血生化指标和瞬时弹性成像技术联合诊断2型糖尿病伴NAFLD肝纤维化程度的价值
陈军 黄斌 李燕青 潘林 汤晓飞 刘 芳
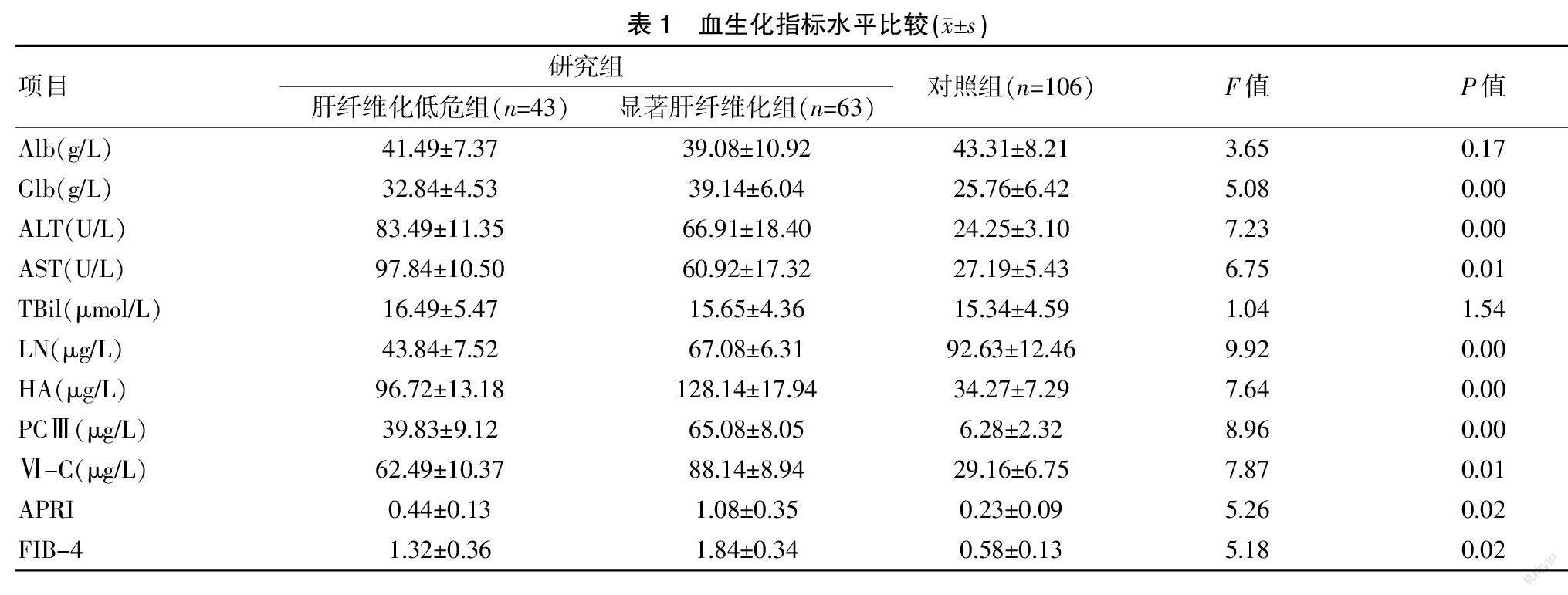
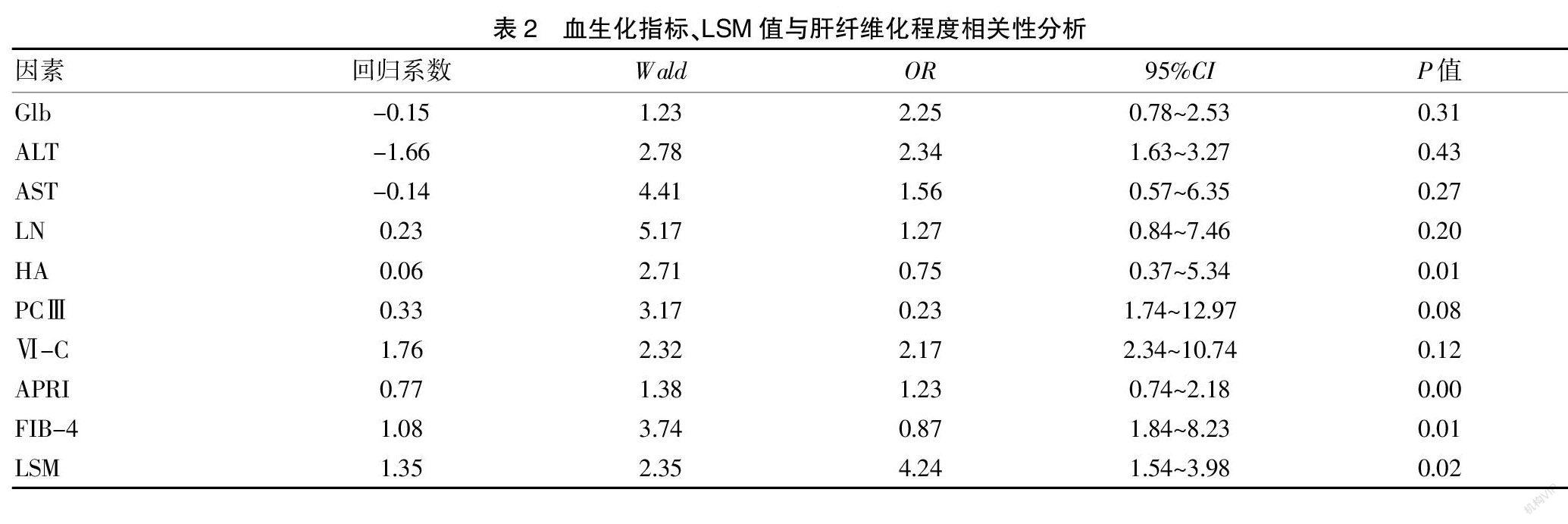
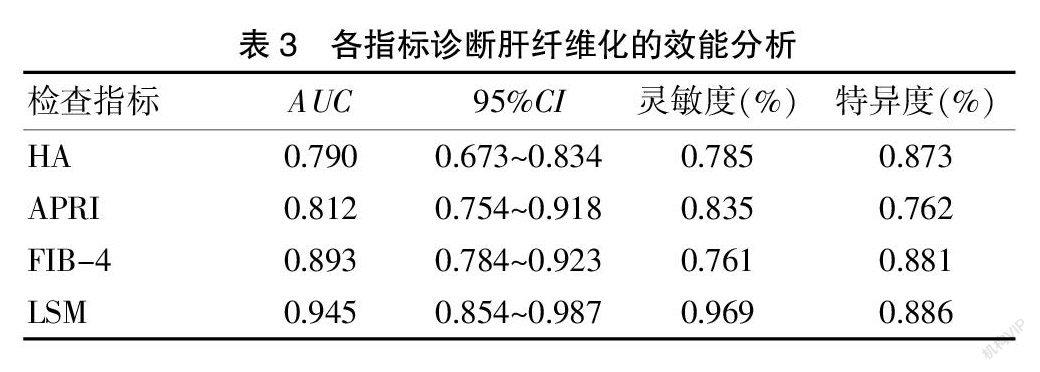
[摘要] 目的 探讨血生化指标和瞬时弹性成像技术(TE)联合诊断2型糖尿病伴NAFLD肝纤维化程度的价值。 方法 选取我院2017年9月至2019年9月间收治的T2DM伴NAFLD患者106例,依据Metavir分期分为肝纤维化低危组(n=43)和明显肝纤维化组(n=63),选取同期健康志愿者106名作为对照组,测定其血生化指标、LSM指标。 结果 三组间APRI、FIB-4、Glb、ALT、AST、LN、HA、PCⅢ、Ⅵ-C水平比较,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);APRI、FIB-4、HA、LSM等指标与肝纤维化呈正相关(P<0.05),是影响肝纤维化程度的因素;HA、APRI、FIB-4、LSM等指标具有较高的肝纤维化程度诊断效能。 结论 HA、APRI、FIB-4、LSM四项指标联合检测可有效提高T2DM伴NAFLD患者的肝纤维化程度诊断效能,具有较高的临床价值,可在临床广泛推广。
[关键词] 血生化指标;瞬时弹性成像技术;2型糖尿病;NAFLD
[中图分类号] R575.5 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)24-0137-04
The value of biochemical blood indexes combined with transient elastography in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in type 2 diabetes with NAFLD
CHEN Jun HUANG Bin LI Yanqing PAN Lin TANG Xiaofei LIU Fang
Department of Ultrasound,Hangzhou Xixi Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,Hangzhou 310023,China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the value of biochemical blood indicators and transient elastography (TE) in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in type 2 diabetes with NAFLD. Methods A total of 106 patients with T2DM and NAFLD admitted to our hospital between September 2017 and September 2019 were selected and divided into low-risk liver fibrosis group (43 cases) and significant liver fibrosis group (63 cases) according to Metavir staging. One hundred six healthy volunteers during the same period were selected as the control group.Their biochemical blood indexes and LSM indexes were measured. Results The differences in the levels of APRI,FIB-4,Glb,ALT,AST,LN,HA,PCⅢ,and Ⅵ-C among the three groups were statistically significant (P<0.05). The APRI,FIB-4,HA,and LSM were positively correlated with liver fibrosis (P<0.05),which were influencing factors of the degree of liver fibrosis.HA,APRI,FIB-4,and LSM had high diagnostic efficiency for liver fibrosis. Conclusion The combined detection of HA,APRI,FIB-4,and LSM can effectively improve the diagnostic efficiency of liver fibrosis in patients with T2DM and NAFLD.It has a high clinical value and can be widely used in clinical practice.
[Key words] Biochemical blood indicators; Transient elastography technology; Type 2 diabetes; NAFLD
糖尿病临床分型以2型糖尿病(Type 2 diabetes,T2DM)较为多见,以胰岛素分泌不足、胰岛素敏感性降低、胰岛素抵抗(Insulin resistance,IR)为主要发病机制[1]。近年来,随着我国人口老龄化和生活方式的改变,我国T2DM发病率逐年攀升,已成为临床慢病防治的重点[2]。非酒精性脂肪性肝病(Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)是指除酒精和其他明确肝损因素之外的原因导致肝细胞内脂肪过度沉积,从而引起肝细胞脂肪变性的臨床病理综合征[3],属获得性代谢应激性肝损伤,与IR、肥胖、脂代谢紊乱、遗传因素等密切相关。该病可参与T2DM和动脉粥样硬化的发病,并直接导致肝细胞癌、移植肝复发和失代偿期肝硬化[4],对患者身体健康构成严重威胁。临床研究显示[5],NAFLD常伴随T2DM出现,为临床准确诊断和治疗增加了难度。有文献报道[6],肝纤维化及部分早期肝硬化是可以逆转的,因此,准确评估患者肝纤维化程度对临床治疗具有重要意义。基于此,本研究采用血生化指标联合瞬时弹性成像技术(Transient elastography,TE)诊断T2DM伴NAFLD纤维化程度,探究其临床价值,现报道如下。

