences between groups of SAC and NAC before surgery(allP<0.05; Figures 3 and 4). ACV in groups of SAC and NAC before surgery were 91.24 (84.23, 109.57) and 145.11(115.62, 159.06).
Postoperative Anterior Segment Comparison AOD750,ARA750 in nasal and inferior quadrants, TISA750 in all quadrants except temporal, and TIA750 in all quadrants inSAC group are significantly smaller than those in NAC group at 3mo postoperatively (allP<0.05; Figure 5). ACD and ACV were prominently larger in the NAC group than the SAC group 3mo after operation (3.69±0.38vs3.85±0.39 mm,P=0.025;161.37±19.47vs178.26±20.30 mm3,P=0.002; Figure 4).
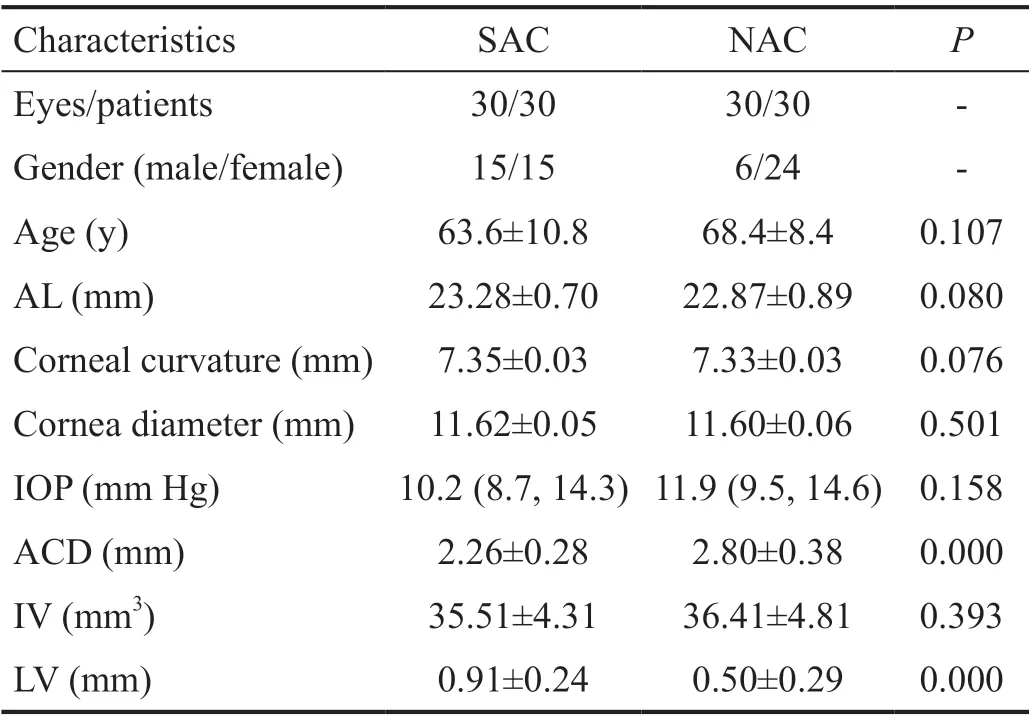
Table 1 Demographic characteristics
DISCUSSION

Figure 2 AS-SS-OCT examination A: AOD750 and ARA750; B:TISA750 and TIA750; C: LV.

Figure 3 AOD750, ARA750, TISA750, TIA750 showed significant differences between groups of SAC and NAC before surgery aP<0.05.
Previous studies demonstrated that the thicker lens, the shallower ACD, the narrower anterior chamber angle and the higher hyperopic spherical equivalent, the more likely the chamber angle closure occurred[20]. Cataract surgery can deepen the anterior chamber and widen the anterior chamber angle[19,21-24]. Shinet al’s[25]study showed that in narrow or closed angle eyes, cataract surgery resulted in a deeper anterior chamber and a lower IOP than in open angle eyes, suggesting that phacoemulsification could prevent acute angle closure.However, due to the inspection characteristics of UBM and gonioscopy at early years, some more detailed parameters could not be investigated[19,21-22,24].Further studies have been carried out to explore the changes of the angle structure of the anterior chamber after phacoemulsification by AS-OCT[3,6-7,10-11,26]. It has the advantage of allowing faster the anterior chamber cross-sectional imaging than UBM,without contacting with the eyeball.Kasaiet al[26]investigated change of ACD and angle related parameters based on AS-OCT after cataract surgery in eyes with narrow and open angles, confirmed that early postoperative ACD and all angle parameters were increased by cataract surgery. Whereas, they found the extent of angle widening in narrow-angle eyes was less than that in openangle eyes, although the increase of ACD in narrow-angle eyes was similar as that in open-angle eyes, indicating that there were other factors affecting the angle closure besides the lens. However, AS-OCT can only detect the horizontal angle information and cannot fully represent the 360-degree anterior chamber angle and the changes of the three-dimensional space of the anterior chamber.
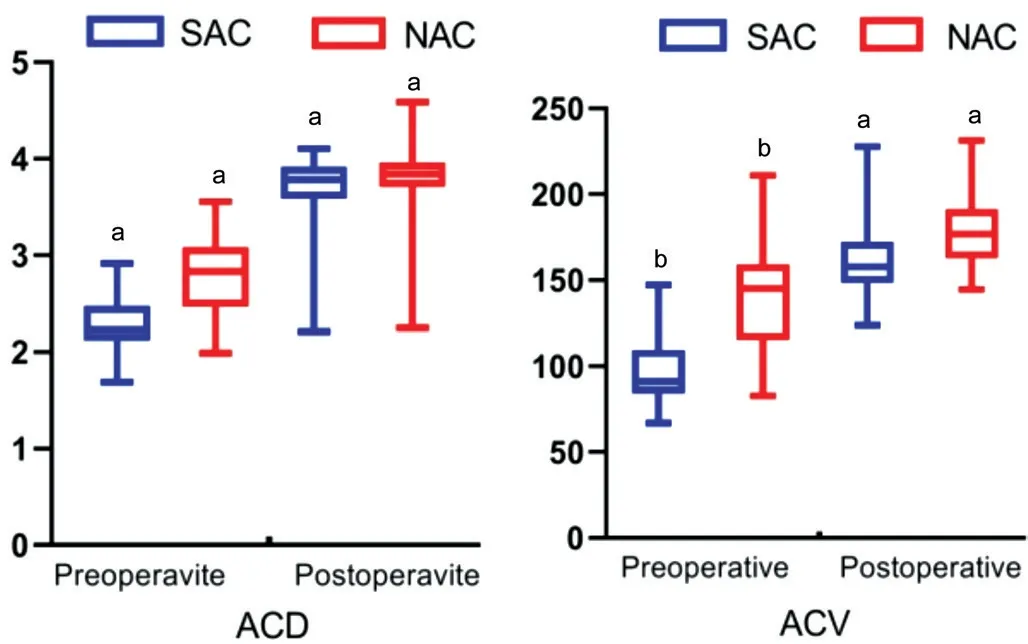
Figure 4 ACD and ACV of SAC and NAC groups before and 3mo after surgery aP<0.05, bP<0.001.
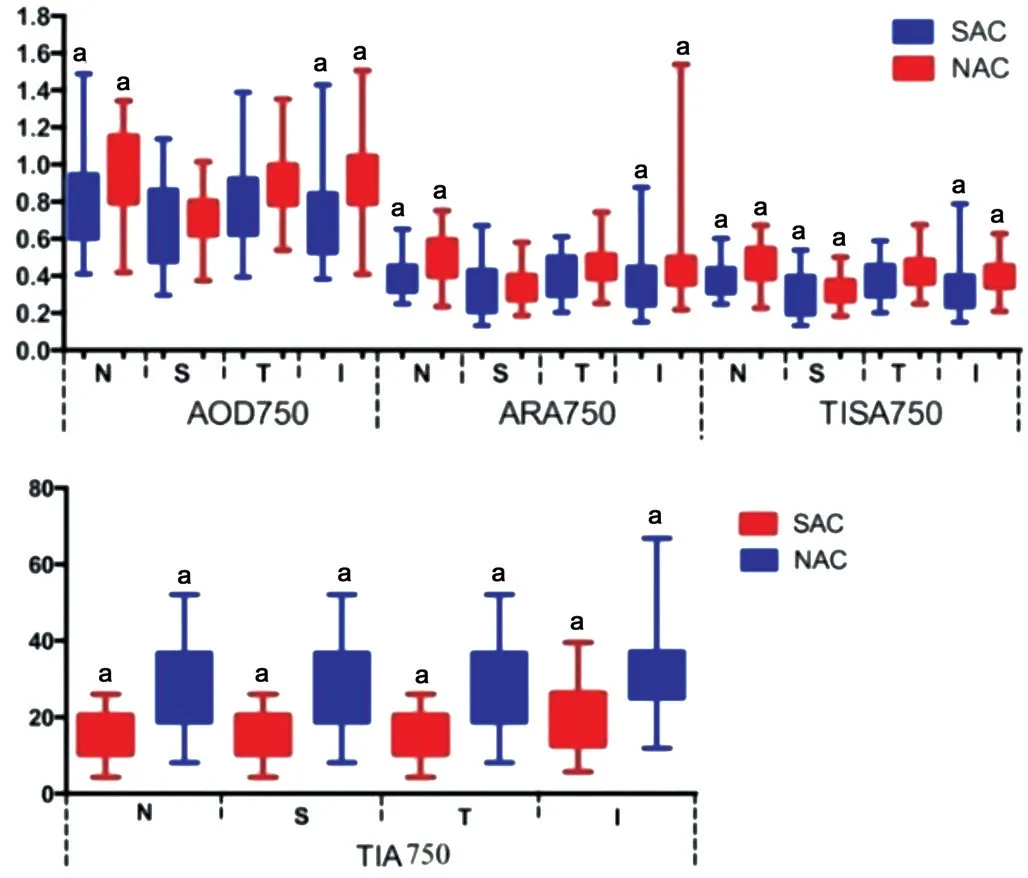
Figure 5 AOD750, ARA750 in nasal and inferior quadrants,TISA750 in all quadrants except temporal, and TIA750 in all quadrants in SAC group are significantly smaller than those in NAC group at 3mo postoperatively aP<0.05.
AS-SS-OCT was verified to be suitable for assessment of angle and angle-related parameters by some authors[16,27-30]. The anterior chamber angles can be sharply imaged in 128 crosssections (each with 512 A-scans) 360° around the anterior segment scanning in 2.4s, with an increasement in scan speed(30 000 A-scans per second)[26]. Therefore, through the AS-SSOCT examination, we can understand the anterior chamber and anterior chamber angles more comprehensively than previous studies. To the best of our knowledge, there is no comparative study on the fine structure of anterior chamber angle using ASSS-OCT before and after cataract surgery in Chinese subjects.In our study, cataract patients with normal IOP were divided into two groups by ACD and ACA: shallow anterior chamber with narrow angle and normal anterior chamber with wide angle. Before surgery, all the anterior segment parameters,ACD and ACV were markedly smaller in the SAC group than in the NAC group. LV were oppositely larger in the SAC group, except IV. Although, all the anterior segment parameters, ACD and ACV in both groups were larger after surgery, ACD, ACV, and angle related parameters of some quadrants in the SAC group were still significantly smaller than those in the NAC group at 3mo after surgery. The results were similar to Kasaiet al’s findings[26]. However, they only evaluated angle-related parameters horizontally and did not measure the ACV because of AS-OCT limitations. Also, there is no long-term observation after operation.
Our results showed that it was similar in the preoperative axial length, corneal curvature, and corneal diameter between the two groups. But in patients with shallow anterior chamber narrow angle, angle related parameters, ACD and ACV didn’t recover to normal level compared with patients of normal anterior chamber after surgery. We postulate the possible reason is more anterior insertion of the iris of the eyes in the SAC group, due to embryologic and anatomic factors.Meanwhile, whether there are ciliary body abnormalities remains to be further investigated.
There are some limitations in this study. First, as AS-SS-OCT could not measure the ciliary body as UBM or gonioscopy does, the data of ciliary body structure could not be obtained.Second, we didn’t confirm whether the anterior insertion point of the iris was different between two groupsviagonioscopy.In this study, the anterior chamber morphological changes in the SAC and NAC groups before and 3mo after cataract surgery were quantitatively evaluated by AS-SS-OCT. We proved that cataract surgery can deepen anterior chamber and widen the anterior chamber angle in Chinese subjects, but the ACD, ACV, and some angle-related parameters in patients with shallow anterior chamber with narrow angle did not reach the normal level, presumably because the iris root of the SAC group inserted more anteriorly than that of the NAC group.This needs to be proved by further study.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Conflicts of Interest:Zheng Q, None; Hu M, None; Li ZL,None; Chang PJ, None; Zhao YE, None.
 International Journal of Ophthalmology2021年10期
International Journal of Ophthalmology2021年10期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Exosomal miR-29b found in aqueous humour mediates calcium signaling in diabetic patients with cataract
- Intraluminal stenting versus external ligation of Ahmed glaucoma valve in prevention of postoperative hypotony
- Visual acuity after intravitreal ranibizumab with and without laser therapy in the treatment of macular edema due to branch retinal vein occlusion: a 12-month retrospective analysis
- Dexamethasone intravitreal implant (Ozurdex) in diabetic macular edema: real-world data versus clinical trials outcomes
- Comparative analysis of the clinical outcomes between wavefront-guided and conventional femtosecond LASlK in myopia and myopia astigmatism
- Reliability of the ocular trauma score for the predictability of traumatic and post-traumatic retinal detachment after open globe injury
