The clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine in the auxiliary treatment of grade 1 hypertension: A systematic review and metaanalysis
Jinghan Wang, Zhen Hua, Chao Li, Yunlun Li
1 Shandong University of traditional Chinese medicine, Jinan 250014, China.
2 Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of traditional Chinese medicine, Jinan 250014, China.
Abstract Objective: To systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in auxiliary treatment of grade 1 hypertension.Methods: The China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wan Fang Data, VIP, PubMed were searched to screen the literature of randomized controlled trials of TCM or non-drug therapies assisting conventional medicine to treat grade 1 hypertension.The search time was from the establishment of the database to October 1, 2020.Revman5.3 was used for meta-analysis.Results: 8 Chinese literatures were included.The results of the study showed that 24h diastolic blood pressure (DBP),24h systolic blood pressure (SBP), DBP lowering effect and TCM syndrome curative efficacy of the experimental group using TCM was better than that of the control group.However, TCM combined conventional medicine did not show an advantage on SBP lowering effect, antihypertensive efficacy rate and total clinical efficacy rate.Conclusion: TCM has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure for adjuvant treatment of grade 1 hypertension and can significantly improve clinical symptoms.
Keywords:Grade 1 hypertension, Traditional Chinese medicine, Meta-analysis, Systematic review, Effectiveness
Grade 1 hypertension is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is mainly characterized by increased systemic arterial pressure.With the change of lifestyle, the intake of high-sugar, high-salt, high-fat diet, lack of exercise, the number of people with essential hypertension is increasing, and it has become a public health problem which attracted the attention of all mankind [1].Grade 1 hypertension can not only cause damage to target organs such as the heart, brain, and kidneys, but also lead to lethal complications such as heart failure and renal failure [2].
Grade 1 hypertension is the initial stage of hypertension.It refers to measuring the blood pressure in the office three times on different days, SBP < 160 mmHg, ≥ 140 mmHg and (or) DBP < 100 mmHg, ≥ 90 mmHg, mainly manifested as dizziness and head symptoms such as bloating, depression and irritability [3-4].According to incomplete statistics, about 90% of the hypertensive population in China were patients with mild to moderate hypertension, of which more than 60% suffer from grade 1 hypertension [5].If the blood pressure of patients with grade 1 hypertension fluctuates greatly for a long time, the possibility of developing grade 2-3 hypertension will be higher, and it will bring a series of cardiovascular complications [6].It can be seen that the interventions for grade 1 hypertension need to be studied and completed continuously to bring better treatments and therapeutic effects for patients.
TCM has a long history of treating hypertension.Hypertension belongs to the category of "vertigo disease" in TCM.Wind, phlegm, deficiency, and blood stasis are the main causes of vertigo.Ancient books recorded treatments of TCM, acupuncture and moxibustion, Daoyin, massage and so on [7].TCM has strong pertinence and advantages in the treatment of grade 1 hypertension, due to its “preventive treatment of disease” concept and diverse treatment methods [8].At present, the commonly antihypertensive therapy of TCM includes Chinese medicine therapy, acupuncture therapy, acupoint application, auricular point pressing, auricular acupuncture therapy and so on.In this study, a systematic evaluation method was used to comprehensively evaluate the clinical efficacy of TCM for grade 1 hypertension.
Materials and Methods
This meta-analysis was performed to elaborate the effect of TCM in the auxiliary treatment of grade 1 hypertension according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines.
Inclusion criteria
(1) Publication time: between database inception and December 31, 2020; (2) Research type: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCT) for the adjuvant treatment of grade 1 hypertension with TCM therapy; (3) Research object: patients with grade 1 hypertension; (4) Interventions: the control group was treated with conventional antihypertensive drugs, such as Valsartan, Losartan potassium and so on, and the experiment group was treated with TCM on the basis of the control group; (5) Outcome indicators: 24h ambulatory blood pressure value (24h SBP, 24h DBP), blood pressure value (SBP, DBP), TCM syndrome curative effect, antihypertensive curative effect, clinical total effective rate, blood pressure variability.
Exclusion criteria
(1) Literature with incomplete or incorrect data; (2) Literature with repeated publications or data; (3) Included patients with mental illness or other serious diseases, such as acute myocardial infarction, stroke and so on; (4) RCTs with intervention time of less than 12 days.
Literature retrieval methods and strategies
Computer retrieval of clinical RCTs of TCM therapies for the adjuvant treatment of grade 1 hypertension included in CNKI, Wan Fang Data, VIP, PubMed, and supplemented by manually search for grey literatures.Use title, keywords, abstract, and full text as search items.Chinese search strategy: 主题 = ('高血压' or '1级高血压' or '轻度高血压' or '高血压病') AND主题 = ('中医' or '中医疗法') AND 全文 = ('随机对照' or '随机 ' or 'RCT'); English search strategy: ((("Hypertension" [Mesh]) OR (((((((Blood Pressure, High [Title/Abstract]) OR (Blood Pressures, High [Title/Abstract])) OR (High Blood Pressure [Title/Abstract])) OR (High Blood Pressures [Title/Abstract])) OR (grade 1 hypertension [Title/Abstract])) OR (mild hypertension [Title/Abstract])) OR (essential hypertension [Title/Abstract]))) AND (("Chinese Medicine" [Mesh]) OR (TCM Law [Title/Abstract]))) AND ((((((randomized controlled trial [Publication Type]) OR (randomized controlled study [Title/Abstract])) OR (randomized trial [Title/Abstract])) OR (randomized study [Title/Abstract])) OR (RCT [Title/Abstract])) OR (randomized [Title/Abstract])).
Literature screening and data extraction
After two researchers strictly formulated the inclusion and exclusion criteria based on the research content, they imported the searched literature into NoteExpress for preliminary screening and eliminated duplicates and non-compliant literature.After reading the full text information, the literatures were re-screened, and the final included literatures were extracted.Use Excel to design a data extraction table to collect the data and analyzed, including the following information: the author of the included study, the year of publication and other basic information, the research method, the number of samples, the characteristics of the research object, intervention measures, and outcome indicators, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.Flow Diagram of Study Selection
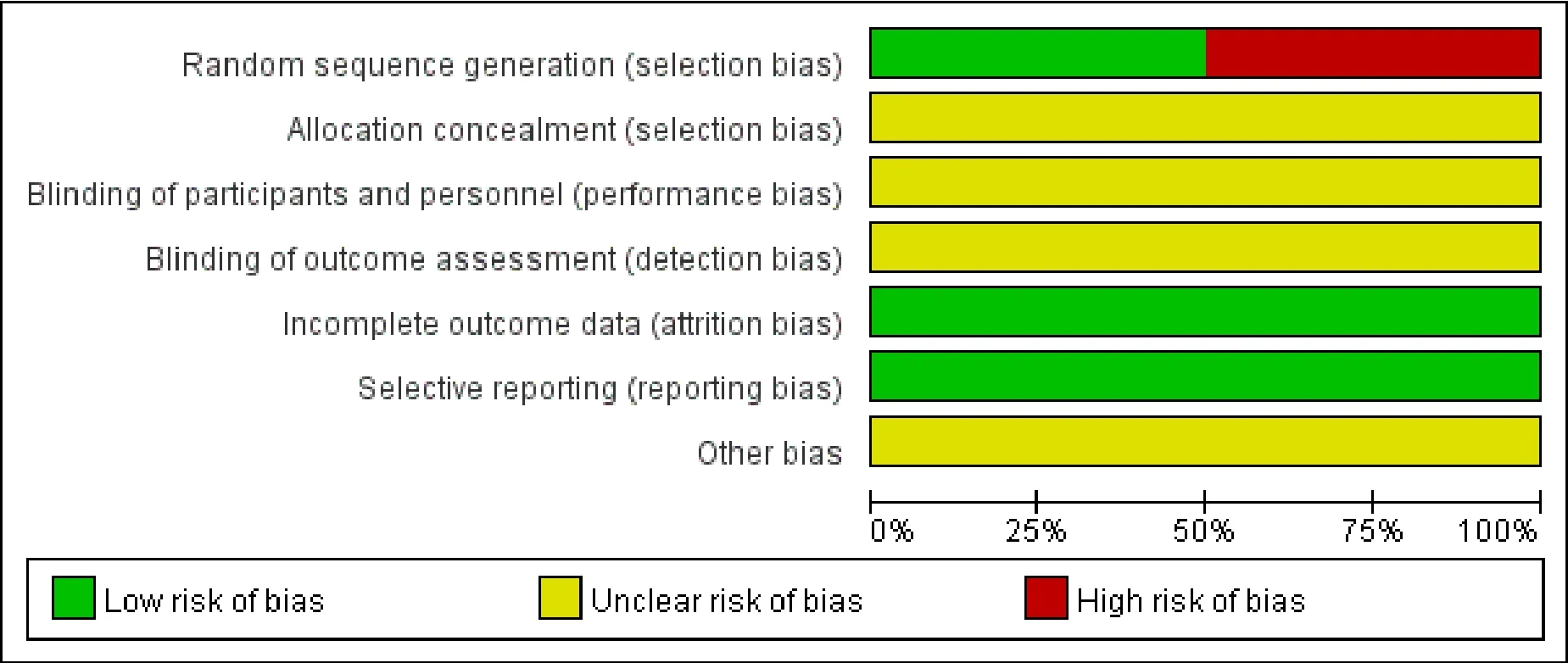
Figure 2.Risk of Bias Graph.
The quality of included studies and the risk of bias
Using the Cochrane manual quality evaluation tool to evaluate the quality of included literatures and the risk of bias.Evaluation items include: (1) Whether to explain the random sequence generation plan; (2) Whether to implement allocation hiding; (3) Whether to implement blinding; (4) Whether to lose outcome data; (5) Whether to selectively report results; (6) Are there other sources of bias.Use the following three levels to express the risk of bias: low-risk, unclear, and high-risk.
Statistical methods
RevMan5.3 was applied for meta-analysis, the odds ratio (OR) was used for the effect scale of binary variables, the mean difference (MD) was used for the effect scale of continuous variables, and the 95% confidence interval (CI) was used for the effect size.This study usedPvalue andI2value to express heterogeneity.IfP> 0.1 andI2≤ 50%, it is considered to be homogeneous, and fixed effects model will be used.On the contrary, random effects model will be used, and the source of heterogeneity will be analyzed at the same time.If necessary, sensitivity and subgroup analysis will be performed.
Results
Document retrieval process and results
190 Chinese literatures and 0 English literatures were retrieved and downloaded.After excluding duplicate studies, one hundred and thirty-four literatures were obtained.one hundred and twenty-six literatures were obtained after excluding 8 reviews and non-RCT trial articles.one hundred and eighteen literatures whose contents did not meet the inclusion criteria were eliminated, and 8 documents were finally included, all of them in Chinese.
Characteristics of included literatures
A total of 8 RCTs were included, with sample size of 800 cases, 399 cases in the experimental group, and 401 cases in the control group.All studies showed baseline comparability.The basic characteristics of the included literature were shown in Table 1.

Table 1.Basic Characteristics of Included Literatures
Results of bias risk assessment
Among the 8 included RCTs, 4 studies [9,10,13,15] adopted random number table grouping, and others [11,12,14,16] mentioned randomness, but did not specify which randomization was used.All studies did not mention allocation concealment and blinding.There was no attrition or intentional analysis in all studies, no selective outcome reports were applied in the included studies, and it was unclear whether there were other biases.The risk of bias ratio chart of the included literatures is shown in Figure 2.
24h DBPThe 24h DBP was compared between the experimental group and the control group in 2 studies [9, 12].After the heterogeneity test,P= 0.69 andI2= 0% could be obtained.The included studies had high homogeneity, and the fixed effects model was adopted.Analyzing the forest pot in Figure 3, it could be demonstrated that the 24h DBP lowering effect of the experimental group using TCM was better than that of the control group, and the difference is statistically significant [MD = -8.89, 95%CI (-11.08, -6.07),P< 0.001].
24h SBPTwo researches [9, 12] reported the 24h SBP of the experimental group and the control group after treatment.P= 0.34 andI2= 0% could be calculated after heterogeneity analysis, so the fixed effects model should be utilized.The result was shown in Figure 4.The 24h SBP reduction effect of the experimental group after treatment was significantly better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -10.16, 95%CI (-12.32, -8.00),P< 0.001].
DBPFour literatures [9,10,11,13] compared the DBP between the experimental group and the control group after treatment.Heterogeneity test showed included studies had high heterogeneity (P= 0.09, I2= 53%).The sensitivity analysis found after excludingHu Xiaoqin 2020[9],P= 0.47 andI2= 0%, so we used a fixed effect model.The intervention of the experimental group inHU 2020was to apply Cangzhu Erchen Soup combined with Ear-point Pressing on the basis of conventional medicine, while other studies just used single TCM method.It was reasonable to believe this study was a heterogeneous source.Analyzing the forest plot in Figure 5, it could be found the DBPlowering effect of the experimental group using TCM was better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -4.23, 95%CI (-5.93, -2.54),P< 0.001].
SBP A total of 4 studies [9,10,11,13] compared the value of SBP in the experimental group and the control group after treatment.The included studies had high heterogeneity withP= 0.01 andI2= 73%.After sensitivity analysis, it was found the heterogeneity results were hard to change, so the random effects model was adopted.Analyzing the forest plot in Figure 6 demonstrated the SBP-lowering effect of the experimental group using TCM was not different from that of the control group.[MD = -4.29, 95%CI (-8.63, 0.04),P= 0.05].
TCM syndrome curative efficacyTCM syndrome curative efficacy was analyzed between 2 groups after intervention in 6 studies [9-13, 16].A total of 626 cases were included in the studies, including 313 cases in the experimental group and 313 cases in the control group.After the heterogeneity test,P= 0.36,I2= 8%, and the fixed effects model was selected.As shown in the results in Figure 7, the experimental group had obvious TCM syndrome curative effect compared with the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [RR = 0.76, 95%CI (0.69, 0.83),P< 0.001].

Figure 3.Forest Plot Comparing the 24h DBP between the Experimental Group and the Control Group

Figure 4.Forest Plot Comparing 24h SBP between the Experimental Group and the Control Group
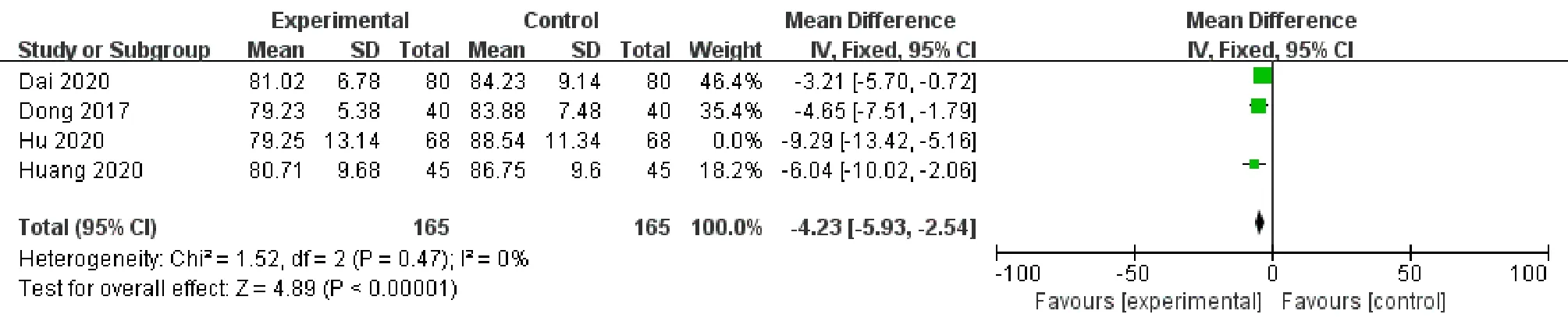
Figure 5.Forest Plot Comparing the DBP between the Experimental Group and the Control Group

Figure 6.Forest Plot Comparing SBP between the Experimental Group and the Control Group
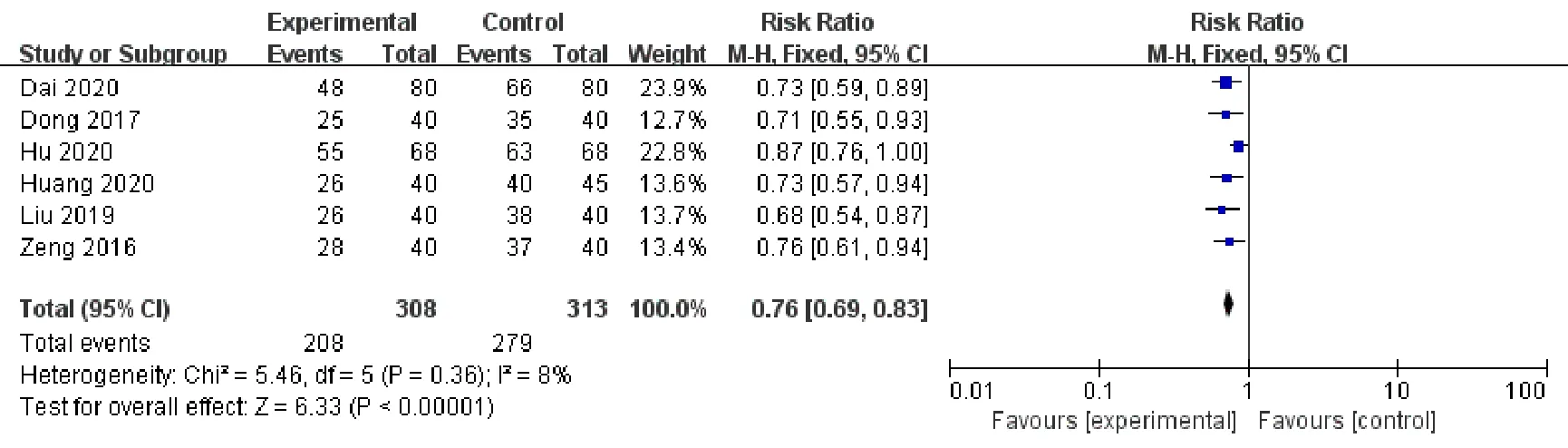
Figure 7.Forest Plot Comparing TCM Syndrome Curative Efficacy between the Experimental Group and the Control Group

Figure 8.Forest Plot Comparing the Antihypertensive Efficacy Rate between the Experimental Group and the Control Group

Figure 9.Forest Plot Comparing the Clinical Total Efficacy Rate between the Experimental Group and the Control Group
Antihypertensive efficacy rateIn the included studies, 4 articles [10,11,13,16] reported the comparison results of the antihypertensive efficacy rate between 2 groups.A total of 410 subjects were included, including 205 in the experimental group and 205 in the control group.P= 0.35,I2= 8%, using fixed effects model.As shown in Figure 8, the antihypertensive effect rate of the control group preceded the experimental group, and the difference was statistically significant [RR = 1.46, 95%CI (1.27, 1.69),P< 0.001].
Total clinical efficacy rateThree studies [9,14,15] reported the comparison results of total clinical effectiveness between 2 groups.A total of 410 cases were included, including 205 in the experimental group and 205 in the control group.Low heterogeneity could be seen after heterogeneity analysis (P= 0.60,I2= 0%), so the fixed effect model was utilized.As shown in Figure 9, the total clinical effectiveness rate of the control group was better than that of the experimental group, and there was no statistically significant difference [RR = 1.20, 95%CI (1.08, 1.33),P= 0.0005].
Discussion
According to the survey statistics, the death rate of cardiovascular diseases ranks first in China, among which hypertension is the main factor leading to cardiovascular diseases and has become an important public health problem in the world [17].And it is generally believed that the difficulty of controlling is a major feature of essential hypertension, which is also the main reason why it has become the largest cause of death worldwide [18].Grade 1 hypertension is the initial stage of hypertension and belongs to the category of "vertigo" in TCM.Treatment of grade 1 hypertension should be treated non-drug intervention first of all, including improving lifestyle, scientific diet and exercise, and maintaining favorable mood.Conventional medicine treatment is mainly to take single or combined antihypertensive drugs, including ACEI/ARB, CCB, β-receptor antagonists, diuretics and so on [19].Because of complicated hypertension pathogenesis and lengthy medication process, patients are called to have a high degree of compliance and cooperation.Patients with grade 1 hypertension usually has no obvious symptoms and may be feel more uncomfortable after taking some drugs with side effects and strong drug resistance.Therefore, poor compliance and poor improvement of clinical symptoms are the shortcomings of taking antihypertensive drugs [20].In addition, after taking antihypertensive drugs, the blood pressure value may drop lower than expected, so it will bring the harm of insufficient blood supply to some patients.Based on this perspective, the advantages, and characteristics of TCM should be seen by us.TCM includes drug and non-drug therapies.Because of its "simple, convenient, inexpensive, and experimental" characteristics, it has unshakable advantages in the treatment of grade 1 hypertension [21].Based on the research of physicians from ancient times to the present, the treatment options for grade 1 hypertension include ear point pressing, Baduanjin, TCM syndrome differentiation treatment, acupuncture, and ear acupuncture.In addition to its antihypertensive effect, TCM can specifically improve the clinical symptoms and the quality of life of the patients, and has small side effects [22].
This study conducted a meta-analysis of the RCTs on TCM assisting conventional medicine in the treatment of grade 1 hypertension, and further studied the treatment effectiveness of TCM on the 24h SBP, 24h DBP, SBP, DBP, and antihypertensive effect, TCM syndrome curative effect, the clinical total effective rate.The results of the study showed that the 24h DBPlowering effect of the experimental group using TCM was better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -8.89, 95%CI (-11.08, -6.07),P< 0.001]; the 24h SBP reduction effect of the experimental group after TCM treatment was significantly better than that of the control group [MD = -10.16, 95%CI (-12.32, -8.00),P< 0.001]; with the application of TCM, the DBP reduction effect of the experimental group was better than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -4.23, 95%CI (-5.93, -2.54),P< 0.001]; the SBP of the experimental group decreased the compression effect was not much different from that of the control group[MD = -4.29, 95%CI (-8.63, 0.04),P= 0.05]; the experimental group had obvious curative effect on TCM syndromes compared with the control group , and the difference was statistically significant [RR = 0.76, 95%CI (0.69, 0.83), P < 0.001]; while the antihypertensive effect rate of the control group preceded the experimental group, and the difference was statistically significant [RR = 1.46, 95%CI (1.27, 1.69), P<0.001]; the total clinical effectiveness rate of the control group was better than that of the experimental group, and there was no statistically significant difference [RR = 1.20, 95%CI (1.08, 1.33), P = 0.0005].Compared with conventional medicine treatment alone, TCM has been proven to be effective in lowering patients' SBP and DBP, has obvious effects in improving TCM syndromes.
Limitation
Although this study confirmed that some TCM methods have obvious antihypertensive effects and improve TCM syndromes in the auxiliary treatment of grade 1 hypertension, it also has some limitations: (1) The number of RCTs included in this study was few, and the quality of part of these was not high.The randomization scheme and allocation concealment were not clear, and blinding was not used in all; (2) The documents included in this study were all Chinese with positive results, and the credibility of the articles was doubtful, so there was potential publication bias; (3) The studies of TCM methods included in were not comprehensive, so it was impossible to prove the clinical efficacy of other-types TCM methods in the treatment of grade 1 hypertension.
Conclusion
This study adopted meta-analysis methods to confirm that some TCM methods, including TCM syndrome differentiation treatment, ear-point pressing beans, have obvious clinical effects on the adjuvant treatment of grade 1 hypertension.Grade 1 hypertension is the low-risk stage of primary hypertension.The use of TCM intervention has the advantages of reducing blood pressure, stable antihypertensive effect, minimizing side effects, obviously improving clinical accompanying symptoms, and benign adjustment [22].This study found that there is still a lack of high-quality RCTs of a variety of TCM interventions for grade 1 hypertension in clinical practice.Therefore, to further popularize the clinical thinking of TCM treatment of grade 1 hypertension, and use high-quality, multi-center, large sample clinical RCTs to confirm, provide a stronger evidence-based basis for the application of TCM, and it is development direction with the future prevention and treatment of grade 1 hypertension.
 TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2021年4期
TMR Modern Herbal Medicine2021年4期
- TMR Modern Herbal Medicine的其它文章
- Research progress on mechanism of Chinese material medica in preventing and treating insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- lncreased macrophage inflammation response in pancreatic cancer patients with a diagnosis of Shi-Re
- Experimental study on the effect of Huangqi and Danshen ultramicro gel on vascular healing of wound in rats based on network pharmacology
- Network pharmacology-based analysis on bioactive compounds and mechanisms in Yiqifumai formula in the treatment of heart failure
- Application of Chinese Herbal Medicine in the lnhibition of Salmonella and its virulence
- Differential expression of exosomal circRNAs and regulatory framework genes in myocardial infarction patients with cardiac remodeling in response to Tongguan Capsules
